Document

Student must include this instruction when submitting the assignment.
Instruction:
Read chapter 10 of Kalpakjian, Serope. Manufacturing Engineering and
Technology
Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall – Fourth Edition, 2001. ISBN # 0-
201-36131-0
Complete the homework assignment below.
Do not use attached file for homework assignment. You must copy and paste all data in your email.
Type answer below each question.
Reduce Grade: if the assignment is received after the due date, it will be deducted by 1 letter grade.
NO grade will be assigned for homework with more than 7 days late or improper format as indicated above.
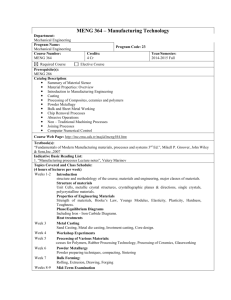
Manufacturing Processes - INMT-1248 - Assignment 10
QUESTIONS
10.1 Why is casting an important manufacturing process?
Answer (from page number _241, 242___):
Casting is an important manufacturing material in the industry because of its complex shape, which can be obtained by easy process of manufacturing. It is also important because of it can withstand compressive residual stresses which, in turn, allow the vessel to sustain high internal pressure.
10.2 What is the difference between the solidification of pure metals and metal alloys?
Answer (from page #_242, 243____):
Pure metals are solidified at a constant temperature. The solidified metal, called the casting, is taken out of the mold and is allowed to cool at the ambient temperature. Pure metals generally have a freezing point that approaches zero and that the solidification front moves as a plane without forming a mushy zone.
Solidification in alloys begins when the temperature drops below the liquidus, Tl, and is complete when it reaches the solidus, Ts. Within this temperature range, the alloy is a mushy or pasty. In alloy the width of the mushy zone, where both liquid and solid phases are present, is an important factor during solidification. This zone is described in terms of a temperature difference, known as a freezing range for alloy.
10.3 What are dendrites?
Answer (from page #_244____):
Dentrites means "akin to," and drys, meaning tree. Dentrites have three-dimensional arms and branches, which eventually interlock, as can be seen. The study of dentritic structure although complex, is important because such structure contribute to dentrimental factors such as compositional variations, segregation, and microporosity.
10.4 State the difference between short and long freezing ranges. How is range determined?
Answer (from page #_244____):
Short freezing range generally involves a temperature difference of less than 50 degree centigrade. The main difference between the short and long range is that when the temperature drops below the liquidus, Tl, and is complete when it reaches the solidus, Ts. Within this temperature range, the alloy is mushy or pasty.
The range is determined by the formulae Tl-Ts (freezing range = Tl-Ts).
10.5 Describe the parameters on which solidificatbion time depends.
Answer (from page #_250____):
The solidification is a function of the volume of a casting and its surface area (chvorinov's); that is solidification time = C (volume) square/(surface area) square. Where C is a constant that reflects the mold material, metal properties and temperature.
10.6 Define shrinkage and porosity. How can you tell whether cavities in a casting are due to porosity or to shrinkage?
Answer (from page #_252, 255____):
The shrinkage is contraction during solidification, which causes dimensional changes and, sometimes, cracking, is the result of the following three events.
Porosity in a casting may be caused by shrinkage or gases or both. Porosity is detrimental to the ductility of a casting and its surface finish, making it permeable and thus affecting pressure tightness of a cast pressure vessel.
We can distinguish by the events during solidification for example. If Contraction of the molten metal as it cool prior to its solidification. Contraction of the metal during phase change from liquid to solid. Contraction of the solidified metal as it temperature drops to ambient temperature.
Whereas in porosity Porous region may develop at their centers because of contraction as the surface of the thicker region begin to solidify first.
10.7 What is the function of chills?
Answer (from page #_255____):
Porosity caused by shrinkage can be reduced or eliminated by various means. Adequate liquid metal should be provided to avoid cavaties caused by shrinkage. Internal or external chill used in sand casting, also are an effective means of reducing shrinkage porosity.
10.8 How are dissolved gases removed from molten metal?
Answer (from page #_256____):
Dissolved gases may be removed from the molten metal by flushing or purging with an inert gas, or by melting and pouring the metal in a vacuum. If the dissolved gas is oxygen the molten metal can be deoxidized.
10.9 Describe the features of a gating system.
Answer (from page #__247___):
The gate is that portion of the runner through which the molten metal enters the mold cavity. The important features of the gating system are to be relatively simple, successful casting requires proper designs and control of the solidification process to ensure adequate fluid flow in the system. Furthermore, a properly designed gating system avoids or minimizes problems such as premature cooling, turbulences, and gas entrapment. Even before it reaches the mold cavity.
10.10 How is fluidity defined? Why is it important?
Answer (from page #__249___):
The capacity of the molten metal to fill mold cavaties is called fluidity; it consists of two basic factors: characteristics of the molten metal, and casting parameters.
10.11 Explain the reasons for hot tearing in castings.
Answer (from page #__254___):
Such as cracks, cols or hot tearing, and cold shuts. If the solidifying metal is constraint from shrinking freely, cracking and tearing can occur. Although many factors are involve in tearing, coarse grain size and the presence of low melting point segregates along the gain boundaries increase the tendency of hot tearing.
10.12 Name various defects in castings.
Answer (from page #_253____):
The various defects identified during casting are metallic projection, cavities, discontinuities, defective surface, incomplete casting, incorrect dimension or shape, inclusions, shrinkage and porosity.
10.13 Why is it important to remove dross or slag during the pouring of molten metal into the mold? What methods are used to remove them?
Answer (from page #_248____):
Re value of up to 2000 represents laminar flow; between 2000 to 20000. Represents a mixture of laminar and turbulent flow. Such a mixture is generally regarded harmless in gating systems. Re values in excess of 20000, however, represent severe turbulence resulting in air entrainment and the formation of dross (the scum that forms on the surface of the molten metal) form the reaction of the other metal and other gases. Thus it is important to remove dross or slag during pouring. It is removed and can be eliminated completely by the vacuum casting conventional atmospheric casting mitigates dross or slag by skimming, by using properly designed pouring basins and runner system, or by using filters.
10.14 What are the effects of mold materials on fluid flow and beat transfer?
Answer (from page #_249____):
The higher the thermal conductivity of the mold and the rougher the surfaces, the lower the fluidity of the molten metal. Although heating the mold improves fluidity, it slows down solidification of the metal and the casting develops coarse gain and hence has lower strength.
Whereas the effect by heat transfer is that it directly affects the viscosity of the liquid metal.
10.15 Why is Bernoulli's equation important in casting?
Answer (from page #_247____):
Bernoulli's equation because that the flow rate must be maintained anywhere in the system. The permeability of the wall of the system is important because otherwise some liquid will permeate
through the walls of the system and the flow rate will decrease as the liquid moves through the system.
10.16 What is a riser?
Answer (from page #_247____):
Rises serve as reservoirs to supply the molten metal necessary to prevent shrinkage during solidification.
10.17 What is the purpose of an inoculant?
Answer (from page #_246____):
A typical cast structure of a solid solution alloy with an inner zone of equiaxed grain can be extended throughout the casting by adding inoculants to the alloy. The inoculants induce nucleation of the grains throughout the liquid metal (heterogeneous nucleation).
======================= End of Homework Assignment
=======================
To display this page you need a browser with JavaScript support.