A Novel Mechanism of Deriving Energy from Urea Hydrolysis
advertisement

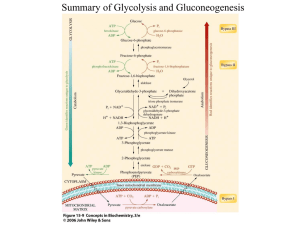
The influence of urea hydrolysis by urease on extracellular pH, on the intracellular pH and on ATP synthesis was evaluated in the lactic acid bacterium Streptococcus thermophilus DSM 20617T. Urea hydrolysis to ammonium and carbon dioxide caused alkalinization of the cytoplasm, the generation of a transmembranic pH gradient and a significant increase in ATP synthesis. Urea-dependent ATP synthesis was completely abolished when cells were treated with acetohydroxamic acid, a bacterial urease inhibitor or when cells of a recombinant urease-negative mutant were used. The addition of the ionophores and ATPase inhibitor did not interfere with ATP synthesis also at high concentration suggesting that a proton electrochemical potential and the membrane ATPase were not involved in the urea-dependent ATP generation. The evaluation of ATP synthesis compared to intra/extra-cellular pH variation in energetically discharged S. thermophilus cells fed with lactose in presence or absence of urea suggested that the ureadependent ATP synthesis was generated by an accelerated glycolytic flux. The results obtained together with the evaluation of lactose, glucose, lactic acid concentration, -galactosidase and lactate dehydrogenase activity and in vivo 13 C NMR analysis suggested that the intracellular urea- dependent alkalinization strongly increase lactose hydrolysis and the activity of glycolytic enzymes thereby determining an increase of ATP synthesis. The overall data revealed new insights in the regulation mechanisms involved in homolactic fermentation of S. thermophilus allowing to develop new strategies to increase the yield in biomass production. Growth competition experiments carried out in laboratory media and in milk between wildtype and urease-negative mutant revealed that urea hydrolysis, the related increase of lactose consumption, and the improvement of glycolytic-dependent ATP generation strongly increased the fitness of milk colonization of S. thermophilus.