ch5a.txt
advertisement

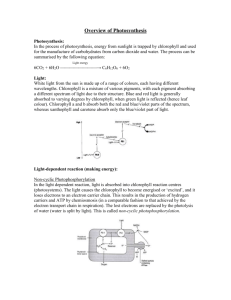
Microbiology 1: Microbial Metabolism (Ch 5) Much of this chapter should be review! I. Metabolism A. what is it? B. parts anabolism catabolism C. need raw materials & energy D. ATP II. Enzymes A. enzyme structure 1. usually protein 2. exception: ribozyme 3. holoenzyme a. apoenzyme b. cofactor B. function 1. catalysts 2. how many? 3. substrate 4. product(s) C. mechanism(s) 1. active site 2. sequence of events: E + S(s) --> ES (transition state) --> E + P(s) D. Factors influencing reactions optimum 1. temperature 2. pH denaturation 3. substrate concentration 4. inhibitors a. competitive b. allosteric/non-competitive 5. feedback inhibition E. “-ase” III. Biological energy production A. oxidation/reduction reactions (redox) 1. oxidation 2. reduction 3. coupled hydrogenation/dehydrogenation B. ATP production 1. substrate level phosphorylation 2. oxidative phosphorylation 3. photophosphorylation ATPase © copyright 2013 Marta D. de Jesus IV. Glucose Catabolism A. glycolysis = Embden-Meyerhoff pathway 1. glucose 2. 8 steps 3. Energy-investment stage Energy-conserving stage 4. net effect: 1 Glucose (6C) ------------> 2 NAD+ + 4 H -----------> also make 4 ATP - use 2 ATP ----> 5. O2 6. bacterial alternatives a. pentose-phosphate pathway b. Entner-Doudoroff pathway B. Fate of pyruvate 1. respiration a. pyruvate b. ATP c. final e- acceptor d. types 1) aerobic respiration (i) transition/preparatory reaction 2 pyruvate (3C) --> 2NAD+ + 4H --> (ii) Krebs/Citric acid/TCA cycle 2 Acetyl CoA (2C) --> Also make ATP (#?) make NADH2 (#?) make FADH2 (#?) (iii) electron transport (ETC) NADH and FADH2 O2 -> H+’s (iv) chemiosmosis H+’s (v)) summary 2) anaerobic respiration (i) no O2 (ii) ATP 2. fermentation a. O2 b. Krebs cycle, ETC, ATPase c. final e- acceptor d. ATP e. NAD+ (and NADP+) f. some types 1) homolactic = homofermentative 2) alcoholic 3) propionic acid 4) acetone & isopropanol 5) heterolactic = heterofermentative V. Other Catabolic Pathways (won’t stress) VI. Biosynthesis = Anabolism A. Photosynthesis 1. several kinds a. Halobacterium (Archaea) 1) bacteriorhodopsin 2) H+ b. green sulfur & purple sulfur bacteria 1) bacteriochlorophylls 2) CO2 3) O2 c. cyanobacteria & photosynthetic eukaryotes 1) chlorophyll a 2) CO2 3) O2 2. oxygenic PS in more detail a. chloroplast anatomy & the 2 kinds of reactions b. light dependent reactions 1) photosystems PSI PSII 2) cyclic photophosphorylation 3) non-cyclic photophosphorylation c. light independent/dark reactions = Calvin-Benson cycle = carbon fixation 1) CO2 2) RUBISCO B. chemosynthesis 1. bacteria (eg: nitrifying, sulfur, iron, hydrogen, carbon) 2. archaea (eg: methanogens, hyperthrmophiles) C. Other biosynthesis pathways (won’t stress) 1. gluconeogenesis 2. formation of fatty acids & glycerol 3. formation of amino acids 4. formation of nucleotides D. amphibolic pathways Online Metabolic Maps IUBMB-Nicholson Metabolic Maps, Minimaps & Animaps http://www.iubmb-nicholson.org/ KEGG PATHWAY Database: Wiring diagrams of molecular interactions, reactions, and relations http://www.genome.jp/kegg/pathway.html