Cells
advertisement

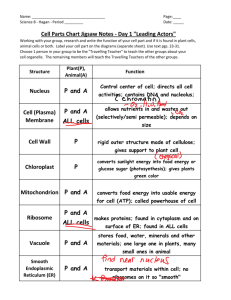
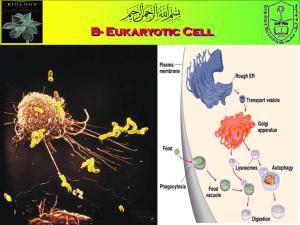
Cells Discovery of the Cell: Robert Hooke (1665)-observed a thin slice of cork under a compound microscope and saw thousands of tiny, empty chambers he called “cells.” Anton van Leeuwenhoek-observed pond water with a single lens microscope and found thousands of tiny organisms floating around. Cell Theory: All living things are composed of cells. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. New cells are produced from existing cells. Prokaryotic Cells - cells that do not contain nuclei. Generally smaller and simpler. Genetic material is not contained in the nucleus. Example: bacteria Eukaryotic Cells – cells that contain nuclei. Generally larger and more complex. Contain dozens of structures and internal membranes and are highly specialized. Genetic material contained in nucleus. Inside the Cell “Factory” Organelles – structures found in eukaryotic cells that act as specialized “organs” for the cell. The cell is divided into two major parts: the nucleus and the cytoplasm. Cytoplasm - the portion of the cell outside the nucleus. Fluid-like substance. Nucleus – the control center of the cell. “main office of factory” or brain. Contains nearly all the cells’ DNA and with it the coded instructions for making proteins and other important molecules. Surrounded by a nuclear envelope. o Two membranes o Contains nuclear pores that allow material to move in and out of the nucleus. Contains chromatin o DNA bound to protein that is spread throughout the cell. o Condenses to chromosomes during cell division that contain genetic information passed from one generation of cells to the next. Contains a nucleolus o Small, dense region in the center of the nucleus o Where ribosomes are assembled. Ribosomes – site of protein assembly. Small particles of RNA and protein found throughout the cytoplasm. Endoplasmic Reticulum – two types: Rough & Smooth. Site where lipid components of the cell membrane are assembled, along with proteins and other materials that are exported from the cell. Rough ER – lined with ribosomes. Involved in protein synthesis. Smooth ER – no ribosomes present. Contain enzymes that perform specialized tasks such as synthesis of membrane lipids and detoxification of drugs. Golgi Apparatus – the “packaging” area of the cell. Modifies, sorts and packages proteins and other materials from the endoplasmic reticulum for storage in the cell or secretion outside the cell. Lysosomes – the “clean-up crew” of the cell. Small organelles filled with enzymes Function in the digestion or breakdown of lipids, carbohydrates and proteins in the cell so they can be used. Also breakdown organelles that are too old to function correctly. Vacuoles – “storage room” of the cell. Found primarily in plant cells and small single-celled organisms. Function to store materials such as water, salts, proteins and carbohydrates. Mitochondria – “power plant” of the cell. Convert chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use. Have 2 membranes – outer and the inner is folded up inside the organelle. Contains it’s own DNA Chloroplasts – solar energy supply Found only in plants Capture the energy from sunlight and convert it into chemical energy in the process called photosynthesis. Have 2 membranes and inside have large sacs of membranes that contain chlorophyll. Contains it’s own DNA. Cytoskeleton – support structure and transportation system of the cell. Network of protein filaments that help the cell to maintain its shape and are also involved in movement. Contains 2 primary protein filaments – microfilaments and microtubules. Cell Membrane – the entry gate of the cell. Regulates what enters and leave the cell and also provides protection and support. Consists of a lipid bilayer with proteins embedded within. Cell Wall – found mainly in plants. Provides support and protection for the cell. Lies outside the cell membrane.