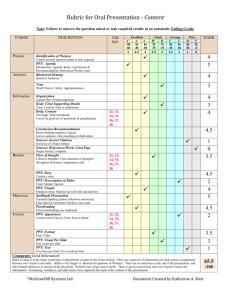
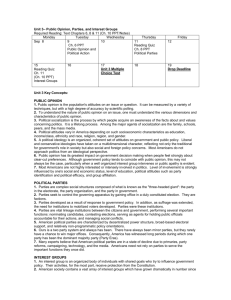
COMM 2713 – Spring 2011 – Midterm Review Sheet
advertisement

COMM 2713 – Final Review – Page 1 of 4 COMM 2713 – Spring 2011 – Final Review Sheet (Final: Wed., May 11th at 8 a.m.) MC Items / 150 Points Social Judgment Theory – Sherif – Ppt. Slides & Ch. 14 - Objective - Examines how we weigh new ideas by comparing them to our present point of view. - Latitudes of Acceptance, the number of messages about a new idea a person finds acceptable (in terms of being consistent with existing attitudes and beliefs). -Latitudes of Rejection the number of messages about a new idea a person finds unacceptable (or objectionable). -Latitudes of Noncommitment the number of messages about a new idea in which a person is undecided or has no opinion. - Ego-Involvement how important a particular idea or issue is to our identity. Elaboration Likelihood Model (ELM) – Petty & Cacioppo – Ppt. Slides & Ch. 15 - Objective - Theory examines attitude formation and change; used extensively in social influence research. - Motivation & Ability to Process a Message - 2 Routes for Processing: 1) Central & 2) Peripheral Cognitive Dissonance Theory – Festinger – Ppt. Slides & Ch. 16 - Objective - Cognitive Dissonance—a feeling of imbalance between attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors; an uncomfortable state that typically motivates people to take steps reduce dissonance. - Types of Selective Perceptions Used to Avoid Dissonance (Selective Exposure, Selective Attention, Selective Interpretation, Selective Retention) - Minimal Justification Small Group Communication – Ppt. Slides - Number of interactants increases the number of potential relationships and complexity of communication. - Group Roles & Norms / Group Cohesion Groupthink – Janis – Ppt. Slides (Concept covered in Ch. 17, but we didn’t cover Ch. 17) - What is groupthink? / - Antecedent Conditions of Groupthink Structuration Theory – Giddens – Ppt. Slides & Ch. 18 (Adaptive Structuration - Poole) - Interpretive - Rules & Resources (Allocative & Authoritative) / - Duality of Structure - System & Structural Levels / - Agents & Agency Cultural Approach to Organizations – Geertz, Pacanowsky, Trujillo – Ppt. Slides & Ch. 19 COMM 2713 – Final Review – Page 2 of 4 - Interpretive - Physical, Behavioral, & Verbal Manifestations of ORG Culture - Rituals (Personal, Task, Social, Organizational) Critical Theory of Communication in Organizations – Deetz – 1Ppt. Slide on D2L & Ch. 20 - Model (page 264 in 7th ed.): Top half, Managerial Control, bad: voices of those affected by management are excluded; Bottom half, Codetermination, good: open dialogue with all parties Schema Theory – Ppt. Slides - What are Schema? - Memory Organization Packets (MOPs) - Social Schemata Types (Person, Self, Role, Event) Extended Parallel Process Model (EPPM) – Witte – Ppt. Slides - Use of Emotional Appeals in Persuasion - Perceptions of Risk/Susceptibility (Susceptibility, Severity, Self-Efficacy, Response Efficacy) - 2 parallel types of processing / - Moderate fear appeals seem to work best. Rhetorical Theory (Classical Rhetoric) – Aristotle – Ppt. Slides & Ch. 21 - Rhetoric—the study of practical discourse. / - 5th Century Greece - Types of Rhetoric (Forensic, Deliberative, Epideictic) - Types of Proofs (Ethos, Pathos, Logos) - Canons of Rhetoric: Invention, Arrangement, Style, Delivery, Memory Inoculation Theory/Psychological Reactance – McGuire – Ppt. Slides - What is inoculation? / - Inoculation leads to increased resistance to persuasion. - When does reactance occurs? How can reactance be controlled? Dramatism – Burke – Ppt. Slides & Ch. 22 - Assumptions of Dramatism - Concepts: Substance, Identification, Division, Consubstantiation, Guilt, Victimage (Mortification, Scapegoating), Redemption - Pentad: Act, Scene, Agent, Agency, Purpose Narrative Paradigm – Fisher – Ppt. Slides & Ch. 23 - Interpretive - Humans are essentially storytellers. / - “Good Reasons” - Narrative Rationality (Coherence & Fidelity) / - Examples of Narratives (Health & Campaign) Semiotics – Barthes – Ppt. Slides & Ch. 25 (Ppt. Slides with Cultural Studies Material) - Semiotics deals with the study of signs/symbolic communication with the mass media. - Signs/symbols are cultural and meanings for signs/symbols are socially constructed. Cultural Studies – Hall – Ppt. Slides & Ch. 26 - Stems from Critical Theory - People are part of a hierarchical structure of power / - Hegemony & Resistance COMM 2713 – Final Review – Page 3 of 4 - Popular Culture and Texts / - Types of High & Low Culture in the Media - Cultural Artifacts & Stages: Representation, Identity, Production-Consumption, & Regulation Cultivation Theory – Gerbner - Ppt. Slides & Ch. 27 - “Magic bullet” or direct influence of media / - Two-step flow model of media influence. - What does Cultivation Theory predict & explain? - Cultivation Differential / - Mainstreaming / - Resonance / - First & Second-Order Effects Agenda-Setting Theory – Process, McCombs & Shaw – Ppt. Slides & Ch. 28 - Objective - Media gatekeepers and other individuals set the news agenda /- Public Vs. Media Agenda - Framing Theory: Examines media bias in the presentation of information and news (Sensationalism, Message Source Characteristics) Uses & Gratifications Theory – Katz, Blumler, & Gurevitch – Ppt. Slides - Examines the motives individuals have for using various types of mass media. - Theory assumes people play an active role in using the mass media. - Types of Gratifications Sought and Obtained from the Media (Information Seeking, Personal Identity, Integration and Social Interaction, Entertainment) Communication Accommodation Theory (CAT) – Giles – Ppt. Slides & Ch. 30 - Objective - Roots in Social Identity Theory / - In-Groups & Out-Groups - Central Concepts: Convergence, Divergence, Maintenance, Over/Underaccommodation Face-Negotiation Theory – Ting-Toomey – Ppt. Slides & Ch. 31 - Objective - Draws upon Politeness Theory (Brown & Levinson) and Goffman’s Work - Concept of Face (Goffman): Positive & Negative - Face-Threatening Acts, Face-Saving Behaviors, Face Restoration - Face Management Strategies: Avoidance, Obliging, Comprising/Integrating, Dominating Intercultural Communication Theory – Ppt. Slides - Culture / - Speech Codes - Individualism vs. Collectivism / - High-Context Culture vs. Low-Context Culture Argumentation – Toulmin’s Model – Ppt. Slides - Toulmin’s model is a helpful framework for constructing arguments. - Fallacies associated with Grounds: Unsupported Assertions, Distorted Evidence, Isolated Examples, Misused Statistics - Fallacies associated with Claims: Red Herring, Arguing in a Circle - Fallacies associated with Warrants & Backing: Halo Effect, Ad Hominem, Hasty Generalization, Stereotyping, False Dilemma, False Analogy, Post Hoc, Slippery Slope - Fallacies associated with Qualifiers: Hyperbole, Loaded Language - Fallacies associated with Rebuttals: Ignoring the Issues, Non Sequitur COMM 2713 – Final Review – Page 4 of 4 *Know definitions of key terms and concepts. *Be able to apply theories & concepts to examples.