File
advertisement

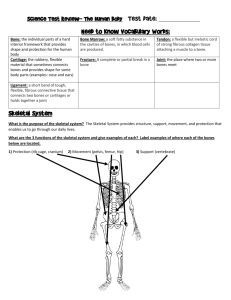
Name: _____________________________ SCP BIOLOGY ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Date: ____________ Block: _____ UNIT 3 STUDY GUIDE: INTEGUMENT (SKIN), SKELETAL, MUSCULAR, NERVOUS AND IMMUNE SYSTEM I. What to Study Notes: o Skeletal and Muscular System Notes o Nervous System Notes o Immune System Notes o Integument/Skin Notes Handouts: o Joints in the Human Body Worksheet o Video Worksheet: Muscular System and The Nervous System o Neuron and Brain coloring worksheet Diagrams: o Skeleton Diagram o Brain Diagram o Neuron Diagram o Skin diagram II. Integument Vocabulary Terms – QUIZLET QUIZLET QUIZLET!!! Tendon Peripheral NS Thermoregulation Bursa Central NS Sweat glands/pores Osteoblasts Neuron (and all parts) Sebaceous gland Osteoclasts Neurotransmitters 3 skin layers – Epidermis, Arthritis Synapse Dermis, and Subcutaneous Marrow Receptor Spongy bone Stimulus/response nervous, connective and Compact bone Pathogen muscular Voluntary/involuntary Antibody Melanin Smooth muscle Antigen Keratin Cardiac muscle Nonspecific/Specific responses Axial and appendicular Skeletal muscle White blood cells/Killer T Four tissues (epithelial, skeleton Muscle contraction Joints (moveable/immovable) Brain (and all parts) Ligament Spinal cord cells/Macrophages immunity Name: _____________________________ SCP BIOLOGY ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY III. Date: ____________ Block: _____ What to Know 1. The Skeletal System Chapter 37.2 Understand six primary functions of the Skeletal System. Be sure to understand the difference between the appendicular and axial skeletons. Ligaments and tendons help to form joints. Cartilage and bursae is found between joints and helps to cushion where the bones meet. Review Question: What are at least FIVE functions of the skeletal system? Review Question: Explain the difference between ligaments and tendons. Be able to describe the two types of bone tissue. Spongy bone is usually located at the located at the end of long bones. Compact bone is found in the middle of long bones and helps to keep them strong. Bone marrow is found in the in the cavity in the center of the bone and is responsible for the production of red blood cells. Review Question: Homeostasis is a balanced state in the body. In terms of the skeletal system, describe three ways homeostasis is maintained. A. B. C. 2. The Muscular System. Chapter 37.3 Be able to compare and contrast the three different types of muscles. Understand which are voluntary, involuntary, skeletal, striated and smooth. Understand the main functions of each type of muscle. Review Question: What at least FIVE main functions of the muscular system? Review Question: Be able to explain how the muscular system maintains homeostasis when the body is too hot or cold. (this is called thermoregulation) Name: _____________________________ SCP BIOLOGY ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Date: ____________ Block: _____ 3. The Integumentary System (Skin) Chapter 37.1 Understand that the skin is made up of all four types of tissue, and is for protection and support. Review Question: Describe the structures that are in the three layers of the skin. Be able to describe multiple aspects and structures found in each. 4. The Nervous System Chapter 40.1 Understand the nervous systems parts, functions and most importantly the most basic unit of the nervous system: the neuron. Also be able to identify parts of the brain and the synapse. Review question: How are messages chemically sent throughout our body? (think about what occurs at the synapse and between the neurons) Review question: What happens when the chemical neurotransmitters are blocked or if they are increased into your body? 5. The Immune System Chapter 42 The immune system serves as a defense system against pathogens that are harmful to your health. It maintain homeostasis by providing a barrier against and responding to infections. Review question: What are pathogens and what are nonspecific defenses that keep them out? Review question: What occurs when you have an infection? (a nonspecific response) Review question: Describe how anti-bodies and antigens help macrophages and Killer T cells destroy infectious cells.