Cell transport, energy, and division
advertisement

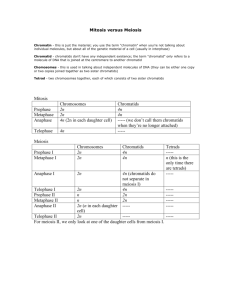
Name: ______________________________________ SCIENCE – THE CELL CTED-1 April 15, 2008 Section #/color: ___ / ________ SCIENCE – THE CELL What, Why, Where, When and How of Cell Transport, Energy, and Division An Introduction and Comparison Activity How is The Cell Cycle connected to the life processes and our 3 focus topics? 1. In each box, fill in where each life process happens. 2. In each star, fill in where cell energy, transport and division are happening. E, T, D E,T E,T E,T Use the chart below to compare and organize your current knowledge about cell transport, energy, & division. The WHAT's, WHY's, WHERE's, WHEN's, WHO's, and HOW's of Cell Transport, Energy, and Division ? What Why Where When Who How TRANSPORT The process of how cells get materials into and out of themselves across the cell membrane In order to do the life processes, cells have to import certain materials and export the materials that the make as well as wastes Cell Membrane ENERGY The process by which cells obtain and use energy DIVISION The process by which a cell divides to become to new cells In order to do the life processes, cells need energy to make them happen Cells are limited in size; when they become too big, they can’t do the life processes and must divide Mitochondria Chloroplast When materials are needed by Whenever the cell needs the cell for moving, responding to energy to move, respond to change, growing and developing, change, grow and develop, metabolizing, reproducing reproduce When important materials and/or wastes are made by the cell when Energy is made in the life it has been moving, responding to process of metabolism change, growing and developing, metabolizing, reproducing ALL ORGANISMS! ALL ORGANISMS! Passive Transport: Obtain energy via Diffusion – movement of photosynthesis in the molecules down the gradient chloroplast (water, sunlight, from high to low concentration chlorophyll, carbon dioxide Osmosis – movement of WATER combine to make oxygen and down the gradient from high to glucose), chemosynthesis, and low concentration “eating” (ominvores, herbivores, carnivores, Active: decomposers, scavengers, etc.) Protein Pumps – uniport (one molecule against the gradient), Use the energy via symport (two different molecules RESPIRATION! Glucose against the gradient in the same and oxygen combine to make direction), antiport (two different ATP, carbon dioxide and molecules against the gradient in water. opposite directions) When no oxygen is present, Anaerobic respiration is Vesicle/Vacuole Assisted – performed…ATP is made but Endocytosis (large molecule w/o oxygen and other bibrought IN), Exocytosis (large products are created. molecule sent OUT) Nucleus and cytoplasm When the cell has become to big for it to be able to sustain the life processes ALL ORGANISMS! Six steps: Interphase – DNA doubles Prophase – nuclear membrane disappears, chromatin becomes rod-like sister chromatids Metaphase – chromatids attach to spindle and line up in the middle of the cell Anaphase – sister chromatids separate Telophase – nuclei form around sister chromatids and chromatids become chromatin again Cytokinesis – cell completely separates into two identical cells.