Bio 160: Introduction to Human Anatomy and
advertisement

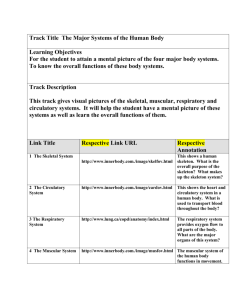
Bio 160: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Spring 2012 Instructor: Tammy Gillespie Phone: 928-428-8364 Email: tammy.gillespie@eac.edu Office: Math and Science Bldg Rm 304 Office Hours: MWF 8-9 am, 12-1 pm Website: http://eacfaculty.org/tgillespie Course Description: This course is designed as an introduction into human anatomy and physiology. Course Objectives: By the end of this course you should be able to… 1. Understand and give examples of the role energy has in human organisms. 2. Understand the structure, function, and relationships between human body systems. 3. Gain an awareness of the anatomical and physiological results of disruptions to the normal status of the human organism. 4. Use case studies to investigate normal function and dysfunction of human body systems. Tests and Grading: There will be 5 concept tests, posttest, and a comprehensive final exam. There will also be quizzes, homework assignments, reading assignments, and case studies. An exam can only be made up in the event of a verifiable student absence, provided that the student has notified the instructor prior to the scheduled time of the exam. You must schedule an appointment to take the exam prior to the next scheduled class meeting. Any student who enters an exam or quiz late will not be given any extra time to take the exam, and if sufficiently late, will not be allowed to take the exam at all. Grades: A: 89.5-100% B: 79.5-89.4% C: 69.5-79.4% D:59.5-69.4% F: 0-59.4% Academic Dishonesty: Acts of academic dishonesty, including plagiarism and cheating, will not be tolerated and are considered serious offenses. Any such action by the student will be reported to the administration. Penalties could range from loss of points to permanent expulsion from the institution. Please consult the institutions Academic Integrity policy for further information. Assignments: 1. You will be required to complete the review exercises at the end of each lab exercise. A schedule and list of questions to answer are found at the end of this syllabus. 2. At the beginning of each body system you will complete a case study that deals with some aspect of that system. You will be required to submit your answers to the case study when we conclude that system. 3. You will also do a group presentation on an additional case study of your choosing with your group. You will be assigned to a group at the beginning of the semester and be presented with a list of the case studies from which you may choose. The guidelines for the project will be given to you shortly. What you need: You need access to a computer and the internet. There are many readings and activities that we will be doing from the cyber world and tools on the computer that we will be utilizing. Bio 160 Class Schedule Spring Semester 2012 Date Topic 1/12/12 Pretest, Introduction to Energy, Cell respiration 1/17/12 Cell structures/transport, Cell chemistry 1/19/12 Cell structures, Cell biology lab 1/24/12 Mitosis/Meiosis/Inheritance 1/26/12 Inheritance/Evolution 1/31/12 Test #1/ Tissues and Skin 2/2/12 Tissues and Skin Skeletal System 2/7/12 Skeletal System 2/9/12 Skeletal System/Joints 2/14/12 Muscular System 2/16/12 Muscular System 2/21/12 Muscular System 2/23/12 Test #2/ Nervous System 2/28/12 Nervous System 3/1/12 Nervous System 3/6/12 Nervous System/Senses 3/8/12 Endocrine System 3/13/12 Test #3/ Blood 3/15/12 Circulatory System 3/27/12 Circulatory System 3/29/12 Circulatory System 4/3/12 Lymphatic System/Immunity 4/5/12 Test #4/ Respiratory System 4/10/12 Respiratory System 4/12/12 Respiratory System Digestive System 4/17/12 Digestive System 4/19/12 Digestive System 4/24/12 Urinary System 4/26/12 Reproductive System 5/1/12 Test #5/ Posttest/Review for Final 5/3/12 Final Exam Readings (online and text) Class Notes Ch. 14, p. 488-502 Ch. 2, p. 25-58 Lab Exercise 3 Ch. 3, p. 63-75 Lab Exercise 4 Ch. 3, p. 63-75 Class Notes Class Notes Ch. 3, p. 87-100, Ch. 4, p. 109-128, Lab Ex. 5 Ch. 3, p. 87-100, Ch. 4, p. 109-128, Lab Ex. 6 Ch. 4, p. 134-144 Lab Exercise 7 Ch. 5, p. 145-157 Lab Exercise 8 Ch. 5, p. 158-173 Lab Exercises 9, 10 Ch. 6, p. 181-195 Lab Exercise 11 Ch. 6, p. 196-204 Lab Exercise 12 Ch. 6, p. 205-214 Ch. 7, p. 226-239 Lab Exercise 13 Ch. 7, p. 240-254 Lab Exercise 14 Ch. 7, p. 255-269 Lab Exercise 15, 16 Ch. 8, p. 279-301 Lab Exercise 17 Ch. 9, p. 308-330 Lab Exercise 18 Ch. 10, p. 337-352 Lab Exercise 19 Ch. 11, p. 357-369 Lab Exercise 20 Ch. 11, p. 370-382 Lab Exercise 21 Ch. 11, p. 383-391 Lab Exercise 22 Ch. 12, p. 398-428 Ch. 13, p. 436-444 Lab Exercise 23 Ch. 13, p. 445-452 Lab Exercise 24 Ch. 13, p. 453-455 Ch. 14, p. 464-473 Ch. 14, p. 474-488 Lab Exercise 25 Ch. 14, p. 474-488 Ch. 15, p. 512-532 Lab Exercise 26 Ch. 16, p. 539-568 Lab Exercise 27 Laboratory Experiences: These lab experiences are designed to allow you to reflect on the ideas and information that we discuss in each of the learning objects, to help you construct an understanding of the world in which we live. You will question, challenge and explore science. You will design and perform relevant experiments, following which you will discuss with your classmates what you have learned and how your observations and experiments helped, or did not help, you better understand the concept. Your design of your experiments will be inquiry-based and “hands-on” that you will be able to model in your own classroom. Below you will find the topics that we will be covering through the semester. They encompass all of the concepts that are required for students to master by the Arizona Department of Education. Arizona Department of Education Science Competencies and Performance Standards covered: 1. Energy of the Earth Learning objectives What you will learn as you master the competency: Identify the ultimate source of energy for the earth and the forms in which it can be found Describe how energy causes earth materials to change from one form to another Describe how energy is involved in chemical and physical changes Describe how energy of sunlight is changed to chemical energy in plants, transferred between living organisms, and utilized. 2. Cell Biology Learning objectives What you will learn as you master the competency: Describe the structure and function of the cell and its component parts (organelles and cell membrane/cell wall) Explain how cellular respiration in plants and animals convers food energy into mechanical energy and heat Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and identify their relationships to growth and repair and sexual reproduction Understand how traits are passed on from parent to offspring 3. Human Anatomy and Physiology Learning objectives What you will learn as you master the competency: Describe the structure and function of the digestive system in vertebrates Describe the structure and function of the respiratory system in vertebrates Describe the structure and function of the cardiovascular/circulatory systems in vertebrates Describe the structure and function of the skeletal system in vertebrates Describe the structure and function of the muscular system in vertebrates Describe the structure and function of the nervous system in vertebrates 3. Evolution Learning objectives What you will learn as you master the competency: Explain how variations/mutations within organisms through sexual reproduction could give species an advantage for survival in a particular environment Give examples of how changes in the environment lead to natural selection