Document
advertisement
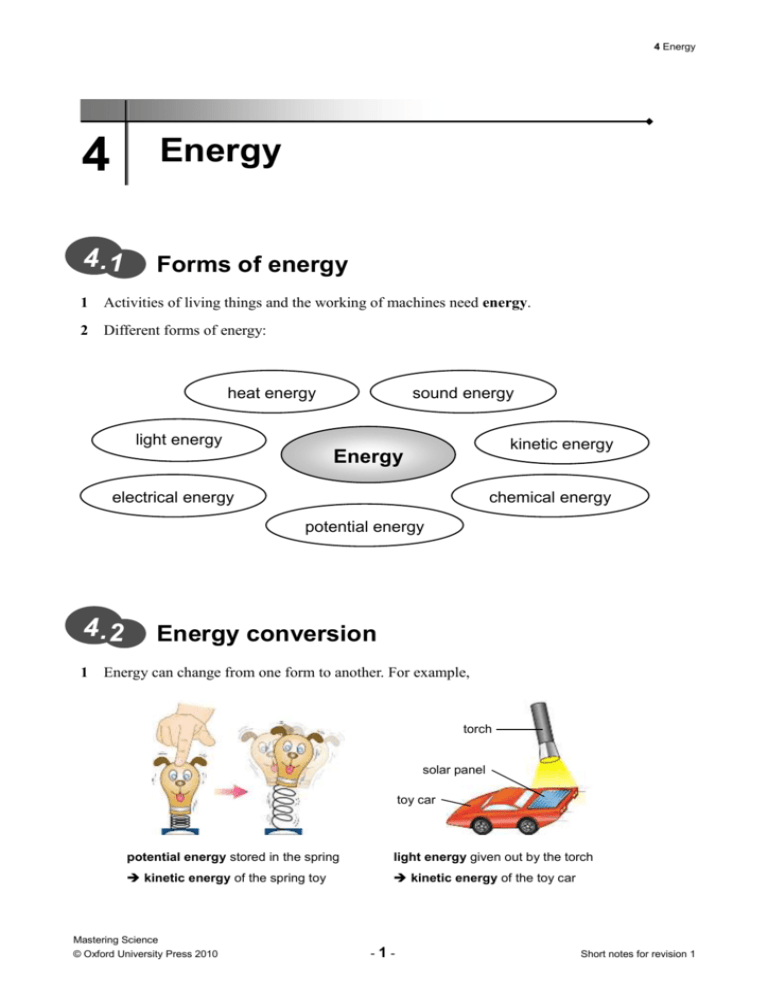
4 Energy 4 Energy 4.1 Forms of energy 1 Activities of living things and the working of machines need energy. 2 Different forms of energy: heat energy sound energy light energy kinetic energy Energy electrical energy chemical energy potential energy 4.2 1 Energy conversion Energy can change from one form to another. For example, torch solar panel toy car potential energy stored in the spring light energy given out by the torch kinetic energy of the spring toy kinetic energy of the toy car Mastering Science © Oxford University Press 2010 -1- Short notes for revision 1 4 Energy Е 2 During an energy conversion, intermediate forms of energy may be involved between the initial and the final forms of energy. 3 Energy converters can change energy from one form to another. Motors and generators are common energy converters. 4 Motors change electrical energy to kinetic energy. cells pulley switch motor weights electrical energy from the cells 5 motor kinetic energy of the pulley kinetic energy of the rising potential energy gained by the weights weights Generators change kinetic energy to electrical energy. light bulb pulley switch generator weights potential energy lost by the falling weights kinetic energy of the pulley and the generator generator electrical energy light energy and heat energy given out by the light bulb 6 Controlled energy conversions can provide us with useful forms of energy in a safe way. 7 If energy conversions get out of control, disasters may result. Mastering Science © Oxford University Press 2010 -2- Short notes for revision 1 4 Energy 4.3 Common fuels 1 Fuel Main uses Town gas For cooking and heating Remarks Does not give out black smoke when burnt Liquefied For cooking and powering vehicles petroleum gas (LPG) Does not give out black smoke when burnt Petrol and diesel For powering vehicles Give out black smoke when burnt Kerosene For cooking; high quality kerosene Gives out black smoke when for powering aeroplanes burnt Mainly for generating electricity Gives out black smoke when Coal burnt Mastering Science © Oxford University Press 2010 -3- Short notes for revision 1 4 Energy Е 2 3 Properties of good fuels: a easy to light; b clean when burnt; c safe to use; d give out a lot of heat energy when burnt; e easy to store and transport. Safety precautions should be taken when using, transporting and storing fuels. 4.4 Generating electricity 1 Electricity is the most common energy source used at home today. 2 Steam engines are used to supply kinetic energy to drive a generator to generate electricity. steam pipe boiler containing water fuel chamber light bulb steam turbine generator Steam engine model chemical energy stored in the fuels 3 heat energy and kinetic energy of the steam kinetic energy of the steam turbine generator electrical energy The principle of generating electricity is to change kinetic energy to electrical energy using a generator. Mastering Science © Oxford University Press 2010 -4- Short notes for revision 1 4 Energy 4 pollution reduction system generator boiler steam to consumers turbine air steam water coal sea water condenser cold sea water hot sea water The steps in the generation of electricity in a coal-fired power station: Coal is crushed into fine powder so that it can be burnt more completely. The coal powder is burnt in a boiler. A large amount of heat energy is given out to heat the cold water in the tubes inside the boiler. Water boils and changes to steam. The steam turns the turbine. The turbine drives the generator to generate electricity. 5 The energy conversions involved in generating electricity by burning fuels in a power station: chemical energy stored in the fuels Mastering Science © Oxford University Press 2010 heat energy and kinetic energy of the steam generator -5- kinetic energy of the turbine electrical energy Short notes for revision 1 4 Energy 4.5 Energy sources and us 1 Fossil fuels are non-renewable sources of energy. Burning fossil fuels gives out a large amount of carbon dioxide and many air pollutants. 2 Effects of air pollutants include: 3 a making us sick when breathed in; b forming acid rain; c leading to global warming. We can reduce the use of fossil fuels and hence air pollution by saving energy and using alternative energy sources. Alternative energy source a) Energy conversions involved Solar power Solar panels: light energy given out by the sun electrical energy solar panel Solar power stations: heat energy given out by the sun heat energy and kinetic energy of steam kinetic energy of the turbine electrical energy generated by the generator A solar power station in the United States Mastering Science © Oxford University Press 2010 -6- Short notes for revision 1 4 Energy potential energy of the water upstream b) Hydroelectric power water upstream kinetic energy of the running water generator kinetic energy of the turbine electrical energy generated by the generator turbine c) kinetic energy of the wind Wind power kinetic energy of the turbine turbine wind electrical energy generated by the generator generator d) Nuclear power turbine generator heat energy given out when nuclear materials undergo reactions steam heat energy and kinetic energy of steam kinetic energy of the turbine water electrical energy generated by the generator nuclear materials (e.g. uranium) e) potential energy of the water in reservoir Tidal power sea reservoir kinetic energy of the running water kinetic energy of the turbine electrical energy generated by the tide falls generator generator turbine Mastering Science © Oxford University Press 2010 -7- Short notes for revision 1 water coal 4 Energy f) heat energy deep underground Geothermal power turbine generator heat energy and kinetic energy of steam kinetic energy of the turbine electrical energy generated by the steam coming up generator water pumped down hot rocks deep underground g) Biofuels chemical energy stored in plants heat energy and kinetic energy of steam kinetic energy of the turbine electrical energy generated by the generator Mastering Science © Oxford University Press 2010 -8- Short notes for revision 1






