File - joe's chemistry webpage
advertisement

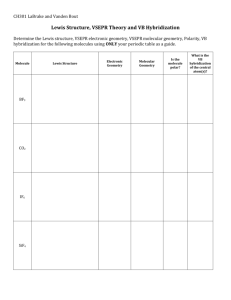
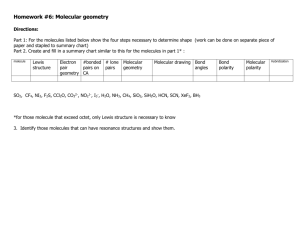
Organic Chemistry Lab – Molecular Geometry & VSEPR Theory Name_______________ Date___________B____ OBJECTIVES: Use e- dot structures and model kits to build organic molecules Use VSEPR Theory to determine geometry, bond angles, and symmetry of a molecule Recognize basic nomenclature and functional groups of organic molecules Understand the connection between molecular geometry and the properties of molecules PROCEDURE: On separate paper… 1. Write the problem number, chemical formula, and name of the molecule. 2. Draw the e- dot structures and circle shared pairs of e3. Build the molecule using models. 4. Re-draw the molecule in 3D (using the model). Use lines, dashes, or wedges. Use subscripts for multiple central atoms. 5. For each central atom, write the molecular geometry (name of the shapes). 6. For each central atom, write the bond angle(s) 7. Write whether the molecule is Symmetrical OR Unsymmetrical PRE-LAB SIMPLE MOLECULES #1-15: JOE WILL PROVIDE HELP IF ASKED 1. Cl2 Chlorine Gas is a yellow-green toxic gas that has been used as a weapon in war. 2. O2 Oxygen gas is a product of photosynthesis and consumed by humans during respiration. 3. H2S Hydrogen Sulfide is a colorless, very poisonous, flammable gas with the foul odor of rotten eggs. 4. HCl Hydrogen Chloride is a colorless gas that forms an acid when dissolved in water. 5. BCl3 Boron Trichloride. Boron bonds covalently to become stable without an octet, stable with just 6 v e- 6. NH3 Ammonia is used as cleaning product and is recognized by its strong odor. 7. H2O Water is essential to life on earth and has many unique chemical and physical properties. 8. H2O2 Hydrogen Peroxide has a wide of range of uses including: rocketry, disinfection and bleaching. 9. CH4 Methane is the simplest “hydrocarbon” meaning made of C and H atoms. 10. CH3Cl Chloromethane is a colorless, extremely flammable, slightly sweet smelling gas. Common Prefixes: meth = 1, eth = 2, prop = 3, but = 4, and pent hex hept oct non dec = 5 6 7 8 9 10, respectively. MOLECULES #11-15: JOE WILL PROVIDE LIMITED HELP IF ASKED 11. CH3OH Methanol is colorless, flammable, and has a sweet smell. 12. C2H6 Ethane is a hydrocarbon and is an odorless, colorless, and flammable gas. 13. C2H4 Ethene is one of the chemicals that triggers fruits to ripen. 14. C2H2 Ethyne can be used for the welding of metals. 15. C6H14 Hexane, like other hydrocarbon fuels it can undergo combustion reactions to produce CO 2 + H2O Organic Chemistry Lab – Molecular Geometry & VSEPR Theory Name_______________ Date___________B____ MOLECULES #16-24: JOE WILL PROVIDE VERY LIMITED HELP #16 on may have multiple geometries around different Carbons. Use C1, C2, etc. to differentiate. 16. C6H12 Cyclohexane is a simple 6 Carbon ring that is colorless and flammable liquid. 17. C6H6 Benzene is a colorless, highly flammable liquid with a sweet smell. 18. CH3CN Acetonitrile is a colorless liquid solvent used in battery application and pharmacueticals. 19. CH3CH2NH2 Aminopropane is colorless gas that has a strong fishy and ammonia-like odor. 20. CH3CHO Ethanal occurs naturally in coffee, bread, and ripe fruit. 21. CH3OCH3 Dimethyl ether is a colorless gas used as a precursor (use to make other chemicals). 22. (CH3)2CO Acetone is the common ingredient in nail polish remover. ( C=O in the middle ) 23. CH3COOH Ethanoic Acid, commonly known as Acetic acid or Vinegar. ( Both O’s bonded to C2) 24. CH3COOCH3 Methyl acetate is used as a solvent in paints, glues, and nail polish removers. (O’s bonded like #23) CHALLENGE MOLECULES Choose ___ FLAVOR, SCENT, or PHARMACUETICAL C9H8O Cinnamon C8H8O3 Vanilla C6H12O2 Apple flavor C9H8O4 Aspirin Cinnamaldehyde is the primary flavor molecule in cinnamon. It has a benzene ring base. Off a single carbon on the ring there is a C=C followed by an aldehyde –CHO group. Vanillin is the primary component of the extract of the vanilla bean. It has a benzene ring base, with a –COH on C1, -OCH3 on C3, and a -OH on C4. Butyl Acetate is the main components of apple flavor. As an ester (RCOOR’), after it’s “butyl” chain (meaning 4 C) the R’ is a simple methyl group –CH3 Acetylsalicylic acid or asprin is used as an analgesic to relieve minor aches and pains It has benzene ring, -COOH on C1 and on C2 an –O –CO –CH3. Choose ___ ENDOCRINE DISRUPTORS – Ideally, choose the one you studied in 9th Grade Science! For these molecules no e- dot structure is required. Re-draw the structure then label all of the geometries. Butyl Benzyl Phthalates - C10H10O4 Aldrin - C12H8Cl6 Atrazine - C8H14 N5Cl Phthalate (BBP) C19H20O4 Glycol Ethers - C3H8O2 Perfluorooctanoic acid C8HF15O2 Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDE's) C12H(8)Br2O Bisphenol A - C15H16O2 Organic Chemistry Lab – Molecular Geometry & VSEPR Theory Name_______________ Date___________B____ DISCUSSION QUESTIONS: 1. The dot structure of water (H20 - ex. #7 from the lab) shows that the central Oxygen atom is surrounded by four pairs of electrons, but measurements show that the bond angles in water are not 109.5° as expected for tetrahedral geometry. Describe what VSEPR theory is and then use it to explain why the bond angles in water are less than the 109.5º predicted for tetrahedral geometry. 2. Bond dissociation energy is one way to measure bond strength because it is the energy required to break that bond. Make a claim about the relationship between the number of bonds and bond length vs. bond strength. [use “As the… inc or dec … the inc or dec…] style claims defended by evidence from the data table. Bond C–C C=C C≡C alkane alkene alkyne Dissociation Energy (in kJ) C-to-C Distance (in picometers) 346 kJ 600 kJ 835 kJ 154 134 120 Organic Chemistry Lab – Molecular Geometry & VSEPR Theory Name_______________ Date___________B____ 3. Ethane is a molecule that can rotate around the single bond between the two Carbon atoms to make either the staggered and eclipsed arrangements of Ethane. Make a claim about which arrangement of ethane is more stable. Defend your claim using VSEPR theory. Staggered Rotate 180º Eclipsed 4. Organic chemistry is the study of molecules containing carbon. Almost every biological molecule in your body, the food you eat, and the medicines you take are made of mainly just six elements (H, O, S, P, N, Cl, C)!! Using what you have learned of covalent bonding and molecular geometry, explain what is responsible for the nearly infinite diversity of organic molecules important to life on Earth. Refer to specific examples from your lab as evidence to support your answer. Organic Chemistry Lab – Molecular Geometry & VSEPR Theory Name_______________ Date___________B____ Cyclohexane, C6H12, has different conformations (arrangements). Which is more stable, the boat or chair conformation of cyclohexane? Make a claim about which conformation of cyclohexane is more stable and defend it using what you know about VSEPR Theory. Chair Boat Cyclohexane, C6H12, has different conformations (arrangements). Which is more stable, the boat or chair conformation of cyclohexane? Make a claim about which conformation of cyclohexane is more stable and defend it using what you know about VSEPR Theory. Chair Boat Cyclohexane, C6H12, has different conformations (arrangements). Which is more stable, the boat or chair conformation of cyclohexane? Make a claim about which conformation of cyclohexane is more stable and defend it using what you know about VSEPR Theory. Chair Boat Organic Chemistry Lab – Molecular Geometry & VSEPR Theory Name_______________ Date___________B____ For molecules #11 and on, write “This molecule is a(n) [ see Functional Group Chart ] because there is a _____ group” Functional Group Reference Chart: CYCLIC Naming: cycloe.g. cyclopentane For molecules #11 and on, write “This molecule is a(n) [ see Functional Group Chart ] because there is a _____ group” Functional Group Reference Chart: CYCLIC Naming: cycloe.g. cyclopentane For molecules #11 and on, write “This molecule is a(n) [ see Functional Group Chart ] because there is a _____ group” Functional Group Reference Chart: CYCLIC Naming: cycloe.g. cyclopentane Organic Chemistry Lab – Molecular Geometry & VSEPR Theory Name_______________ Date___________B____ CYCLIC Naming: cycloe.g. cyclopentane CYCLIC Naming: cycloe.g. cyclopentane CYCLIC Naming: cycloe.g. cyclopentane Organic Chemistry Lab – Molecular Geometry & VSEPR Theory Name_______________ Date___________B____ CHALLENGE MOLECULES to BUILD - Molecules of Life For these molecules no e- dot structure is required. Simply build it Show Joe Re-draw the structure then label all of the geometries. C6H12O6 Glucose C4H5N3O Cytosine C9H13NO3 Adrenaline Glucose is one of the simplest sugars. Cells use it as the primary source of energy and it is one of the main products of photosynthesis. Cytosine (C) is one of the four main bases found in DNA and RNA, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine. It increases heart rate, constricts blood vessels, dilates air passages and participates in the fight-or-flight response. CHALLENGE MOLECULES to BUILD - Molecules of Life For these molecules no e- dot structure is required. Simply build it Show Joe Re-draw the structure then label all of the geometries. C6H12O6 Glucose C4H5N3O Cytosine C9H13NO3 Adrenaline Glucose is one of the simplest sugars. Cells use it as the primary source of energy and it is one of the main products of photosynthesis. Cytosine (C) is one of the four main bases found in DNA and RNA, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine. It increases heart rate, constricts blood vessels, dilates air passages and participates in the fight-or-flight response. CHALLENGE MOLECULES to BUILD - Molecules of Life For these molecules no e- dot structure is required. Simply build it Show Joe Re-draw the structure then label all of the geometries. C6H12O6 Glucose C4H5N3O Cytosine C9H13NO3 Adrenaline Glucose is one of the simplest sugars. Cells use it as the primary source of energy and it is one of the main products of photosynthesis. Cytosine (C) is one of the four main bases found in DNA and RNA, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine. It increases heart rate, constricts blood vessels, dilates air passages and participates in the fight-or-flight response.