Diffusion lab worksheet
advertisement
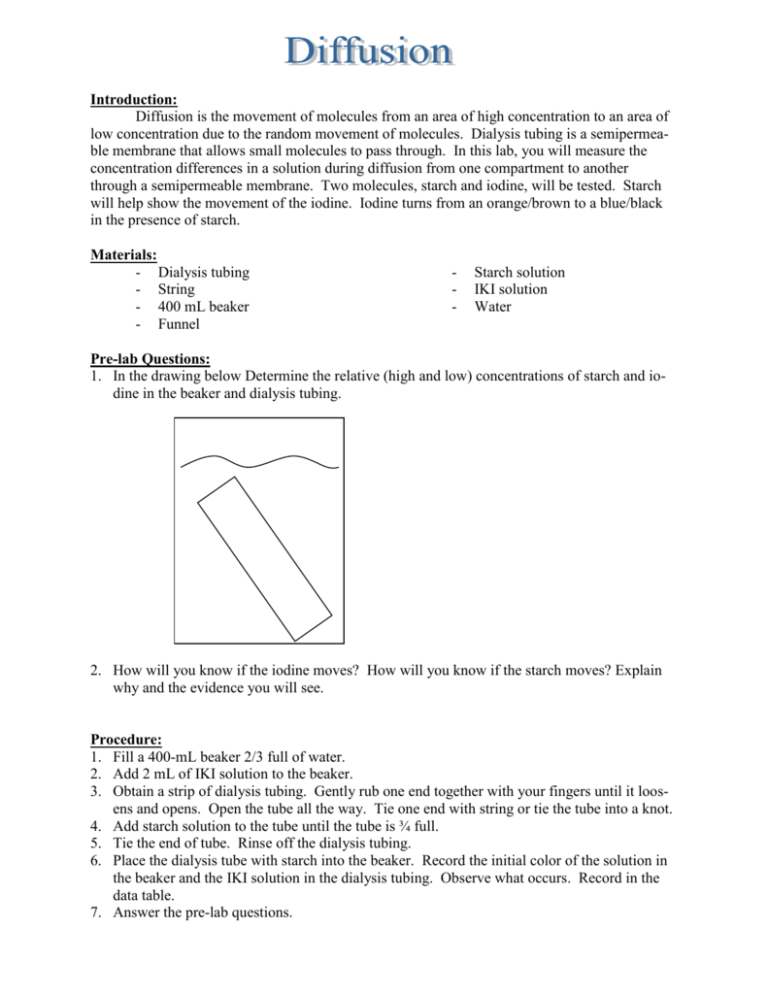
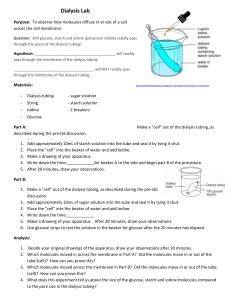
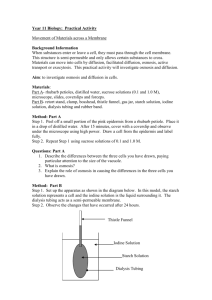
Introduction: Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration due to the random movement of molecules. Dialysis tubing is a semipermeable membrane that allows small molecules to pass through. In this lab, you will measure the concentration differences in a solution during diffusion from one compartment to another through a semipermeable membrane. Two molecules, starch and iodine, will be tested. Starch will help show the movement of the iodine. Iodine turns from an orange/brown to a blue/black in the presence of starch. Materials: - Dialysis tubing - String - 400 mL beaker - Funnel - Starch solution IKI solution Water Pre-lab Questions: 1. In the drawing below Determine the relative (high and low) concentrations of starch and iodine in the beaker and dialysis tubing. 2. How will you know if the iodine moves? How will you know if the starch moves? Explain why and the evidence you will see. Procedure: 1. Fill a 400-mL beaker 2/3 full of water. 2. Add 2 mL of IKI solution to the beaker. 3. Obtain a strip of dialysis tubing. Gently rub one end together with your fingers until it loosens and opens. Open the tube all the way. Tie one end with string or tie the tube into a knot. 4. Add starch solution to the tube until the tube is ¾ full. 5. Tie the end of tube. Rinse off the dialysis tubing. 6. Place the dialysis tube with starch into the beaker. Record the initial color of the solution in the beaker and the IKI solution in the dialysis tubing. Observe what occurs. Record in the data table. 7. Answer the pre-lab questions. 8. When the color change has occurred, clean up the lab, throw away the dialysis tubing and wash beakers. Answer lab questions. Data table: Initial color Final Color Solution in beaker B Solution in Dialysis tubing Questions: 1. What occurred to the iodine? Why did this occur? (In your explanation, include the relative concentrations of iodine and starch.) Is this what you expected? 2. Why did one molecule move and not the other? 3. Define selectively permeable. 4. Was this an example of diffusion? Why or why not?