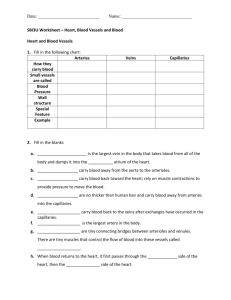
Clues
advertisement

44. The second Korotkoff sound occurs when the sphynomanometer is measuring the ____ pressure. 46. The blood from capillaries flow into a ___ before small veins. ACROSS 47. The 5 cm ascending aorta leads in to the aortic ___ that bends posteriorly and to the left. 3. The tunica ___ consists of mainly smooth muscle 48. Circulatory ___ is an inadequate blood flow and elastic tissue. throughout the body. 4. Degenerative changes in arteries that make them 50. General term given to the larger blood vessels less elastic are referred collectively as _____. leading to the heart. 6. A pulse can be felt in the ___ artery on the lateral side of the anterior forearm just proximal to the wrist. 51. A circle of interconnecting arteries around the pituitary and base of the brain is called the ___ _ ___. 10. Medium sized arteries that regulate the blood 55. Another term used for dead tissue. supply to different regions of the body by either 58. A ___ is a sudden neurological disorder often constricting or dilating are ____ ____. caused by a decreased blood supply to the brain. 13. An area of dead tissue is called an ____. 15. The condition of excessive accumulation of tissue 59. Epithelial cells of the alveolar membranes are tightly joined so that ions and fluids do not escape into fluid. the alveoli thus keeping them ___. 16, Renin causes the production of this 60. Neurogenic shock results from rapid loss of ___ vasoconstrictor from plasma proteins. tone that causes vasodilation which severely 17. The external ____ arteries lead to the femoral decreases blood pressure. artery. 18. Also know as ADH, causes water reabsorption in 61. Hormone released from the adrenal cortex in response to low BP or Na+, which causes the kidney the kidneys and vasoconstriction which results in to reabsorb Na+ and water. elevated blood pressure. 21. The right & left vertebral arteries unite to form this 62. Major arteries and veins leading to the kidney are termed ___. artery at the pons. 63. Tissue swelling in carotid artery that contains 22. Substances diffuse across ___ walls to tissue pressoreceptors (for BP) and chemoreceptors ( for cells or blood stream. 24. The pressure that moves the fluid outward at the oxygen and pH). 64. The circulatory circuit with freshly oxygenated arteriole end of a capillary. blood pumped to all parts of the body by the left 25. When the smooth muscles in a blood vessel contract and the diameter of the vessel decreases this ventricle. 66. The internal and external____ are major veins is called ___constriction. that drain the head and neck into the subclavian. 26. Blood capillaries that branch from thoroughfare channels have intermittent blood flow regulated by smooth muscle cells called ___ ____. 29. Small blood vessels that supply the larger many tissue layer blood vessels with nutrients are called ____ ____. 33. ___blood pressure is normally around120mm of Hg. 34. ___veins are caused by incompetent valves in veins in the leg. 37. The ____is the entire lining of the circulatory system made up of simple squamous epithelial cells. 38. A ___ is an arteriovenous anastomoses that consists of arterioles arranged in a convoluted fashion surrounded by a collagenous tissue. 43. A floating clot that becomes lodged in a smaller blood vessel. Peripheral Vessels Puzzle 32. Blood pressure may be measured directly by inserting a ___ into a blood vessel and connecting a manometer to it. 35. Highly permeable capillaries found in the kidney DOWN and intestine have a ___ structure. 36. From the lumen to the outer wall of a blood vessel 1. Nerve impulses are inhibited to smooth muscles of the tissue layers are called ___. blood vessels causing an increase in the diameter of 39. Soft masses of fatty materials deposited on the blood vessel. arterial walls. 2. The heart rate, rhythmicity and other 40. As the blood passes through the capillaries the characteristics can be determined by feeling the ____. blood colloid proteins in the capillaries cause ____ 3. ___ connect arterioles to capillaries or directly to pressure which tends to move fluid inward at the venules forming arteriovenous shunts. venule end. 4. The routine method of taking BP is called the 41. The presence of blood cells and plasma proteins ____method. increase the ___ (flowing ability ) of the blood. 5. Term given to a stationary blood clot. 42. The tunica ___ is the outer connective tissue 7. A bulge caused by a weakened spot in the aortic covering a blood vessel. wall. 45. Inflammation of varicose veins in the legs can 8. Name give to major veins and arteries connected to result in a condition called ____ which can lead to the diaphragm. gangrene. 9. The kidneys release an enzyme called ___ when 49. Condition of widespread edema, especially in the BP is low or Na+ ‘s are low which leads to the the peritoneal cavity, due to failure of the right production of angiotensin. ventricle which causes back pressure on the veins. 11. The pressure within the right atrium is called ___ 50. Retention of water by the kidneys increase the ____ pressure. blood ___ and BP. 12. Veins having diameters greater than 2mm contain 52. The inner most tunic ___ is composed mainly of ___ that allow blood to flow toward the heart but not in endothelium. the opposite direction. 53. The circulatory circuit from the heart through the 14. The ___ ___ pressure is the pressure at which a lungs. blood vessel will collapse when blood pressure drops 54. Blood ___ depends on heart action, blood due to shock. volume, peripheral resistance, and blood viscosity. 19. Normal cardiac rhythm regulated by the S-A node 56. General name given to a blood vessel that carries is called ___rhythm. blood away from the heart. 20. Accumulation of fluid with the pericardial cavity 57. The volume discharged from the ventricle per causing pressure on minute is called the cardiac ___. the heart thus interfering with heart action is called 65. Another name for a stroke. abbr. acute cardiac ___. 23. The hepatic ___ system begins with capillaries in the viscera and ends with sinusoidal capillaries in the liver. 24. Another term for high blood pressure. 27. Systolic and diastolic BP are determined by listening for ___ ___ while using the spygomanometer. 28. The osmotic pressure caused by plasma proteins is called __ ___ osmotic pressure. 30. Capillaries located in the liver that are large in diameter and also very permeable are called ____. 31. A large vein that empties into superior vena cava and drains the posterior thoracic veins. Peripheral Vessels Puzzle