Chicken leg lab
advertisement

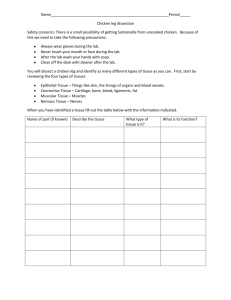
Name ____________________________________ OLS Chicken Leg Dissection Date ___________ Homeroom____# _____ INTRODUCTION: Similar in some respects to the human leg, the chicken leg and thigh are composed of numerous different cells, tissues and organs. These body parts interact and cooperate to allow the chicken to perform a variety of activities such as walking, hopping, sitting, and standing. In this lab you are to investigate the various tissues and structures of the leg and thigh of a chicken. MATERIALS: Chicken leg Blunt and sharp dissecting probes Scalpel Paper towels Forceps Dissecting pan Scissors PROCEDURE: 1. Become familiar with your chicken leg. Using the terms from last night, identify if it is a right or left leg by deciding lateral, medial, dorsal and ventral regions based on the cut of the lower abdominal/pelvic area. Which leg do you have, right or left? (circle one) 2. Place a chicken leg in your dissecting pan, medial side up. CAUTION: Scalpels and scissors are very sharp. Use extreme care. Only cut downward and/or away from your body. 3. Carefully remove the skin and subcutaneous fat. Use fingers, blunt probe, and scalpel. Do not cut any muscle tissue yet! Where is the fat more numerous, in the thigh or leg? More in the medial, lateral, anterior, or posterior? 4. You may be able to pull the skin off of the end of the drumstick. When through, be sure to return the leg to the medial side. 5. Now that the skin and fat are off, you can more easily see the muscle tissue. Describe the muscles that you see; focus on color and texture. _____________________________________________________________________________ 6. Beginning with the lower leg, separate the epimysium from each muscle. Use your fingers, the blunt probe. What is the purpose of the thin epimysium? Refer to last nights terms and write your answer below. _____________________________________________________________________________ 8. Now remove the muscles of the femur. You need not be a delicate as this could be a time consuming task. Be aggressive, as we have seen most of the important tissues already. You will be able to see the movement of the tendons as they contract. Again, try to remove as much of the muscle tissue as possible to get to the leg bone. _____________________________________________________________________________ 9. Locate the tendons that were attached. Briefly describe these. _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 10. You will notice that there are a number of blood vessels deep within the mass of muscles. They probably will be found 2-3cm, posterior to the femur with fat and nerves near by. Describe the physical appearance of any blood vessels you see. _____________________________________________________________________________ 11. There are two main types of blood vessels; arteries and veins. Arteries are generally more muscular (thicker) than veins. What type of blood vessel do you think you found?___________ Did you notice both types of blood vessels? Did you see any physical difference between the two?____________. If so, what is the difference? ______________________________. 12. Nerves are generally thin, threadlike white strands found between the muscle and the nearest bone. Look for the nerve in your specimen. Do you see any? Yes or No _____________________________________________________________________________ 13. Once the bone is fully cleaned off, ask Mrs. Mallay to “snap” the bone in half. Do not do this yourself as it can be difficult and the bone may splinter. Explain what you saw on the inside of your bone. _____________________________________________________________________________ WHEN THIS LAB IS COMPLETED: • BE SURE TO WASH (with soap) AND DRY ALL INSTRUMENTS -Your homework is to write a comprehensive conclusion about what you've learned. I expect a minimum of one side of one page for your conclusion. Do not simply summarize the lab, I know what went on. Discuss the levels of cellular organization and how it applies to what you saw. Attach this summary to the front of these pages and turn in on Monday. Terms to know Lateral- side medial – at the middle dorsal –of the back ventral-lower body at front anterior-in front posterior-near the back/bottom subcutaneous-under the skin epimysium-covering of connective tissue surrounding a muscle tendon- an inelastic cord or band of tough white fibrous connective tissue that attaches a muscle to a bone or other part ligament- a sheet or band of tough fibrous tissue that connects bones or cartilage at a joint or supports an organ, muscle, or other body part marrow-soft red/yellow tissue inside bones where blood cells are produced. femur-main bone in vertebrate leg