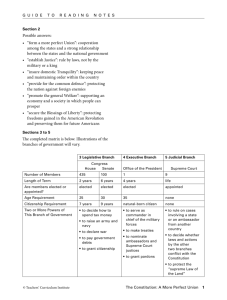
File - Ms. Mazzini-Chin
advertisement

AMERICAN HISTORY REGENTS REVIEW IT IS TIME TO PREPARE FOR THE AMERICAN REGENTS EXAM There are many things that you can do to make sure that you are well-prepared for the regents exam. 1. REVIEW PACKET Here you will find some materials that were organized by theme to help you prepare for the AMERICAN REGENTS exam. This packet covers the major themes of the 11th grade topics that most frequently appear on the exam. PLEASE USE THIS GUIDE TO HELP YOU PREPARE for the exam. Your teacher will LIKELY give you extra credit for each packet you fully and accurately complete. GOOD LUCK. Step one: ACTIVELY READ THE INFROMATION. Read the document with a pen and highlighter. Underline the important information and vocabulary words in each section in a way that you can easily make a connection to the topics. Step two: FILL IN THE CHART. Use the information you underlined to complete the chart with important information on each topic in neat, clear words that you understand and can use to study. Then, answer the M.C. questions. Step three: ANSWER THE ESSAY QUESTIONS. Use the information from the completed charts to answer the essay questions. REMEMBER: This packet was created for you to prepare yourself for the Regents Exam that you need to pass in order for you to graduate from High School. Do it well for YOU. 2. REVIEW SESSIONS Each review session will last from 3:00-4:00 (room TBD) June 2015 Mon 1 Review Tues 2 Review Weds 3 Review Thurs 4 No Review Friday 5 Review 8 9 Review 10 Review 11 Review 12 Review Review 15 NO REVIEW 16 US Exam 8:00 3. WEBSITES THE MORE YOU PRACTICE, THE BETTER YOU WILL DO! Visit these websites below for more practice WEBSITE: http://www.regentsprep.org http://www.myfreshprep.org Note: Click “PRACTICE” after you read the sections, there are Multiple Choice questions you can take at the end and read a vocabulary words to study. 4. TUTORING SESSIONS room 281 MONDAY - A, C, D TUESDAY –C, E, G WEDNESDAY –G, C THURSDAY –A, C, D FRIDAY -A 5. KNOW THE EXAM The Regents is a THREE HOUR exam Question are on topics, concepts, skills and themes from your 9th and 10th grade Global classes. THEMATIC topics for the exam are: Change, Citizenship, Constitution Principles, Culture & Intellectual Life, Diversity, Economic Systems, Environment, Foreign Policy, Geography, Government, Immigration, Individuals, Interdependence, Reform Movements, Presidential Actions & Decisions and Science & Technology. EXAM TIME: 3 Hours Part 1: Multiple-Choice Part 2: Thematic Essay Part 3a: Doc. Based Questions Part 3b: Document Based Essay YOU MUST ANSWER EVERY QUESTION. 50 Questions 55% of Test 1 Question 15% of Test 9 Questions 15% of Test 1 Question 15% of Test MAKE YOUR BEST ATTEMPT AT EVERY QUESTION! 6. MAKE A PLAN TO STUDY Schedule time each day to complete parts of your “Review Packet” and set time aside to visit the website to complete practice questions. # 1 Colonies and the Revolutionary War Information Sheet 1. Coming to America Did Christopher Columbus the famous explorer discover America? Not really. Many other explorers came before him, but Columbus landing in the Caribbean in 1492 was very important because his travel led to the colonization of the New World (North, Central, and South America) by European countries. Colonization is when a country tries to take control of land that doesn’t belong to them. Spain colonized most of the Caribbean, Central and South America, while France and Britain colonized most of North America. England’s greatest possession was its 13 colonies along the East Coast of North America (what is now present-day United States), these were known as The American Colonies. The Mother Countries get rich from colonization because they would take natural resources from the land, sell their products and collect taxes from their colonists. Colonists were restricted on trade with other countries and limited manufacturing. The economic system they created was known as mercantilism. Another reason why Columbus did not discover America was that America was never empty. Native American Tribes, what many people call Indians, were living in America for thousands of years before the Europeans arrived. The arrival of the Europeans led to the destruction of the Indian tribes, as Europeans stole Indian land, killed their people and brought new diseases to America that killed as many as one in three Indians. Eventually the massive Trans-Atlantic Slave Trade was established to import African slaves to the New World to be used as workers on European farms. MAIN IDEAS- 2. American Colonies In the American Colonies under Great Britain, colonists come settle for political, economic, social and religious freedom (such as the Quakers and Puritans) and opportunity. The colonies were divided into three sections based on geography – the New England Colonies, the Middle Colonies and Southern Colonies. Due to geography, each had a different type of economy and lifestyle (New England colonies had rocky soil but many harbors so focused on shipping and trade, but the Southern colonies had hot weather and good land so focused on farming and relied on slave labor). The America colonists slowly began to form early steps of self-government and early representative democracies (governments based on the people—consent of the governed). The Mayflower compact, New England town meetings, and the Virginia House of Burgesses are early examples of democratic practices in early American history. The British policy of Salutary Neglect, being left alone by Britain, allowed for the growth of democratic government. At this time there was movement called the Enlightenment where many great thinkers began to question things like human rights and the role of government. The ideas of philosophers like John Locke, and John Jacques Rousseau greatly affected the way people viewed Britain’s control over her 13 American colonies – the relationship between the two was about to be strained! By the mid 18th century, North America was divided up between the European powers of France, England, and Spain. The competition between France and England for control of North America, particularly over land between the Ohio River Valley, resulted in The French & Indian War, seven years of brutal warfare. War had left England deep in debt. Britain looked to tax its 13 American colonies to help pay off that debt and created many new taxes such as the Stamp Act and Townshend Acts (which included a Tea Tax). The Colonists protested using slogans such as “no taxation without representation” – the colonists wanted a say if they were being taxed. The colonists boycotted British goods, but eventually tension led to armed conflict such as The Boston Tea Party, Boston Massacre and Battles of Lexington and Concord (“The shot heard round the world!”). All of this tension, including Enlightenment ideas such as Thomas Paine’s pamphlet “Common Sense” led the colonists to write The Declaration of Independence and fight the American Revolution. Under the leadership of George Washington, using the American terrain to our advantage, and with some help from the French (after the battle of Saratoga), a British army surrendered at Yorktown and England signed The Treaty of Paris, giving America our independence! MAIN IDEAS- Key Vocabulary Words 1) Geography – the study of the political (states, countries) and physical (rivers, mountains) features of the earth 2) Colonization - when a country tries to take control of land that doesn’t belong to them 3) Colony - land taken over and controlled by a "mother" country 4) Colonists - the people living in colonies 5) Mother Country -- country that economically and politically controlled a colony. 6) Democracy – a representative government run by many people that includes equality, freedom and voting 7) Mayflower Compact- document of democratic government, written by the Pilgrims aboard the Mayflower ship 8) Virginia House of Burgesses - A representative government in the British colony of Virginia 9) Mercantilism - a system in which England made money by taking natural resources from the American colonies and forcing colonists to trade only with England. 10) Salutary Neglect - period of time when England was at war and allowed the colonies to manufacture and trade with little interference 11) Stamp Act (1765) - British plan to tax colonists by forcing them to purchase special stamps 12) Townshend Acts 1767 – Series of acts passed by British Parliament to tax the colonists (including tea) 13) Intolerable Acts 1774 – laws passed by Britain to punish the citizens of Boston for the Boston Tea Party – includes Quartering Act, closing the Boston Harbor, no town meetings and trying criminals in England. 14) Boston Tea Party- the dumping of British tea into Boston Harbor as a form of protesting English taxes 15) Boston Massacre -- when British soldiers shot colonists who were throwing snowballs packed with rocks at them. 16) Representative Democracy—government based on consent of the governed, with elected representatives to make decisions. 17) “No Taxation Without Representation” – slogan used by the colonists to protest England making laws without colonial representatives in Parliament. 18) Boycott- refusing to purchase goods or services as form of protest 19) Enlightenment – a movement of philosophers that believed government was responsible for its citizen’s well-being 20) John Locke - Enlightenment philosopher who believed people had “natural rights” (life, liberty, property) 21) Common Sense – pamphlet written by Thomas Paine that convinced many colonists to support the revolution. 22) Sons of Liberty – a radical organization that used terror tactics and propaganda against the British government 23) American Revolution - when the American colonies fought England in order to become a free country 24) Declaration of Independence – a document that stated why America was right in breaking away from England 25) Continental Congress – Colonial government in charge of governing during the Revolutionary War. 26) Treaty of Paris -- Treaty that gives America its freedom. Questions: 1. Which phrase from the Declaration of Independence most clearly reflects the idea that the people are the source of government? 1. “. . . that all men are created equal,...” 2. “. .. all men are . . . endowed by their Creator with certain unalienable rights 3. “. . . deriving their just powers from the consent of the governed. . .“ 4. “. . . governments long established should not be changed for light and transient causes . 2. The British system of mercantilism was opposed by many American colonists because it 1. placed quotas on immigration 2. discouraged the export of raw materials to England 3. placed restrictions on trading 4. encouraged colonial manufacturing 3. The British benefited from their mercantilist relationship with the American colonies primarily by 1. supporting the growth of colonial industries 2. prohibiting colonists from fishing and fur trading 3. taking large amounts of gold and silver from the southern colonies 4. buying raw materials from the colonies and selling them finished products 4. In the Colonial Era, developments such as the New England town meetings and the establishment of the Virginia House of Burgesses represented 1. colonial attempts to build a strong national government 2. efforts by the British to strengthen their control over the colonies 3. steps in the growth of representative democracy 4. early social reform movements 5. The Mayflower Compact is important to the concept of a democratic society because it represents 1. an effort by the colonists to use force to resist the King 2. a clear step toward self-government 3. an early attempt to establish universal suffrage 4. an attempt by the colonists to establish freedom of religion 6. During the Revolutionary War period, Thomas Paine’s Common Sense was important because it 1. described a military plan for the defeat of England 2. convinced many Americans who had been undecided to support independence 3. contained a detailed outline for a new form of government 4. argued for the addition of a bill of rights to the Constitution 7. The Mayflower Compact and the House of Burgesses were important to the development of democracy in colonial America because they 1. expanded freedom of religion 2. promoted self-government 3. protected private ownership of property 4. granted voting rights to all white males 8. Which heading best completes the partial outline below? I. ____________________________________ A. Committees of Correspondence B. Nonimportation Agreements C. Boston Tea Party D. First Continental Congress 1. Protests Against Slavery in the American Colonies 2. British Parliamentary Actions to Punish Colonial Americans 3. Colonial Responses to British Mercantile Policies 4. Colonial Attempts to End the British Policy of Salutary Neglect 9. According to the Declaration of Independence, the fundamental purpose of government is to 1. protect people’s natural rights 2. equalize opportunities for all citizens 3. provide for the defense of the nation 4. establish a system of free public education 10. The colonists' slogan, "No taxation without representation," expresses a belief in 1. free trade 2. economic interdependence 3. the supremacy of Parliament 4. the consent of the governed 11. What was the main cause of the French and Indian War (1754–1763)? 1. disputed land claims in the Ohio River valley between the French and the British 2. conflicts between American colonists and the French over control of the Great Plains 3. taxation of American colonists without representation in Parliament 4. violation of trade agreements between European nations and Native American Indians 12. “The only representatives of the people of these colonies are persons chosen therein by themselves; and that no taxes ever have been, or can be constitutionally imposed on them but by their respective legislatures.” -Statement by the Stamp Act Congress, 1765 What is a valid conclusion that can be drawn from this quotation? 1. The colonial legislatures should be appointed by the English King with the consent of Parliament. 2. Only the colonists’ elected representatives should have the power to levy taxes. 3. The English King should have the right to tax the colonists. 4. The colonists should be opposed to all taxation. 13. The British system of mercantilism was opposed by many American colonists because it 1. placed quotas on immigration 2. discouraged the export of raw materials to England 3. placed restrictions on trading 4. encouraged colonial manufacturing 14. The Mayflower Compact of 1620 is considered an important step in the development of democracy in America because it 1. expressed the importance of self-government 2. established freedom of religion 3. created the first colonial judiciary 4. granted all males the right to vote 15. The Virginia House of Burgesses was important to the development of democracy in the thirteen colonies because it 1. provided an example of a representative form of government 2. created the first written constitution in America 3. provided for direct election of senators 4. began the practice of legislative override of executive vetoes 16. The pamphlet Common Sense, by Thomas Paine, aided the American cause in the Revolutionary War because it 1. convinced France to join in the fight against England 2. led to the repeal of the Stamp Act 3. created a new system of government for the United States 4. persuaded individuals who were undecided to support independence 17. In its economic relationship with its North American colonies, Great Britain followed the principles of 18th-century mercantilism by 1. outlawing the African slave trade 2. limiting the colonies’ trade with other nations 3. encouraging the development of manufacturing in the colonies 4. establishing laws against business monopolies 18. Which statement is most accurate about the movement for independence in the thirteen colonies? 1. The independence movement began soon after the founding of the Plymouth Colony. 2. Protests against British colonial policies gradually led to the demands for independence. 3. The King of England required the colonists to become economically self-sufficient. 4. The movement for independence was equally strong in all of the colonies. 19. During the colonial period, the British Parliament used the policy of mercantilism to 1. limit manufacturing in America 2. prevent criticism of royal policies 3. deny representation to the colonists 4. force colonists to worship in the Anglican Church 20. Which conclusion about the American Revolutionary War is most clearly supported by information in this chart? 1. 2. 3. 4. England had few advantages in a war with her American colonies. The thirteen colonies had more advantages than disadvantages upon entering the war. England did not believe that the thirteen colonies were worth the expense of a war. The thirteen colonies had few, but important advantages in the war with England. # 2 Creating A New Government – The Critical Period (1776-1787) Information Sheet 1.New Nation The former colonies, now the free and independent United States of America, needed to create their own government after winning the American Revolution. Many American leaders did not trust powerful governments since America was originally controlled by the English King. Therefore, the first U.S. government, The Articles of Confederation, was kept weak on purpose. Although this weak government prevented one person from controlling the government, it also proved too weak to make laws and protect the country. The Articles did not allow for taxation or even raising an army, but was successful at creating guidelines to admit new states into the Union. After Shay’s Rebellion (a farmer’s rebellion), the Founders knew it was time for a change. Representatives from the now 13 states, met at the Constitutional Convention (1787-1789) to create a new government. MAIN IDEAS- 2. Constitutional Compromise Getting all of the states to agree on how a new and more powerful government would operate was not easy. Many compromises had to be agreed upon so that all the states could be sure that they would not be overpowered by the new national government. There were many differences especially between Northern and Southern States (over slavery and taxation), big states and small states (over representation in Congress) and Federalists (people who wanted a strong central government) and Anti-Federalists (people who wanted a weak central government and argued that the central government held power). The Compromises included the Great Compromises (creating a Bi-Cameral – two-house legislature), the controversial 3/5’s compromise over how slaves are counted for representation/taxation and the Bill of Rights. The U.S. Constitution split the national government up into three branches so that there would be a separation of powers. One branch would make the laws (Legislative- Congress), another branch would enforce the laws (Executive – President), and the third branch would judge and decided the meaning of the laws (Judicial- Supreme Court). Power was separated into three branches and each branch was given the ability to limit the power of the other branches. This is called checks and balances. The Constitution also divided power between the national government and state governments. This system is called federalism and it allows state governments and the national government to share power and responsibilities. The new government created by the U.S. Constitution was not immediately accepted by all the states. People began to argue for and against the Constitution. Many people felt that the new government was too powerful and would violate the rights of the citizens just as Britain had done. In order to get the Constitution approved, a Bill of Rights was added that guaranteed that certain important rights such as freedom of speech would not be taken away by the new national government. These became the First Ten Amendments. The Convention also created a Ratification Process to add and change amendments, and The Elastic Clause – where the Constitution can change as the needs of the country change over time. Despite all of the compromises, it took a lot of effort to convince people to ratify the Constitution. James Madison, Jon Jay and Alexander Hamilton wrote The Federalist Papers to convince the other states and their representatives to do ratify the constitution. In September 1787, the Constitution was ratified. MAIN IDEAS- Key Vocabulary Words 1) Federalism – the sharing of power between state governments and the national government 2) State Government – Government in charge of individual states. (NY’s is located in Albany, NY) 3) Federal/Central/National Government – Government in charge of the country. (this is located is in DC) 4) Federalists- argued for a strong federal government 5) Anti-Federalists- argued for a weak federal government, strong state governments and a Bill of Rights 6) Articles of Confederation- the first attempt at a US government. It had a weak federal government and didn’t have the power to collect taxes or raise an army. 7) Shay’s Rebellion – farmers’ rebellion which convinced people the Articles of Confederation were too weak. 8) Constitution- a document that outlines how the government is structured 9) Amendment- a change to the Constitution 10) Bill of Rights- The first 10 Amendments to the Constitution that guarantee basic freedoms for citizens 11) 3/5ths Compromise- 5 slaves would count as 3 people when determining a state’s representation and taxes. 12) Great Compromise- made states with small population and states with large populations happy by creating a bi-cameral legislature. It creates the Senate (2 representatives from each state) and the House of Representatives (each state has an amount of representatives based on its population). 13) Checks and Balances- the system where each branch of government can limit the powers of the other branches 14) Legislative Branch- branch of government that makes laws called the Congress. 15) Bicameral Legislature - the two-house system in Congress made up of the Senate & House of Representatives 16) Senate- the upper house of Congress where each state gets the same 2 votes 17) The House of Representatives- the lower house where each state gets more or less votes based on its population 18) Bill- an idea for a law 19) Veto- when the President refuses to sign a Congress approved bill into a law 20) Executive Branch- branch of government that enforces laws. Run by the president 21) Electoral College- a controversial system by which the U.S. President is selected indirectly – each state has a certain number of electors (points) which the president receives based if he wins the popular vote of the state. A president can win without the majority of the popular vote. 22) Judicial Branch- the branch of government that interprets the laws. Run by the courts. 23) Elastic Clause – part of the Constitution which allows it to “stretch” or change based on needs of the time. 24) Federalist Papers – papers written to convince people to support the constitution 25) Ratify – approve/give consent. Questions: 1. At the Constitutional Convention of 1787, the Great Compromise resolved the issue of 1. representation 2. taxation 3. slavery 4. control of trade 2.Which heading best completes the partial outline? I.____________________________________ A. Representation B. Slave trade C. Taxation D. Election of the president 1. Causes of the Revolutionary War 2. Provisions of the Treaty of Paris, 1783 3. Protections under the 10th Amendment 4. Compromises at the Constitutional Convention 3. A major reason the Antifederalists opposed the ratification of the United States Constitution was because the Constitution 1. created a national bank 2. lacked a provision for a federal court system 3. failed to provide for the direct election of members of the House of Representatives 4. changed the balance of power between the state and national governments 4. In terms of representation in the United States Congress, which state benefited most from the three-fifths compromise reached at the Constitutional Convention of 1787? 1. Massachusetts 2. New Jersey 3. New York 4. Virginia 5. Which idea did the Founding Fathers include in the Constitution that allows Congress to meet the needs of a changing society? 1. federalism 2. separation of powers 3. the elastic clause 4. States rights 6. "There can be no liberty if the same man or the same group has executive, legislative, and judicial control." Which political idea would the author of this statement most likely support? 1. States rights 2. separation of powers 3. socialism 4. Federalism 7. Which statement about the United States House of Representatives is accurate? 1. Representatives are chosen by the legislatures of their states. 2. The Constitution allows each state two representatives. 3. The number of representatives from each state is based on its population. 4. The political party of the president always holds a majority of House seats. 8. A system of checks and balances was included in the United States Constitution because the authors were concerned about 1. one branch of government becoming too strong 2. the states having too much power 3. the people having a voice in government 4. the military gaining control of the United States 9. Those who supported the ratification of the United States Constitution promised to add a bill of rights in order to 1. encourage economic development 2. prevent the return of English control over the new nation 3. increase the power of the National Government over the states 4. persuade the anti-Federalists to accept the Constitution 10. At the Constitutional Convention of 1787, the Great Compromise resolved the issue of 1. representation 2. taxation 3. slavery 4. control of trade 11. Federalism is best described as the 1. authority to make and enforce decisions based on a written constitution 2. difference in the function of the public and private sectors of the economy 3. divisions of power between a national government and state governments 4. use of checks and balances between the three branches of government 12. Which statement about the electoral college system is accurate? 1. The number of electoral votes a state receives is based on its geographic size. 2. A candidate can be elected president without the majority of the popular vote. 3. Presidential candidates are forced to campaign equally in every state. 4. The total number of electoral votes has increased with each census. 13. What was the primary reason for holding the Constitutional Convention of 1787? 1. outlaw slavery in both the North and the South 2. place taxes on imports and exports 3. revise the Articles of Confederation 4. reduce the power of the federal government 14. In the 1780’s, many Americans distrusted a strong central government. This distrust is best shown by the 1. lack of debate over the ratification of the United States Constitution 2. plan of government set up by the Articles of Confederation 3. development of a Federal court system 4. constitutional provision for a strong President 15. The authors of the United States Constitution believed that the voice of the people should be heard frequently. Which part of the Government was instituted to respond most directly to the will of the people? 1. Senate 2. House of Representatives 3. Supreme Court 4. Presidency 16. One way in which the United States Constitution differed from the Articles of Confederation was that the Constitution 1. created a national government having three branches 2. provided for the direct election of the President by the voters 3. made the amendment process more difficult 4. increased the powers of the states 17. One way in which the authors of the Constitution tried to create “limited government” was by providing for 1. a loyal opposition through a two-party system 2. a division of power between the national and state governments 3. the establishment of naturalization laws 4. the popular election of Federal judge 18. Antifederalists criticized the United States Constitution primarily because governing power was concentrated in the 1. State legislatures 2. President’s Cabinet 3. delegates to the Constitutional Convention 4. National Government 19. The United States Government is considered a federal system because 1. national laws must be passed by both houses of Congress 2. powers are divided between the State and National Governments 3. the States are guaranteed a republican form of government 4. the President is selected by the electoral college 20. The Bill of Rights was added to the United States Constitution to 1. provide the president with the power to enforce the laws 2. protect individuals’ civil liberties 3. establish a presidential cabinet 4. guarantee voting privileges to all citizens 21. What was an important accomplishment of the central government under the Articles of Confederation? 1. elimination of debts from the Revolutionary War 2. removal of all British troops from North America 3. formation of a national policy relating to Native American Indians 4. development of guidelines for the admission of new states into the Union 22. The Federalist Papers were published in 1787 and 1788 to help gain support for 1. a bill of rights 2. the ratification of the Constitution 3. a weaker central government 4. the abolition of slavery and the slave trade # 3 Building A New Nation and the Age of Jacksonian Democracy Information Sheet. 1. Early Republic After the Constitution was ratified, the representatives unanimously elected George Washington to be America’s first President. Washington knew that he would be setting important precedents (important firsts). Washington was the first person to create a cabinet (groups of advisors and specialized departments). This was part of the Unwritten Constitution (powers not specifically listed in the Constitution). Washington set another example on the home front by demonstrating the Federal Government would exercise their power to strike down domestic uprisings during the Whiskey Rebellion. Another part of the Unwritten Constitution that Washington establishes is that Presidents only serve for two terms – after Washington’s second term, he chose not to run again. His Farewell Address, at the end of his presidency is also important because in it, Washington outlines a policy of isolationism – warning America to stay away from foreign affairs. Washington also established Future Presidents would both follow and debate this policy. Washington also warned against political parties, but people took sides over political issues and eventually formed the Federalist Party and the Democratic-Republicans. In 1796, John Adams defeated Thomas Jefferson to become the 2 nd President. During Adams’ Presidency, America almost went to war with France over the XYZ Affair and in response Adams passed the Alien and Sedition Act which limited rights during time of war. The election of 1800 saw the peaceful transfer of power between two presidents after Adams lost to Jefferson (this was known as “The Revolution of 1800). In 1803 the 3rd U.S. President, Thomas Jefferson, made the Louisiana Purchase from the French Emperor Napoleon. This purchase, which Jefferson made Constitutional by calling it a treaty, more than doubled the territory of the U.S (westward expansion). The Louisiana Purchase demonstrates that Jefferson changed his original view that the constitution should be interpreted strictly to that it should be interpreted loosely. This treaty between the US and France gave the U.S. full control of rich natural resources and the Mississippi River and the port of New Orleans. This rich and plentiful land was attractive to many American settlers. As America began expanding, it began having problems. England began instigating America and America’s 4 th President, James Madison, declared war (with Congress’s approval) on England. This became known as The War of 1812. It was a draw, but its long term significance is that America established itself as a legitimate power. America used its new power to protect its interests. In 1823, President James Monroe in his State of the Union Address to Congress issued the Monroe Doctrine which declared that the Western Hemisphere was not allowed to be colonized any more by the European Powers – this was now America’s area. It is debated if the policy was expansionist (expanding America’s power) or keeping with George Washington’s policy of isolationism. Regardless, America, in just under 40 years as a nation, was becoming a powerful country. MAIN IDEAS- 2. Jacksonian Democracy Throughout his political career as a representative from Tennessee and then as President, Jackson was a champion of the common man. Jackson’s support for changes and the following era of those changes became known as “The Age of Jacksonian Democracy.” Jacksonian democracy was built on the following general principles: extended suffrage (voting rights) – voting rights were given to all white men, manifest destiny (it is our right to expand West), patronage (giving offices to supporters – such as Jackson’s Spoil System), strict constructionism (strict reading of the Constitution – although many debate how much Jackson did this), laissez-faire economics (government should stay out of economics) and an opposition to banks. In order to help laissez-faire economics and stop what Jackson believed was the corruption of the Bank of the United States (Jackson believed that too few were getting too rich at the price of farmers and laborers), Jackson refused to renew the Bank re-Charter Act in 1832. As a result, the national bank closed down. This unfortunately led to the Panic of 1837 and an economic depression because local banks ran out of gold and silver and had to shut down. Jackson also believed the two other branches of government were becoming too powerful and corrupt. During his time as President, he vetoed most of the bills that came from Congress. He also was the first President to challenge the Supreme Court’s power of judicial review. In 1830, Jackson signed the Indian Removal Act which allowed the President to buy Indian lands and then give them new lands in the West and put them onto reservations. The Cherokee Nation sued the U.S. government and the case went all the ways up to the Supreme Court. In the case of Worcester v. Georgia the Supreme Court said that this act was illegal. However, in response Jackson stated, “John Marshall has made his decision, now let him enforce it!” Jackson and the following President Martin Van Buren moved thousands of Indians onto reservations (now present day Oklahoma). This was unfortunately a sad episode in American History because 800 Indians died along the way from starvation, poor nutrition and drowning in poor government transports and became known as The Trail of Tears. Jackson also strengthened the system of Federalism and enforce that the Federal Government was stronger than the states. States’ Rights have been an issue since the founding of America, and this issue came to a head with the Nullification Crisis of 1832. When North Carolina wanted to nullify (cancel) a federal tariff (trade tax that was being placed on good being brought into the nation. It was to protect domestic manufacturers to having to compete with lower priced goods made by other countries), Jackson was prepared to send the army to the state to enforce the tariff. Fortunately, Congressman Henry Clay stepped in and created a compromise tariff. However, the issue of sectionalism (northern vs. southern states) and states’ rights was becoming an issue that was going to tear the country apart. MAIN IDEAS- Key Vocabulary Words 1) Precedent – something done that is followed by others. 2) Unwritten Constitution – powers, procedures and traditions that become precedent but are not specifically listed in the Constitution 3) Cabinet – the President’s group of political advisors. (part of unwritten Constitution) 4) Whiskey Rebellion – farmers’ rebellion over a whiskey tax. President Washington uses the army to put down the rebellion to show the strength of the Federal Government. 5) Farewell Address – Washington’s letter to the nation when he chooses not to run again. In it, Washington stresses a future policy of isolationism/neutrality and warns against political parties. 6) Isolationism – a policy of neutrality – America should not be involved in foreign affairs. 7) Political Parties – organizations that represent a set of political (and social and economic) beliefs. The first two political parties where the Federalists and Democratic-Republicans. 8) XYZ Affair – When France tried to blackmail America to pay France to stop attacking ships. Leads to “The Quasi-War” between America and France. 9) Alien and Sedition Acts – Acts passed by President Adams that limit rights and speech against the government during time of war and are anti-immigrant. 10) Revolution of 1800 Jefferson defeats Adams in the election of 1800. Adams peacefully transfers the Presidency to Jefferson. This is the first peaceful political exercise of democracy/exchange of office in American history. 11) Louisiana Purchase a treaty President Thomas Jefferson made with France that doubled the size of the U.S and gave the U.S. full control of the Great Plains, Mississippi River and New Orleans. 12) Strict Constructionist - a person who interprets the Constitution exactly as it is written, word for word. 13) Loose Constructionist- a person who interprets the Constitution in a loose flexible way and may stretch the meaning of the Constitution. 14) War of 1812 – A war between the US and England which was fought over trade rights. The US barely won and the White House was burned down. The significance is that America is now respected as a legitimate and powerful nation. 15) Alexander Hamilton – advisor to President Washington who supported the creation of a National Bank 16) Lewis and Clark - explorers hired by President Jefferson explore the Louisiana Territory 17) State of the Union Address – Part of the unwritten Constitution – the President addresses Congress (and now the nation) and tells them his plans for America, what he wants done, etc. 18) Monroe Doctrine- This was the nickname for President Monroe’s State of the Union Address that said that Europe should not interfere with the West (North & South America), the Western Hemisphere is the U.S.’s area, and the U.S. would not get involved in European affairs. 19) Spoils System – Jackson gave political posts to his supporters. 20) Rotation System – Government employees can only serve 4 years 21) Kitchen Cabinet – Jackson consulted with his friends more than his cabinet. 22) Indian Removal Act of 1830 – Jackson orders the Cherokee and other Indian nations removed West onto reservations (special land just for Indians). 23) Worcester v. Georgia – Cherokees sue in the Supreme Court saying that they cannot be removed. The Supreme Court sides with the Cherokees, but Andrew Jackson ignores the Supreme Court’s ruling and moves the Indians onto reservations anyway. (“Marshall made his ruling, now let him enforce it.”) 24) Trail of Tears – When the Cherokees were moved from Georgia to Nebraska, 800 of them die on the way due to traveling in bad conditions and using poor equipment to travel with. 25) Vetoing Congress – Jackson did not like the power that Congress and Congressmen had too much power and were corrupt. He vetoed many of Congress’s bills and did not take their advice in foreign and domestic policy. 26) War with the Bank of the U.S. (BUS) – Jackson believed that the national bank only helped the wealthy class and hurt the poor. He vetoed its re-charter (renewal). When the bank closed, every state had its own main bank. This complication led to The Panic of 1837. 27) The Panic of 1837 -- where many banks closed and people lost their money. 28) Nullification Crisis – When North Carolina wanted to not follow and nullify a federal law and Jackson was prepared to send the army to enforce the law. 29) Sectionalism – conflict between Northern and Southern interests in the country. 30)States Rights: the political ideology that states have individual rights and do not have to listen to everything the federal government says. 31) Jacksonian Democracy: time period in American history, when suffrage was extended to all men, and there was increased participation by people in government and politics. 32) Manifest Destiny: belief America has the God-given right to expand West and fill the entire continent. 33) laissez-faire economics – economic ideology that government should stay out of economics. Questions: 1. What were two key precedents established by George Washington during his presidency? 1. aid to farmers and the end of the slave trade 2. universal male suffrage and support for political parties 3. foreign policy of neutrality and the use of presidential advisors 4. protective tariffs and foreign alliances during peacetime 2. An example of the use of the unwritten constitution is the creation of the 1. presidential veto 2. United States Navy 3. federal postal system 4. president's cabinet 3. A major purpose of the president's cabinet is to 1. offer advice on important issues 2. nominate ambassadors 3. conduct impeachment trials 4. regulate the amount of money in circulation 4. "It is our true policy to steer clear of permanent alliances with any portion of the foreign world..." George Washington, Farewell Address. In the 1920s and 1930s, some Americans used this statement to justify a policy of 1. isolationism 2. collective security 3. mercantilism 4. imperialism 5. Washington's Proclamation of Neutrality (1793) and the Monroe Doctrine (1823) were efforts to 1. avoid political conflicts with European nations 2. directly support European revolutions 3. aid Great Britain in its war against France 4. promote military alliances 6. The Louisiana Purchase had great geographic significance for the United States because it 1. reduced British control of North America 2. focused the United States on westward expansion 3. extended United States control over Mexico 4. decreased tensions with Native American Indians 7. The Louisiana Purchase initially presented a dilemma for President Thomas Jefferson because he believed it would 1. lead to war with Great Britain 2. bankrupt the new nation 3. force Native American Indians off their lands 4. violate his strict constructionist view of the Constitution 9. Which proposal was included in Secretary of the Treasury Alexander Hamilton's financial plans in the 1790s? 1. incentives to encourage agricultural expansion 2. creation of a national bank 3. direct taxes on the states to support government operations 4. free trade with other nations 10. On what grounds would strict constructionists of the United States Constitution have questioned the purchase of the Louisiana Territory? 1. It violated the guarantee of states' rights. 2. The president was not specifically given the power to purchase new land. 3. Congress was opposed to expansion west of the Mississippi River. 4. The Constitution applied only to the original thirteen states. 8. In 1823, the Monroe Doctrine was established mainly because the United States wanted to 1. keep control of Alaska and Hawaii 2. establish more colonies in Latin America 3. support England's attempt to keep its empire in Central America 4. warn Europe against any further colonization in Latin America 11. During the presidency of Andrew Jackson, the spoils system resulted in 1. federal laws being nullified by the states 2. elected officials rewarding their supporters with government jobs 3. all free males being given the right to vote 4. the end of political corruption in the federal government 12. The United States government is creating memorials along the Trail of Tears because it was 1. an important road used by settlers going to the frontier 2. the location of injustices against many Native American Indians 3. the site of victories by General Andrew Jackson during the War of 1812 4. the route followed by the first transcontinental railroad 13. Which Supreme Court decision is most closely associated with the Trail of Tears? 1. McCulloch v. Maryland (1819) 2. Gibbons v. Ogden (1824) 3. Worcester v. Georgia (1832) 4. Dred Scott v. Sanford (1857) 14. According to the theory of laissez faire, the economy functions best when the government 1. subsidizes business so that it can compete worldwide 2. regulates business for the good of the majority 3. owns major industries 4. does not interfere in business 15. Which term did Americans use in the 1840s to describe the idea that the United States should possess the entire continent? 1. containment 2. globalization 3. Manifest Destiny 4. popular sovereignty 16. At times, the United States Government has passed protective tariffs to 1. encourage foreign trade 2. help the nation’s manufacturers 3. reduce the cost of consumer goods 4. improve the quality of goods 17. A major reason for the issuance of the Monroe Doctrine (1823) was to 1. discourage United States trade with Latin America 2. defend the Panama Canal from Great Britain 3. prevent further European colonization in the Caribbean region 4. provide economic aid to Latin American nations 18. President Andrew Jackson claimed that use of the spoils system increased democracy in the federal government because it 1. passage of an amendment ending religious qualifications for voting 2. extension of suffrage to Native American Indians 3. end of property requirements for voting by many states 4. arrival of more immigrants from nations with democratic governments 19. President George Washington set a precedent for all future presidents by 1. appointing a career soldier to be Secretary of War 2. choosing a friend to be Chief Justice of the Supreme Court 3. campaigning actively for the office 4. creating a cabinet of advisors 20. One goal of Alexander Hamilton's financial plan was the establishment of a 1. 2. 3. 4. stock exchange national sales tax federal income tax national bank # 4 The Road to Civil War (1820-1861) and Reconstruction (1865-1877) 1. Expansion and Division of the Nation The expansion of the US throughout the 1800’s made the US larger, richer, and stronger, but the new territories also brought about major conflict. At first, most people believed that the country could exist with half of its economy based on slave labor (the South) and the other half based on manufacturing (the North). As new territory was added, many of the compromises over slavery began to break down. This slowly led to increased sectionalism. Northern States wanted these new states to be “free states” to stop the expansion of slavery and to get enough representatives to make a law to end slavery. The South was scared of this, so they wanted the new states to become “slave states” so there would be a balance of power in Congress. Compromises, such as the Missouri Compromise, the 1850 Compromise and the Kansas-Nebraska Act tried to make both sides happy, but actually made things worse. In the Kansas territory, because of the idea of popular sovereignty, people started fighting each other, which became known as Bleeding Kansas. Tensions greatly escalated with the Dred Scott Decision. Chief Justice Robert Tawney ruled that not only was slavery legal in the North, but the Missouri Compromise which separated free and slave states was illegal – Congress cannot regulate property – it was now legal to own slaves in any state! This infuriated abolitionists and gave the new anti-slavery Republican Party even more momentum. Republican Congressman Abraham Lincoln in his debates with Senator Stephen Douglas in the Lincoln-Douglas Debates made it clear that “a house divided cannot stand” with the issue of slavery. The South saw this is a threat that if a Republican President won, slavery would be made illegal. Harriet Beecher Stowe’s Uncle Tom’s Cabin (which depicted the life of a slave very negatively) and the abolitionist John Brown’s Raid on Harper’s Ferry to try to create a slave revolt both increased the anger of Southern “Fire Eaters” (outspoken politicians), and convinced many that the only choice left for the South was to secede (leave) the United States and form their own country. They believed in the principle of States Rights – they did not want a Northern-controlled Federal Government to tell the states what to do or take away their property. Poor Presidential leadership just allowed the situation to get worse. Due to Abraham Lincoln’s popularity, he was nominated as the Presidential candidate for the Republican Party in 1860. South Carolina stated that if Lincoln won, they would secede from the Union. Lincoln, thanks to a divided Democratic party, did win, and on December 20, 1860, South Carolina voted and left the Union! Through early 1861, ten more Southern States seceded and formed a new government – The Confederate States of America – they had their own constitution, flag, president (Jefferson Davis) and government. The war started with the Battle of Fort Sumter. From 1861 to 1865, Americans from the North fought Americans from the South in one of the bloodiest wars ever fought in order to preserve the union of the US! The American Civil War changed the United States forever. The federal government showed that the U.S was a union of people and that the states couldn’t be allowed to secede from the country. MAIN IDEAS- 2. Reconstruction As the Southern Confederacy lay in ruins after its defeat, the American North had to decide on how to reintroduce The South back into the United States. Abraham Lincoln’s Reconstruction Plan wanted to make it easy for The South to rejoin the US and slowly give rights to the freed African Americans. The Radical Republicans Reconstruction Plan wanted The South punished for their actions during the Civil War and wanted to make it difficult to reenter the Union and wanted to create equality right away. When Lincoln was assassinated on April 15, 1865, his Vice President, Andrew Johnson became President. Johnson and the Radical Republicans would continue to fight over the two competing visions of reconstruction. During the Civil War, Abraham Lincoln issued The Emancipation Proclamation, which only freed slaves in the rebelling states. After the Civil War, Congress issued the Thirteenth Amendment, which ended slavery throughout the United States and granted all slaves freedom. Although slaves were officially “free.” The Radical Republicans also passed the Fourteenth Amendment that granted former slaves citizenship and they suffered persecution and The Fifteenth Amendment was supposed to protect voting rights for all adult males, regardless of race or color. Congress also created the Freedman’s Bureau to help freed Blacks find work and living. To protect Blacks from the South and to punish the South, Congress passed The Reconstruction Act that kept soldiers in the South and kept the army in charge of the South until they ratified their new Constitutions (that didn’t have slavery) and became states in the United States again. Andrew Johnson did not like any of these efforts and continually tried to veto Congress, but Congress kept overturning his veto with a 2/3 majority vote. Congress then tried to impeach Johnson for violating the Constitution by not helping the freed Blacks, but fell one vote shy. Reconstruction would not end until 1877 with the election of Alexander Hayes, during a complication, when there was a tie and Congress decided to elect him President if he removed soldiers from the South and ended Reconstruction. Even though Reconstruction would end after 12 years, there were lasting problems during and after, as the South also tried to stop all of the improvements that Congress was creating for the freed Blacks. To keep them working on the plantations, they developed a system known as Sharecropping. Citizens joined the Ku Klux Klan to use terror tactics (such as lynching) to intimidate African Americans to leave the South and to not practice voting rights. States tried to prevent them from voting by passing literacy tests, poll taxes and grandfather clauses. States also tried to prevent Blacks from becoming equal by creating Black Codes and Jim Crow Laws which segregated them. In 1896, in the Supreme Court case of Plessy v. Ferguson, the Supreme Court held that segregation was legal as long as it was separate but equal. With so much resistance, early Civil Rights leaders Booker T. Washington and W.E.B. DuBois offered two different opinions on how African Americans should try to achieve equal rights. However, it would not be until Brown vs. Board of Education in 1954 that this case was overturned and segregation was illegal and it would not be until the Civil Rights Movement of the 1950’s and 1960’s that African Americans would truly gain equal rights. MAIN IDEAS- Key Vocabulary Words 1) Sectionalism- when each part of the U.S. (North, South, & West) puts its own needs before the needs of the country as a whole. 2) Secession/Secede- to break away from 3) Abolitionist- a person who tried to end (abolish) slavery 4) Underground Railroad- a system of hideouts Harriet Tubman and many others used to help slaves escape slavery in the South 5) Frederick Douglas- escaped slavery and published a newspaper (The North Star) discussing the evils of slavery 6) Cotton Gin- an invention that made cotton-farming easier. This device increased demand for slavery. 7) Nullification – the idea that a state can nullify (ignore) a law of the national government 8) Missouri Compromise (1820)- allowed the state of Missouri to enter the US as a "slave state", Maine to enter as a "free state", and outlawed the spread of slavery above a certain boundary line. 9) Compromise of 1850- allowed the state of California to enter the US as a "free state" and created a stronger fugitive slave act. 10) Fugitive Slave Act- made it a crime for Northerners to help runaway slaves from the South 11) Kansas-Nebraska Act (1854)- allowed Kansas and Nebraska to use popular sovereignty (states could vote to decide if they would be "free" or "slave" state) 12) Popular Sovereignty – the idea that the people living in a state will vote to decide if they would be "free" or "slave" state. 13) Bleeding Kansas- Fighting between pro-slavery and anti-slavery supporters in Kansas. 14) Dred Scott Decision- Supreme Court decision that made it illegal for Congress to ban slavery in any US territory. 15) John Brown- a radical abolitionist who wanted slaves to rise up and fight. 16) Raid at Harper’s Ferry—John Brown’s attempted slave rebellion. Harper’s Ferry was a military warehouse. The rebellion fails but the South is very angry at the North. 17) Uncle Tom's Cabin- a very important anti-slavery novel written by Harriet Beecher Stowe. 18) States’ Rights – The idea that states do not have to listen the Federal Government if they disagree. 19) Lincoln-Douglas Debates – Debates that made Abraham Lincoln famous and called attention to that the country cannot survive half slave and half free. 20) Abraham Lincoln – Republican politician. Became America’s 16th President. His election caused the Civil War, but his leadership helped the U.S. win it. 21) Election of 1860- Election where South Carolina said that if Abraham Lincoln won then they would secede from the Union. Lincoln wins and they secede. 22) Civil War- a war between different groups within one country. The American Civil War was when 11 Southern States tried to break apart and form their own country – the Confederate States of America. From 1861-1865, the United States fought to conquer the Confederacy and reunite the country. 23) The Confederate States of America – the new “rebel” country formed by the southern states during the Civil War. It had a government and Constitution similar to America’s and a President (Jefferson Davis). 24) Reconstruction- 12-year period after the U.S. Civil War where the southern states were rebuilt and allowed back into the U.S. 25) Freedmen- term used after the Civil War that referred to recently freed slaves. 26) Radical Republicans- group of Congressmen who wanted to punish the South after the Civil War. Soldiers were kept in the South, Civil Rights laws were passed and the South tried to fight the legislation. It ends in the “backdoor” deal of the election of 1876. 27) Emancipation Proclamation – a letter that President Lincoln signed ending slavery during the Civil War 28) Thirteenth Amendment- officially ended slavery, except as punishment for a crime, in the U.S. 29) Fourteenth Amendment- gave citizenship to Freedmen and “equal protection under the law.” 30) Fifteenth Amendment- gave voting rights to all adult male citizens regardless of race or color 31) Freedmen's Bureau – organization that created schools and work training for Freedmen 32) Reconstruction Act – Act that keeps the military in charge of the South during Reconstruction. 33) Ku Klux Klan (KKK)- a group that terrorized and killed Freedmen after the Civil War 34) Lynching – a group led hanging meant to terrorize black citizens in the South 35) Jim Crow Laws and Black Codes- state laws in the South that restricted the rights of African Americans and created segregation. 36) Sharecropping/Tenant Farming- a system of renting land that kept many Freedmen poor farm workers after slavery was made illegal 37) Literacy tests- confusing exams given only to blacks in the South to prevent them from voting 38) Poll taxes- fees that kept poor Freedmen from voting. 39) Grandfather clauses- a racist southern law that said you can vote only if your grandfather could vote. This prevented Freedmen from voting. 40) Segregation- the separation of people based on color, race, or religion 41) Plessy v. Ferguson (1896) - U.S. Supreme Court case that legalized segregation, saying that segregation is legal as long as it is separate but equal. 42) Jim Crow Laws- laws that enforced segregation in southern places (restaurants, train cars, bathrooms) 43) Booker T. Washington - African American leader who accepted segregation, and believed that working from the bottom up and education was the best way to achieve equality. 44) W.E.B. Dubois - African American leader who rejected segregation and believed that blacks must fight for equality through the court system and by protest. 45) Brown v. Board of Ed (1954) – Supreme Court case that overturns Plessy v. Ferguson stating that “separate but equal in inherently unequal Questions: 1. Sectional differences developed in the United States largely because 1. the Federal Government adopted a policy of neutrality 2. economic conditions and interests in each region varied 3. only northerners were represented at the Constitutional Convention 4. early Presidents favored urban areas over rural areas 2. Early in his Presidency, Abraham Lincoln declared that his primary goal as President was to 1. 2. 3. 4. enforce the Emancipation Proclamation preserve the Union end slavery throughout the entire country encourage sectionalism 3. Which phrase best completes the title for the partial outline shown below? I. Reasons for the ______________________ A. Increasing sectionalism B. Disagreements over states’ rights issues C. Breakdown of compromise D. Election of 1860 1. Start of the Revolutionary War 2. Adoption of the Bill of Rights 3. Failure of the Whiskey Rebellion 4. Secession of Southern States from the Union 4. Which term refers to the idea that settlers had the right to decide whether slavery would be legal in their territory? 1. nullification 2. sectionalism 3. popular sovereignty 4. southern secession 5. The Supreme Court decision in Dred Scott v. Sanford (1857) was significant because it 1. allowed slavery in California 2. outlawed slavery in the Southern States 3. upheld the actions of the Underground Railroad 4. ruled that Congress could not ban slavery in the territories 6. Which situation was the most immediate result of Abraham Lincoln's election to the presidency in 1860? 1. Kansas and Nebraska joined the Union as free states. 2. A constitutional amendment was adopted to end slavery. 9. In their plans for Reconstruction, both President Abraham Lincoln and President Andrew Johnson sought to 1. punish the South for starting the Civil War 2. force the Southern States to pay reparations to the Federal Government 3. allow the Southern States to reenter the nation as quickly as possible 4. establish the Republican Party as the only political party in the South 10. The 14th and 15th Amendments, passed during Reconstruction, resulted in 1. equal rights for women in the United States 2. expanded rights for Native American Indians on reservations 3. increased individual rights for African Americans 4. additional rights for Southern segregationists 11. The underlying reason for the impeachment of President Andrew Johnson was 1. the Credit Mobilier scandal 2. a power struggle with Congress over Reconstruction 3. his refusal to appoint new justices to the Supreme Court 4. his policies toward Native American Indians 12. The Articles of Confederation and the theory of nullification were both attempts to 1. strengthen the national government 2. form new political parties 3. protect states' rights 4. strengthen the presidency 13. Which problem did the Missouri Compromise, the Compromise of 1850, and the Kansas-Nebraska Act attempt to solve? 1. extension of slavery into the western territories 2. equitable distribution of frontier lands to the owners of small farms 3. placement of protective tariffs on foreign imports 4. need for internal improvements in transportation 14. In which case did the United States Supreme Court rule that segregated public facilities were constitutional? 1. Worcester v. Georgia 2. Plessy v. Ferguson 3. Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka 4. Miranda v. Arizona 15. Many Southern States tried to limit the effects of Radical Reconstruction by 1. adopting federal laws mandating segregation 2. enacting Jim Crow laws 3. abolishing the Southern sharecropping system 4. securing passage of new amendments to the United States Constitution 3. Missouri entered the Union as a slave state. 4. Several Southern States seceded from the Union. 7. After the passage of the 13th, 14th, and 15th amendments, African Americans continued to experience political and economic oppression mainly because 1. the amendments were not intended to solve their problems 2. many African Americans distrusted the Federal Government 3. Southern legislatures enacted Jim Crow laws 4. poor communications kept people from learning about their legal rights 8. Poll taxes and grandfather clauses were devices used to 1. deny African Americans the right to vote 2. extend suffrage to women and 18-year-old citizens 3. raise money for political campaigns 4. prevent immigrants from becoming citizens 16. In which area did the views of Booker T. Washington and W.E.B. DuBois differ most? 1. the need to stop violence against African Americans 2. the speed with which full equality of the races should be achieved 3. the need to integrate the armed forces 4. the idea of including white Americans in their political action organizations 17. Which statement best explains President Abraham Lincoln’s justification for the Civil War? 1. As an abolitionist, President Lincoln wanted to end slavery in the United States. 2. President Lincoln wanted to keep the South economically dependent on the industrial North. 3. President Lincoln’s oath of office required him to defend and preserve the Union. 4. To keep the support of Great Britain and France, President Lincoln had to try to end slavery immediately. 18. "By the 1850’s, the Constitution, originally framed as an instrument of national unity, had become a source of sectional discord." This quotation suggests that 1. vast differences of opinion existed over the issue of States rights 2. the Federal Government had become more interested in foreign affairs than in domestic problems 3. the Constitution had no provisions for governing new territories 4. the Southern States continued to import slaves 19. "Compromise Enables Maine and Missouri To Enter Union" (1820) "California Admitted to Union as Free State" (1850) "Kansas-Nebraska Act Sets Up Popular Sovereignty" (1854) Which issue is reflected in these headlines? 1. enactment of protective tariffs 2. extension of slavery 3. voting rights for minorities 4. universal public education 20. "A house divided against itself cannot stand. . . . I do not expect the Union to be dissolved; I do not expect the house to fall; but I do expect it will cease to be divided. It will become all one thing, or all the other. . . .” -Abraham Lincoln, 1858 The “divided house” referred to in this speech was caused primarily by 1. expansionism 2. war with Mexico 3. slavery 4. the suffrage movement 21. "Although important strides were made, Reconstruction failed to provide lasting guarantees of the civil rights of the freedmen.” Which evidence best supports this statement 1. passage of Jim Crow laws in the latter part of the 19th century 2. ratification of the 13th, 14th, and 15th amendments 3. refusal of Southern States to allow sharecropping 4. passage of the Civil Rights Acts of 1866 22. Base your answer to the question below on the passage below and on your knowledge of social studies. "[The registrar] brought a big old book out there, and he gave me the sixteenth section of the constitution of Mississippi, . . . I could copy it like it was in the book, but after I got through copying it, he told me to give a reasonable interpretation and tell the meaning of the section I had copied. Well, I flunked out." Source: A History of the United States since 1861 The main intent of the literacy test described in the passage was to 1. encourage reform of the political system 2. encourage Mississippi residents to learn about their state’s legal system 3. prevent African Americans from exercising a basic right 4. enforce the provisions of the United States Constitution 23. “No state shall make or enforce any law which shall abridge the privileges . . . of citizens . . . nor shall any state deprive any person of life, liberty, or property, without due process of law. . . .” The major purpose of these provisions of the 14th Amendment was to 1. limit the power of the federal government 2. expand the civil rights of women 3. maintain competition in business 4. protect the rights of African Americans 24. Which statement is best supported by the data in the table? 1. 2. 3. 4. The Confederate troops lost the Civil War as a result of their higher numbers of injuries and fatalities. The Union army had better generals during the Civil War. The Civil War had more casualties than any other war. More soldiers died from disease than from wounds. 25. What is the most accurate title for this map? 1. 2. 3. 4. Closing the Frontier Results of Reconstruction A Nation Divided Compromise of 1850 # 5 The Gilded Age--The Rise of Industry & Immigration (late 1800’s) 1.The Post- Civil War Industrialization of the United States Industrialization is when a country goes from making products by hand to mass-producing products in factories with machines. Industrialization was made possible by inventions like steam engines, railroads, iron, steel, electricity, and the production of raw materials (gas, coal, and oil). Industrialization boosted the economy of the U.S. and made it a very powerful and wealthy nation. However it has also created many serious problems for people and the environment. Industrialization was fueled by the United States Economic System of Free Market Capitalism, an economic system based on no government interference in the economy, private ownership of business and businesses competing with each other. This was also known as laissez-faire—the government does not get involved in businesses. Capitalism benefits consumers by increasing the variety of goods available and keeping prices low. At the same time, capitalism can hurt certain workers as owners attempt to increase profits through poor working conditions and low wages. Monopolies eventually became powerful enough to influence politicians in the government. They pressured politicians to pass laws that would benefit the monopolies but not the public. The government tried to limit monopolies using anti-trust laws, but it was not until Theodore Roosevelt became President during the Progressive Era, that the power of monopolies was limited. “New Immigrants” came to the U.S. during this period of industrialization seeking jobs and religious freedom, which led to the rapid growth of cities. Cities grew too fast for governments to handle and many problems such as pollution, crime, poverty, and anger towards new immigrants quickly spread. Anti-immigration laws such as the Chinese-Exclusion Act were passed to limit them. Workers formed Labor Unions to try to fight for their rights and protect American jobs against immigrants. They used strikes, boycotts and collective bargaining to try to fight the monopolies, but the early labor unions and their efforts were usually not successful. Employers were very hostile towards workers trying to organize. The Knight of Labor fell apart after the Haymarket Riot, and the government took the sides of big business during strikes such as the Pullman Strike and Homestead Strike. Again, it would not be until the Progressive Era where unions started to gain more power and workers began receiving more rights. America was growing, becoming richer and more powerful, but there were many underlying problems. This is why America during this time was known as The Gilded Age (gilded means shiny but dull inside). MAIN IDEAS- Key Vocabulary Words 1) Industrialization - the rise of technology, factories and big business. 2) Gilded Age – nickname for the industrial era in which rich Americans dominated the US. There were many successes but also many problems. 3) Free Market Capitalism - an economic system where individuals can privately own and run their own businesses without government interference. 4) Urbanization - when people move from rural areas (the countryside) to urban areas (cities) 5) Laissez-faire - when the government keeps its "hands off" business 6) Corporation - a large company where many investors own a part of the business by purchasing stock 7) Entrepreneur - a person who starts his or her own company 8) Social Darwinism – “Survival of the fittest” in society and economics 9) Rugged Individualism – people must help themselves. People need a good work ethic. 10) Supply and Demand: Prices are determined by consumers and businesses 11) Monopoly/Trusts - a company that has complete control over an industry and prevents competition 12) Robber Barons – a nickname for very rich Monopolists that were accused of being too greedy 13) Captains of Industry: nicknames for rich monopolists that helped grow industry and make affordable products for the public. 14) Andrew Carnegie - businessman who ran a steel monopoly by destroying his competition. He also donated large amounts of money to build libraries and theaters (philanthropist). 15) John D Rockefeller - businessman who ran an oil monopoly and forced his competition out of business. He also donated large amounts of money to build public spaces (philanthropist). 16) Knights of Labor – Labor union created by Terrence V. Powderly. 17) Labor Union- organization of workers that fought for workers’ rights and pay using strikes, boycotts and collective bargaining. 18) Haymarket Riot- riot that ends the Knights of Labor. 19) American Federation of Labor – Created by Samuel Gompers. Largest labor union in America. Did not accept blacks, women or immigrants though. Focused on the rights of skilled workers. 20) Pullman Strike and Homestead Strike: Workers strikes on railroads that was put down with force by the government and workers did not get benefits. 21) Importance of Railroads : As America was growing, railroads connected America and transferred its population (including immigrants) all over. The main railroad monopolist was John Vanderbilt. 24) The Old Immigrants - immigrants from Northern and Western Europe who moved to America between 1607-1880. 25) The New Immigrants – immigrants from Eastern and Southern Europe who moved to America between 1880-1920 for jobs and to escape poverty. 26) Pluralism – diversity, a mixture of people from different religions and cultures 27) Assimilation – the process of immigrants becoming culturally American (learning English/eating American food) 28) Nativism - the dislike of immigrants and a strong pride for those born in the U.S. 29) Chinese Exclusion Act – (1882) law that completely banned immigrants from China 30) Gentleman’s Agreement - (1907) law that limited immigrants from Japan 31) Immigration Quotas – laws that restricted the number of immigrants from certain countries 4. strengthen the rights of workers Questions: 1. In the United States, the main purpose of antitrust legislation is to 1. protect the environment 2. increase competition in business 3. encourage the growth of monopolies 2. After the Civil War, one way business leaders tried to eliminate competition was by 1. forming monopolies or trusts 2. developing overseas markets 3. increasing the prices of their products 4. paying high wages to their workers 3. In the United States, organized labor made its greatest membership gains when 1. the right to unionize and bargain collectively was guaranteed by legislation 2. international competition began to threaten jobs in the United States 3. the major business groups encouraged unionization 4. the economy began to shift from manufacturing to service employment 4. Many reformers who opposed the laissez-faire attitude of the late 19th century argued that 1. the National Government should not interfere in the activities of big business …big business 2. national wealth could best be assured by the accumulation of gold 3. the idea of rugged individualism is vital to the nation’s economic growth 4. government should protect society through the regulation of business 7. Jacob Riis, Jane Addams, and Margaret Sanger are most closely associated with efforts to 1. educate and train formerly enslaved persons 2. preserve the natural environment 3. advance the interests of organized labor 4. improve conditions for the poor 8. The term business monopoly can best be described as 1. the most common form of business in the United States 2. government control of the means of production 3. an agreement between partners to manage a corporation 4. a company that controls or dominates an industry 5. Nativism in the late 19th century was motivated primarily by 1. hostility toward immigrant workers 2. the need to reduce overcrowding in western states 3. cultural conflicts with Native American Indians 4. the migration of African Americans to northern cities 9. One reason John D. Rockefeller, Andrew Carnegie, and J. Pierpont Morgan were sometimes called robber barons was because they 1. robbed from the rich to give to the poor 2. made unnecessarily risky investments 3. used ruthless business tactics against their competitors 4. stole money from the federal government 6. The Rockefeller Foundation, Carnegie Hall, and the Morgan Library illustrate various ways that entrepreneurs and their descendants have 1. suppressed the growth of labor unions 2. supported philanthropic activities to benefit society 3. applied scientific discoveries to industry 10. Which statement describes a result of the Industrial Revolution in the United States? 1. Farm production decreased. 2. Slavery in the South increased. 3. The population of the cities decreased. 4. Immigration to the United States increased 4. endorsing a third political party for workers only 11. “Prices and wages should be determined by the marketplace.” The author of this statement would most probably support 1. government ownership of utilities 2. minimum-wage laws 3. wage and price controls 4. laissez-faire capitalism 12. Which factor most limited the growth of labor unions during the late 1800’s? 1. Most employers were very hostile toward workers’ efforts to organize. 2. Most factory workers were satisfied with their wages and working conditions. 3. The Federal Government declared that unions were illegal. 4. Workers preferred to negotiate with factory owners as individuals rather than as members of a group. 13. In the 19th century, the major national labor unions wanted to improve the position of workers mainly by 1. obtaining the legal right to organize and bargain collectively 2. using government troops to settle labor disputes with management 3. supporting government ownership of major industries 4. attempted to undermine the United States economic system 14. In response to the demands of farmers and small business owners, Congress enacted laws in the late 19th century that 1. supported the organization of farm cooperatives 2. regulated the activities of railroads and trusts 3. provided direct payments to farmers to help them buy modem machinery 4. dropped tariff rates to the lowest point in the century 15.The American Federation of Labor became the first long-lasting, successful labor union in the United States mainly because it 1. refused to participate in strikes against employers 2. concentrated on organizing workers in industries in the South 3. formed its own political party and elected many prolabor public officials 4. fought for the rights of skilled workers 16. One way in which the Chinese Exclusion Act, the Gentlemen’s Agreement, and the National Origins Act were similar is that all were expressions of 1. imperialism 2. nativism 3. militarism 4. Manifest Destiny 17. The main purpose of this 1886 poster was to 1. oppose immigrants who took jobs from American workers 2. support nativist calls for limitations on labor unions 3. organize a protest against acts of police brutality against workers 4. show support for police actions against foreign revolutionaries 18. Which generalization about population growth is supported by information in this chart? 1. For every census listed, rural population exceeded urban population. 2. By 1920, more people lived in cities than in rural areas. 3. The Civil War significantly slowed the rate of population growth. 4. Most urban population growth was due to people migrating from rural areas. 19. What is the main idea of this cartoon? 1. The Standard Oil Company was a harmful monopoly. 2. The best way to develop major industries was to form proprietorships. 3. Government regulations were strangling the Standard Oil Company. 4. Foreign competition in the oil industry was hurting American companies. 20. According to the graph, which was the first year in which more Americans lived in urban areas than in rural areas? (look to the right) 1. 2. 3. 4. 1860 1890 1920 1930 # 6 The Progressive Era (1890’s to late 1910’s/early 1920’s) 1. Problems of Labor, Farmers, Immigrants The Progressive Era is a period of reform in which many of the problems that the U.S. faced during industrialization were addressed or solved. During industrialization, it was common for children to work in unsafe factories alongside their parents who would work 70-80 hours a week. Life at home wasn’t any better as most American were poor, ate spoiled food and lived in crowded, dirty tenements. During The Progressive Era, the U.S. government moved away from its Laissez-faire policy and began to regulate businesses. The movement grew from the Granger Movement and Populist Party that organized farmers in an attempt to break up the railroad monopoly that had been exploiting (taking advantage of) farmers by overcharging them for shipping. The Populist Platform called for more popular involvement in government such as direct election of senators, initiative, referendum and recall. Even though they lost, they paved the way for many reforms. The Populist Party and Progressives were third political parties that focused on a particular person and issue. The Progressives were a political, social and economic movement, which fought for the poor and working class people that were being exploited during industrialization. Many writers, reporters, and social activists like Upton Sinclair and Jacob Riis contributed to solving the many problems that developed during industrialization. Workers began to group together in labor unions in order to fight for better wages, shorter work hours, and safer working conditions. The public and government did not support unions at first but key events like the Triangle Shirtwaist Factory Fire eventually made people realize that workers' rights were being violated by big businesses. Presidents read the works of the Progressive writers and made reforms based on their writings; they became known as The Progressive Presidents. President Theodore Roosevelt is considered to be the American President at this time most responsible for protecting Americans from the abuses of business. Roosevelt worked tirelessly to pass Anti Trust Acts, improve health and safety conditions in factories and make sure the food we eat is safe. President William Howard Taft and Woodrow Wilson were also Progressive Presidents who passed reforms. The Progressive movement continued to 1920 when women received the right to vote with the passing of the Nineteenth Amendment. However, the Progressive Movement ends when America enters World War I. MAIN IDEAS- Key Vocabulary Words 1) The Granger Movement - farmers who pushed for government regulation of railroads 2) The Populist Party – a new political party started by William Jennings Bryan to represent workers and farmers against railroads, banks and big business, and to get political reforms. Advocated fore free silver—new currency reform. 3) The Progressive Movement – Movement where people (Muckrakers) identified and fought against the social, political and economic problems in the United 4) States due to urbanization (growth of cities) and industrialization (growth of businesses) 5) Theodore Roosevelt - Progressive President (1901-1908) who’s Square Deal Policies broke up monopolies, created the Meat Inspection Act and was also a trustbuster – breaking up monopolies. 6) Trustbusting - when the government uses antitrust acts to break up trusts/monopolies 7) Anti Trust Acts - laws that tried to stop the spread of monopolies such as the Clayton Anti-Trust Act and Sherman AntiTrust Act. 8) Meat Inspection Act (1906) - cleanliness requirements for all meat plants that were enforced with inspectors 9) Pure Food and Drug Act (1906) - required companies to label ingredients in food and drug products 10) Muckrakers - reporters who expose problems, corruption and the abuse of industry 11) Upton Sinclair - wrote The Jungle a book about the unclean and unsafe conditions of the meatpacking industry. 12) Jacob Riis - photographed the horrible living conditions of the urban poor in his book How the Other Half Lives 13) Initiative - allows citizens, instead of politicians, to come up with state bills (ideas for laws) 14) Referendum - allows citizens, instead of politicians, to vote on certain state bills 15) Recall - allows citizens, instead of politicians, to remove a politician from office 16) Seneca Falls Convention (1848) – a meeting of women, led by Susan B. Anthony to demand Women's Suffrage. 17) Suffrage - the right to vote. The 19th Amendment grants Women’s Suffrage 18) Labor Unions- Groups of workers who used the threat of going on strike in order to bargain for better working condition and higher salaries. (Terrence Powderly’s Knights of Labor, Samuel Gomper’s American Federation of Labor - AFL) 19) Triangle Shirtwaist Factory Fire (1911) - 150 women die in a factory fire because of unsafe conditions 20) Tenements – small, unsafe apartments that immigrants in NYC would often live in. 21) Boss Tweed and Tammany Hall - The corrupt government of New York City that took advantage of people and immigrants through taxes, corrupt deals, etc. 22) Thomas Nast – cartoonist who exposed corruption, especially against Boss Tweed. 23) Ida Tarbell – Wrote about the corruption of the Standard Oil Company. 24) Jane Adams – worked in Hull Houses that were houses for the poor. 25) Woodrow Wilson – another Progressive President. His “New Nationalism Program” targeted child labor, better working conditions, regulating banks and breaking up trusts. 26) Interstate Commerce Act (1887) – Congressional Act that stated only the government controls trade between states (and not businesses) 27) Sherman Anti-Trust Act (1890) – Congressional Act that tries to make monopolies and trusts illegal, but does not have initial success. Questions: 1. In passing the Sherman Antitrust Act (1890), 2. In the late 1800s, many business practices of the Congress intended to railroads led to 1. prevent large corporations from eliminating their 1. an increase in the unemployment rate competition 2. an increase in the demand for government 2. distinguish good trusts from bad trusts regulation 3. regulate rates charged by railroads 3. a decrease in the demand for raw materials 4. force large trusts to bargain with labor unions 4. a decrease in the variety of products available for consumers 3. A goal of the Granger and Populist movements was to 1. expand rights for African Americans 2. help western farmers fight unjust economic practices 3. provide support for the banking industry 4. enable big business to expand without government interference 5. A main purpose of President Theodore Roosevelt’s trust-busting policies was to 1. reduce corruption in government 2. save the nation’s banks 3. encourage competition in business 4. end strikes by labor unions 6. During which period in United States history were the amendments concerning the income tax, direct election of Senators. Prohibition, and women’s suffrage enacted? 1. Reconstruction 2. The Gilded Age 3. Progressive Era 4. New Deal 7. The Populist and the Progressive movements were similar in their approaches to reform in that both 1. supported the return of powers to the state governments 2. promoted the use of violent strikes and protests against big business organizations 3. opposed the strict laissez-faire attitudes of the federal government 4. lobbied for immediate social and economic equality for African Americans 8. In How the Other Half Lives, Jacob Riis described the living conditions of 1. workers in urban slums 2. African Americans in the segregated South 3. the rich in their mansions 4. Native American Indians on reservations 9. Which president was known as a trustbuster? 1. George Washington 2. Calvin Coolidge 3. Theodore Roosevelt 4. Dwight Eisenhower 10. In the late 1800s, the Homestead steel strike and the Pullman railcar strike were unsuccessful because 1. the government supported business owners 2. most workers refused to take part in the strike 3. the Supreme Court ruled both strikes were illegal 4. factory owners hired children to replace the strikers 11. In 1906, the publication of The Jungle, written by Upton Sinclair, led Congress to 1. enact stronger prohibition laws 2. support the national conservation movement 3. establish a system for meat inspection 4. legalize strikes and boycotts by labor unions 12. Which 19th-century event supported the movement for women's rights? 1. Seneca Falls Convention 2. Dred Scott decision 3. formation of the Republican Party 4. Lincoln-Douglas debates 13. A major purpose of the Chinese Exclusion Act (1882) was to 1. limit immigration of certain ethnic groups 2. enrich America's cultural diversity 3. treat all Asian and European immigrants equally 4. relocate Asians displaced by war 4. The Populist movement was most interested in improving conditions for 1. farmers 2. business leaders 3. African Americans 4. Native American Indians 14. Which conclusion can be drawn about the impact of the Populist and the Progressive parties on the United States? 1. Some third-party goals eventually become planks in the platforms of the major parties. 2. The United States has steadily moved from a twoparty system to a multiparty system. 3. Religious ideals have most often motivated people to splinter away from major parties . 4. An increasing number of citizens have grown weary of party politics and fail to vote in elections. 15. The Populists believed that most of the United States economic problems would be solved by establishing 1. currency reform 2. postal savings banks 3. a national property tax 4. a renewed policy of open immigration 16. A common characteristic of third political parties in the United States is that they 1. tend to focus on one person or one issue 2. come into existence only during periods of corruption 3. have dealt mainly with foreign policy issues 4. have frequently forced Congress to decide Presidential elections 17. The Farmer is the Man When the farmer comes to town With his wagon broken down, Oh, the farmer is the man Who feeds them all. . . . The farmer is the man, The farmer is the man, Lives on credit till the fall; Then they take him by the hand And they lead him from the land, And the middleman’s the man Who gets it all. . . . — American folk song The problem identified by this folk song was a result of 1. low profits forcing many people out of farming 2. farm productivity declining for several decades 3. too many Americans entering the occupation of farming 4. poor farming practices destroying cropland 18. Speaker A: "The business of America is business, and we would be wise to remember that." Speaker B:"Government ownership of business is superior to private enterprise." Speaker C:"Strict government regulation of business practices is a means to insure the public good." Speaker D:"Only through personal effort can wealth and success be achieved." Which speaker would most likely have supported the ideas of the Progressive movement? 1. Speaker A 2. Speaker B 3. Speaker C 4. Speaker D 19. The purpose of the Interstate Commerce Act (1887), the Sherman Antitrust Act (1890), and the Clayton Antitrust Act (1914) was to 1. eliminate unfair business practices 2. reduce imports from foreign nations 3. reduce the power of the unions 4. increase the power of local governments # 7 World War I (1914-1919) & The Roaring 20’s and American Prosperity (1920-1929) 1. World War I During the turn of the 20th century, America became stronger from its imperialist and expansionist policies. Many people in the U.S. supported these actions because it made the US strong since the country now had more places to sell goods. However, as America became stronger, it also got more involved in European affairs (just as Washington warned about in his Farewell Address!) In 1914, the Alliances of Great Britain, France and Russia (Triple Entente) went to war against Germany, Austria-Hungary and the Ottoman Empire (Triple Alliance). During 1914-1917, despite the efforts of President Woodrow Wilson, the U.S. was slowly pulled into World War I with the Zimmerman Telegram, Sinking of the Lusitania and Russian Revolution. The U.S. began selling weapons to the more democratic countries of Britain and France as they fought against the more autocratic (rule of one person) governments of the Triple Alliance. Eventually U.S. civilians became victims, as German unrestricted submarine warfare sank the cruise ship the Lusitania. Germany claimed that the Lusitania was secretly transporting weapons and ammunition from the U.S. to Britain. In 1917, after Wilson’s reelection and the Russian Revolution put Russia out of the war, America joined the war on Britain and France’s side in 1917. They wanted to maintain freedom of the seas. With fresh soldiers, the Triple Entente won and in 1919, Germany surrendered. Wilson was determined to create a lasting peace, with America at the lead. He believed that the United States had a democracy to protect and spread democracies and the freedoms of peoples around the world. Wilson’s 14-Points tried to create a post-WWI world with no alliances, no military build-up, no colonialism and self-determination by all nations (nations should be independent) as well as an international peace keeping organization known as The League of Nations. The Europeans however, wanted to punish Germany and only kept The League of Nations in the final peace treaty, The Treaty of Versailles. However, after the war the Senate (which ratifies (approves) all treaties) did not want to sign the Treaty of Versailles because of the League of Nations and wanted to follow a policy of isolationism – not getting involved in foreign affairs. The U.S. isolated itself from European U.S. isolationism would last until the U.S. entered World War II in 1941. The war’s greatest significance might have actually been felt on the home front, though. At home, the war changed America; the important Supreme Court case Schenk v. U.S. limited freedom of speech during times of war. The Supreme Court ruled that speech or actions that creates a clear and present danger (such as “shouting fire in a crowded theatre”) are not protected by the Constitution—Constitutional protection of liberties are not absolute. However, rights were also gained. While the men were away fighting, women worked in factories – their work at home helped America send millions of men overseas and win the war. The government rewarded the sacrifice of women and finally gave them the right to vote with the ratification of the new 19th Amendment. MAIN IDEAS- 2. Roaring Twenties The Roaring Twenties was a very exciting time in U.S. History for many levels of society. Women, who now had the right to vote, went to college in greater numbers and experienced social freedom. They were much more independent, wearing skirts, smoking, drinking, dancing and became known as flappers. New inventions such as the toaster, washing machine, and vacuum made life at home easier on housewives. Mass production of the automobile allowed more Americans the opportunity to travel within the country. There was also the birth of radio, television and movies. Presidents Warren Harding and Calvin Coolidge were presidents for most of the '20's. They believed in capitalism – the use of capital (resources) to make profit, laissez-faire policy (the government should stay out of the economy), supply-side economics (the government should make taxes that support the growth of businesses. However, there was also one major scandal known as The Teapot Dome Scandal where the Harding Administration was caught selling oil rights to companies which violated American business practices. Due to their policies, the United States experienced great economic growth. Henry Ford developed the assembly line to mass produce cars. Cars as well as other luxury goods became more affordable. The 1920’s was also a great time for African Americans. During the Great Migration African Americans moved from the South and Mid-West to Northern cities looking for job opportunities. Cities such as Chicago and New York City became centers for the growth of African American culture. This led to the Harlem Renaissance - when African Americans expressed themselves and pride in culture through art, literature, music, acting. They created jazz music and created the Apollo theatre where black artists and musicians performed. However, the 1920’s was also controversial. There was much intolerance, especially towards immigrants. With the growth of Communism in Russia, Americans were scared of immigrants especially from Russia and Eastern Europe and America went through the “Red Scare.” Attorney General Palmer launched the “Palmer Raids” where the state department arrested and deported thousands of immigrants under suspicion of being communist. In the Sacco and Vanzetti Case, Italian immigrants Sacco and Vanzetti were sentenced to death because of an anti-immigrant jury. The Ku Klux Klan also had a rebirth, with hundreds of thousands joining in an effort to keep White American supremacy. People were also intolerant against the new evolution theory, and in a famous case, “The Scopes Monkey Trial,” the controversy was made public. Lastly, people became intolerant towards alcohol and pushed the government to pass the 18th Amendment – Prohibition – which banned the sale of alcohol. People violated these unpopular prohibition laws and it became common for people to drink alcohol illegally in places called speakeasies. With alcohol illegal, mafia crime lords such as Al Capone became rich by operating black market liquor sales. Prohibition was eventually appealed with the 21 st Amendment. The U.S., while we enjoyed exporting all of our new products, reverted (went back to) a policy of isolationism, rejecting President Wilson’s plan for the League of Nations; causing further division between Democrats and Republicans. MAIN IDEAS- Key Vocabulary Words 1) President Woodrow Wilson -tried to keep the U.S. out of W.W.I, but was forced to after the Sinking of the Lusitania, Zimmerman Telegram and Russian Revolution put Russia out of the war. He was also the creator of the 14 Point Plan for peace and the League of Nations. 2) Lusitania – American cruise ship that was sunk by German U-Boats (submarines) for suspicion of carrying supplies to England. Many wanted war with Germany because of this. 3) Unrestricted submarine warfare - Germany's plan to attack all non German ships. The need to protect its military and commercial ships pushed the US government to enter WWl. 4) Zimmerman Telegram – Letter from Germany to Mexico that supposedly said that Germany wanted Mexico to attack America. Many wanted war with Germany because of this. 5) Russian Revolution – When the people of Russia overthrew the Tsar and Russia exited the war. America had to join England and France or they would lose. 6) 14 Point Plan- Wilson’s plan for after the war that would create world peace. It called for self-determination of colonized nations, no alliances and decrease size of militaries and the creation of a League of Nations. 7) League Of Nations - an organization that promoted world cooperation and peace. However, since the U.S. did not join, and the League did not have the power to prevent World War II. The League of Nations is the first try/original version of the current United Nations. 8) Treaty of Versailles (1919) - blamed and punished Germany for starting World War I and created a League of Nations. 9) Isolationism – a foreign policy of not getting involved in foreign affairs 10) Foreign Policy – Relations/actions towards other countries. 11) Farewell Address – Washington’s Farewell letter to the nation (1796) that recommend a foreign policy of isolationism 12) Schenk v. U.S. (1919) - The U.S. Supreme Court decided that the government can limit freedom of speech during wartime if the speech/actions represent a clear and present danger such as “shouting fire in a crowded theater.” 13) 19th Amendment – This gave women the right to vote. It was created after they worked in factories for men on the home front during World War I. 14) Ratify – to approve 15) Home front -- how the war affects life at home. 16) Prohibition- The 18th Amendment that banned the sale of alcohol. Unpopular and removed by the 21st Amendment. 17) Flappers- name given to a new type of woman who smoked, drank, wore less restrictive clothing 18) Scopes "Monkey" Trial - the trial of a science teacher was fired for teaching Darwin's theory of evolution 19) Harlem Renaissance – Growth of African American culture. 20) Great Migration – When African Americans moved up from the South to the North. 21) Laissez-Faire – Policy of no government interference in the economy 22) Supply-side Economics – Government policies that help businesses grow 23) Capitalism – When Entrepreneurs use privately owned capital (resources) to create profit. 24) Roaring 20’s – A time of great prosperity in America 25) Red Scare – When Americans were scared of immigrants and communist influence. 26) Sacco and Vanzetti Case – Two Italians were sentenced to death because of a prejudice jury. 27) Scopes Monkey Trial – Court case which exposes the conflict over teaching evolution in classrooms 28) Assembly Line – Created by Henry Ford to mass produce cars and make goods more available and cheaper. 29) Henry Ford – Innovator of the “assembly line; a businessman who helped revolutionize producing and selling goods to people (especially cars – Ford Model-T) 30) Palmer Raids – Attorney General Palmer’s “raids” to arrest and deport Russian immigrants due to fear from Communism spreading. 31) Ku Klux Klan – organization whose agenda was to create a White Supremacist Society. 32) Intolerance – not accepting of other people. 33) Teapot Dome Scandal – When the Harding Administration was accused of selling oil rights to one company without a bidding by other companies. 34) Bootlegger: Someone who made and/or smuggled alcohol during Prohibition. 35) Speakeasy: Place where people went to illegally drink during Prohibition. 36) Al Capone: Mafia boss who ran illegal alcohol rings (networks) during Prohibition. 37) Presidents Warren Harding and Calvin Coolidge: Presidents from 1921-1929 who followed capitalist and free market ideas and policies of isolationism 4. What was a major reason for United States entry into Questions: World War I? 1. to overthrow the czarist government of Russia 1. The "clear and present danger" ruling of the Supreme 2. to keep Latin America from being attacked by Court in Schenck v. United States illustrates the Germany continuing conflict between 3. to maintain freedom of the seas 1. free speech and governmental authority 4. to break up the colonial empires of the Allies 2. the use of search warrants and the rights of the accused 3. state powers and Federal powers 5. Which situation was the immediate cause of the 4. religious freedom and separation of church and United States entry into World War I in 1917? state 1. The League of Nations requested help. 2. President Woodrow Wilson’s Fourteen Points were 2. The Maine was blown up in Havana Harbor. intended to 3. Nazi tyranny threatened Western democracy. 1. make the United States, Great Britain, and France 4. German submarines sank United States merchant into leading world powers ships. 2. redistribute Germany’s colonies among the Allied 6. During World War I, many American women helped nations gain support for the suffrage movement by 3. prevent international tensions from leading to war 4. punish Germany for causing World War I 1. protesting against the war 2. joining the military service 3. A major reason for the isolationist trend in the United 3. lobbying for child-care facilities States following World War I was 4. working in wartime industries 1. a desire to continue the reforms of the Progressives 7. The Harlem Renaissance of the 1920’s was a period 2. the public’s desire to end most trade with other when African Americans nations 3. the failure of the United States to gain new territory 1. left the United States in large numbers to settle in 4. a disillusionment over the outcomes of the war Nigeria 2. created noteworthy works of art and literature 3. migrated to the West in search of land and jobs 4. used civil disobedience to fight segregation in the Armed Forces 2. Constitutional protections of liberty are not absolute. 3. The Supreme Court can eliminate freedoms listed in the Bill of Rights. 4. The Bill of Rights does not safeguard individual liberties. 8. The 1920’s are sometimes called the "Roaring Twenties" because 1. foreign trade prospered after World War I 2. the United States assumed a leadership role in world affairs 3. political reforms made government more democratic 4. widespread social and economic change occurred 13. After World War I, the opposition of some Members of Congress to the Versailles Treaty was based largely on the idea that the Treaty 9. In the United States, the decade of the 1920’s was characterized by 1. a willingness to encourage immigration to the United States 2. increased consumer borrowing and spending 3. the active involvement of the United States in European affairs 4. major reforms in national labor legislation 1. did not punish the Central Powers harshly enough 2. did not give the United States an important role in world affairs 3. would require the United States to join the League of Nations and might result in a loss of United States sovereignty 4. would require the United States to assume the cost of rebuilding the war-torn European economies 10. The 1925 trial of John Scopes reflects the conflict between 1. science and religion 2. isolation and international involvement 3. traditional roles and new roles for women 4. Prohibition and organized crime 14. Which pair of events illustrates an accurate causeand-effect relationship? 1. Sacco and Vanzetti trial ---> ratification of the woman suffrage amendment 2. rebirth of the KKK ---> formation of the Populist Party 3. Red Scare ---> demand for limits on immigration 4. high food prices ---> start of the Great Depression 11. Which factors were the major causes of the Red Scare and the Palmer Raids, which followed World War I? 1. success of the Communist Party in congressional and Presidential elections 2. race riots in Los Angeles and the revival of the Ku Klux Klan 3. failure of the United States to join the League of Nations and the unpaid German war debts 4. the Bolshevik Revolution of 1917 in Russia and workers’ strikes in the United States “Public Ignores Prohibition Restrictions” “Evolution and Creation Debated in Scopes Trial” “Women Bring Change to the Industrial Workforce” 12. “The most stringent protection of free speech would not protect a man in falsely shouting fire in a theater and causing a panic."-Justice Oliver Wendell Holmes Which interpretation of the Bill of Rights does this statement illustrate? 1. The needs of the government are more important than civil liberties. 15. What do headlines such as these from the 1920s illustrate? 1. conflict between traditional and modern values 2. trend toward mass consumption of consumer goods 3. hostility of certain groups toward ethnic minorities 4. debate over the role of government in the economy 16. Data from this graph support the conclusion that World War I 1. 2. 3. 4. caused the United States trade deficit to increase cost the United States many billions of dollars was a significant benefit to the American economy created an unfavorable balance of trade # 8 Great Depression (1930-1945), FDR and the New Deal (1930s-), WWII (1941-1945) 1. The Great Depression The economy was booming in the early 20s due to new inventions and the birth of modern advertising. Also, for the first time in history, people could buy products without having the cash to pay for them. Consumers were offered credit and installment plans, which let them buy now and pay later. The more people bought, the better the economy did. But eventually, people couldn’t afford all the items that they bought and the economy collapsed. This happened with the stock market too. Stock Market Speculation and buying on margin led to “Black Tuesday” when the stock market crashed in 1929. The Stock Market Crash of 1929 signaled the beginning of The Great Depression. A depression is when the economy is not producing, but shrinking. There is also very high unemployment. The Stock Market Crash was the main cause, but this led to other problems such as the run on the banks where 5,000 banks closed when people panicked and started taking their money out. There were underlying problems that led to the Depression and led to it getting worse such as over-production and underconsumption, businesses taking advantage of laissez-faire policies and a growing income gap – less and less were able to afford all of the consumer products of the Roaring ‘20’s. All of these problems combined together to form the worst economic period in our nation’s history – unemployment hovered around at least 15% for 12 years and reached as high as 25% in 1933. During the depression, 1 out of every 4 Americans was out of a job. In the cities people waited on lines for bread. In the countryside, farmers lost their land during The Dust Bowl – when farmland turned to dust due to drought and abusive farming practices (over producing). President Herbert Hoover didn't believe the government should get involved in trying to fix the economy. He thought that government involvement in the economy was similar to socialism or communism and believed in rugged individualism instead. The people who lost their home and lived in the streets and parks in newspaper and cardboard tents called their new dwellings “Hoovervilles” at their anger of Hoover. It wasn’t until the election of 1932, when new President Franklin Deleanor Roosevelt (FDR) that the US government spent money to help Americans get back to work. FDR’s created policies, which he called his New Deal to provide Relief, Recovery and Reform and to pump and prime the economy. FDR’s relief policies like the Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC) and the Works Progress Administration (WPA) were designed to provide people with emergency jobs and income. FDR also created benefits to help people such as Social Security Act, unemployment benefits and early Medicare programs. To fix the banking and stock market he instituted a bank holiday and approved the creation of the Security Exchange Commission to monitor stock trading. To restore calm he spoke to the nation weekly through his fireside chats. FDR was so popular that he broke tradition and ran and won a 3rd and 4th term as President. However, there was much controversy to the New Deal – the Supreme Court challenged many of the programs Constitutionality stating the government was overstepping its limits and regulating business. In response, FDR tried to “pack” the Supreme Court – changing the Constitution to add 7 more judges (who would agree with him), but this failed to pass through Congress. Women and African Americans also did not benefit from many of the New Deal Programs. Although the New Deal did much to fix the economy, it wasn’t until the start of World War II that many American were hired for war related jobs and the Great Depression came to an end. MAIN IDEAS- 2. World War II In 1938, Adolf Hitler, Chancellor of Germany annexed Austria. Britain and France first responded through appeasement by letting Hitler take the country in order to prevent war. In 1939, Hitler continued to try to take over Europe by invading Poland. Fearing that Hitler intended to dominate all of Europe and maybe the world, Britain and France declared war on Germany officially beginning World War II.In the early 1930s, after the end of World War I, the American public wanted to remain isolationist and out of world problems. Many Americans believed that Europe and the newly formed League Of Nations should attempt to bring about a peaceful solution to this European conflict. This didn’t work. The American government first foreign policy was to pass Neutrality Acts, which prevented Americans from selling weapons to countries at war. America would only sell non-military weapons on a cash and carry basis. By 1940, France was conquered by Germany and the US feared that without arming Great Britain all of Europe could be under Hitler’s control. Roosevelt proposed the Lend Lease Act to lend war materials to any country fighting Germany. The US also refused to sell weapons and materials to Japan, an ally of Germany. On the morning of December 7, 1941 Japanese airplanes sneak attacked the US navy in Pearl Harbor, Hawaii. The day after the attack, President Roosevelt asked Congress to declare war on Japan making the US officially part of WWII. The attack on Pearl Harbor made Americans fearful of Japanese immigrants living in America. Many Americans thought Americans of Japanese heritage might be spies or loyal to the Japanese Emperor. In the Supreme Court Case Korematsu v. US (1944), the court agreed to relocate Japanese Americans to prison like areas called Internment Camps. America fought both against Germany in Africa and Europe and Japan in the Atlantic, but new Hitler was the toughest enemy and we sent most of our army against Germany and Italy. The war against Germany was difficult, but slowly America invaded Italy and then France (D-Day invasion). By May 1945, Allied Forces (America, England and Russia) were outside of Berlin. Hitler committed suicide and Germany surrendered. After Hitler was defeated, the leaders of the Allied Powers, new President Harry Truman, British Prime Minister Winston Churchill and Soviet Secretary General Joseph Stalin (known as “the Big Three”), met at the Potsdam Conference. This conference determined how Germany and Europe would be divided after the war – Berlin would be split into sections – America, France and England controlling the West and the Soviet Union the East. The Soviet Union would also be given control of Eastern Europe to use as future protection. This agreement helped to set up The Cold War where Germany and Europe would be divided into a free and capitalist West and a communist controlled East. After the war, Nazi war criminals who were responsible for The Holocaust were put to trial at The Nuremburg Trials. The war in the Pacific was equally difficult. General Douglas MacArthur developed the strategy of “Island Hopping” – moving from one island to the next, getting closer and closer to Japan. However, each battle had many casualties – the Japanese usually always fought to the last man. In the Battle of Midway, we destroyed most of the Japanese ready and by 1945, we were ready to invade Japan. However, FDR died in 1945 and the new American President Harry Truman believed that an invasion of Japan could take a long time and lead to millions of American deaths. In August 1945, the American military dropped two atomic bombs on the cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in Japan. Japan surrendered shortly after the second explosion. This action possibly saved the lives of millions of American soldiers but resulted in the deaths of over hundreds of thousands of Japanese.World War II had many positive effects for America on the homefront. US entry into World War II helped the US economy out of The Great Depression, expanded women’s rights as women were encouraged to work in factories and improved relations between blacks and whites that fought in integrated units in the army. The saving and rationing that took place at home for the war set up a culture that was ready to buy after the war. The US attack on Hiroshima and Nagasaki has been the only time in history to date that atom bombs have been used in war and changed war forever. The war also stressed the need for a better peace-keeping organization than the League of Nations which clearly failed. During the Yalta Conference (February 1945), the leaders of the Allied Powers decided a new organization had to be made, which would become the United Nations. However, World War II, the Yalta Conference and the Potsdam Conference set up the Cold War between the only two superpowers remaining –America and the U.S.S.R vying for control over a divided capitalist and communist Europe. Key Vocabulary Words 1) Great Depression (1929-1940) - when many businesses and banks failed, and unemployment became as high as 25%. 2) President Herbert Hoover- Believe the government should not get involved in hiring people during the Great Depression. Believed this would be like socialism/communism. 3) Stock Market Speculation- the buying stock in an irresponsible fashion. Lead to the Stock Market Crash of 1929 (which starts the Great Depression on Black Tuesday – October 29, 1929) 4) Run on Banks – when people panicked and started removing their money from banks forcing banks to close and thousands to lose money. 5) Overproduction and Under consumption – businesses were overproducing goods but no one was buying them. 6) Widening Income Gap – Fewer people were earning more money but an increasing amount of people were earning less. 7) The Dust Bowl- a series of droughts that turned the fertile Great Plains of middle-America into a dust wasteland 8) Hoovervilles- makeshift homes where homeless people lived (named after Hoover because they believed he did not help them). 9) Bonus Army – WWI Veterans who camped out on the White House lawn to demand their pensions from Hoover, who sent out the army to drive them away. 10) Rugged Individualism – Hoover’s belief that people need to individually work hard without government help or interference in the economy. 11) Franklin Demeanor Roosevelt (FDR) – President during the Depression who increased employment and government involvement in the economy through his New Deal. 12) The New Deal – FDR’s policies that provided Relief, Recovery and Reform and pump and priming to the American economy. This was a major change to capitalism as there was now much more government involvement and spending in the economy. 13) Relief – programs to bring immediate relief – Civilian Conservation Corps, Tennessee Valley Association, Public Works Administration and Works Public Administration, Works Progress Administration are 4 famous ones. 14) Recovery – Programs to start increasing production and regulating business to keep distribution fair – such as the Agricultural Adjustment Act (AAA) and National Recovery Administration (NRA). 15) Reform -- Programs to fix the American economy so problems that started the Great Depression would not happen again, along with creating entitlement programs to help people who need it. These included The Bank Holiday, Social Security Act and Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (F.D.I.C.) which regulated banks and insured peoples’ deposits in them. 16) FDR’s Alphabet Soup -- Nickname gave to all of the New Deal Programs because of their initials. 17) Fireside Chats – FDR’s weekly radio address to the nation to build confidence. 18) Butler v. U.S. – Supreme Court case which said the AAA was illegal because it was over-regulating farmers. 19) Schecter Poultry v. U.S. Supreme Court case which said the NRA was illegal because it was over regulating businesses and the government cannot set prices. 20) Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC) – New Deal program that hired young men to build schools and create parks during The Depression 21) Works Progress Administration (WPA) - New Deal program that hired artists, musicians and architects during The Depression. 22) FDR’s Court Packing Plan – President Roosevelt’s unconstitutional plan to hire Supreme Court Justices that agreed with his New Deal. This violated checks & balances and failed. 23) World War II ends the Depression—The massive production needed by WW2 and employment of millions of soldiers and factory workers, along with forced savings and rationing helped bring America out of the Depression. 24) Appeasement – the idea to let Hitler take land that didn’t belong to Germany so Europe could avoid war before WWII 25) Isolationism - the US foreign policy of not getting involved in European problems at the beginning on WWII. 26) League Of Nations - an organization that promoted world and peace. However, since the U.S. did not join, the League had less power to prevent World War II. 27) United Nations – the new “League of Nations” which was created after WWII ended. Its headquarters is in NYC. 28) Neutrality Acts – US isolationist policies, which prevented Americans from selling weapons to countries at the beginning of WWII. 29) Lend Lease Act/ cash and carry – US policies which allowed the US to sell weapons to Britain, France and Russia at the middle of the war. 30) Pearl Harbor Attack - December 7, 1941, when Japanese airplanes sneak attacked the US navy in Hawaii 31) Korematsu v. US – Supreme Court case that required Japanese Americans being relocated to restricted prison like areas called Internment Camps. 32) The Draft/Selective Service – lotteries that selected US men to register for the army to fight in WWII 33) The Manhattan Project – secret US programs to help build the atomic bomb used on Japan to end the war. 34) President Harry Truman – US President after FDR died. Made the decision to drop atomic bombs on Japan. 35) Nuremberg Trials – Nazi war crimes trials that took place after WWII. Nazi leaders convicted of killing innocent people were imprisoned or executed. 36) Rosie The Riveter - cultural symbol representing the American women who worked in factories during WWII 37) GI Bill – US law that gave all US soldiers involved in WWII a way to buy a home and attend college after the war 38) Ration Cards – coupons that were needed to buy goods during WWII in order to save materials for war 39) War/Victory Bonds – money given to the government as an investment so the US could pay for war 40) Potsdam Conference – Conference in which Truman, Churchill and Stalin (Big Three – leaders of Allied Powers) met to decide how to divide up Germany and Europe after the war. Helps set up Cold War. 41) Hiroshima and Nagasaki: The two cities that America dropped the Atomic bomb on to end the war in the Pacific against Japan. 42) End of Great Depression – the massive spending on military items, employment of people in the army and at home and the saving and rationing done by people at home helped lead to the end of the depression. 43) Propaganda – when different forms of media are used to influence people. This was done in the U.S. to recruit people to fight, buy war bonds and ration. 44) Yalta Conference – Conference in which Roosevelt, Churchill and Stalin (also known as Big Three – leaders of Allied Powers) set up idea for United Nations and how to divide up Europe after the war. 45) Homefront – Everything that takes place back in the United States. 46) Women and WWII – Women once again worked in wartime factories and industries to support the men fighting the war. Propaganda like Rosie the Riveter motivated many. 47) Integration of the Army – When the U.S. army allowed all races to serve together and not in separate units. 48) Holocaust – The systematic elimination of Jews and other races by the Nazis. Many German officers were convicted at the Nuremberg Trials of war crimes. 49) DDay – The invasion of France by the Allied powers and turning point in the war against Germany. 50) Island Hopping – Strategy of slowly conquering islands to get closer to Japan. 51) Allied vs. Axis Powers – The Allied Powers were America, England and the Soviet Union vs. the Axis powers of Germany, Italy and Japan. Questions: 1. During the second half of the 1920s, which economic trend was a major cause of the Great Depression? 1. deficits in the federal budget 2. reductions in tariff rates 3. creation of national and state sales taxes 4. overproduction and under consumption 11. President Franklin D. Roosevelt’s response to Supreme Court decisions that declared several New Deal laws unconstitutional was to 1. ask Congress to limit the Court’s jurisdiction 2. propose legislation to increase the size of the Court 3. demand the resignation of several justices 4. ignore the Court’s rulings 2. A significant cause of the Great Depression of the 1930’s was that 1. some banking policies were unsound and had led to the overexpansion of credit 2. a decrease in protective tariffs had opened American business to competition from abroad 3. a wave of violent strikes had paralyzed the major industries 4. consumer goods were relatively inexpensive 12. "The great rule of conduct for us in regard to foreign nations is, in extending our commercial relations, to have with them as little political connection as possible." This quotation supports a foreign policy of 1. imperialism 2. appeasement 3. neutrality 4. economic sanctions 3. Which New Deal program was chiefly designed to correct abuses in the stock market? 1. Federal Emergency Relief Act 2. Civilian Conservation Corps 3. Works Progress Administration 4. Securities and Exchange Commission 4. What were two basic causes of the Dust Bowl during the early 1930s? 1. strip mining and toxic waste dumping 2. overfarming and severe drought 3. clear-cutting of forests and construction of railroads 4. overpopulation and urban sprawl 5. During the Great Depression, expressions such as Hoovervilles and Hoover blankets showed that President Hoover 1. was seen as a role model 2. used the military to aid the unemployed 3. was blamed for the suffering of the poor 4. supported relief and public housing for the needy 6. National Prohibition, as authorized by the 18th Amendment, stated that 1. Americans must be 18 years old to purchase alcoholic beverages 2. only imported alcoholic beverages would be sold 3. alcoholic beverages could be sold only in government-run stores 4. the manufacture and sale of alcoholic beverages was banned 7. One of the major causes of the stock market crash of 1929 was 1. excessive buying of stocks on margin 2. overconsumption of goods and services 3. failure of international banking systems 4. low prices of stocks and bonds 8. New Deal programs such as the Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC) and the Works Progress Administration (WPA) were primarily intended to help 1. farmers 2. homeowners 3. businesses 4. unemployed workers 13. Which action best illustrates the policy of isolationism followed by the United States before it entered World War II? 1. signing of a collective security pact with Latin American nations 2. passage of neutrality legislation forbidding arms sales to warring nations 3. embargo on the sale of gasoline and steel to Japan 4. President Franklin D. Roosevelt’s exchange of American destroyers for British naval and air bases 14. An immediate effect of the Lend-Lease program was that 1. Western Europe recovered from the damage caused by World War I 2. the Soviet Union formed the Warsaw Pact 3. Japan declared war against the United States 4. the United States provided critical aid to Great Britain and the Soviet Union 15. The United States became involved in World War II primarily because 1. Germany refused to pay its debts from World War I 2. European democracies supported United States policies toward Germany and Japan 3. President Franklin D. Roosevelt did not enforce the Neutrality Acts 4. Germany and Japan achieved important military successes in Europe and Asia 16. The United States Supreme Court decision in Korematsu v. United States (1944) concerned 1. restricting freedom of the press 2. the president’s right to use atomic weapons 3. limiting civil liberties during wartime 4. the right of women to serve in military combat 17. During World War II, women and minorities made economic gains mainly because 1. a shortage of traditional labor created new opportunities in the workplace 2. more educational opportunities increased the number of skilled workers in these groups 3. labor unions successfully demanded equal opportunities for these groups 4. new civil rights legislation forced businesses to change their hiring practices 18. A major cause of the internment of Japanese Americans during World War II was 1. national segregation policies 2. immigration quotas 3. racial prejudice 4. economic depression 4. Defeated nations can be occupied by the victors. 9. Which precedent was established by the Nuremberg war crimes trials? 1. National leaders can be held responsible for crimes against humanity . 2. Only individuals who actually commit murder during a war can be guilty of a crime. 3. Defeated nations cannot be forced to pay reparations. 10. In 1944, Congress enacted the GI Bill of Rights in order to 1. provide economic aid to veterans 2. reduce military expenditures 3. ban racial segregation in the armed forces 4. create government jobs for returning soldiers 19. President Harry Truman justified using atomic bombs on Japan in 1945 on the grounds that the 1. world was ready for a demonstration of nuclear power 2. Axis powers deserved total destruction 3. early ending of the war would save many lives 4. American public demanded that the bombs be used 20. What was one result of World War II? 1. The arms race ended. 2. The Cold War ended. 3. Communism was eliminated. 4. Two superpowers emerged. # 9 The Cold War (1945-1990), Civil Rights (1950’s-1960’s), Warren Court (1960’s-1970’s) and Globalization (1990’s to Present Day) 1.The Cold War After World War II, America and The Soviet Union (Russia) were the only two superpowers left in a devastated world. However, America, a capitalist and democratic country and Russia (known as The Soviet Union – U.S.S.R.) a Communist country, wanted to shape the post-war world in a way that would benefit them the most – either spreading capitalism or communism. This started The Cold War – a war in which the two sides never fought each other, but fiercely competed in the arms race, space race and to protect and spread their ideologies across the world. As World War II was ending, the Soviets were marching to Germany from the East, and the Americans from the West. At the Yalta Conference (February 1945), the Big Three (America, Great Britain and Russia) agreed to let all of the countries they liberated from the Nazis stay free. However, after Franklin Roosevelt died, Stalin broke the deal and at the Potsdam Conference (May 1945) he told British Prime Minister Winston Churchill and new U.S. President Harry S. Truman that he will keep his soldiers in the Eastern European countries and they will become part of a new Soviet Empire. World War II was over, but Europe was split in two – the West being capitalist, democratic and free, but the East becoming Soviet Satellite States behind what was now known as the Communist “Iron Curtain.” To stop the spread of Communism, U.S. President and The National Security Council developed NSC-68 or The Containment Policy – stating that America will help other countries’ stop communism from spreading into them. President Truman gave a speech known as The Truman Doctrine, which emphasized this. His Secretary of State George Marshall developed The Marshall Plan to give financial aid to countries. Germany was the center of the Cold War. Berlin, the capital of Germany, was split into a free West and a Communist East. Russia tried to starve West Berlin by blockading it (Berlin Blockade), but America helped West Berlin with The Berlin Airlift. The U.S. also developed The North Atlantic Treaty Organization to protect European countries from Communism. In response, the USSR formed the Warsaw Pact with its satellite nations. President Dwight D. Eisenhower began a policy known as The Domino Theory – this followed the containment policy; warning that if America did not stop Russia from spreading communism, neighboring countries would fall. Eisenhower’s Presidency also saw the start of The Space Race, with Russia launching The Sputnik Satellite. America would win the space race under President Richard M. Nixon, when America landed on the moon first (1969). On the home front during Eisenhower’s Presidency, there was another Red Scare and wave of McCarthyism, where many Americans were suspected of being Communists and Russian spies. People also became conformist to fit in and show they were true Americans. In 1949, China became Communist when Chairman Mao Zedong overthrew the Democratic Government. To avoid a Communist Domino effect in all of Asia, the United States needed to make a stand in Asia. From 1950-1953, America fought The Korean War, protecting capitalist South Korea, from Communist North Korea. This was one of two proxy (side) and limited wars (limited objectives America fought to protect its Democratic friends from Communism. In 1954, America began getting involved in Vietnam (which, like Korea, was split into a Communist North and Capitalist South), when the North tried to unite the country under Communism. From 1965-1975, America fought The Vietnam War, trying to protect capitalist South Vietnam from Communist North Vietnam, but unfortunately failed to do so, and Vietnam and eventually most of South East Asia became Communist. Many protested against the Vietnam War. They did not like the draft, the numerous lives lost, and felt the U.S. should not be the international police. Both the Korean War and Vietnam War were not officially declared wars by Congress! MAIN IDEAS- 2. The Civil Rights Movement For almost a hundred years after Reconstruction, African Americans in the South were living in fear and oppression as second-class citizens. Segregation, racial separation, was the law of the land. The Segregated South existed unchecked by the federal government until the Civil Rights Movement exploded in the 1960s. The first response to segregation came as The Great Migration (1916-1930). During this time seven million African-Americans from the Segregated South fled to large cities in the North (New York, Chicago, Detroit) in search of a better, desegregated life. The Great Migration had a tremendous cultural effect on the North as black performers and artists expressed themselves in theatre, dance and jazz music. The Harlem Renaissance was a cultural movement started by artists living in the Harlem neighborhood of New York City. The movement impacted urban centers and challenged white racism. In 1954, the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People(NAACP) won a landmark Supreme Court Case called Brown V. The Board of Education, which ruled that segregation was unconstitutional and that The South would have to desegregate “with all due deliberate speed.” Although the government told The South to do away with Segregation, many whites resisted fiercely. As whites resisted integration, many African American leaders like Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. began the march to equality during the Civil Rights Movement through civil disobedience and non-violent protests. Rosa Parks began a 13-month strike of Alabama’s segregated buses (The Montgomery Bus Boycott) after refusing to give up her seat to a white passenger. In 1964, President Johnson created The Great Society Program to fight poverty and racism. In 1964, he signed The Civil Rights Act which prohibited discrimination based on race, color, religion or ethnic origin. Shortly after the Civil Right Act, The Voting Rights Act (1965) passed which ended poll taxes and literacy tests, allowing African Americans to vote in The South. Civil Rights continue to be a major issue today as racism still exists in America. In 1965, President Johnson signed the first Affirmative Action program, which allows colleges and professions to increase minority representation. Some critics have challenged these programs as a form of reverse discrimination, which unfairly hurts whites. Although affirmative action was upheld by the Supreme Court in California v. Bakker (1987), affirmative action faces an uncertain future. During this time, the Warren Court (the Supreme Court under Chief Justice Earl Warren) also ruled on many cases that affected the rights of the accused and the rights of all citizens. These Supreme Court cases changed how law enforcement can find evidence and prosecute the accused. MAIN IDEAS- 3. The Cold War and Domestic Changes The 1960’s and 1970’s in America was a time of great controversy. In 1953, President Dwight D. Eisenhower appointed Earl Warren as Chief Justice of the Supreme Court. During this time, the Warren Court (the Supreme Court under Chief Justice Earl Warren) also ruled on many cases that affected the rights of the accused and the rights of all citizens. Supreme Court cases such as Miranda v. Arizona, Escobedo v. Illinois, Mapp v. Ohio and Gideon v. Wainright changed how law enforcement can find evidence and prosecute the accused. Engel v. Vitale made it illegal to force students to pray in school, separating Church and State. The Warren Court’s most famous and impactful decision, though, was Brown v. Board of Ed, which helped to start the Civil Rights Movement by declaring segregation illegal. To try to help the Civil Rights Movement, President John F. Kennedy launched his “New Frontier Program” which tried to pass civil rights laws, end segregation and help blacks with job opportunities. The New Frontier program also put money towards winning the Space Race with Russia and helping impoverished Americans. While Kennedy did try to help America, the failed Bay of Pigs invasion of Cuba to overthrow Fidel Castro made him look very bad, although he was able to avoid nuclear war with Russia during the Cuban Missile Crisis. Kennedy also began to get America deeper involved in Vietnam. Kennedy was unfortunately assassinated in November 1963. His vicepresident, Lyndon B. Johnson took over for him. Johnson continued domestic and foreign policies. Domestically, Johnson continued both Kennedy’s New Frontier and FDR’s New Deal as he spent lots of government money, on his Great Society Program which wanted to help blacks (such as through his Civil Rights Act of 1964 and Affirmative Action) and all impoverished groups through his “War on Poverty” (creating Medicare, Medicaid and other spending). MAIN IDEAS- 4. Modern Presidents President Johnson also increased America’s involvement in Vietnam (which began under Eisenhower and increased under Kennedy), and with the Gulf of Tonkin Resolution, he received permission from Congress to use force in Vietnam (although Vietnam was an undeclared war with no formal declaration of war) to protect South Vietnam from Communist North Vietnam. The War lasted from 1965-1975. The Vietnam War was very unpopular because many did not understand the need to go there to stop Communism from spreading and there was a draft, which many rich people were able to buy their way out of. There were many protests, which were especially led by college students. In the worst incident which occurred at Kent State, 4 students were killed by the Ohio National Guard. High School students even protested; in a high school in Des Moines, students were suspended for wearing black armbands to protest the war, however, they sued and in the case of Tinker v. Des Moines, the Supreme Court said that the school violated their first amendment right. Along with students, Civil Rights leaders and even Veterans (Vietnam Veterans Against the War) protested. President Johnson did not run for re-election and when President Richard M. Nixon won, he began the process of Vietnamization – withdrawing from Vietnam. However, when America left, South Vietnam fell to Communism along with neighboring Cambodia and Laos. Nixon also tried to create a policy of détente (reduction of nuclear arms) with Russia and open diplomatic talks with Communist China. There was several legal backlash from the Vietnam War. Congress passed the War Powers Act to limit how long the President can use soldiers without a declaration of war (although future Presidents will ignore this rule since they are Commander-in-Chief). The worst controversy came when papers showing the secret history of the Vietnam War were stolen from the Pentagon (military command center of U.S.) and then leaked to and published by the New York Times. In Nixon v. N.Y. Times, the Supreme Court sided with the New York Times citing the First Amendment’s Freedom of Speech and Press. Yet for all Nixon’s good work on foreign policy, he will probably go down as one of America’s most controversial Presidents for The Watergate Scandal. Nixon was accused of covering up a break-in at the Democratic Headquarters at the Watergate Hotel. Nixon tried to withhold evidence (claiming executive privilege), but in the case of U.S. v. Nixon, the Supreme Court ruled that no President was above the law. Instead of facing an impeachment trial, President Nixon resigned (and is the only President to do so). Tensions in the Middle East also began to come about. In the 1970s, the Middle East did not want to recognize Israel as a nation because they claimed that Israel stole the land that belonged to them. With the support from Egypt, they fought with Israel. Carter wanted to make peace because he supported Israel between the two nations, so he invited both to his vacation home, Camp David. Carter helped the two sides come up with an agreement called the Camp David Accords. This was a treaty in which Egypt recognized Israel’s right to exist and promised to stop making war against Israel. Issues in Iran began as well, known as the Iran Contra Affair. Iranians hated their Shah (leader) that was put into power by the U.S. The Shah got sick and got care in the U.S. Iranians were mad because they wanted to kill him. Iranians took control of the U.S. embassy in Iran, where 66 Americans were held as hostages until their demands were met to have to Shah return to Iran. Carter did not give in and placed OPEC oil embargos (oil from Iran would not be allowed in the U.S.). The embargo caused a shortage of oil in the U.S. and the prices of gas to rise (inflation). The hostages were not released until Reagan’s presidency. The Reagan administration secretly sold weapons to Iran in exchanged for the release of U.S. hostages who were being held in Lebanon by pro-Iranian groups. The weapons were used to support rebel groups (“contras”) who were fighting the communist government in Nicaragua. This went against the laws made by Congress that said that the government could not give weapons to “contras”. The American public lost respect for these government leaders, who were convicted of lying to Congress and went to prison. Reagan was cleared from any wrongdoing. The economy was not good in the 1980s. Regan cut federal taxes on businesses and individuals, especially for those who were rich. He believed by doing this it would stimulate business growth. This means that if businesses had money, they would hire more workers, more goods would be made, and services would be more available. Due to supply side economics, government programs got cut or less money, such as Medicare and food stamps. This was similar to Hoover’s Trickle Down Theory. A Recession hit the U.S. in the 1990s. The U.S. was in a lot of debt and was costing the U.S. taxpayers billions of dollars in money they had to pay back to countries that the U.S. borrowed money from. This pushed the economy into a recession (a time when the economy slows down and unemployment rises). Many companies went bankrupt and people lost their jobs. At the same time, President George Bush was trying to free Kuwait. Iraq’s dictator, Saddam Hussein, ordered his army to invade Kuwait and take control over the oil and expand Iraq’s border. The United Nations and the U.S. launched an attack against Iraq to liberate (free) Kuwait. This was to assist nations against repelling aggressors (Iraq). A few days after the invasion, Hussein agreed to withdraw Iraqi troops and pay damages. During Clinton’s administration, tensions between ethnic groups in the former Yugoslavia led to war in Bosnia in the early 1990’s. The United States helped win an agreement between the two sides in 1995. In 1998, violence erupted in Kosovo, where Serbian forces massacred ethnic Albanian civilians. A brief bombing by NATO forced the Serbs to withdraw. Many Serbian leaders then were arrested for war crimes and tried. The U.S. got involved in both events because the U.S. the actions taken in these countries violated human rights. Domestically, the U.S., Canada, and Mexico signed an agreement to limit taxes to trade between these countries—North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA). This made these 3 countries economically interdependent on each other and opened up the U.S. to globalization, exchanges of national and cultural resources. In 1998, a special prosecutor accused President Clinton of several offenses, including lying under oath about his relationship with a White House Intern Monica Lewinsky. On December 19, 1998, the House impeached (placed on trial) President Clinton on charges of perjury and obstruction of justice. The Senate acquitted (found not guilty) the President two months later. The Middle East issues arose more when George W. Bush became president. The U.S. fought a War on Terrorism and still continues. Bush focused largely on foreign policy after the September 11, 2001 attacks on the World Trade Center in New York City and the Pentagon in Washington, D.C. Bush called the attacks “acts of war” and committed the country to a campaign against terrorists. American forces attacked military sites and terrorists training camps in Afghanistan. Bush also warned Saddam Hussein to eliminate Iraq’s weapons of mass destruction. The United Nations sent an inspection team, which reported little success in finding these weapons. More than 200,000 American troops were sent into that area. The Patriot Act because of the attacks on September 11, 2001 on the World Trade Center and the Pentagon. This increased the authority (control) given to the federal, state, and local police agencies to investigate crime. Critics argue that this law gives the government too much power and limits civil liberties (people’s freedom). However, the government says this protects national security. Key Vocabulary Words 1) Appeasement – the idea to let Hitler take land that didn’t belong to Germany so Europe could avoid war before WWII 2) Isolationism - the US foreign policy of not getting involved in European problems at the beginning on WWII. 3) League Of Nations - an organization that promoted world and peace. However, since the U.S. did not join, the League had less power to prevent World War II. 4) United Nations – the new “League of Nations” which was created after WWII ended. Its headquarters is in NYC. 5) Neutrality Acts – US isolationist policies, which prevented Americans from selling weapons to countries at the beginning of WWII. 6) Lend Lease Act/ cash and carry – US policies which allowed the US to sell weapons to Britain, France and Russia at the middle of the war. 7) Pearl Harbor Attack - December 7, 1941, when Japanese airplanes sneak attacked the US navy in Hawaii 8) Korematsu v. US – Supreme Court case that required Japanese Americans being relocated to restricted prison like areas called Internment Camps. 9) The Draft/Selective Service – lotteries that selected US men to register for the army to fight in WWII 10) The Manhattan Project – secret US programs to help build the atomic bomb used on Japan to end the war. 11) President Harry Truman – US President after FDR died. Made the decision to drop atomic bombs on Japan. 12) Nuremberg Trials – Nazi war crimes trials that took place after WWII. Nazi leaders convicted of killing innocent people were imprisoned or executed. 13) Rosie The Riveter - cultural symbol representing the American women who worked in factories during WWII 14) GI Bill – US law that gave all US soldiers involved in WWII a way to buy a home and attend college after the war 15) Ration Cards – coupons that were needed to buy goods during WWII in order to save materials for war 16) War/Victory Bonds – money given to the government as an investment so the US could pay for war 17) Potsdam Conference – Conference in which Truman, Churchill and Stalin (Big Three – leaders of Allied Powers) met to decide how to divide up Germany and Europe after the war. Helps set up Cold War. 18) Hiroshima and Nagasaki: The two cities that America dropped the Atomic bomb on to end the war in the Pacific against Japan. 19) End of Great Depression – the massive spending on military items, employment of people in the army and at home and the saving and rationing done by people at home helped lead to the end of the depression. 20) Propaganda – when different forms of media are used to influence people. This was done in the U.S. to recruit people to fight, buy war bonds and ration. Yalta Conference – Conference in which Roosevelt, Churchill and Stalin (also known as Big Three – leaders of Allied Powers) set up idea for United Nations and how to divide up Europe after the war. 21) Homefront – Everything that takes place back in the United States. 22) Women and WWII – Women once again worked in wartime factories and industries to support the men fighting the war. Propaganda like Rosie the Riveter motivated many. 23) Integration of the Army – When the U.S. army allowed all races to serve together and not in separate units. 24) Holocaust – The systematic elimination of Jews and other races by the Nazis. Many German officers were convicted at the Nuremberg Trials of war crimes. 25) DDay – The invasion of France by the Allied powers and turning point in the war against Germany. 26) Island Hopping – Strategy of slowly conquering islands to get closer to Japan. 27) Allied vs. Axis Powers – The Allied Powers were America, England and the Soviet Union vs. the Axis powers of Germany, Italy and Japan. 28) Potsdam Conference – Meeting between Big Three where Stalin stated he will keep soldiers in Eastern Europe and make them satellite nations (nations under Soviet control). 29) Cold War - where the Superpowers of America and Russia competed with each other for global dominance and to spread capitalism vs. communism. 30) Arms Race - Competition between America and the Soviet Union to build their armies and nuclear weapons arsenal 31) Space Race – Competition between America and the Soviet Union to send satellites and space ships into space and to land on the moon (U.S. wins) 32) National Security Council – special Congressional/military panel to advise the president on military matters. 33) NSC-68/Containment Policy – American foreign policy to contain the spread of Communism. 34) Marshall Plan – Secretary of State George C. Marshall’s Plan to send financial aid to limit the spread of Communism (used to help Greece and Turkey). 35) Berlin Airlift – America and its Allies efforts to help Western Berlin from Soviet Berlin Blockade. 36) Berlin Blockade -- when the Soviets blockaded West Berlin to try to control entire city. 37) The Truman Doctrine – President Truman’s speech (and new foreign policy) announcing that America will stop Communism wherever it tries to spread. 38) The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) – Military Alliance between America and democratic Western European countries to protect each other from a Russian attack. 39) Warsaw Pact – Military Alliance between USSR and its Eastern European Satellites to protect each other against a Western attack. 40) Iron Curtain – the division between Western and Eastern Europe. All communist nations were considered “behind the iron curtain.” 41) The Domino Theory – Foreign Policy (mostly applied to Middle East and South East Asia) under Eisenhower that said that if one country falls to Communism, other countries will as well. 42) McCarthyism – when Senator McCarthy led a committee that found and persecuted possible Communists and accused many of being communists. 43) Second Red Scare – When people were scared of Russian/Eastern European immigrants of possibly being Communist spies. 44) House of Un-American Activities Committee (HUAC) – Congressional committee to try to find communists and Russian spies. 45) Conformity – adjusting your lifestyle to fit in with “what is normal.” Heavily done during the 1950’s. 46) Korean War – Limited War (war with specific objectives) and Proxy War (not a direct war between America and Russia) where America stopped Communist North Korea from invading capitalist South Korea. 47) 38th Parallel – Latitude line that divided North from South Korea. 48) Vietnam War – Proxy War when America tried to stop North Vietnam (Communist) from conquering South Vietnam. America lost the war and 58,000 soldiers. 49) The Civil Rights Movement – the movement to end segregation and gain equality for African Americans which exploded in the 1960s. 50) N.A.A.C.P - (Nation Association for the Advancement of Colored Persons) a legal organization which fights for African American rights in court. 51) The Great Migration – (1916-1930) seven million African-Americans from the Segregated South fled to large cities in the North in search of a better life 52) The Harlem Renaissance - a cultural movement started by artists living in the Harlem. The movement challenged white racism in art and music. 53) Brown V. The Board of Education (1954) - the Supreme Court Case that ruled that segregation was unconstitutional and that The South would have to desegregate schools and public facilities. 54) Integration - desegregation, blacks & whites together. Federal Soldiers had to be called in to enforce integration. 55) The Little Roc k Nine – 9 courageous black high school students that were integrated into Little Rock High School and faced much opposition from the south 56) Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. – African American leader who fought for equality through civil disobedience, non-violent protests and boycotts. 57) Malcolm X - African American leader who argued for black supremacy and violent resistance movements 58) Rosa Parks – an African American leader who began a boycott of Alabama’s segregated buses 59) Civil Rights Act – (1964) law that banned discrimination on race, color, religion or ethnic origin. 60) Freedom Riders (1961)—When African Americans tested segregation on buses by riding on buses all over Alabama. They often faced protests and attacks. 61) Civil Disobedience – using peaceful, non-violent protest to achieve goals 62) March on Washington (1963)– When 400,000 African Americans marched to Washington, D.C. to demand rights. 63) Selma March (1965)– When African Americans marched 57 miles to Selma, Alabama to fight for voting rights. They met protest and were even attacked by people and state police (Bloody Sunday). 64) Greensboro Sit-ins (1960)– When African Americans sat in and refused to leave restaurants, department stores and colleges. They often met protest. 65) Montgomery Bus Boycott (1955)– When African Americans refused to ride buses in Montgomery Alabama to protest segregation of buses. 66) The Voting Rights Act - (1965) law that ended poll taxes and literacy tests, allowing African Americans to vote in The South. 67) California v. Bakke (1978) – A Supreme Court case which established Affirmative Action 68) Affirmative Action – a controversial program that allow colleges and professions to increase minority representation 69) The Great Society Program – President Lyndon B. Johnson’s series of acts to fight racism, poverty and inequality in American Society. 70) Miranda vs. Arizona (1966)– Establishes police cannot violate a persons 5th Amendment right to no self incrimination (confession) without being read their rights (become known as Miranda Rights) 71) Gideon v. Wainwright (1963) – Establishes people have the right to a lawyer in court (6 th and 14th Amendment rights) 72) Escobedo v. Illinois (1964) – Establishes people have the right to speak to a lawyer when arrested (5th and 14th Amendment right) 73) Mapp v. Ohio (1961) – Establishes Police cannot violate a persons 4th Amendment right to no illegal searches and seizures. Police need a warrant. 74) New Jersey v. TLO (1985) – Establishes that students have 4th Amendment rights to no illegal searches and seizures. 75) Tinker v. Des Moines (1969) – Students wore black arm bands to school to support the Vietnam War. The Supreme Court upheld their First Amendment (freedom of speech) right to do so. 76) New Frontier Program: President John F. Kennedy’s program to help civil rights, impoverished citizens and win the space race with Russia. 77) Bay of Pigs: Failed invasion of Cuba by America to overthrow Fidel Castro. 78) Cuban Missile Crisis: 14 days in October when Russia put missiles in Cuba and America and Russia became dangerously close to nuclear war. Kennedy and Russia had secret talks and Kennedy was able to avoid war by withdrawing missiles from Turkey and Italy. 79) Great Society Program: multi-purpose program by President Lyndon B. Johnson to create Civil Rights laws, affirmative action programs, Medicare, Medicaid and a “War on Poverty.” 80) Civil Rights Act of 1964: Act which ends segregation. 81) Gulf of Tonkin Resolution: When Congress gives President Johnson permission to use U.S. soldiers in Vietnam. 82) Vietnam War: 1965-1975. controversial undeclared war where America tries to stop Communist North Vietnam from conquering South Vietnam. Costs 58,000 American lives. There were many protests (mostly lead by students) against the war. 83) Kent State Massacre: When 4 Ohio students are killed protesting the Vietnam War. 84) Tinker v. Des Moines (1969): Supreme Court rules that children’s first Amendment rights were violated when they were suspended for wearing black arm bands to protest the Vietnam War. 85) Vietnamization: President Richard M. Nixon’s policy of withdrawing American soldiers and letting South Vietnam fight war by itself. 86) Détente: President Nixon’s foreign policy with Russia to try to reduce nuclear tension and weapons arsenal. 87) S.A.L.T. I: Strategic Arms Limitations Treaty I. America and Russia’s agreement to reduce nuclear arms. 88) War Powers Act: Congress’s limiting the amount of time a President can send soldiers overseas without a declaration of war. 89) Nixon v. New York Times: After Pentagon papers were stolen then leaked to the New York Times and published by them, Nixon tried to stop it, but the Supreme Court said that it was Constitutional because of the First Amendment Freedom of Speech and Press. 90) Watergate Scandal: Scandal where President Nixon was accused of covering up a break-in of the Democratic headquarters. President Nixon resigned instead of facing an impeachment trial. 91) U.S. v. Nixon: Supreme Court ruled that the President does not have executive privilege to withhold evidence. No one is above the law. 92) Miranda vs. Arizona (1966)– Establishes police cannot violate a person’s 5th Amendment right to no self incrimination (confession) without being read their rights (become known as Miranda Rights) 93) Gideon v. Wainwright (1963) – Establishes people have the right to a lawyer in court (6 th and 14th Amendment rights) 94) Escobedo v. Illinois (1964) – Establishes people have the right to speak to a lawyer when arrested (5th and 14th Amendment right) 95) Mapp v. Ohio (1961) – Establishes Police cannot violate a person’s 4th Amendment right to no illegal searches and seizures. Police need a warrant. 96) New Jersey v. TLO (1985) – Establishes that students have 4th Amendment rights to no illegal searches and seizures. 97) Engel v. Vitale (1962) – it is illegal to have an official school pray 98) Camp David Accords: Under president Carter, he held a meeting for Egypt to recognize Israel as a country 99) Iran Contra- Iran took over the U.S. Embassy in Iran and held Americans hostage. They were not released until Reagan’s presidency 100) Supply Side Economics- Reagan wanted to cut federal taxes to stimulate business growth 101) NAFTA- the U.S., Canada, and Mexico opened up trade between each other. Questions: 1. President Harry Truman supported a containment policy after World War II in an attempt to 1. limit the use of atomic bombs and other nuclear weapons 2. end colonialism in Africa and Asia 3. bring German and Japanese war criminals to justice 4. reduce the influence of the Soviet Union in European countries 12. After World War II, the Marshall Plan was proposed as a way to 1. improve diplomatic relations with the Soviet Union 2. help European nations recover economically 3. remove nuclear weapons from Western Europe 4. bring Nazi war criminals to justice 3.In the 1950’s, Senator Joseph McCarthy was most closely associated with issues related to 1. Communist infiltration and the denial of civil liberties 2. farm problems and taxation 3. military preparedness and foreign aid 4. collective bargaining and the rights of unions 4. The successful launching of Sputnik by the Soviet Union in 1957 signaled the beginning of 1. American fears that the Soviets had achieved technological superiority 2. the Cold War with the United States 3. Soviet aggression in Afghanistan and China 4. disarmament discussions between the superpowers 5. Most Americans who opposed sending United States troops to fight in the Vietnam War believed that 1. nuclear weapons should be used to end the war 2. the war should be extended into China 3. 4. the United States should not police the world international trade would be interrupted 6. In the years just after World War II, the United States attempted to prevent the spread of communism in Europe mainly by 1. taking over the governments of several Western European nations 2. increasing opportunities for political refugees to settle in the United States 3. holding a series of summit meetings with leaders of the Soviet Union 4. establishing policies of economic and military aid for European nations 7. A constitutional issue that was frequently raised about United States involvement in the Korean conflict and the Vietnam conflict was the 1. right to regulate commerce with foreign nations 2. use of deficit spending to finance wars 3. lack of a formal declaration of war by Congress 4. Supreme Court’s role in foreign policy decision-making 8. Which is a valid conclusion based on United States involvement in the Korean War? 1. The policy of containment was applied in Asia as well as in Europe 2. United Nations economic sanctions are more effective than military action. 3. The American people will support United States participation in any war, whether declared or undeclared. 4. United States cooperation with a wartime ally ends when the war ends. 9. The United States experience in the Vietnam War supports the idea that the outcome of a war 1. is determined mainly by technological superiority 2. is dependent on using the greatest number of soldiers 3. is assured to countries dedicated to democratic ideals 4. can be strongly affected by public opinion 10. Issuing the Truman Doctrine, defending South Korea, and sending military advisors to Vietnam were actions taken by the United States to 1. encourage membership in the United Nations 2. promote American business in Asia 3. limit the spread of communism 4. gain additional overseas colonies 11. Which development is most closely associated with the belief in the domino theory? 1. military involvement in Vietnam 2. construction of the Berlin Wall 3. signing of the nuclear test ban treaty 4. end of the Korean War 12. The major goal of the civil rights movement of the 1960’s was to 1. establish a separate political state for African Americans 2. gain passage of an equal rights amendment to the Constitution 3. end segregation based on race 4. permit unlimited immigration to the United States 13. The Civil Rights Act of 1964 was passed in an effort to correct 1. racial and gender discrimination 2. limitations on freedom of speech 3. unfair immigration quotas 4. segregation in the armed forces 14. Martin Luther King, Jr. first emerged as a leader of the civil rights movement when he 1. led the bus boycott in Montgomery, Alabama 2. refused to give up his seat on a bus to a white man 3. challenged the authority of the Supreme Court 4. was elected as the first black congressman from the South 15. The main goal of affirmative action programs is to 1. enforce racial segregation laws 2. secure equal voting rights for African Americans 3. provide affordable child care 4. promote economic gains for minorities and women 16. The decisions of the United States Supreme Court in Miranda v. Arizona, Gideon v. Wainwright, and Escobedo v. Illinois all advanced the 1. voting rights of minorities 2. guarantees of free speech and press 3. principle of separation of church and state 4. rights of accused persons 17. President John F. Kennedy supported the 1961 Bay of Pigs invasion of Cuba as an effort to 1. remove a communist dictator from power 2. stop the flow of illegal drugs to the United States 3. support Fidel Castro's efforts for reform 4. rescue hostages held by Cuban freedom fighters 18. The Great Society programs of the 1960’s used the power of the Federal Government to bring about 1. an all-volunteer military 2. antipoverty reforms 3. deregulation of business 4. reduced defense spending 19. President Lyndon Johnson’s Great Society programs were similar to Progressive Era programs in that both 1. strictly enforced antitrust laws 2. focused on expanding civil rights for African Americans 3. used federal government power to improve social conditions 4. made urban renewal their primary concern 20. The main significance of the Watergate affair was that it 1. led to the impeachment and conviction of President Richard Nixon 2. showed that the laws of the United States are superior to the actions of a President 3. was the first time a President had disagreed with Congress 4. proved that Presidential powers are unlimited 21. The easing of Cold War tensions between the United States and the Soviet Union during the 1970s was called 1. containment 2. détente 3. neutrality 4. isolationism 22. The main purpose of the War Powers Act of 1973 was to 1. expand the power of Congress to declare war 2. limit the president’s ability to send troops into combat abroad 3. allow people to vote on the issue of United States commitments overseas 4. end the Vietnam War on favorable terms 23. In the Camp David Accords (1978), President Jimmy Carter succeeded in 1. returning the Panama Canal Zone to Panama 2. suspending grain sales to the Soviet Union and China 3. providing a foundation for a peace treaty between Egypt and Israel 4. freeing hostages being held in Iran 24. Which situation in the 1970s caused the United States to reconsider its dependence on foreign energy resources? 1. war in Afghanistan 2. oil embargo by the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) 3. meetings with the Soviet Union to limit nuclear weapons 4. free-trade agreements with Canada and Mexico 25. One way in which the Watergate controversy and the IranContra affair are similar is that each led to 1. the addition of new amendments to the Constitution 2. the impeachment of a President 3. a loss of respect for government leaders by the American public 4. convictions of several military leaders for sexual harassment 26. The "trickle down" economic theory of President Herbert Hoover and the "supply side" economic policies under President Ronald Reagan were based on the idea that 1. balanced budgets are essential to economic success 2. the Federal Government needs to assume more responsibility for solving economic problems 3. economic growth depends on making increased amounts of capital available to business 4. economic stability is the responsibility of Federal monetary agencies 27. President Ronald Reagan used the concept of supply-side economics when he proposed 1. reducing income taxes to stimulate growth 2. providing direct payments to people living in poverty 3. creating government jobs to keep people working 4. increasing regulations on business to promote competition 28. One direct result of the Persian Gulf War was that the United States 1. gained control of oil resources in the Middle East 2. liberated Kuwait from Iraqi control 3. brought about peaceful relations between Israel and its neighbors 4. obtained overseas colonies in the Middle East 29. Evidence that the United States has become more economically interdependent since 1990 is shown by its 1. participation in the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) 2. change from a service economy to a manufacturing economy 3. increased dependence on domestic farm products 4. policy of restricting imports 30. Which event of Bill Clinton's presidency best illustrates the use of checks and balances? 1. hosting peace talks between Israelis and Palestinians 2. reelection to a second term 3. selection of Al Gore as vice president 4. impeachment for alleged perjury and obstruction of justice Thematic Summary 1: Geographic Themes in American History Geographic Theme 1) Different geography of 13 colonies 2) Northern vs. Southern States 3) Appalachian Mountains 4) Louisiana Purchase 5) Great Lakes and Eerie Canal 6) Westward Expansion 7) Canada and Mexico and Rio Grande 8) Oceans Impact on American History New England Colonies = cold weather, rocky soil and good harbors = based on trade and manufacturing Middle Colonies = harbors = based on trade Southern Colonies = hot weather, good farmland = plantations, cash crops and slave labor Northern states are factories and industries and don’t need slavery Southern states are farms and plantations and economy relies on slavery Creates sectionalism between the two sides and eventually leads to Civil War First boundary (border) of the colonies that limited (blocked) westward expansion. It established by the Proclamation of 1763 which was unpopular with colonists Doubles size of country, gain Mississippi River, Ohio River Valley, Gulf of Mexico, Port of New Orleans Creates manifest destiny (desire to expand entire continent) and starts Westward Expansion First major trade network between New York and Ohio River Valley (Chicago, Cleveland) Steamboats provided trade Settling the entire continent from Atlantic to Pacific Ocean. The major treaties which completed and encouraged the United States are the Louisiana Purchase, Louis and Clarke Expedition, Indian Removal, Trail of Tears, Mexican-American War, Mexican Cession, Homestead Act, Settling the Great Plains, Texas Annexation, Oregon Territory, California Gold Rush Transcontinental Railroad unites East and West Canada is to the North of America, Mexico is to the South of America and the Rio Grande is the border between Mexico and America 9) New York 10) 11) 12) 13) Urban Rural Suburban Dustbowl 14) Latin American and Pacific Imperialism 15) Natural Resources Atlantic Ocean = East (New York) Pacific Ocean = West (California). This keeps us isolated and neutral from rest of World. Japan breaks this isolation when they attack Pearl Harbor (in Pacific) which starts WW2 (1941) Centers of trade, close to Eerie Canal. New York has natural harbors (ports for commerce – which means trade) Cities = New York, Chicago Farms and agriculture = Virginia, Montana Outside of cities = Levittown, Long Island. 1950’s, highways, Private houses, use of cars, malls. Great Depression, massive drought (dry, dusty farms), caused by over production, takes place in Great Plains, Latin America is South of United States. Late 1900’s we take economic control of many of their countries (Cuba, Panama, Panama Canal, Roosevelt Corollary, Dollar Diplomacy, Big Stick Policy, Guam, Puerto Rico, Spanish American War, Yellow Journalism, Good Neighbor Policy). China (other side of Pacific) – Open Door Policy, Spheres of Influence Japan (other side of Pacific) – Matthew Perry, Gentleman’s Agreement, Inspire Japan to Westernize Coal, Copper, Oil, Iron, Cotton, Tobacco, Cash Crops Imperialism Unit Review Overview America's first foreign policy was set by President George Washington who favored neutrality while the U.S. was still young and weak. However, as early as 1823, when the Monroe Doctrine (the State of the Union by President James Monroe) declared Latin America off limits to further European colonization, the U.S. had begun to move away from neutrality. By the late 1800s many factors (especially industrialization and the settling of the frontier) began to push the U.S. further away from neutrality and towards imperialism. The US had long wanted control of the Spanish colony of Cuba that lay only 90 miles south of Florida for both military and economic purposes. A Cuban uprising against Spanish rule led the U.S. to send the U.S.S. Maine battleship to Cuba. When the ship mysteriously exploded, yellow journalists were quick to blame Spain so the U.S. would have a reason to declare war on Spain. The U.S. emerged from the Spanish American War with the colonies of Puerto Rico, Guam, and the Philippines. The U.S. also annexed (absorbed) Hawaii in 1898 and expanded business opportunities into China. President Theodore Roosevelt wanted America and the European powers to share China and they all agreed on an Open Door Policy in which they would divide China into Economic Spheres of Influence. America was now ready to expand both into Latin America and Asia. In Latin America, Theodore Roosevelt issued The Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine which was an addition to the Monroe Doctrine that gave America the power to intervene in Latin American affairs and protect our economic and political interests there. To protect our interests, Roosevelt practiced a Big Stick Policy, threatening force when necessary. Using this policy, we used the military several times in different Latin American countries. Roosevelt also began production on the Panama Canal to connect our Latin American and Asian/Pacific Empires. After Roosevelt, President William Taft did not want to use military force so practiced Dollar Diplomacy, using America’s economy to control the smaller economies of Latin America. Vocabulary Words: 1) Foreign Policy - a country's plan on how to deal with other countries (neutrality, imperialism, isolationism) 2) Imperialism- the policy of a country maintaining colonies or control over distant lands. 3) Big Stick Policy/Roosevelt Corollary (1904-1909) - declared that the U.S. could "police" the Caribbean and Far East to ensure U.S. economic interests were protected. 4) Open Door Policy - U.S. policy that stated that they had rights to operate and profit from business in China. 5) Panama Canal - a man made water way that was built to increase the power of the US navy and connect America’s growing Empire. 6) Yellow Journalism - propaganda or exaggerating news stories to make something exciting and convincing. 7) William Randolph Hearst and Joseph Pulitzer - reporters who used yellow journalism to help provoke the Spanish American War by blaming the sinking of the USS Maine on Spain. 8) Spanish American War (1898) – a war in which the U.S. easily defeated Spain and became a world power with control of Puerto Rico, Guam, and the Philippines. 9) Dollar Diplomacy – President Taft’s policy to use money to control Latin America. 10) Physical features: things that are naturally found and can be touched. Examples: rivers, mountains, lakes 11) Southern Colonies- growing seasons, Plantations, tobacco, indigo, rice, farm products, furs 12) Middle Colonies- soil, grain, livestock, iron, furs 13) New England Colonies- dry rocky soil, lumber, fish, furs, ships, livestock 14) Terrain- layout of the land 15) Mississippi River- used to transport goods, gained during the Louisiana Purchase Questions: 1. Which city is paired with the geographical feature that 5. directly contributed to its growth? 1. San Francisco – Rocky Mountains 2. New Orleans – Mississippi River 3. Pittsburgh – Hudson River 4. Cleveland – Atlantic Coastal Plain 2. Which geographic advantage did the United States gain by purchasing the Louisiana Territory from France in 1803? 1. warm-water ports on the Atlantic coast 2. rich fishing areas in the Great Lakes 3. full control of the Mississippi River 4. vast coal reserves in the region west of Pennsylvania 3. Which group benefited most from the United States acquisition of the port of New Orleans? 1. farmers in the Ohio River Valley 2. Native American Indians in the Southwest 3. fur trappers in the Columbia River Valley 4. gold miners in northern California 4. Which type of map shows the most detailed information about Earth’s natural features, such as rivers, lakes, and mountain ranges? 1. political 2. demographic 3. weather 4. physical 11. The practice of yellow journalism most directly influenced the 1. purchase of Alaska 2. acquisition of the Mexican Cession 3. start of the Spanish-American War 4. end of the Russo-Japanese War 12. The annexation of Hawaii, the Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine, and Dollar Diplomacy are all associated with United States efforts to 1. meet the demands of antiwar movements 2. isolate itself from international problems 3. expand its power and influence in certain regions of the world 4. implement policies of global cooperation throughout Asia 13. As a result of the Spanish-American War, the United States saw the need to build the Panama Canal because 1. new colonies had been acquired in Africa 2. Spanish opposition to the canal had ended 3. the United States navy could then move more quickly between oceans 4. United States railroads could not transport enough manufactured goods 5. Which region of the United States is correctly paired with an industry that is dominant in that region? 1. Southwest — timber 2. Pacific Northwest — citrus crops 3. Great Plains — grain crops 4. Atlantic Coastal Plain — iron mining 14. During the first half of the 1800s, geographic factors influenced the economy of New England by 1. encouraging the establishment of large plantations 2. promoting the growth of trade and manufacturing 3. increasing the region’s reliance on slave labor 4. supporting rice and indigo farming 6. Which United States foreign policy action resulted from the close geographic relationship between the United States and Latin America? 1. Monroe Doctrine 2. Truman Doctrine 3. Marshall Plan 4. Open Door policy 15.The Big Stick policy and Dollar Diplomacy were attempts to 1. increase United States power in Latin America 2. contain the spread of communism in eastern Europe 3. protect free trade on the Asian continent 4. strengthen political ties with western Europe 7. In the United States, regional differences in economic development are primarily due to 1. settlement patterns of immigrant groups 2. pressure from various religious groups 3. state and federal election laws 4. Geographic factors in various parts of the nation 16. A goal of President Theodore Roosevelt's Big Stick policy and President William Howard Taft's Dollar Diplomacy policy toward Latin America was to 1. join Western Hemisphere nations in a military alliance 2. protect American economic and political interests 3. encourage foreign nations to establish colonies 4. raise Latin America's standard of living 8. Because of fertile land and a long growing season, plantations in the thirteen colonies developed in 1. New England 2. the Middle Atlantic region 3. the South 4. the upper Mississippi River valley 9. The principle that the United States has the right to act as the "policeman of the Western Hemisphere" and intervene in the internal affairs of Latin American nations was established by the 1. Good Neighbor policy 2. Open Door policy 3. Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine 4. Marshall Plan 10. As a result of the establishment of the Monroe Doctrine (1823), the United States was able to 1. acquire parts of South America as land for settlement 2. expand its influence in the Western Hemisphere 3. increase its trade with Asia 4. form military alliances with European nations 17. The Dust Bowl experiences of the Oklahoma farmers during the Great Depression demonstrated the 1. effect of geography on people's lives 2. success of government farm subsidies 3. limitation of civil liberties during times of crisis 4. result of the Indian Removal Act 18. The Mississippi River system was an important economic resource during the first half of the 1800s because it was used to 1. irrigate desert lands 2. transport farm goods to market 3. move immigrants to the Northeast 4. produce hydroelectric power CONTINUE ON THE NEXT PAGE 19. Base your answer on the accompanying map and on your knowledge of social studies. Each letter on the map represents a specific geographic feature Which geographic feature most limited the westward movement of American colonists before 1750? 1. H 2. I 3. C 4. F 20. Base your answer on the accompanying map and on your knowledge of social studies. A conclusion supported by the information on the map is that slavery in the American colonies was 1. declining by the start of the Revolutionary War 2. concentrated in areas suitable for large plantations 3. becoming illegal in the northern colonies 4. growing fastest in the New England colonies 21. Base your answer on the accompanying map and on your knowledge of social studies. The states with the largest percentage of land used for agriculture are located in areas with 1. relatively flat terrain 2. the warmest year-round climate 3. easy access to the West Coast 4. ocean ports 22. Base your answer on the accompanying map and on your knowledge of social studies. Which geographic feature was used to establish the Proclamation Line of 1763? 1. Great Lakes 2. Rocky Mountains 3. Appalachian Mountains 4. Mississippi River Thematic Summary 2: The Supreme Court The Supreme Court is one of the three branches of the Federal Government. It is the highest court in the United States; its job is to settle legal disputes and interpret the law, when a ruling from a lower court (local, state, or district – group of states) is appealed (challenged). The Supreme Court is comprised (made) of 9 judges who rule on majority opinion. These 9 judges are appointed by the President with Senate approval, serve for life and can only be removed from office on bad behavior. During the early history of America, the Supreme Court heard few cases and had little power. When John Marshall became chief justice (the head judge of the Supreme Court) in 1801, he had an agenda and wanted to use the Supreme Court to achieve it; he wanted to increase the powers of the national/central government, wanted to limit the power of the states and promote business. In the case of Marbury v. Madison, the court said the Constitution gave the implied power (not specifically in the Constitution, but meant to be there and becomes precedent), of judicial review – that the Supreme Court has the power to rule if a city, state or national law or action is constitutional or unconstitutional. Marshall used this new power to carry out his agenda. In McCullough v. Maryland (1819) upheld the right of Congress to charter (create) a national bank and did not allow the states to tax the national government. In Gibbons v. Ogden (1824) the court gave the national government undisputed control over interstate commerce (businesses trading between two or more states). Many people disagreed (and still disagree today) with Marshall’s actions; stating that the Supreme Court is creating laws without going through the democratic process (legislating from the bench). Thomas Jefferson called the Supreme Court an “oligarchy of tyrants” (strict rule by a group of people with total power) The first President to challenge the power of the Supreme Court was President Andrew Jackson. In the case of Worcester v. Georgia (1832) the Cherokees sued in the Supreme Court saying that they cannot be removed by President Jackson. The Supreme Court sides with the Cherokees, but Andrew Jackson ignores the Supreme Court’s ruling and moves the Indians onto reservations anyway. Jackson famously stated, “Marshall made his ruling, now let him enforce it!” Over the course of our history, the Supreme Court has used the power of judicial review to rule laws both constitutional and unconstitutional and to even adjust laws to make them Constitutional. The Supreme Court has even made decisions in which it reversed (overturned) previous decisions it made. Overall, some rulings have benefited America, but some have not. Vocabulary Words 1) Supreme Court – Third branch of government and highest court in the United States. Responsible for interpreting the Constitution. 2) Judicial review – implied power (not specifically written in the Constitution, but becomes precedent) that gives the Supreme Court the power to rule laws and actions Constitutional or Unconstitutional 3) Marshall Court (1801-1832) – uses his decisions to strengthen federal government power over the states 3a) Marbury v. Madison (1803, Early Republic) – gives the Supreme Court the power of judicial review 3b) McCulloch v. Maryland(1812, Early Republic) -- supremacy of the federal law in taxation 3c) Gibbons v. Ogden (1812, Early Republic) -- supremacy of federal law in interstate commerce 3d) Worcester v. Georgia (1832, Age of Jacksonian Democracy) – Cherokees sue to stop their removal to reservations. Supreme Court sides with Cherokees, but President Jackson moves them anyway. 4) Dred Scott Decision (Scott v. Sanford) (1857, Pre-Civil War) -- slaves are property; slavery cannot be banned in U.S.; overturns Missouri Compromise 5) Plessy v. Ferguson (1896, Post-Reconstruction) -- separate but equal; legalizes segregation (forced separation of races) 6) Schenck v. U.S. (1919, WWI) -- clear and present danger -- limits 1st Amendment rights; limitation of rights during wartime 7) Scopes "Monkey" Trial (1925, Roaring 20’s) – not a Supreme Court case, but still important -- no evolution in Tennessee schools; example of religious fundamentalism dominating a society 8) Schecter Poultry v. U.S.; Butler v. U.S.; Carter v. Coal (1935-36, New Deal) -- Company -- Supreme Court rules parts of Franklin D. Roosevelt’s New Deal Unconstitutional (too much business regulation). This leads to FDR trying to “pack the court” with 6 additional judges and remove judges over 70 years old. 9) Korematsu v. U.S. (1944, WWII) - interment of Japanese Americans; limitation of rights during war 10) Brown v. Board of Education (1954, Start of Civil Right Era): separate but equal is illegal; segregation is illegal; overturns (reverses) Plessy v. Ferguson; starts the Civil Rights Movement 11) The Warren Court (1953-1969, Chief Justice Earl Warren, Civil Rights Era) – Under this court, Chief Justice Warren greatly increases the right of the accused in rulings of cases such as Miranda v. Arizona, Escobedo v. Illinois, Mapp v. Ohio, Gideon v. Wainwright 11a) Miranda v. Arizona (1966, Civil Rights Era) – Criminals must be read their 5th and 6th Amendment Rights. These are now nicknamed “Miranda Rights” because of this case. 11b) Escobedo v. Illinois (1964, Civil Rights Era) – criminal suspects have right to a lawyer (6th Amendment) 11c) Mapp v. Ohio (1961, Civil Rights Era) – protects against unreasonable searches and seizures (4th Amendment) 11d) Gideon v. Wainwright (1963, Civil Rights Era) – States must provide attorneys for criminal suspects (6th Amendment) and give all suspects due process (fair treatment – 14th Amendment) under the law 11e) Engele v. Vitale (1962, Civil Rights Era) – States cannot enforce prayer in school. 11f) Tinker v. Des Moines (1969, Vietnam, Civil Rights) - 1st Amendment rights are allowed in school as long as speech is not dangerous 12) New Jersey v. T.L.O (1985) – 4th Amendment rights are not absolute in school; students have less rights in school. 13) California v. Bakke (1978) -- affirmative action is legal but quotas are not 14) President Richard M. Nixon's Constitutional Issues 14a) The New York Times v. U.S. (1971, Vietnam) - Pentagon Papers (top secret files) are leaked and printed by New York Times and President Nixon tries to stop it; Supreme Court says 1st Amendment allows printing of pentagon papers 14b) Watergate Scandal (1972, Vietnam) -- Nixon allegedly has people sneak into Democratic HQ and steal documents. Entire administration is implicated. 14c) U.S. v. Nixon (1971, Vietnam) - Nixon tries to claim executive privilege to not allow evidence in, but Supreme Court says no one is above the law 14d) Nixon’s Resignation(1974, Vietnam) -- Nixon resigns instead of facing Impeachment Trial New President Gerald Ford -- gives Nixon a Presidential Pardon (Nixon is forgiven, doesn't face any trial) 15) Roe v. Wade (1973, Post-Vietnam)-- right to privacy for women for abortion; right to choose 16) Bush v. Gore (2000, Modern America) – Supreme Court prevents a continued recount in Florida, ending the election of 2000, finalizing that George W. Bush wins the Presidency Thematic Summary #3: Presidential Actions The Executive Branch, President of the United States was a debated branch during the Constitutional Convention. Many did not want a President to have too much power, but others recognized the need for a strong central government. The President has many powers including signing and vetoing (canceling laws), being the Commander-in-Chief and Chief Diplomat, and can create Executive Orders (although this is more part of the Unwritten Constitution) and creates foreign and domestic policy. However, the President’s powers are also checked by the Congress (who creates laws, can overturn an Presidential veto and can even impeach the President) and the Supreme Court (who can rule on the Constitutionality of the actions and laws). Presidents have each interpreted their powers and responsibilities differently. Presidents have also interpreted American domestic and foreign policy differently. Vocabulary Words 1) Executive Branch: The President as defined by Article II of the Constitution 2) Commander-in-Chief: Power of the President to control the armed forces and deploy them as necessary 3) Chief Diplomat: Power of the President to negotiate with other countries and leaders (although all treaties must be approved by Congress). 4) Veto: The power of a President to refuse to sign a bill into law. 5) Impeachment: The power of Congress to investigate and remove the President from office 6) Checks and Balances: each branch has powers which can limit the power of other branches 7) Domestic Policy: policies that affect America at home 8) Foreign Policy: policies that affect America’s relations with other countries 9) George Washington (1789-1797, Early Republic): First President of the United States. Hero of the American Revolution. 9a) Farewell Address (Foreign Policy): George Washington suggests foreign policy of neutrality and isolationism because the American nation is young. The effect is America is isolationist and many future American presidents model foreign policy after this. 9b) Creation of the Cabinet (Washington Precedent): Washington created a group of Presidential advisors to help him. This was part of the Unwritten Constitution (not listed in the Constitution) but has become precedent (first action used as future example) 9c) Putting Down Whiskey Rebellion (Domestic Policy): When farmers rioted over an excise (tax) on whiskey, Washington used his power as Commander-in-Chief to send the army to stop the rebellion. 10) John Adams (1797-1801, Early Republic): Alien and Sedition Acts (Domestic Policy)– Laws that limit freedom of speech and immigration Cause -- Democratic-Republicans (led by Jefferson) heavily criticize John Adams. Effect -- Americans hate the act and Adams loses the next election to Jefferson 11) Thomas Jefferson (1801-1809, Early Republic): 11a) Louisiana Purchase (Domestic Policy) —Jefferson buys the Louisiana territory from Napoleon for 25 million dollars Cause – Jefferson wants to buy New Orleans for 10 million dollars but is offered the entire Louisiana territory for 25 million dollars. Effect – Even though the President isn’t allowed to make purchases, Jefferson doesn’t follow Constitution and doubles size of U.S. and gives us control of Mississippi River 11b) Virginia and Kentucky Resolution (Domestic Policy) – In direct response to the passing of the Alien and Sedition Acts under Adams, Thomas Jefferson encouraged Virginians and residents of Kentucky to ignore the acts limiting freedom of speech, stating that the acts passed under Adams were a direct violation of a citizens First Amendment rights. When he becomes President he repeals (removes) them. 12) James Madison (1809-1817, Early Republic): Declaration of War Against England (Foreign Policy). England was violating American neutrality at sea, violating borders on land and encouraging Indians to attack us. The war is a tie, but America proves herself as a nation, grows militarily and economically and actually becomes friends and trading partners with England. 13) James Monroe (1817 – 1825, Early Republic, “Era of Good Feelings”): Monroe Doctrine (Foreign Policy) – Proclamation that says Europe cannot try to colonize or re-colonize Latin America Cause – Europe is trying to re- conquer Latin America and control trade in the area. Effect – United States gets involved in foreign policy and starts having control in the hemisphere. 14) Andrew Jackson (1829-1837, Expansion and Age of Jacksonian Democracy): 14a) Indian Removal Act (Domestic/Foreign Policy): Jackson orders the Cherokee Nation and other nations to be sent to reservations in Nebraska. Cause – White Americans want the land the Indians are on. Effect – Cherokee try to sue in Supreme Court (Worcester v. Georgia), the Supreme Court rules in favor of the Indians, but Jackson ignores them (John Marshall has made his ruling now let him enforce it!”). 800 Indians die in the “Trail of Tears,” when the act is enforced under President Martin Van Buren. 14b) Closing the Bank of the U.S. (Domestic Policy): Cause -- Jackson does not want to renew the charter on the Bank of the U.S. because he feels banks are corrupt and take advantage of farmers and working class men. Effect – the bank closes and state banks take advantage of situation which leads depression – Economic Panic of 1837. 14c) Nullification Crisis (Domestic Policy): North Carolina does not want to pay a tariff (tax) and threaten to nullify (cancel/not listen to Federal law). Jackson threatens to send soldiers and hang John C. Calhoun (his Vice President) if they don’t listen, but it is resolved with compromise. 15) James K. Polk – (1845-1849, American Expansion) – Polk was known as “Manifest Destiny’s President” because he devoted his foreign policy to extending America to the Pacific Ocean. He did this by Declaring War on Mexico (Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo gave America much of the modern Southwest) and buying Oregon (“54-40 or fight!”)from England. 16) Millard Fillmore, Franklin Pierce, James Buchanan (1849-1861, Sectionalism) – known as the “Do Nothing Presidents” because they failed to address the issues dealing with slavery. Under the guidance of Pierce, the Kansas-Nebraska Act is passed by Congress which leads to the initial battles of the Civil War. 17) Abraham Lincoln (1861-1865, American Civil War) 17a) Emancipation Proclamation (Domestic Policy) – Frees the slaves only in the rebelling states. Path to the 13th Amendment after the Civil War. 17b) Suspends Habeus Corpus (Domestic Policy) – Lincoln suspends the right to a speedy trial during the Civil War to run the war more effectively (liberty v. national security) 17c) Handling the Draft (Domestic Policy) – Lincoln approves the Draft Act of Congress and sends soldiers into New York City (NYC Draft Riots) to stop the draft riots and restore order. 18) Andrew Johnson (1865-1869, Reconstruction) – Andrew Johnson tried to use the power of veto to limit the Radical Republicans efforts of passing Civil Rights Amendments (domestic policy), laws and administrations. He was brought to impeachment trial where Congress fell one vote short. 19) Ulysses S. Grant (1869-1877, Reconstruction) – enforces the Reconstruction Acts by creating military districts in the South to protect the rights of African Americans outlined in the 13th, 14th, 15th Amendments. 20) William McKinley (1897-1901, American Imperialism) – 20a) Spanish-American War (foreign policy) -- McKinley asked for a declaration of war against Spain after the Sinking of the USS Maine. The war helped to expand the American empire in the Atlantic and Pacific. McKinley annexes the Philippines instead of giving them their freedom. 20b) Open Door Policy (foreign policy) – America joined the European powers in dividing China into economic spheres of influence. 21) Theodore Roosevelt (1901-1909, American Imperialism and Progressive Era) – 21a) “Trust Buster” (domestic policy) – Roosevelt helps pass the Sherman Anti-Trust Act and enforce antitrust laws on monopolies. Monopolies are taking advantage of workers and small business Effect – Roosevelt creates Federal organizations to bring monopolies to court and have them broken up. 21b) “Square Deal” (domestic policy) – series of laws passed to regulate business Cause – Industries are taking advantage of workers and producing unsanitary meat Effect – Meat Inspection Act and Pure Food and Drug Act are passed to monitor meat packing industries 21c) Roosevelt Corollary to Monroe Doctrine and Big Stick Policy (foreign policy) – New foreign policy that states United States will protect interests in Latin America with force Cause – United States wants to expand into Latin America to gain resources and cheap labor and reinforce Monroe Doctrine to keep Europe out. Effect – United States becomes a policeman of Latin America and sends soldiers in to control several countries. 21d) Conservationism (domestic policy)– Conserving (preserving) the American landscape and creating national parks (Yellow Stone National Park). 21e) Genteleman’s Agreement with Japan – Roosevelt agreed to tell California to stop discriminating against the Japanese in return for Japan limiting immigration to America. 22) William Howard Taft (1909-1913, American Imperialism, Progressive Era) -- Dollar Diplomacy (foreign policy) – using economic pressure to control Latin American countries. 23) Woodrow Wilson (1913-1921, Progressive Era and World War I) – 23a) Entry into WWI (foreign policy) – After Germany’s violation of freedom of the seas, Wilson asked Congress to enter into WWI and make the world “safe for democracy.” 23b) 14 Points (foreign policy) – At the end of WWI, Wilson created 14 points of peace to try to end world conflict and create national determination – an end to colonies. The only part of the 14 points accepted in the Treaty of Versailles was a League of Nations (world collective security organization), but this was rejected by the Senate in favor of being isolationist. 23c) New Freedom Programs (domestic policy): Wilson’s New Nationalism programs were created to continue the Progressive Era Reforms, such as Clayton Act (anti-Trust) and Keating-Owen (ending Child Labor) 24) Warren Harding, Calvin Coolidge, Herbert Hoover (1921-1933) – Republican Presidents of the 1920’s who supported “Return to Normalcy” (foreign policy) of isolationism and “the business of America is business” (domestic policies) – laissez-faire policies to leave the government out of business and “trickle down economics” – helping businesses with tax breaks. 25) Franklin Delano Roosevelt (1933-1945, Great Depression and World War II) – 25a) New Deal (domestic policy) – series of acts, government agencies and government spending to stimulate the economy. Cause – Great Depression leads to massive unemployment. Effect – Some acts work, helping to stabilize economy and some acts do not work and are ruled unconstitutional by the Supreme Court because of too much interference. 25b) Entry into WWII (foreign policy) – leading up to the attacks on Pearl Harbor, Roosevelt tried to maintain neutrality (Neutrality Acts), but slowly started to help the allies (Cash and Carry and Lend-Lease). After Pearl Harbor, America went to war against Germany and Japan. 25c) Good Neighbor Policy (foreign policy) – the policy of treating Latin American nations better with the hopes of better relations and more trade. 26) Harry Truman (1945-1953, Early Cold War) – 26a) Dropping the Atomic Bomb (foreign policy) – As commander-in-chief Truman made the choice to end World War II quickly, to save American lives and to stop Soviet invasion of Japan by dropping the atomic bomb on Hiroshima and Nagasaki. 26b) Truman Doctrine (foreign policy) – Truman states that United States will “contain” Communism anywhere it tries to spread. Cause – Soviet Union is trying to expand communism. Effect—Increases Cold War tension, commits U.S. to aid other countries threatened by Communism. 26c) Entry into Korean War (foreign policy) – Truman had the United States lead United Nations forces to stop North Korea trying to invade South Korea. 26d) Desegregation of the Armed Forces (domestic policy) – Truman used an executive order to end segregation of the armed forces – integrating all army units. Part of the Fair Deal (which was an extension of the New Deal). 27) Dwight D. Eisenhower (1953-1961, Early Cold War, Civil Rights) – 27a) Troops into Little Rock (domestic policy) – Eisenhower sends troops to enforce Brown v. Board of Education. Cause – Governor Wallace refuses to allow desegregation of schools after court decision. Effect – Eisenhower enforces court decision with soldiers 27b) Interstate Highway Act (domestic policy) – Eisenhower approves the building of the interstate highway system. Effect – this leads to increases in the use of the automobile and moving to and growth of the suburbs. 27c) Domino Theory (foreign policy) – Eisenhower believes that if one country in South East Asia falls to Communism that the neighboring countries will as well. This starts our involvement in Vietnam. 27d) Eisenhower Doctrine (foreign policy) – Policy that if Middle Eastern nations asked for American financial or military aid to stop Communism, we would send it. 28) John F. Kennedy (1961-1963, Cold War Heats Up, Civil Rights) – 28a) New Frontier Program (domestic policy) – Program to help Civil Rights, Education and escalate the Space Race. 28b) Troops to Mississippi University (domestic policy) – Kennedy sent soldiers to Mississippi University to enforce the ruling in Brown v. Board of Education. 28c) Cuban Missile Crisis (foreign policy) – Kennedy negotiated a secret truce with Russian Secretary General Nikita Kruschev to remove missiles from Cuba in exchange for removal of missiles in Italy and Turkey. 28d) Peace Corps (foreign policy) – Kennedy made this volunteer organization to go overseas and help people in need. 29) Lyndon Johnson (1963-1969, Cold War Heats Up, Civil Rights) – 29a) Great Society Program (domestic policy) – Johnson pushes for Civil Rights Legislation. Cause – Many states are still resistant to equal opportunity for African Americans Effect – Programs such as Voting Rights Act, Affirmative Action Programs and Civil Rights Act help to create opportunities and end poll taxes for African Americans. 29b) Entry into Vietnam War (foreign policy) – Johnson uses the Gulf of Tonkin incident to send American soldiers to help South Vietnam fight off an invading Communist North Vietnam. 30) Richard M. Nixon (1969-1974, Cold War Heats Up) – 30a) Vietnamization (foreign policy) – With the Vietnam War becoming very unpopular, Nixon tries to have “peace with honor” as America slowly withdraws and turns the war over to the South Vietnamese and ends the draft at home. 30b) Détente (foreign policy) – Nixon and Russia sign the Strategic Arms Limitation Treaty to reduce nuclear arsenal and tensions. 30c) Opening of Relations with China (foreign policy) – Nixon is the first President since China became Communist in 1949 to start diplomatic relations with them and even visits China backed by the success of “Ping Pong Diplomacy” (American vs. Chinese Ping Pong Teams). 31) Jimmy Carter (1977-1981, Cold War Heats Up) 31a) Camp David Accords (foreign policy) – Carter’s greatest accomplishment was having Egypt and Israel sign a peace treaty at Camp David. 31b) S.A.L.T. II (foreign policy) – Carter continued Nixon’s policy of détente with Russia. 32) Ronald Reagan (1981-1989, End of Cold War) 32a) Supply-Side Economics (domestic policy) – Also known as Trickle-Down or Reaganomics, this economic policy focused on helping businesses and giving tax breaks to increase production and capital and lower prices. This helped lead to a booming economy in the ‘80’s. 32b) Reagan Doctrine (foreign policy) – Reagan’s greatest achievement is bringing the Cold War to an end. Reagan used increased military spending (although this led to a deficit with the tax cuts), supporting enemies of the Soviets, “rolling back” Communism and diplomacy with Soviet Secretary General Mikhail Gorbachev. The Cold War officially comes to end under George H.W. Bush when the Berlin Wall comes down and the Soviet Union is dismantled. 33) George H.W. Bush (1989-1993, End of Cold War, Globalization) 33a) Entry into Persian Gulf War (foreign policy) -- America leads United Nations forces to stop Iraq’s invasion of Kuwait – to free the Kuwaitis and to protect a large oil supply from Saddam Hussein. 34) William (Bill) Jefferson Clinton (1993-2001, Globalization) 34 a) NAFTA (foreign policy) – the North Atlantic Free Trade Agreement allows for free trade (no borders or taxes) between Mexico, America, Canada). This allows us to get products cheaper but also hurts America’s jobs. 34b) Bosnia (foreign policy) – America leads United Nations soldiers to stop ethnic cleansing in Bosnia. 35) George W. Bush (2001-2009, Globalization) 35a) Iraq-Afghan Wars (foreign policy) – In response to the terrorist attacks of 9/11/01, Bush sends soldiers to attack Afghanistan and overthrow the Taliban, who sheltered and gave aid to Al-Qaeda. In part of a larger global war on terror, in 2003, Bush sent American soldiers to liberate Iraq from Saddam Hussein under the basis that he was creating weapons of mass destruction. 35b) Patriot Act (domestic policy) -- this act limits rights to more effectively search, detain and question terrorists. The Department of Homeland security was also coordinated to help American security. 36) Barack Obama (2009 – Present, Globalization) 36a) Stimulus Package (domestic policy)– 787 billion dollar spending to help fix the American economy and to bail out the car companies. Effects – slight improvement but lots of debt. 36b) ObamaCare (domestic policy) -- nick name for the Affordable Health Care Act -- President Obama’s domestic policy to make it mandatory for all Americans to have health care. 36c) Support for Arab Spring (foreign policy) – President Obama lent limited military support to Arab revolutions in Spring 2011. 37) Presidential Scandals: 37a) Teapot Dome – A bribery scandal for oil fields in Wyoming. Harding was cleared of any wrong doing but his administration became very unpopular. 37b) Court Packing – In response to the Supreme Court ruling several New Deal programs Unconstitutional, FDR tried to “pack the court” – remove older judges and add 6 new ones. This was not allowed by Congress. 37c) Watergate – The Nixon administration was implicated (accused) of breaking into the democratic convention at the Watergate hotel and then covering it up. Nixon resigned instead to avoid impeachment and President Gerald Ford gave him a presidential pardon. People begin to lose faith in the government. 37d) Iran Contra – The Reagan administration was accused of selling weapons to Iran and then using the money to fund anti-Communist rebels (Contras) in Nicaragua. Reagan was cleared from any wrong doing. 37e) Monika Lewinsky – President Clinton was caught having an extra marital affair in his office, which he lied about under oath. He went to impeachment trial but was acquitted. 37f) Benghazi Cover-up – After the attacks on American embassies in 2012, the Obama administration is under investigation for covering up information on the causes and failures to react and protect our embassies. American History Regents Prep Thematic Essay Topics that Appear on the American History Regents *REMEMBER EVERYTHING YOU WRITE ABOUT HAS TO DEAL WITH THE U.S.!* ESSAY TOPIC: SUPREME COURT DECISIONS SOME COURT CASES YOU CAN WRITE ABOUT: 1. Schenck v. United States (1919): Charles Schenck had mailed pamphlets encouraging people not to serve in WWI. He wanted Americans to resist the draft. Schenk was arrested because the government said he was encouraging people to break the law and resist the draft. This would hurt the war efforts. Schenck was arrested and went to Supreme Court. He argued that he was allowed to protest and speak out against the draft because of his First Amendment Rights. He said he was denied his freedom of speech. The Supreme Court ruled that Charles Schenck did not have the First Amendment Right of freedom of speech against the draft during WWI. This is because if Schenck spoke out against the war, it would cause a “clear and present danger”. 2. Koresmatsu v. United States (1944): Fred Korematsu, a Japanese American did not want to go to the internment camp. Internment camps were set up by the U.S. government. FDR signed an executive order saying that Japanese Americans must go to the camps during WWII. Korematsu refused to go and was arrested. This went to Supreme Court. Korematsu argued that he was a U.S. born citizen and he should have the same rights as other American citizens. The Court ruled that civil liberties (people’s rights/freedom) can be limited in times of war. He was a “clear and present danger”. Korematsu had to go to the internment camp. 3. Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka (1954): Oliver Brown of Topeka, Kansas, decided to challenge the Kansas law. He asked the school board to let his daughter, Linda, attend a nearby white school rather than a distant black school to which she had been assigned. When board members refused, Brown filed a suit against the school board with the help of the NAACP. The case reached the Supreme Court arguing that they wanted schools to be integrated (blacks and whites ARE not separated, but together) not segregated. The Court ruled in favor of integration, stating that segregation created feelings of inferiority. This overturned the Plessey v. Ferguson case of 1896, which said segregation was allowed in the ruling that separate is equal. 4. United States v. Nixon (1974): President Richard Nixon was accused of taking part in the Watergate scandal. Nixon officials broke into Democratic Party office at the hotel. They took information from files and bugged the phones to find out what the democrats were planning for their campaign. Nixon lied and pretended he did not know about the break in. Officials in the White House began to admit that they knew about the break in and that Nixon had taped conversations about the break in. Nixon was investigated and was told to turn over the tapes, but did not want to. This went to the Supreme Court. They told Nixon he had to turn over the tapes and when he did they noticed that one a piece of the tape was erased. Congress wanted to impeach Nixon because he tried to cover up the scandal. In 1974, the tapes proved Nixon was aware of the break in at the Watergate Hotel and broke the law. Before Nixon could get impeached, he resigned, meaning he gave up his job as president. This showed that no person, even the president is above the law. 5. Miranda v. Arizona (1966): Ernesto Miranda was a poor Mexican immigrant living in Arizona. Miranda was arrested for rape and kidnapping when a victim identified him in a police lineup. He was questioned for two hours while in police custody. The police officers questioning him did not tell him of his right against self-incrimination or his right to the assistance of an attorney. As a result of the interrogation, he confessed, in writing, to the crime. Miranda’s attorney argued that his confession should have been kept out of trial because he was not told his rights and did not have an attorney been present when questioned. The police officers admitted that they had not given Miranda any explanation of his rights. The Supreme Court ruled that Miranda was denied due process of the law (14th Amendment). Miranda must be told “You have the right to remain silent and that anything said can and will be used against you in court. They also needed to tell him of the consequence if he did speak and that he has the right to meet with a lawyer and have the lawyer with him when questioned. ESSAY TOPIC: INDIVIDUALS, GROUPS, INSTITUTIONS—WRITING AND REFORM SOME TOPICS YOU CAN WRITE ABOUT: 1. Uncle Tom’s Cabin by Harriet Beecher Stowe (1852): Stowe wrote the novel to show the evils of slavery and unfairness of the Fugitive Slave Act. Stowe told the story of Uncle Tom, an enslaved African American noted for his kindness and faithfulness. Tom’s world is shattered when is bought by a brutal Simon Legree. When Tom refuses to reveal the whereabouts of two runaways, Leegree whips him to death. Uncle Tom’s Cabin was popular among northern readers. The printing sold out in just two days! Although Uncle Tom’s Cabin was popular in the North, southerners did not like the book. They claimed that it did not give a true picture of slave life. Despite the objections, Uncle Tom’s Cabin helped to change the way northerners felt about slavery. No longer could they ignore slavery as a political problem for Congress to settle. 2. How the Other Half Lives by Jacob Riis (1890): This was written in the Progressive Era. Riis was a muckraker who wrote vivid articles and books exposing the evils of society and demanded social and economic reform. Riis wrote about tenement life and the horrible conditions many immigrants lived in. Some had no windows, no pipes for water or sewage, no heat. Disease (tuberculosis, lung disease) spread quickly. Fires spread quickly. Often, 10 people shares a single room. As a result, fire escapes were built, sewage systems were implement, etc. 3. The Jungle by Upton Sinclair (1906): This book was fiction, but it was based on fact. It revealed horrific details about the meatpacking industry. Sinclair told how the packers used meat from sick animals. He described how rats often got ground up in the meat, which was then dyed to make it seem healthy. This took place during the Progressive Era when people wanted to change/reform society. They wanted conditions improved. As a result of this book, President Theodore Roosevelt created the Meat Inspection Act, that inspected all meats, and the Pure Food and Drug Act which did not allow the sale of infected or falsely labeled goods on national market. ESSAY TOPIC: CONSTITUTIONAL PRINCIPALS—INDIVIDUAL RIGHTS SOME TOPICS YOU CAN WRITE ABOUT: 1. Native Americans: In 1830, President Andrew Jackson pushed a new piece of legislation called the “Indian Removal Act.” The removal was supposed to be voluntary and peaceful, but when some Cherokee nations resisted, Jackson forced them to leave. Between 1831 and 1833, around 15,000 Native Americans were forced out west. At least 4,000 of them died along the way. This was called the Trail of Tears. In the case of Worcester v. Georgia the Supreme Court said that this act was illegal and the Native Americans were allowed to stay in Georgia even though the people of Georgia wanted them gone. Jackson ignored the Court and still forced the Natives to leave. 2. African Americans: After the Civil War, African Americans were given the right to vote, slavery was banned, and given citizenship. However, they were denied the right to vote because Southern states created poll tax, which charge a tax to vote, Grandfather Clause, which stated you can only vote if your grandfather was able to vote before 1865. Before 1865, most blacks were slaves. They also created literacy tests that blacks had to pass to vote. Jim Crow laws allowed segregation. The Supreme Court Case, Plessy v. Ferguson, ruled that “separate if equal”, which allowed segregation. Blacks had to ride in separate cars, different schools, even drink at different water fountains. In the 1960’s the Civil Rights Movement fought for equality for blacks. The Brown v. Board of Ed case allowed integration in schools. No longer could blacks and whites be separated. JFK made public transportation systems integrated. The Civil Rights Act of 1965 was signed by LBJ. The 24 th Amendment was passed that did not allow poll taxes. The Voting Rights Act of 1965 also banned literacy tests, grandfather clause, and other things that denied people the right to vote. ESSAY TOPIC: CHANGE (OTHER THAN PRESIDENTS) SOME TOPICS YOU CAN WRITE ABOUT: 1. Martin Luther King Jr.—Civil Rights: MLK was a Civil Rights activist that encouraged civil disobedience. This means that people should protest peacefully and not act violent. MLK was part of the Montgomery Bus boycott with the NAACP and Rosa Parks. They did not ride the buses in Montgomery, Alabama for almost a year. They car pooled or walked. They wanted integration on the buses not segregation. MLK also had his March on Washington where he said his “I Have a Dream” speech calling for racial harmony. 2. Margaret Sanger—reproductive rights (birth control): legalizing birth control and making it universally available for women. The ‘Comstock Act’ existed when she was a young girl—it made it illegal to learn or talk about birth control. Margaret Sanger believed that the only way to change the law as to break it. Starting in the 1910’s, Sanger actively challenged federal and state Comstock laws to bring birth control information and contraceptive devices to women. Her ambition was to find the perfect contraceptive to relieve women from the horrible strain of repeated, unwanted pregnancies. Margaret Sanger was tired of waiting for science to come up with a pill as a contraceptive. She looked for someone who could make a pill that was as easy as taking an aspirin. She wanted the pill to be cheap and sage for females. Sanger finally accomplished her lifelong goal of a pill and later to see that the Supreme Court case Griswold v. Connecticut, made contraception legal. 3. **YOU CAN ALSO TALK ABOUT JACOB RIIS, UPTON SINCLAIR AS MENTIONED IN THE ESSAY TOPIC INDIVIDUALS ABOVE.** ESSAY TOPIC: MOVEMENTS OF PEOPLE—MIGRATION SOME TOPICS YOU CAN WRITE ABOUT: 1. European immigration (1880-1910): Both push and pull factors led to European immigrants coming to America. People who disagreed with the governments in power fled cruelty and civil wars. They came from England, Germany, and Ireland. They included the Scots-Irish and Puritans. In many European countries, there was an official state religion. If you did not belong to it, you were mistreated. Groups that were persecuted included: English Puritans, Pilgrims, Catholics, and Quakers. From Germany came Mennonites, Baptists, and Jews. From Catholic France came Protestants. Jews came from Spain and Portugal. Catholics and nonLutherans came from Scandinavian countries. The United States provided freedom of religion. Overall economic conditions, this had been the major reason for immigration. Many fled famines and semi-feudal systems especially Ireland. Land was scarce and factory conditions were poor. It was very hard to make a living. The United States provided new job opportunities for immigrants and a higher standard of living. Most European countries did not give people the opportunities to move up. They were stuck in their social status. The United States provided social advancement. Many arrived through Ellis Island where they were inspected. The impact of their migration resulted in tenement living. Most were poor and business men took advantage of hiring poor immigrants to work for cheap. They were not paid well in factories and worked long hours. Other immigrants grew wealthy and created large businesses. Immigrants also fought for better working conditions, particularly in the Progressive Era. They were successful in the 1900s at getting higher wages and short work hours. Immigrants contributed greatly to the growth of America. They built bridges and other architecture that we still use today. 2. Suburbanization (1950s-1960s): People began to buy homes in the suburbs, communities outside the cities. Builder, William Levitt, began his first big project in 1947 on Long Island, where he put up 17,000 new suburban homes. He called this project Levittown. In these areas, not only were the houses the same, but people were expected to look, act, and follow the same rules, which is known as conformity—Women were expected to go back to tradition roles of housewives and more men became white-collar workers, meaning that more had jobs as doctors, lawyers, managers, etc. rather than working in factories. African Americans were not allowed to own or rent in Levittown because he feared that if he sold to blacks, whites would not buy. Shopping centers with modern department stores sprang up near the suburban housing developments. No longer did consumers have to travel to the city to buy what they wanted. As a result, cities began to decline. During the 1950s, cars became more important to daily life. People living in the suburbs usually needed a car to drive to work. By 1960, 9 out of 10 families living in the suburbs owned a car. Because there were more cars, the federal government built thousands of miles of highways. In 1956, Congress passed the Federal-Aid Highway Act. This called for a network of high-speed roads linking the nation. It set aside $41 billion to build 40,000 miles of highway. The new highway system boosted the economy. Americans could travel more easily for business or pleasure (only if they could afford a car). As a result, a new roadside culture of motels and fast-food restaurants came about. However, many Americans were stuck in traffic and the environment was affected by gas emissions. ESSAY TOPIC: PRESIDENTIAL ACTIONS SOME TOPICS YOU CAN WRITE ABOUT: 1. Lyndon B. Johnson-Civil Rights Act 1964: During the 1950s and 1960s, African Americans fought for their civil rights and equality. Segregation still took place in the South due to the Jim Crow Laws. Blacks were separated from whites in public places, like bathrooms, lunch counters, restaurants, buses, trains, and other public facilities. African Americans were also denied voting rights due to the Grandfather Clause, poll taxes, and literacy tests. Blacks were also denied employment opportunities based on their race. African Americans, such as MLK, Malcolm X, NAACP, and other activists began to protest for equality. Some methods were civil disobedient methods that were peacefully done, such as boycotts, speeches, and sit-ins. Other acted more violently. LBJ finally signed the Civil Rights Act 1964, which stated that it is a crime to discriminate based on race in employment and voting. It also stated that public facilities must be integrated. This impacted society because now blacks and whites were integrated, they were given their 15th Amendment right to vote, and they could not hire someone based on their race. 2. George Washington’s Proclamation of Neutrality: George Washington was the first president of the U.S. The U.S. was just starting to create its own government, build up a military, and grow economically. George Washington stated in his Farwell Address that the U.S. should stay neutral. He said that the U.S. should not be entangled in foreign alliances. This is because the U.S. was a new country that was starting to grow and develop. He believed having alliances would lead to wars and that it was better to observe good faith and justice towards all nations. Peace and harmony were important because friendly ties are going to cause problems. Washington encouraged the U.S. to only have trade relationships to help the U.S. grow economically through business, but leave political connections out of foreign relationships. Staying neutral has prevented the U.S. from being part of world problems. However, many presidents have ignored this advice and drag the U.S. into World Wars, which weakened our relationships with some countries and created enemies. 3. President Truman’s decision to drop the Atomic Bomb: WWII ended in Europe when Nazi Germany surrendered. However, the U.S. was still at war with Japan, who continued to fight. AS a result, to end the war quickly and save soldier’s lives, Truman decided to drop the Atomic Bomb on the Japanese cites of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. He justified this by saying millions of soldiers lives were being lost and war. The results of the Atomic bomb were terrible for Japan. Although it caused the Japanese to surrender and the U.S. to win the war and economically practical because the U.S. would save money on aiding the war to continue on, Japan was destroyed. It is estimated that almost 200,000 Japanese civilians, who were innocent, died instantly in the bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. Over 100,000 Japanese died from radiation exposure over the coming years. Other effects were hair loss, nausea (vomiting), bleeding from the mouth, gums, and throat, weakened immune systems, internal bleeding, radiation burns, and/or killed or permanently damaged fetuses in the womb. An atomic bomb has not been dropped since. ESSAY TOPIC: CHANGE (TIME PERIODS) SOME TOPICS YOU CAN WRITE ABOUT: 1. Roaring 20’s (1920s): The 1920s was a period of change and prosperity for the U.S. The19th Amendment to the United States Constitution became law, and women could finally vote in elections, including in the Presidential election. Young women were beginning to challenge the traditional ways. They wanted more freedom and rights. They wanted to be allowed to be educated just like men. They wanted to go out and be more independent. They wanted to go on dates that were not chaperoned by their parents. These women were known as flappers. They smoke, drank, wore short skirts, and cut their hair short. Also this was a time when African Americans began to also demand more rights and to explore their culture. They did not want to be held down and oppressed any longer. Rather, they began to look at their culture and celebrate their talents. They began to write about their experiences as African Americans. African Americans began to write, sing, dance and develop new styles of music that expressed and celebrated what it were like to be African American, such as Billie Holiday, Langston Hughes, and Marcus Garvey. This time period was called the Harlem Renaissance. The 1920’s was also a period of great violence. In the year 1920 the U.S. government had made it illegal to drink or sell any alcoholic beverage. This was called Prohibition. Many people began to make and sell alcohol illegally. Gangs and the Mafia (many of whom were Irish and Italian) began to sell alcohol – making them very rich. Small gangs became organized and organized criminals grew out of control. As a part of organized crime, gang members would even get local politicians and police officers to help them out – corruption was everywhere. Al Capone was the most famous mobster. Other people opened up speakeasies which were secret places that sold alcohol. Discrimination and intolerance were also big problems during the 1920’s. After WWI, the United States isolated themselves from the rest of the world. This made it easy for Americans to “hate” all foreigners (or anyone who was not a white protestant.) The KKK was gaining membership, and for many white Americans, there was a growing belief that anyone who looked and thought differently or who did not believe in Christianity was a “bad” person. There was a great amount of intolerance towards people who believed in Communism or evolution. Events like Scopes Monkey Trial and Sacco Vanzetti are just a few examples. 2. Gilded Age: Natural resources were one of the main causes of industrialization, such as coal, iron, lead and copper. Factories used these resources to run machines and make goods. Railroads, airplanes, automobiles, and canals allowed cities to grow. In the 1830’s, railroads developed quickly. They moved people, goods, and resources. The transcontinental railroad (1869) stretched across the continent from the east to the west coast, which made goods available in more places for more money. The Erie Canal was the nation’s first transportation system. It is located in New York that runs about 363 miles from Albany, New York, on the Hudson River to Buffalo, New York, at Lake Erie, completing a navigable water route from the Atlantic Ocean to the Great Lakes. New products and machines were created in the 1800s. New machines helped make products faster than people making them by hand. Other inventions included the light bulb, phonograph, and motion picture camera made by Thomas Edison, the telegraph by Alexander Graham Bell who made it easier for people to communicate over miles, the typewriter by Christopher Sholes, and the camera by George Eastman. In the 1800s, immigrants came to the United States and worked for low pay in factories. There was a rapid growth of city population. Cities attracted industry and people migrated to cities for jobs. Major cities included New York, San Francisco, and Chicago. One of the most popular inventions that were created during the Industrial Revolution was the automobile. Henry Ford, an American manufacturer, made the automobile available to millions. Ford perfected a system to mass-produce cars and make them available at a lower price. To speed construction and lower costs, Ford introduced the moving assembly line in 1913. With this method of production, workers stayed in one place as produced edged along a moving belt. At Ford’s auto plant, one group of workers would bolt seats onto a passing car frame; the next would add the roof, and so on. The assembly line greatly reduced the time needed to build a car. Ford’s assembly line allowed mass production of car. Mass production means making large quantities of a product quickly and cheaply. Other industries soon adopted the method. Before the Civil War, most factories were small. A boss knew every worker in the shop. As giant industries grew, close relationships between owners and workers ended. American industry attracted millions of new workers. Most were immigrants or native-born whites. Others were African Americans who left the southern farms for northern factories. Women and children also worked in the factories, especially in the textile mills of New England, tobacco factories of the South, garment sweatshops of New York, and coal mines. The emphasis on mass production also changed the way workers felt about their jobs. Before the growth of factories, skilled workers, or artisans, were proud of the goods they made. The factory owner; however, was more interested in how much could be produced than in how well it was made. Workers could not be creative. Furthermore, unlike artisans, who could have owned businesses, the factory worker was not likely to rise to a management position. To reduce costs, most manufacturers kept wages low. Workers put in 60 to 70 work weeks in unventilated (airless) factories—cold in the winter and hot in summer. Accidents from unsafe machinery were common and blamed on the worker. To persuade big businesses to better conditions, workers came together to create large labor unions. The purpose of a labor union was for workers to try and improve wages and working conditions. As industry grew, owners demanded more of their workers. Management and workers grew further apart. Employees joined together to gain recognition and better working conditions. They created unions. Workers demanded collective bargaining. This meant that workers would be able to form a union and management would able to bargain (make a deal) for their demands. They would speak and act as one united group, instead of acting individually. In the late 1800s, Union workers stages thousands of strikes during the late 1800s. A strike is a refusal to work until workers receive and agreement with their employees. Strikes broke out all around the United States in many industries. Two on the most notorious strikes were the Homestead Strike and Pullman Strike. Company owners did not like the unions because they believed that it threatened their power. They believed that it was their right to be wealthy and no one should challenge their authority. Unions helped workers find their voice and began to demand change. Workers would join unions and the union leaders would organize and teach the workers to fight against the factory owners. Unions finally accomplished some goals and laws emerged such as the Sherman Anti-trust Act, which encouraged business competition and broke up large trusts that were bad. Child labor laws also were another accomplishment, which did not allow young children to work; rather they had to go to school. Workers also worked shorter hours and less days a week. 3. The New Deal Era: When Franklin Delano Roosevelt became president in 1933, nearly all of the institutions that kept the American economy working were broken. Banks, farms, factories, and trade had all failed. The United States was in the middle of the Great Depression and the job of Roosevelt was to get the country out of this economic crisis. Roosevelt’s biggest task was to restart the American economy and restore faith back in the economic system. Not only did Roosevelt need to fix the way government operated, but he also needed to restore the people’s confidence. It was now believed that the federal government’s responsibility was to look after the nation’s well-being. His plan was called the New Deal and had three parts; to provide relief to the people of the United States, to help some of the business recover and get better after the Great Depression and to reform or change parts of the government in order to protect the people of the United States. FDR created social and economic programs. Some were Civilian Conservation Corp (CCC), which provided work to over 2.5 million young men doing nature conservation between1933-1941, Social Security Act (1935), which provides for old age insurance, unemployment insurance, also helped the infirm (sick), elderly, and those with disabilities. Funds were provided though a tax on employers and employees, and Federal Housing Administration (FHA), which created to guarantee mortgages (loans given by bank to people who have to pay it back plus interest) at a 10% interest rate for 20 or 30 years. They made sure that housing was affordable for people and also provide funds to build low-income housing. ESSAY TOPIC: CONSTITUTIONAL AMENDMENTS SOME TOPICS YOU CAN WRITE ABOUT: 1. 13th Amendment—Abolition of slavery: Before 1865, African Americans were slaves in the South. In earlier years, the North had gotten rid of slavery. Tensions grew between the North and South. Sectional differences, such as the Dred Scott Decision, KansasNebraska Act, which allowed popular sovereignty that allowed people to vote on slavery angered Northerners who said the Missouri Compromise said slavery was not allowed above the line, Fugitive Slave Law, which required northerners who were against slavery to return slaves that ran away to the North, and Uncle Tom’s Cabin, which addressed the harsh conditions slaves lived under in the South, caused further divide. The election of 1860, that made Lincoln president angered southerners, who seceded from the Union. By 1861, the north and south fought in the Civil War. The South lost and became part of the Union in 1865. Under Congressional Reconstruction, new amendments were passed, one being the 13 th Amendment, which did not allow slavery anymore. As a result, the south was affected because slaves were their labor on plantations for many years. Now African Americans were free. This resulted in hostility in the South and the emergence of the KKK, Jim Crow Laws, and other hostile and restrictions. 2. 18th Amendment—Prohibition: By 1919, alcohol was illegal in the U.S. Alcohol abuse was serious problem. Prohibition was intended to improve, even make better, the lives of all Americans, to protect individuals, families, and society at large from the upsetting effects of alcohol abuse. Many women reformers were concerned about alcohol. Due to alcohol consumption, husbands were beating their wives and abusing their children. Even industrialists (big business men), such as Henry Ford, were concerned about the impact of drinking on labor productivity (making goods). Those who wanted to ban alcohol argued that outlawing drinking would eliminate corruption in government and help Americanize immigrants. Many Americans hoped the ban on liquor would improve American life. In fact, the ban did have some positive effects. Alcoholism declined during Prohibition; however in the end, it did not work. After a while, more Americans began to think that Prohibition was a mistake. The ban reduced drinking, but never stopped it and people were disrespecting the law, such as buying liquor at speakeasies (underground bars). By the end of the decade, Americans were calling for a repeal, or cancellation, of Prohibition. In 1933, the states ratified the 21 st Amendment, which repealed the 18th Amendment. 3. 19th Amendment—Women’s Suffrage (right to vote): In the early 1800s, changing social conditions and the idea of equality led to the beginning of the woman suffrage movement. By then, more women were receiving education. Women also began to participate in reform movements and become more interested in politics. Women and men began to question why women were not also allowed to vote. Supporters of this were called suffragist. Women's suffrage means the right of women to vote. The women's suffrage movement was the struggle to gain the same right to vote as men. This started in 1848 at the Seneca Falls Convention where women published the Declaration of Sentiments, which demanded equality for women. Fifty years later, their granddaughters continued the fight. Women picketed in front of the White House, got arrested, and went on hunger strikes. Finally, on January 9, 1918, Wilson announced his support for suffrage. The 19th amendment was passed allowing all women the right to vote – this became the law in 1919. ESSAY TOPIC: DOMESTIC CONTROVERSIAL ISSUES—INDIVIDUALS, GROUPS, & INSTITUTIONS SOME TOPICS YOU CAN WRITE ABOUT: 1. Child Labor: During the Industrial Revolution, industrialists and big businesses hired cheap labor. At the time, there were no labor laws. Child labor was popular in factories and coal mines. These children came from poor families who had to help support the family rather than go to school. These children missed out on an educator because there were no laws that required young children to attend school. Children often worked long hours in dangerous factory conditions for very little money. Children were useful as laborers because their size allowed them to move in small spaces in factories or mines where adults couldn't fit. Children were easier to manage and control and perhaps most importantly, children could be paid less than adults. Most workers got $10 per week, worked in unhealthy and unsafe conditions, had no mask to protect against chemicals or gloves, and worked 12 hour days/6 days a week. This caused diseases, burns, injuries, and even death. Supporters of children labor were big business owners because they can give these children low wages and work for long hours. However, other opposed child labor and tried to find ways for the government to reform society and prevent child labor. In 1904 Hunter published his book Poverty. Based largely on his experiences in Chicago and New York, Hunter, attempted to define and measure poverty, describe some of its evils, to point out certain corrective actions, and show that the evils of poverty are repeated. He exposed the evils of child labor taking place. Hunter argued in his book that there were over 10 million people living in poverty in America. Government actions were taking that required children to attend school and ended child labor laws. **Other topics are already listed above, such as Prohibition, women’s suffrage. & Civil Rights Movement** ESSAY TOPIC: GEOGRAPHY—DEVELOPMENT OF THE U.S. ADDRESSING TWO EVENTS and the social, political, and economic impacts SOME TOPICS YOU CAN WRITE ABOUT: 1. Louisiana Purchase: Before the 1800’s the U.S. was made up the 13 colonies. The colonies were along the east coast and the boundary was the Appalachian Mountains. In 1803, Jefferson purchased Louisiana Territory from France. This expanded the U.S. towards the west. It also doubled the size of the U.S. Jefferson used the elastic clause, which means the president is allowed to do things when they are necessary and proper. This went against Jefferson’s views. He originally was a strict constructionist, which means he interpreted the Constitution strictly. After he purchased Louisiana territory, this made him a loose constructionists. Purchasing this land helped the U.S. because it gave Americans access to the Mississippi River. These helped farmers in the Ohio River Valley transport their goods easily. We also gained the city of New Orleans and access to their ports as well as the Gulf of Mexico. 2. Panama Canal: Theodore Roosevelt was president at the time when the Panama Canal was built. During this time, Theodore Roosevelt added to the idea of the “Monroe Doctrine” by writing the Roosevelt Corollary which said it is America’s job to protect and take care of other countries in Latin America. America should be the “international police power” of these countries. President Taft, after Roosevelt, said we should practice “Dollar Diplomacy.” In other words, we should help other countries by investing in them and at the same time trying to make money off of them. America wanted a canal that would link the Pacific and the Atlantic Oceans (so they wouldn’t have to travel all the way around). The U.S. made a Treaty with Panama to give the U.S. a 10-mile wide strip of land across Panama for 99 years. This piece of land would get dug up and create a canal. Local workers made the remarkable achievement of completing the canal ahead of schedule and under budget. Many workers came from other countries to work on the canal but were treated like strangers. This provided many jobs. Americans did not allow the people who lived there to use the canal. It was considered “American” property even though it was in Panama. This is an example of imperialism because America took over another country for its benefit. America increased its trade with Asia because it was now easier and faster to travel there by boat. The Panamanians were upset that the United States had control of the canal and had demonstrations. In response to these demonstrations, the United States agreed in a 1977 treaty to return the canal to Panamanian control. Panama took back the canal on December 31, 1999. ESSAY TOPIC: REFORM MOVEMENTS—goal, action, achievement SOME TOPICS YOU CAN WRITE ABOUT: 1. Progressive Movement: By 1900, the United States was a rich and powerful nation. Industrialization, urbanization, and immigration had changed the United States into a major economic power. The changes in American life also brought some problems. The negative effects of these changes led some people to call for reform. These people were known as Progressives. The Progressives set out to address the problems of this time period (1870-1914). They led to a movement to try and solve the problems caused by industrialization. The muckrakers helped bring change to the United States by brining problems to the attention of the American people. Most were journalists and writers, but others were artists and photographers. Muckrakers exposed these problems in many different ways, but they all wanted to let the people of American know what was going on in their country. Some muckrakers you can addressHow the Other Half Lives by Jacob Riis (1890): This was written in the Progressive Era. Riis was a muckraker who wrote vivid articles and books exposing the evils of society and demanded social and economic reform. Riis wrote about tenement life and the horrible conditions many immigrants lived in. Some had no windows, no pipes for water or sewage, no heat. Disease (tuberculosis, lung disease) spread quickly. Fires spread quickly. Often, 10 people shares a single room. As a result, fire escapes were built, sewage systems were implement, etc. The Jungle by Upton Sinclair (1906): This book was fiction, but it was based on fact. It revealed horrific details about the meatpacking industry. Sinclair told how the packers used meat from sick animals. He described how rats often got ground up in the meat, which was then dyed to make it seem healthy. This took place during the Progressive Era when people wanted to change/reform society. They wanted conditions improved. As a result of this book, President Theodore Roosevelt created the Meat Inspection Act, that inspected all meats, and the Pure Food and Drug Act which did not allow the sale of infected or falsely labeled goods on national market. Theodore Roosevelt was a Progressive president who passed the Sherman Anti-trust Act, which broke up bad trusts. Trusts were large businesses that had complete control over an industry. These industries cut their prices and forced their competition to fail. As a result, these businesses did not allow competition. Roosevelt passed this act to break up these trusts and encourage competition. Theodore Roosevelt was not against big business. However, he saw the difference between good and bad trusts. Good trusts were fair and should be left alone. Bad trusts took advantage of workers and cheated the public. The government should either control them or break them up. He used the Sherman Antitrust Act to break up these bad trusts. Roosevelt was known as a trustbuster, or a person who wanted to destroy all trusts. 2. Women’s Suffrage Movement: In the early 1800s, changing social conditions and the idea of equality led to the beginning of the woman suffrage movement. By then, more women were receiving education. Women also began to participate in reform movements and become more interested in politics. Women and men began to question why women were not also allowed to vote. Supporters of this were called suffragist. Women's suffrage means the right of women to vote. The women's suffrage movement was the struggle to gain the same right to vote as men. This started in 1848 at the Seneca Falls Convention where women published the Declaration of Sentiments, which demanded equality for women. Fifty years later, their granddaughters continued the fight. Women picketed in front of the White House, got arrested, and went on hunger strikes. Finally, on January 9, 1918, Wilson announced his support for suffrage. The 19th amendment was passed allowing all women the right to vote – this became the law in 1919. 3. Civil Rights Movement: By the 1960’s, many black organizations were demanding equality, desegregation, and freedom from discrimination as their major goals. One of major leaders in the Civil Rights Movement was Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. During the Civil Rights movement, these two leaders and their followers had different opinions of the methods they should use to end racial injustice (unfairness and prejudice, ex: segregation and discrimination) in order to achieve full equality and civil rights stated in the U.S. Constitution. Martin Luther believed that civil disobedience was the best way to achieve equality, which meant that protest methods should be non-violent. Martin Luther King, Jr. worked to end racial discrimination and segregation through civil disobedience and other non-violent means. MLK was involved in the Montgomery bus boycott with Rosa Parks, which achieved integration on buses and also hired black bus drivers. MLK is also famous for his political rally in 1963 for civil and economic rights for African Americans known as the March on Washington, where he made his famous “I Have a Dream” speech calling for racial harmony. In April, 1968, Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. was shot in Memphis, Tennessee. Later, his birthday was declared a national holiday. One way African Americans practiced civil disobedience was through peaceful protests that were against discrimination, such as segregated lunch counters and buses. Sit-ins (people sit and refuse to leave) at fast food lunch counters began at Greensboro, North Carolina, in 1960. A group of African Americans sat at a “whites only” lunch counter and refused to leave until served. Crowds of whites against integration would violently attack protestors, throwing ketchup and mustard and dragging them from the lunch counters. Some sympathetic whites often joined the sit-ins. Within months, sit-ins, and boycotts of segregated stores and lunch counters had spread throughout the country. In the 1960s, the Congress of Racial Equality (CORE) organized what was known as “Freedom Rides”. Busloads of young Freedom Riders—black and white—rode from town to town to integrate bus terminals in the South. In 1961, two riders were attacked first in Aniston, Alabama, and later in Birmingham. Photos of the attacks were seen all over the world. Buses were also set on fire. In response to the violence, civil rights organizations from all over the country began staging their own Freedom Rides. As a result of the Freedom Rides of 1961, President John F. Kennedy was forced to finally get involved in the Civil Rights Movement. In November of that year, the Interstate Commerce Commission prohibited (got rid of) segregated transportation facilities. Other results of the CRM were the Civil Rights Act 1964, which stated it is a crime to discriminate based on race in employment and voting. Public facilities must be integrated. The 24th Amendment (1964) stated that poll tax, charging money to vote, is not allowed. The Voting Rights Act (1965): stated DISENFRANCHISEMENT (being the denied the right to vote), such as giving literacy tests (giving people tests to see if they can read and write in order to vote) are not allowed. ESSAY TOPIC: FOREIGN POLICIES SINCE 1900 AND BEYOND—historical circumstance, long term or immediate effects, promoting self-interests SOME TOPICS YOU CAN WRITE ABOUT: 1. Marshall Plan: After WWII, the Cold War emerged between the two super powers, U.S. and Soviet Union. U.S. was a capitalist nation and a democracy, while the Soviet Union was under the control of a Communist government. Communism had a strong influence on Europe, particularly in Eastern European nations. The U.S. feared the spread of Communism and believed that eventually that if Communism continued to spread, it would get closer and closer to the U.S. As a result, the U.S. created the Marshall Plan as a contain policy to limit the spread of Communism. The Marshall Plan particularly provided economic aid to nations European nations to help them rebuild after WWII. The U.S. gave money to free countries so they could rebuild homes, factories, and farms destroyed from war. The U.S. did this to make these countries strong enough so that they would not need help from Communist countries and eventually form democratic governments. 2. SALT: After WWII, the Cold War emerged between the two super powers, U.S. and Soviet Union. U.S. was a capitalist nation and a democracy, while the Soviet Union was under the control of a Communist government. Communism had a strong influence on Europe, particularly in Eastern European nations. The U.S. feared the spread of Communism and believed that eventually that if Communism continued to spread, it would get closer and closer to the U.S. During the 1950s and 1960s, there was an arms race, which meant both the U.S. and Soviet Union were building tons of nuclear weapons to be the strongest nation and be prepared for an attack. Nixon wanted to ease tensions between Communist countries, such as the U.S.S.R. This was known as détente, which means the relaxation of tensions and trying to create a better relationship. In 1972, Nixon visited the U.S.S.R. The U.S. & U.S.S.R. agreed to stop building nuclear weapons, known as the SALT Agreement – Strategic Arms Limitation Treaty. 3. Persian Gulf War: Iraq’s dictator, Saddam Hussein, ordered his army to invade Kuwait and take control over the oil and expand Iraq’s border. The United Nations and the U.S. launched an attack against Iraq to liberate (free) Kuwait. This was to assist nations against repelling aggressors (Iraq). A few days after the invasion, Hussein agreed to withdraw Iraqi troops and pay damages. It was the U.S. interests to use this foreign policy because the Middle East we relied on for oil. ESSAY TOPIC: COLD WAR—2 problems, action to solve problem, extent it was successful SOME TOPICS YOU CAN WRITE ABOUT: After WWII, the Cold War emerged between the two super powers, U.S. and Soviet Union. U.S. was a capitalist nation and a democracy, while the Soviet Union was under the control of a Communist government. Communism had a strong influence on Europe, particularly in Eastern European nations. The U.S. feared the spread of Communism and believed that eventually that if Communism continued to spread, it would get closer and closer to the U.S. 1. Marshall Plan: The U.S. created the Marshall Plan as a contain policy to limit the spread of Communism. The Marshall Plan particularly provided economic aid to nations European nations to help them rebuild after WWII. The U.S. gave money to free countries so they could rebuild homes, factories, and farms destroyed from war. The U.S. did this to make these countries strong enough so that they would not need help from Communist countries and eventually form democratic governments. 2. Truman Doctrine: The U.S. implemented the Truman Doctrine as a contain policy to limit the spread of Communism. Countries, such as Greece and Turkey were in danger of being overthrown by Communists. The U.S. gave military and economic help to free countries that Communists were trying to take over. Truman believed this was necessary to help countries who were trying to resist Communism. Congress agreed. From 1947-1950, the U.S. sent $400 million in aid to Turkey and Greece. 3. Cuban Missile Crisis: After the Bay of Pigs invasion, the Soviet Union gave Cuba more weapons so they can protect themselves against America invading again. JFK learned that Soviets were secretly building missile bases in Cuba. This threatened the security of the U.S. JFK ordered the navy to stop Soviet ships carrying missiles to Cuba. Instead of attacking Cuba, the U.S. decided to have the military blockade against Cuba to prevent any nuclear weapons to be delivered to the island (“quarantine”). The USSR & U.S. reached an agreement. The USSR removed its missiles from Cuba and the U.S. removed its missiles from Turkey (which is near the USSR). 4. SALT: During the 1950s and 1960s, there was an arms race, which meant both the U.S. and Soviet Union were building tons of nuclear weapons to be the strongest nation and be prepared for an attack. Nixon wanted to ease tensions between Communist countries, such as the U.S.S.R. This was known as détente, which means the relaxation of tensions and trying to create a better relationship. In 1972, Nixon visited the U.S.S.R. The U.S. & U.S.S.R. agreed to stop building nuclear weapons, known as the SALT Agreement – Strategic Arms Limitation Treaty. ESSAY TOPIC: CHANGE—WAR—two groups affected by war, social, political, or economic change they experienced, extent change affected American society SOME TOPICS YOU CAN WRITE ABOUT: 1. Women: WWI—During WWI, men went off to fight in war. Factory jobs and other jobs needed workers. Due to so many men off at war, women took the positions that men had. After the war, women were encouraged to gain more rights since they were part of the war effort. As a result women wanted to gain the righto vote. They protested and eventually achieved their goal in 1919 by the passage of the 19th Amendment. Women were granted suffrage, or the right to vote. 2. Civil War—enslaved persons: The Civil War was fought between the North and the South. They had sectional differences. Particularly, the fighting was over states’ rights. One of the major issues was over slavery. Northerners did not have slaves because they were economically and geographically different from the South. The North made its money from manufacturing, while the South used slaves on plantations for agriculture and other economic interests. As a result of the war, new amendments were added to the Constitution during the period of Reconstruction. The 13 th Amendment banned slavery, the 14th Amendment gave blacks citizenship, and 15th Amendment gave suffrage to black men (voting rights). Although these Constitutional Amendments were in place, blacks experienced the Jim Crow laws, which segregated blacks and whites. Poll taxes, literacy tests, and grandfather clause also limited blacks’ equality because it made it hard for blacks to vote. It was not until the 1960s, where equal rights were fully achieved for blacks. 3. Vietnam War—draft: The Vietnam War lasted over a ten year period. The U.S. needed more men to fight. The Draft was a system where young men between the ages of 18 and 26 were forced into military service. The men were chosen to go to war by their birthday. The United States military would select a date and all men born on that date would be sent draft cards. In 1965, over 5,000 young men were being drafted each month. Originally, if selected, one could avoid going by entering a university as a full time student but this option did not last long. Eventually people began “dodging the draft” by leaving the country (many ran away to Canada) and burning their draft cards in protest. If caught draft dodging, one would be thrown in jail. Many college campuses were a place of protest for young adults and students. Berkeley College in California was an active campus of protest. The most famous protest took place on May 4, 1970, when an Ohio National Guard (state police) unit fired 67bullets into a crowd of unarmed students during an anti-war protest on campus, killing four and wounding nine. The event caused an immediate closure of the campus as well as many other college campuses around the nation. The Guard had been called into Kent University after several protests in and around campus had become violent, including riots and the burning of a building where army training was happening.President Lyndon B. Johnson will always be remembered for his role in the Vietnam War. Johnson sent over 535,000 troops to the cause, which cost an estimated $2 billion per month. He made several attempts to end the war, with peace talks in 1965 and 1966, but were rejected each time. Meanwhile Americans were not happy about the war continuing, and protested. They were opposed to sending more troops to a war that was failing. To make matters worse, North Vietnam attacked cities in South Vietnam and the American Embassy there. This was known as the Tet Offensive. Johnson became an unpopular president because of the war. It is believed that the situation in Vietnam made Johnson’s not to run for a second term as president. Due to many Americans being upset about fighting in Vietnam, Congress passed a law about presidents’ decision making in war. The War Powers Act made it harder for presidents to send troops overseas. The act was signed by Nixon, which said that it was only Congress’s role to decide about sending troops to countries to fight, NOT the president’s decision. ESSAY TOPIC: FOREIGN POLICY SOME TOPICS YOU CAN WRITE ABOUT: 1. Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine: Theodore Roosevelt added to the idea of the “Monroe Doctrine” by writing the Roosevelt Corollary which said it is America’s job to protect and take care of other countries in Latin America. America should be the “international police power” of these countries. President Taft, after Roosevelt, said we should practice “Dollar Diplomacy.” In other words, we should help other countries by investing in them and at the same time trying to make money off of them. 2. Lend-Lease Act—1941: Two years into the war, England and France were badly damaged. Soldiers and supplies for the Allied forces were low and they needed more weapons, food, and other supplies. FDR came up with the idea that the U.S. would lend or lease (rent) the weapons to the Allied Powers and collect money later. Some people were upset about this because they felt this was America ‘getting involved’ again. 3. Persian Gulf War: Iraq’s dictator, Saddam Hussein, ordered his army to invade Kuwait and take control over the oil and expand Iraq’s border. The United Nations and the U.S. launched an attack against Iraq to liberate (free) Kuwait. This was to assist nations against repelling aggressors (Iraq). A few days after the invasion, Hussein agreed to withdraw Iraqi troops and pay damages. It was the U.S. interests to use this foreign policy because the Middle East we relied on for oil. 4. Vietnam War: In the 1950s, Vietnam was divided into North Vietnam and South Vietnam at the 17th parallel. North Vietnam became a Communist country ruled by Ho Chi Minh and South Vietnam was a democratic nation. Communist had taken over China and the U.S. feared that communist would start to take over all of Indochina (Southeast Asia). This is known as the domino theory. Military efforts began to prevent Communism from spreading. Presidents Eisenhower and Kennedy sent military equipment, advisors, and money to Vietnam. In 1964, North Vietnam gunboats attacked a U.S. naval ship. President Johnson asked Congress for permission to strike back. Congress passed the Gulf of Tonkin Resolution, which supported Johnson’s efforts to stop communism. Johnson first bombed North Vietnam, then in 1965, sent in regular U.S. military forces. The U.S. involvement turned into a war. Like, the Korean War, the Vietnam War was an illegal war. The presidents never asked Congress for permission to go to war. The Vietnam War was a war officially not declared by Congress. The U.S. continued to bomb North Vietnam and sent over 500,000 troops to fight. Even with a large U.S. military power, the North Vietnam did not grow weaker. The North Vietnamese used a method known as guerrilla warfare. They hid in rainforests and randomly attacked towns. In response to this, the U.S. used a chemical called Agent Orange. This chemical killed plant life to it would be hard for the North Vietnamese, but the communists still managed to get away. Agent Orange was later blamed for many medical problems experienced by Vietnam veterans. Another method used by the U.S. was napalm, a toxic gel that removed leaves that hid enemy forces and allowed American soldiers to pass through the jungles easily. Once, dropped on an area, the napalm would attach itself to trees, grass, homes, and people in the area. When lit, it caused everything it touched to burn. American History Regents Prep Keywords, Groups, & Phrases that Frequently Appear on the American History Regents When you see… Mercantilism New England town meetings, Mayflower Compact, Virginia House of Burgesses American Revolution Declaration of Independence French and Indian War Articles of Confederation Constitutional Convention Anti-Federalists Federalists The words associated with or answer is… Raw materials (colonies), manufactured goods/finished products (mother country), restrictions on trade, limit manufacturing in colonies, All Responses to British to Mercantile PoliciesBoston Tea Party, Constitutional Convention, Nonimportation agreements, Committees of Correspondence, First Continental Congress “no taxation without representation” Only the colonists’ elected representatives should have the power to levy (impose) taxes Self-rule, representative democracy, consent of the governed The thirteen colonies had few, but important advantages in the war with England, received aid from foreign nations, Protests against British colonial policies gradually led to demands for independence. Enlightened, John Locke, Social Contract, natural rights, consent of the governed, no taxation without representation – leads to Revolutionary War (colonies had few, but important advantages in this war), If the government denies its people certain basic rights, that government can be overthrown, revolt against unjust governments, reasons to rebel against Great Britain Britain (England) and France fighting over land in North America, disputed land claims in Ohio River Valley Weak national government, protect states’ rights, feared/distrusted strong national government, guidelines to admit new states into the union, prevent the abuse of power that existed under British rule Representation, Three-Fifths Compromise-dealt with issue of slavery (Southern states, like Virginia benefited the most), Great Compromise-dealt with representation, revise Articles of Confederation, addressed slavery, taxation, representation (New Jersey & Virginia Plan—Congress made up of House of Representatives—based on population of each state & Senate—2 for each state), election of president, small states supported idea of equal representation for the states in the national legislature Bill of Rights (anti-federalist would approve/ratify Constitution if Bill of Rights put in), states’ rights, did not want a strong central/national government Ratification of the U.S. Constitution, Washington, Hamilton, Madison, Federalist papers written to gain support of ratifying Constitution National bank (improve economic condition of U.S.), pay off nation’s debt, loose interpretation of Constitution, elastic clause of Constitution, protective tariff passed to encourage the growth of manufacturing Alexander Hamilton Federalism/Federal System Electoral College Checks and Balances Marbury v. Madison Marshall Court McCulloch v. Maryland Disagreements with Jefferson over the interpretation of the Constitution, which led to the development of political party system Balance of national and state government, division between national and state government, “limited government” by dividing state and national government powers Popular vote does not determine presidency, each states have “points” based on population of their states, majority of these points wins presidency, The ''winner-take-all'' method can distort the relationship between the popular vote and the electoral vote, need majority of electoral votes to win Supreme Court (interprets the law), Congress, Executive, three branches of government, separation of powers, House of Representative (will of the people)/Senate (Congress) has the power to impeach, president veto a bill passed by Congress, The Senate approved the appointment of Clarence Thomas to the Supreme Court JUDICAL REVIEW(**judicial review, elastic clause, amending process the Constitution may be adapted to meet changing conditions**--flexibility) Supreme Court to determine the constitutionality of laws Justice John Marshallexpanded the power of the Federal Government Increase the power of the federal government Supremacy of the federal/national government Gibbons v. Ogden Washington John Adams Thomas Jefferson Mississippi River Physical Features Geography Manifest Destiny Monroe Doctrine Andrew Jackson Trail of Tears Dawes Act Homestead Act Abolitionist Sectionalism The power of the federal government over interstate commerce was strengthened, regulate interstate commerce Precedents, cabinet of advisors, unwritten constitution, political parties, strengthen the federal government, Farewell Address, neutrality, U.S. needed time to gain economic and military strength, isolationism, avoid involvement in the political disputes of Europe Alien and Sedition Acts, XYZ Affair , civil liberties Louisiana Purchase, elastic clause (meet the needs of changing society/times—Founding Fathers put this in the Constitution), violate/contradict belief of strict interpretation of the Constitution, went from a strict constructionist view to a loose constructionist, power granted to the President to make treaties Trade, New Orleans—farmers in the Ohio River Valley, Westward Expansion, Louisiana Purchase, Access to Gulf of Mexico, trade for farmers, transport goods to markets, Rivers, lakes, mountain ranges, Earth’s natural features Regional differences in economic development Fertile land, long growing season, plantations, slaverySouth Agriculture in Midwest flat terrain good harbors, abundant forests, rocky soil, and a short growing seasonNew England Proclamation of 1763 Appalachian Mountains greatest influence on early patterns of industrialization in the United Statesavailability of waterpower to operate machines Africa, North America, Europecolonial trade routes Erie Canal Farmers could more easily ship grain to eastern markets Chicago Great Lakes Westward expansion, expand to the Pacific Ocean, Mexican War, annexation of Texas, Homestead Act, transcontinental railroad, “military conquest, treaty, purchase” , California Gold Rush Western Hemisphere, prevent colonization by the Europeans in Caribbean/Latin America, avoid political conflicts with Europeans, foreign policy that resulted from a close geographic relationship to Latin America Spoils system (rewarding jobs), expand presidential powers, end property requirements, increase voting rights for white men, protective tariffs to encourage manufacturing in U.S., Indian Removal Act Injustice of Native Americans, Worcester v. GeorgiaSupreme Court Assimilation of Native Americans, encourage Native Americans to give up their traditional culture, expansion of settlement to the West West, Great Plains, provide free land to settlers, people pay off land Against slavery, William Lloyd Garrison's publication of The Liberator, Underground Railroad, Harriet Beecher Stowe’s Uncle Tom’s Cabin Economic conditions and interests varied in regions (North-Industrialized vs. South-plantations) Missouri Compromise Compromise of 1850 Fugitive Slave Act (Law) Kansas-Nebraska Act/Bleeding Kansas Popular sovereignty Dred Scott v. Sanford (1857) Extension of Slavery Secession/Secede of Southern states Civil War Reconstruction—South Abraham Lincoln Andrew Johnson 13th, 14th, 15th Amendments Sharecropping Black Codes Poll tax, grandfather clause, literacy tests, Jim Crow Laws Plessy v. Ferguson (1896) Booker T. Washington W.E.B. Dubois Homestead Act Industrialization Immigration Monopolies/Trusts Yellow Journalism Open Door Policy Laissez faire Progressives Women’s Suffrage (Voting Rights) Theodore Roosevelt Anti-trust (Against big businesses) and Business Regulation The balance between free and slave states was maintained, tried to solve issue on extension of slavery into the western territories, admission of states to the Union admission of states to the Union, allow settlers in new territories to vote on the issue of slavery, westward migration caused by the discovery of gold in California, Fugitive Slave Act, cause of the Civil War Runaway slaves, Canada, abolitionists did not like law reaction: Underground Railroad Clashes between pro-slavery and anti-slavery groups, sectional conflict, tried to solve issue on extension of slavery into the western territories, allow settlers in new territories to vote on the issue of slavery allow settlers in new territories to vote on the issue of slavery being legal in their territory, status of slavery in new states ruled that Congress could not ban slavery in the territories, Cause of Sectional Conflict, protected the property rights of slave owners in the territories, sometimes failed to protect the rights of minorities "Compromise Enables Maine and Missouri To Enter Union" (1820) "California Admitted to Union as Free State" (1850) "Kansas-Nebraska Act Sets Up Popular Sovereignty" (1854) Increasing sectionalism (A Nation Divided), Disagreements over states’ rights issues, Breakdown of compromise, Election of 1860 Election of 1860 (Abraham Lincoln becomes president) “By the 1850’s, the Constitution, originally framed as an instrument of national unity, had become a source of sectional discord” shows sectionalism happening in the U.S., vast differences over states’ rights The federal government’s power over the states was strengthened “Solid South”—consistently supported Democratic PartyDemocrats disliked the Reconstruction Programs of the Republicans, “New South”—changes in southern economy, share cropping—kept formerly enslaved persons economically dependent Preserve the Union, expanded powers of presidency, wanted southern states to enter the Union as quickly as possible, rejected harsh punishments for the South, removes habeas corpus, Emancipation Proclamation (frees slaves) allow the Southern States to reenter the nation as quickly as possible, a power struggle with Congress over Reconstruction (separation of powers), impeachment increased individual rights for African Americans, Radical (Congressional) Reconstructionopposed Lincoln’s Plan because it offered amnesty to nearly all Confederates who swore allegiance to the U.S., legal and political rights to African Americans, 13th Amendment officially banned slavery Former slaves earned a living, economically dependent deny equal rights to African Americans limits voting rights of African Americans, preventing African Americans from exercising their basic rights Segregation of public facilities, limit effects of Radical Reconstruction, state and local governments to restrict the freedoms/rights, failed to provide lasting guarantees of civil rights to freedmen Racial segregation, “separate but equal” based on race, separate public facilities were constitutional (allowed), failed to protect rights of minorities African Americans should achieve equality by expanding their opportunities for vocational education, difference than that of W.E.B. Dubois on how racial equality should be achieved African Americans should demand immediate participation in American society, Formal education (science and literature), difference than that of Booker T. Washington on how racial equality should be achieved Great Plains, settle West, decline the Plains Indians, develop the Midwest and western parts of the country (and Pacific Railway Act) Urbanization (cities), increased immigration, investment capital, growth of the middle class, job opportunities, expansion of the railroads, Gospel of Wealth, Social Darwinism (justified big business and the rich, “survival of the fittest”), abundance of natural resources, urbanization, U.S. government aided development of west by granting land to railroad companies, before 1890 few foreign investments Economic advancement, urban areas (north/east U.S.), Industrialization allowed immigration in the U.S. because of shortage of labor—cheap labor, industrial economy was creating new jobs crop failures in Ireland that led to mass starvation made them to U.S. New immigration—southern and eastern Europe (ex: Russia, Italy)—culturally different from older immigrants Old immigration—northern and western Europe (ex: Ireland, Germany) 1920s- limit immigration from southern and eastern European nations, nativism—hatred towards immigrants— “Help Wanted, Irish Need Not Apply”, passage of laws restricting immigration, quotas, National Origins Act, Chinese Exclusion Act (1882), Gentlemen’s Agreement with Japan (1907)—limit immigration of certain ethnic groups Cultural pluralismbecame part of America, but kept language, religions, and traditions Limit competition and increase profits, big businesses, furthered gap between rich and poor, “survival of the fittest”—Social Darwinism used to justify big businessgood businesses will thrive, others will fail, business consolidation Start of Spanish American War, exaggerate events, the Maine blown up in Havana Harbor, media influence U.S. and China, prevent European and Japanese monopoly of Chinese trade and markets, “spheres of influence”, expand trade with China, equal trade opportunities, overseas markets, source of raw materials—also with Spanish American War and annexation of Hawaii (*Imperialism*) Government should not intervene (get involved) in business, “prices and wages should be determined by the marketplace”, those who opposedgovernment should protect through regulation of business Reform, social and economic changes, limit power of big business, Government regulation (control) in business, Prohibition, Suffrage, graduated income tax, direct election of senators, Theodore Roosevelt, Woodrow Wilsonprogress cannot be achieved when at war, 16th Amendmentfederal income tax, Federal Reserve (regulate money supply, interests rates, bank credit), banking and interests rates, money circulationFederal Deposit Insurance Corporation initiative, referendum, and recall electionincrease citizen participation in the political process Progressive income tax belief large income, higher tax rate Susan B. Anthony, Elizabeth Cady Stanton, Seneca Falls Convention, WWI working in war industries (factories), 19th Amendment (gain suffrage/right to vote) *Recent accomplishment*--women serve in combat positions Good and bad trusts, trustbuster limit power of monopolies, imperialism, Big Stick Policy, international police, Western Hemisphere, Latin America, Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine, Panama Canal (links two oceans—Atlantic and Pacific), Square Deal, Food and Drug Administration, Meat Inspection Act Encouraged/increased competition, Sherman Anti-trust Act—Theodore Roosevelt trust busting policy, Clayton Anti-trust Act, Commerce Act, U.S. v. Standard Oil (breaks up Rockefeller’s oil monopoly) trust busting, protect small businesses and farmers, demand for government regulation (ex: the business practices of the railroads led (control) Labor Unions Big Business Leaders Muckrakers Populism & Granger Movement Entrance to WWI Schenck v. U.S. Results of WWI Roaring 20s Harlem Renaissance Intolerance—1920s Causes of the Great Depression Life During the Depression Hoover FDR & New Deal WWII Korematsu v. U.S. After WWII (1945): Early Cold War JFK Cold War Life During the 1950s Civil Rights Movement (late 1950s to 1960s) Warren Court to this demand) Collectively bargain (National Labor Relations Act (Wagner Act), higher wages (pay), improved hours, limited growth of labor unions because employers were hostile towards workers’ efforts to organize, American Federation of Labor (skilled workers), Knights of Labor, Haymarket Riots, Homestead Strike, Pullman Strike (government is anti-unions), **Pullman and Homestead Strike were unsuccessful because government took sides of the businesses**, court injunctions to stop strikes, violence between labor and management John D. Rockefeller (Standard Oil, railroads), Andrew Carnegie (Carnegie Steel), J.P. Morgan, Cornelius Vanderbilt, robber barons (ruthless business tactics against competitors), captains of industry, philanthropic activities (did good things for society—Rockefeller Foundation, Carnegie Hall, J.P. Morgan Library) Make America aware of problems in society, expose the evils in American society, expose the abuses of the government and industry, expose poverty and corruption, publication of articles and books Poor, urban slums: Jacob Riis (How the Other Half Lives)—urban slums, tenements, Jane Addams (Hull House) Meatpacking Industry: Upton Sinclair (The Jungle)—leads to Meat Inspection and Food and Drug Act Political Corruption: Lincoln Steffens (The Shame of Cities) Standard Oil: Ida Tarbell (History of Standard Oil Company) Help western farmers fight against unjust economic practices, lower profits forcing people out of farming, overproduction compared to consumer demand, Farmersrising prices would help them pay back loans (railroad companies charging higher rates for transporting farm products), currency reform (Gold Standard), Williams Jennings Bryan, free coinage, unlimited silver, graduated income tax, direct election of senators, social and political problems, third political parties, focuses on one particular group/issue Other third political parties—Know-nothing party, Greenback Party, Prohibition Party, Bull Moose Parties a single powerful issue can mobilize political activity Sinking of The Lusitania, submarine warfare, freedom of the seas, world safe for democracy, Zimmerman Telegram, Russian Revolution (1917) “clear and present danger”, don’t shout fire in a crowded theater, civil liberties limited for national security, constitutional protection of liberties are not absolute, limits freedom of speech—First Amendment, similar to Korematsu case in WWII Wilson’s Fourteen Points (avoid future wars/conflicts, world peace—usually associated with Atlantic Charter), Treaty of Versailles, League of Nations (U.S. Senate does not join—goes back to neutrality, disillusionment of the war—U.S. becomes isolated/isolationism), led to 1920’s noninvolvement in foreign affairs Consumerism (people spending $), Henry Ford’s assembly line (reduce cost, increase production), flappers (traditional values v. lifestyle changes), social and economic changes/improvements, Harlem Renaissance, Coolidge, Harding, & Hoover (President that practiced trickledown (tax cuts) economics—give money to rich to stimulate economy), farmers failed to experience economic prosperity, traditional v. modern values, Teapot Dome Scandal Margaret Sanger—improve conditions for poor, birth control African American culture, music (jazz), Duke Ellington, Bessie Smith, literature (poetry—Langston Hughes—“I, Too, Sing America) Prohibition (18th Amendment), Temperance (no drinking) Movement, Red Scare & Palmer Raids (scared of Communist; arrest and deport, anti-American political views, caused by Bolshevik Revolution and workers’ strike), KKK revival, The Scopes Monkey Trial (science v. religion, conflict over cultural values), anti-immigration (Sacco and Vanzetti trial—nativist attitudes) Overproduction and under consumption, buying stocks on margin (borrowing), excessive speculation in the stock market, purchase stocks on credit, banks giving too much credit—installment buying, banks crash, Stock Market Crash (October 1929—all stocks lose value), Dust Bowl (Great Plains—grain crops, severe drought and overproduction of farming, Oklahoma), uneven distribution of wealth, distribution of income is unequal, Republicans believed economy would recover on its own Hoovervilles / Hoover blankets (people blamed President Hoover for not helping them), High unemployment (25% of all Americans), racism (African Americans can’t get jobs—50% unemployment for blacks) Rugged individualism (people should rely on themselves not the government), economic theory similar to Reagan’s supply side economics (similar to Reagan’s economic policies), believed federal relief programs would destroy individual initiative Expand power of the presidency, New Deal relief (CCC, WPA—artists, musicians, writers, PWA—give people jobs—helps unemployed workers), recovery (AAA, NIRA—regulate prices), reform (Social Security Act— domestic servants and farmers do not get, bank holiday, SEC—regulate stock market), Tennessee Valley Authority (state intervention to meet regional needs) pump and prime, Court Packing (tries to add supreme court justices when they declare part of New Deal unconstitutional (Butler v. U.S., and Schechter Poultry v. U.S.—Congress says “no”),12 years as president, greater involvement of federal government, made people dependent on the federal government, government role in solving economic problems Lend Lease, cash and carry (U.S. helps England, critical aid to Britain and Soviet Union), Pearl Harbor attacked by Japanese (1941)—Congress declares war, D-Day, atomic bomb (Hiroshima and Nagasaki) – used to save American lives, women work in factories, Nuremberg Trials (crimes against humanity), Cold War starts when WWII ends Internment camps for Japanese in U.S., “clear and present danger” (JUST LIKE SCHENCK CASE), national security is more important than civil liberties, limiting civil liberties in war time, racial prejudice Potsdam Conference sets up Cold War, Superpowers (U.S. and U.S.S.R), Containment (stop Communism from spreading), $ to Greece and TurkeyTruman Doctrine and $ and aid to Europe after WWIIMarshall Plan NATO (collective security), domino theory, Korean War (Congress did not officially declare war, outcome— Korean stays divided at 38th parallel), Berlin Blockade, Berlin Airlift Bay of Pigs Invasion (try to overthrow Fidel Castro—remove communist dictator from power, many people fled from Cuba to U.S. when Castro took over Cuba, eliminate unfriendly governments geographically close— geographic location plays important role in determining foreign policy), Cuban Missile Crisis, early involvement in Vietnam Baby boom, suburbs (automobile and Interstate Highway Act), social conformity, consumerism, technology, McCarthyism (similar to Palmer Raids—fear of Communism in the U.S. and spies, denial of civil liberties were threatened, reputations were ruined by false disloyalty, reckless accusations unsupported by evidence, believed Communist agents were in federal government), Cold War fear (bomb shelters, fear nuclear attack), GI Bill— help veterans economically and give money for school/job training (economic aid to veterans) Brown v. Board of Ed (1954)—(separate, but equal is INEQUAL, overturns Plessy v. Ferguson case, equal protection under the law, Supreme Court has helped to determine public policy), Little Rock Crisis (President Eisenhower acts as commander and chief to enforce school integration) Rosa Parks (Montgomery Bus boycott) Martin Luther King (civil disobedience), Greensborough sit-ins, freedom riders, Selma March (Voting Rights), Million Man March, NAACP, Malcolm X, Black Panthers and Black Power Achieved Civil Rights Act 1964 (racial and gender equality) and Voting Rights Act (1965) Justice Earl Warren “activist” applied a loose interpretation of the Constitution to increase individual rights, Expanded the rights of individuals, Rights of the accused Miranda v. Arizona (denied due process, inform arrested of Constitutional rights, inform of legal rights) Mapp v. Ohio (police enter an individual’s home without invitation or a warrant and seize evidence to be used against the individual, evidence inadmissible in court), Escobedo v. Illinois, Gideon v. Wainright (denied due process of law-- New Frontier (JFK) Great Society (LBJ) Vietnam War Roe v. Wade Richard Nixon Jimmy Carter *like Miranda case**), Engel v. Vitale (No religions in public schools, students rights) Peace Corps (help developing nations, “ask not what your country can do for you, ask what you can do for your country”), Space Program (fear of Sputnik satellite in Russia), tries to get economic and civil rights programs, but dies, Equal pay act (men and women get same pay/wages for same job, improve status of women) War on Poverty (help poor people in America), Medicare and Medicaid, Civil Rights Programs, similar to FDR’s New Deal Program and Teddy Roosevelt’s Square Deal, greater involvement of federal government Domino Theory (used to justify Vietnam War, U.S. becomes militarily involved in Southeast Asia—1950s-1960s), Congress did not officially declare war (just like Korean War), Gulf of Tonkin Resolutionsend troops, LBJ becomes an unpopular president does not run for second term—the people hold a President accountable for his performance, Vietnam War takes away money from Great Society, war protests (Vietnam veterans against the war), counter culture (hippies), draft, Kent State Massacre, Tinker v. Des Moines (1st Amendment, freedom of speech/arm bands allowed in school---can be related to New Jersey v. TLO: civil liberties can be both protected and limited in schools, students rights), guerrilla warfare, Tet Offensive, riots at the Democratic National Convention, outcome of war affects public opinion Women’s right to privacy, struggled to accommodate conflicting viewpoints on the issue Ends Vietnam War (vietnamization and Nixon Doctrine—peace with honor),détente (easing of tension--USSR), SALT Agreement (limit nuclear weapons build up), Visits China to ease tensions (Ping Pong Diplomacy, open trade with China), Watergate Scandal (Nixon resigns)--*President is not above the LAW* (U.S. v. Nixon, Nixon v. NY Times—limit executive power, freedom of the press), the people hold a President accountable for his performance Camp David Accords (Peace with Israel and Egypt—Egypt accepts Israel as a nation), OPEC Crisis (gas)—oil embargo, trying to establish peace in the Middle East, SALT, responded to human rights abuses in South Africa’s apartheid Domestic: Reagonomics--Trickle down (tax cuts), supply side economic (like Hoover, give businesses money to stimulate economy)—economic growth depends on making increased amounts of capital available to business, lower federal income tax rates, corporate business tax were reduced, economic changes favoring businesses Ronald Reagan George Bush Sr. Bill Clinton George W. Bush Financial Crisis Barack Obama Globalization and Global Issues Foreign: Increase defense spending—spending on military (federal deficit), puts pressure on Russia (tension increase again), Reagan Doctrine (support people who want to be free in Communist countries). ALL OF THIS LEADS TO FALL OF THE BERLIN WALL AND END OF COLD WAR! Persian Gulf War (protects Kuwait and prevent Iraq from getting oil, liberate/free Kuwait), third party costs him election, New World Order, used foreign affairs to hid domestic failures NAFTA (free trade, economic interdependence, Globalization), Impeachment Trial (vote him not guilty, impeachment for alleged perjury and obstruction of justice—shows checks and balances), adopts Republican platforms (welfare reform), good economy=high approval ratings, policing overseas for human rights (Bosnia, Kosovo, Haiti) War on Terror as reaction to September 11, 2001—War in Afghanistan and war in Iraq, Patriot Acts (limits rights for national security), department of Homeland Security, trickle down (tax cuts)/supply side, the people hold a President accountable for his performance, the Supreme Court played an important role in the final outcome in 2000 election Stocks and banks crash (like Hoover’s Great Depression), strengthen federal control over the financial system— 2008-2010 economic crisis Stimulus plan (like New Deal), federal deficit, government involvement, Osama Bin Laden killed Global warming, free trade (NAFTA), outsourcing (giving jobs overseas) ANSWER KEY Colonies and Revolutionary War 1-3 2-3 3-4 4-3 5-2 6-2 7-2 8-3 9-1 10- 4 11 - 1 12 - 2 13 - 3 14 - 1 15 - 1 16 - 4 17 - 2 18 - 2 19 - 1 20 - 4 Creating a New Government 1-1 2-4 3–4 4–4 5–3 6 –2 7–3 8–1 9–4 10 – 1 11 – 3 12 –2 13 –3 14 – 2 15 – 2 16 – 1 17 – 2 18 – 4 19 – 2 20 – 2 21 – 4 22 – 2 Building a New Nation and the Age of Jacksonian Democracy 1-3 2-4 3-1 4-1 5-1 6–2 7–4 8–4 9–2 10 – 2 11 – 2 12 – 2 13 – 3 14 – 4 15 – 3 16 – 2 17 – 3 18 – 3 19 – 4 20 – 4 The Progressive Era 1 -- 1 2–2 3–2 4–1 5–3 6–3 7–3 8–1 9–3 10 – 1 11 – 3 12 – 1 13 – 1 14 – 1 15 – 1 16 – 1 17 – 1 18 – 3 19 – 1 20 – 1 21 – 3 22 – 1 World War I and the Roaring ‘20’s 1–1 2–3 3–4 4–3 5–4 6–4 7–2 8–4 9–2 10 – 1 11 – 4 12 – 2 13 – 3 14 – 3 15 – 1 16 – 3 17 – 4 Great Depression, New Deal and WW2 1–4 2–1 3–4 4–2 5–3 6–4 7–1 8–4 9–1 10 – 1 11 – 2 12 – 3 13 – 2 14 – 4 15 – 4 16 – 3 17 – 1 18 – 3 19 – 3 20 – 4 The Road to Civil War and Reconstruction 1–2 2–2 3–4 4–3 5–4 6–4 7–3 8–1 9–3 10 – 3 11 – 2 12 – 3 13 – 1 14 – 2 15 – 2 16 – 2 17 – 3 18 – 1 19 – 2 20 – 3 21 – 1 22 – 3 23 – 4 24 – 4 25 – 3 26 – 2 Cold War, Civil Rights, Warren Court 1–4 2–2 3–1 4–1 5–3 6–4 7–3 8–1 9–4 10 – 3 11 – 1 12 – 3 13 – 1 14 – 1 15 – 4 16 – 4 17 – 1 18 – 2 19 – 3 20 – 2 21 – 2 22 – 2 23 – 3 24 – 2 25 – 3 26 – 3 27 – 1 28 – 2 29 – 1 30 – 4 31 – 4 The Gilded Age 1–2 2 -- 1 3–1 4–4 5–1 6–2 7–4 8–4 9–3 10 – 4 11 – 4 12 – 1 13 – 1 14 – 2 15 – 4 16 – 2 17 – 3 18 – 2 19 – 1 20 – 3 Geography 1-2 2–3 3–1 4–4 5–3 6–1 7–4 8–3 9–3 10 – 2 11 – 3 12 – 3 13 – 3 14 – 2 15 – 1 16 – 2 17 – 1 18 – 2 19 – 1 20 – 2 21 – 1 22 – 3