Chapter 7.5 - I really love math.com
advertisement

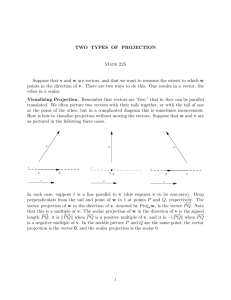
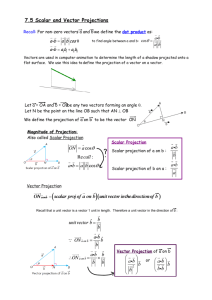
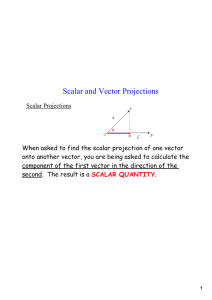
Chapter 7.5 – Scalar and Vector Projections Refer to the diagrams below. The scalar projection of a on b is obtained by drawing a line from the head of vector a perpendicular to OB or to an extension of OB . Note that the scalar projection is zero if 90 and is negative if 90 180 Scalar Projection of a on b The scalar projection of vector a onto b is ON, where ON a cos (include diagram from p. 390) Example: Suppose that the angle between a and b is . a. Determine the scalar projection of a on b b. Determine the scalar projection of b on Example 1 from page 392: a. Show algebraically that the scalar projection of a on b is identical to the scalar projection of a on 2 b b. Show algebraically that the scalar projection of a on b is not identical to the scalar projection of a on -2 b a Example 2 from page 392: For the vectors a 3,4,5 3 and b 2,2,1 , calculate each of the following scalar projections. a. b. a on b b on a Calculating Scalar Projections The scalar projection of a on b is a b b The scalar projection of b on a is a b a In general a b ba b a Example 3 from page 394: Determine the angle that the vector OP 2,1,4 makes with each of the coordinate axes. Direction Cosines for OP a, b, c If , , and are the angles that OP makes with the positive x-axis, y-axis and zaxis, respectively, then cos a, b, c 1,0,0 OP a a b c 2 2 2 ; cos b a b c 2 2 2 ; cos c a b2 c2 2 Example 4 from page 396 For the vector OP 2 2 ,4,5 , determine the direction cosine and the corresponding angle that this vector makes with the positive z-axis. Examining Vector Projections The calculation of the vector projection of a on b is simply the corresponding scalar projection of a on b , multiplied by a unit vector in the direction of b . We know from our earlier work that b is a unit vector in the direction of b . b Vector Projection of a on b The vector projection of a on b = (scalar projection of a on b ) = a b b = a b 2 (unit vector in direction of b ) b b b b a b b , b 0 = bb Example 5 from page 397 Find the vector projection of OA 4,3 on OB 4,1