CELL ORGANELLES REVIEW - Doc Charron's Science
advertisement

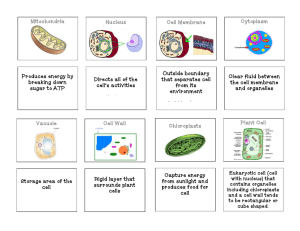
CELL ORGANELLES REVIEW 1. Cells that do not have a distinct nucleus are called: A. eukaryotic B. prokaryotic C. multicellular 2. Cells that have internal membranes surrounding specialised organelles are: A. eukaryotic B. prokaryotic C. unicellular 3. The controlling organelle within a cell is the: A. nucleolus B. gene C. nucleus 4. The jellylike fluid that contains nutrients in a cell is the: A. cytoplasm B. vacuole C. nucleus 5. Small organelles that are responsible for protein synthesis are the: A. ribosomes B. RNA C. genes 6. The system of membranes that help transport chemicals such as proteins through the cell is the: A. golgi body B. ribosome C. endoplasmic reticulum 7. The organelles that are responsible for collecting, sorting, processing and distributing proteins and carbohydrates are the: A. golgi bodies B. ribosomes C. plastids 8. The organelle found in both animal and plant cells that is clear but contains dissolved nutrients is the: A. vacuole B. cytoplasm C. centriole 9. The ‘powerhouse’ of the cell that generates the cell’s energy-rich ATP molecules is the: A. mitochondrion B. chloroplast C. nucleus 10. Water-loving molecules such as glucose are: A. hydrophobic B. hydrophilic C. insoluble in water 11. The cell membrane is differentially permeable. This means that: A. all molecules pass through the membrane at the same rate B. some molecules may pass through but not others C. only glucose passes through easily 12. Diffusion is the movement of substances from: A. high to low concentrations B. low to high concentrations C. equal areas 13. The diffusion of water is called: A. hydrophobic B. osmosis C. concentration gradient True-False Questions 14. The mitochondrion is responsible for photosynthesis. 15. Chloroplasts contain green chlorophyll and are responsible for photosynthesis. 16. All cells have a cell wall but only plant cells have a cell membrane. 17. Metabolism is all the chemical reactions occurring in an organism. 18. An electron microscope is used to view cell organelles. 19. What organelle does an animal cell have that a plant cell doesn’t? What is it’s function? 20. How are the vacuoles in animal cells different from those in plant cells? 21. What two organelles do plant cells have that animal cells don’t? What are the functions? 22. Write the chemical equation for photosynthesis. What organelles does photosynthesis take place in? What substance (pigment) is necessary for this process? 23. Write the word equation for cellular respiration? What organelles does cellular respiration take place in? 24. The job of ribosomes is to assemble _______________________________ from their building blocks __________________ __________________. What makes the surface of rough endoplasmic reticulum, rough? 25. Which organelle contains DNA and uses is it to control the rest of the cell? 26. Why do plant cells need cell walls? 27. What is meant by selectively permeable? What cellular organelle is selectively permeable? 28. The contents of the cell between the cell membrane and the nucleus is collectively called the _______________________________. 29. Label and show the locations of the following organelles on the diagram of a plant cell below: Cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, mitochondria, chloroplast, nucleus, vacuole, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, lysosomes, nuclear membrane, ribosomes, nucleolus. 30. Label the following organelles on the diagram of an animal cell below: 31. Explain why you agree or disagree with the statement that “consumers depend on producers for survival”. 32. What is the cell theory? 33. Define the term Sustainable Ecosystem. 34. Explain the connection between biodiversity and ecosystem sustainability. CELL ORGANELLES REVIEW 35. Cells that do not have a distinct nucleus are called: A. eukaryotic B. prokaryotic C. multicellular 36. Cells that have internal membranes surrounding specialised organelles are: A. eukaryotic B. prokaryotic C. unicellular 37. The controlling organelle within a cell is the: A. nucleolus B. gene C. nucleus 38. The jellylike fluid that contains nutrients in a cell is the: A. cytoplasm B. vacuole C. nucleus 39. Small organelles that are responsible for protein synthesis are the: A. ribosomes B. RNA C. genes 40. The system of membranes that help transport chemicals such as proteins through the cell is the: A. golgi body B. ribosome C. endoplasmic reticulum 41. The organelles that are responsible for collecting, sorting, processing and distributing proteins and carbohydrates are the: A. golgi bodies B. ribosomes C. plastids 42. The organelle found in both animal and plant cells that is clear but contains dissolved nutrients is the: A. vacuole B. cytoplasm C. centriole 43. The ‘powerhouse’ of the cell that generates the cell’s energy-rich ATP molecules is the: A. mitochondrion B. chloroplast C. nucleus 44. Water-loving molecules such as glucose are: A. hydrophobic B. hydrophilic C. insoluble in water 45. The cell membrane is differentially permeable. This means that: A. all molecules pass through the membrane at the same rate B. some molecules may pass through but not others C. only glucose passes through easily 46. Diffusion is the movement of substances from: A. high to low concentrations B. low to high concentrations C. equal areas 47. The diffusion of water is called: A. hydrophobic B. osmosis C. concentration gradient 48. White blood cells engulfing foreign bacteria is an example of: A. phagocytosis B. exocytosis C. diffusion True-False Questions 49. The mitochondrion is responsible for photosynthesis. (F) 50. Chloroplasts contain green chlorophyll and are responsible for photosynthesis. (T) 51. All cells have a cell wall but only plant cells have a cell membrane. (F) 52. Metabolism is all the chemical reactions occurring in an organism. (T) 53. An electron microscope is used to view cell organelles. (T) Label and show the locations of the following organelles on the diagram of a plant cell below: Cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, mitochondria, chloroplast, nucleus, vacuole, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, lysosomes, nuclear membrane, ribosomes, nucleolus. Label and show the locations of the following organelles on the diagram of an animal cell below: Cell membrane, cytoplasm, mitochondria, centrioles, nucleus, vacuole, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, lysosomes, nuclear membrane, ribosomes, nucleolus, cilia. 3. What organelle does an animal cell have that a plant cell doesn’t? ________________________ What is the function of these organelles? ________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ __ 4. How are the vacuoles in animal cells different from those in plant cells? __________________ ______________________________________________________________________ __ 5. What two organelles do plant cells have that animal cells don’t? ________________________ & ______________________________. Give the functions of these two organelles. 1. ______________. Function ________________________________________________ 2. _____________. Function _________________________________________________ Write the chemical equation for photosynthesis. ______________________________________________________________________ _ What organelles does photosynthesis take place in? ________________________________ What substance (pigment) is necessary for this process? ____________________________ This process and these organelles are present only in ___________________ cells. 10. Write the word equation for cellular respiration. ______________________________________________________________________ _ What organelles does cellular respiration take place in? _____________________________ 11. The job of ribosomes is to assemble _________________________ from their building blocks called _____________ ____________. What makes the surface of the “rough endoplasmic reticulum”, rough? __________________________________ Which organelle contains DNA and uses it to control the rest of the cell? ________________ 13. Why do plant cells need cell walls? ____________________________________________ 14. What is meant by “selectively permeable”_______________________________________ __________________.The _________ ______________________ is selectively permeable. 15. The contents of the cell between the cell membrane and the nucleus is collectively called the _____________________________