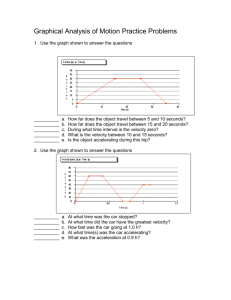
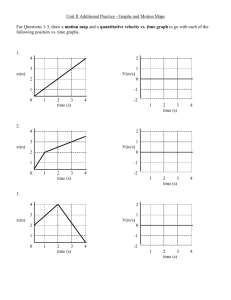
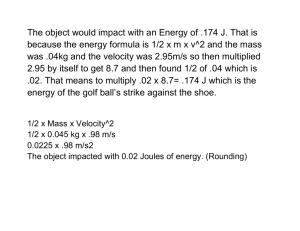Velocity

Velocity
Page 17
Many people use the terms speed and velocity interchangeably in everyday language. However, they have very different meanings in physics. Velocity describes both how fast an object is moving and . Velocity is therefore a vector quantity. Velocity is defined as the of an object per unit time. The symbol for velocity is v. The velocity of the updrafts and downdrafts inside an anvil-shaped cumulonimbus cloud, have been measured at 210 km/h [up or down].
Constant Velocity and Uniform Motion
A motor vehicle that travels along a straight level road at a constant speed has constant velocity.
Constant velocity means
. We know that an object moving at a constant speed covers equal distances in equal time intervals. Therefore, constant velocity also implies that equal distances are covered in equal time intervals. Unlike constant speed however, constant velocity occurs only when the distances have the same direction. A distance in a specific direction represents a displacement. Therefore, an object that travels equal displacements in equal intervals of time has constant velocity. When an object is moving at constant velocity (constant speed in a straight line), we can also say that it has .
Uniform motion means constant velocity. An object moving with a constant speed is not necessarily in uniform motion. Consider a car moving at a constant speed around a circular track.
It does not have a constant velocity (uniform motion). This is because, although its speed is constant, its direction is continuously changing. Now consider a child on the merry-go-round.
She is not moving at a constant velocity but is moving at a constant speed. Can you explain why?
Average Velocity
Objects seldom move at a constant velocity. Rockets speed up as they leave the launch pad.
Trains slow down as they enter the station. Snails change direction as they crawl
Page 18 along. How can we calculate the average velocity when the velocity changes in size or direction?
The average velocity of an object is calculated by dividing the change in position, or the displacement, by the elapsed time. Thus:
The symbol for average velocity is . Thus the equation for average velocity, in terms of the initial and final positions d i
and d f
, and the initial and final times t i
and t f
, is:
The average velocity for an object is the same as the constant velocity it must have in order to cover the same displacement in the same time. Both of these equations can be used to calculate constant and average velocity.
Average Speed and Average Velocity
The difference between average speed and average velocity is demonstrated by the following
Model Problem.
Eg.
Page 19
Notice that the magnitudes of the average velocity and the average speed are different. The average speed is the constant speed that would needed to reach the final position by taking the original path. The average velocity is the same as the constant velocity that would needed to reach the final position by the most direct path, which would be a straight line between the initial and final positions.
Instantaneous Velocity
How do instantaneous speed and instantaneous velocity differ? Instantaneous velocity has a direction, but instantaneous speed does not. Instantaneous velocity equals
. The symbol for instantaneous velocity is the same as for constant velocity.
Consider a Ferris wheel that is revolving at a constant speed. A rider at the top has the same instantaneous speed as a rider at the bottom. However, the instantaneous velocities are in opposite directions. If the rider at the top has an instantaneous velocity of 4 m/s [E], then the rider at the bottom has an instantaneous velocity of 4 m/s [W].
Page 20
Name:
Questions:
1. A spider climbing up a wall at a constant velocity travels 24 mm in 4.0 s. What is the velocity of the spider?
2. A circus van moves 52 km [E] in the first hour, 41 km [W] in the second hour, and 30.5km
[W] in the next half hour. Calculate a) the average speed of the circus van. b) the average velocity of the circus van.
3. A delivery van, parked 202 m [E] of a police car, moves to a position 608 m [E] of the police car in 18 s. What is the average velocity of the delivery van in km/h?
Page 21
4. Annie is playing baseball. She hits a flyball to left field, and rounds first base 3.5 s later. She reaches third base 10.2 s after leaving home plate. The distance between the bases is 27.4 m.
Calculate a) Annie's average speed between first and third base. b) her average velocity between first and third base, if the base lines form an angle of 90° at second base.
5. Sylvester is training for a boxing match. He runs due north at an average speed of 16 km/h for the first 8.0 km and returns to the training camp at an average speed of 10.1 km/h. Calculate a) Sylvester's average speed for the run. b) his average velocity for the run. (Are you surprised at the answer?)