Activity: What is a Compound
advertisement

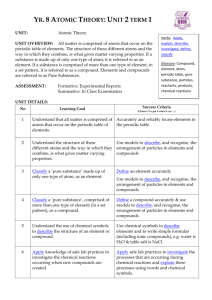
Name ____________________________________________________________ What is a Compound.2015 Date _______________ hydrogen hydrogen Activity: What is a Compound? oxygen Goal: To determine that a chemical formula tells us the kind and number of elements that make up the compound. Water molecule Background Information: When two or more elements combine chemically they form a compound. Water, for example, is a compound made up of the elements hydrogen and oxygen. The chemical abbreviation for water is H2O. From this abbreviation you can tell that a water molecule is made up of 2 atoms of hydrogen and 1 atom of oxygen. (When there is no number in front of an element’s symbol it is understood to be one.) Salt, which is abbreviated NaCl is made up of 1 atom of sodium and 1 atom of chlorine. What other compounds are you familiar with? Materials: A variety of common compounds such as salt, zinc oxide (sun block), chalk, baking soda, silk cloth, a rusty nail, aspartame (NutraSweet), sandpaper Procedure: 1. What I Know: Write two sentences about what you already know or think you know about compounds. 2. Examine the common compounds available for you in this activity. 3. Read the labels showing the chemical abbreviations. 4. Using the chart provided, tell the elements and number of atoms of each element that are represented in each compound. (The chart below is just a sample. You will get a larger chart to use for this activity.) 5. What I Observed: Your observations will include the chart you complete below. Compound Chemical Formula Salt (sodium chloride) NaCl Zinc oxide (sun block) 2ZnO Baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) Silk cloth NaHCO3 Aspartame (NutraSweet) C14H18O5N2 Rust (Iron oxide) 3Fe2O3 Chalk (limestone) CaCO3 Sand paper (aluminum oxide) Al2O3 7. 1st element and number of atoms 2nd element and number of atoms 3rd element and number of atoms 4thelement and number of atoms C10H18O5N4 Questions: Answer the following questions in complete sentences. Be sure to restate the question in your responses. a. What’s the difference between an element and a compound? b. What is the difference between an organic and an inorganic compound? c. List the four categories of organic compounds. 8. What I Wonder: Pose a why or how question that you may still have about the topic of compounds. 9. What I Learned: CER (Claim, Evidence, Reasoning) Writing Prompts: Use the following prompts to help you construct your lab conclusion, What I Learned. Goal: State the goal of this lesson. (See the top of the first page of this activity.) The goal of this lesson is… Claim: What did you learn from the activity that satisfies the goal of this lesson? This is an I Learned statement. I learned that a chemical formula tells me……. Evidence: How can you prove from your observations (data) that you learned what you claim? This can be a general statement that you will explain in detail in your explanation. I know this because…. How does a chemical equation tell you the kind and number of elements in a compound? What did the symbols in the equation tell you? What did the subscripts in the equation tell you? What did the coefficients in the equation tell you? Explanation/Reasoning: Include the scientific principles that connect the evidence and claim. (What’s the science that helps explain your claim and evidence. The information can be from what you learned in our class discussions, the textbook, or other resources that will help support your claim or enhance your explanation. 1. 2. 3. 4. What is an atom? What are the parts of an atom? What is an element? What is a compound? Conclusion: Summarize the claim of the lesson (reword the claim) and include a connection to self, text, or world. 1. What are the common elements found in living things? 2. Are you made up of compounds? 3. What are some compounds that make up living things, including you? You can also use your warm-ups and previous labs as sources for your connections.