Click Here - Mark E. Moore
advertisement

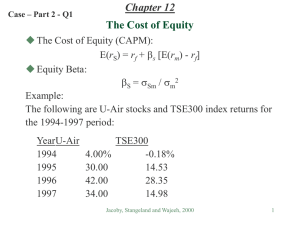
Cost of Capital Estimation Finance – Fin3321 – Moore Cost of Capital Basics: Recall, there are essentially three basic types of cost of capital: Cost of Equity (Ke) Cost of Debt (Kd) – Comes in both a before and after-tax variety Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC) – comes in both a before and after-tax variety Different valuation models use different cost of capital inputs Cost of Equity (applications): Used for valuation models that are valuing distributions solely to shareholders (equity) Example models include Discounted Dividends, Discounted Residual Income, Discounted Abnormal Earnings Growth, and the Long-run Residual Income Perpetuity Model 1 Cost of Equity (Estimation Methods): Regression Method using CAPM o Recall the Capital Asset Pricing Model o CAPM is a linear equation model (just like Y = a + bX from stats) o CAPM may be estimated using linear Regression analysis o Data inputs required: Firm Returns (monthly) in cum-dividend form and split adjusted Market Returns (monthly) – use the S&P 500 as a proxy for the market Risk-Free Rate (return) information o Sources of Data You will need to compute the firm’s monthly return from price and dividend data. Download the past 80 months of price and dividend data for the firm you are analyzing from Yahoo Finance’s historical price data for the company you are interested. You can save this in Excel format. You can click on the Yahoo Finance link for the S&P 500. Get the past 80 months of price data for the index. The return is simple as it can be computed at the monthly change in the price index. 2 Riskless return data may be obtained from the St. Louis Federal Reserve website. Use the following link: http://research.stlouisfed.org/fred2/ Follow the interest rate link an go to the Treasury Constant Maturity information. Since CAPM is silent as to the appropriate riskless return, we will test (empirically) whether the point on the yield curve matters. Hence, download the following 5 treasury series for the past 80 months of yields: o 3month, 1 year, 2 year, 7 and 10 year. o Running the Regressions: After you organize the data, take the monthly difference between the market return and the riskless yield to get the market risk premium. For the regression model, your dependent variable is the firm’s return and the independent variable is the market risk premium. For each point on the yield curve, run 5 regressions: most recent 72 months, 60 months, 48 months, 36 months and 24 months. The purpose of this is to test the stability of Beta over time (you have just estimated the firm’s Beta). For each point on the yield curve, pick the beta for the model with the highest adjusted R-squared (explanatory power). When you have finished, you should have 5 estimates of Beta (one for each point on the curve). 3 Take the best Beta and plug it back into CAPM in order to estimate the firm’s cost of equity. You must determine the appropriate MRP You will need to size adjust your estimated returns. You will need to estimate a 95% confidence interval on your cost of capital. You will need to perform an analysis of the statistical results from the regression analysis to address issues such as Beta stability, significance, explanatory power of CAPM and whether or not the point on the yield curve really matters. If the point on the yield curve does matter, then you can say something important regarding the investment horizon of the equity class for your firm. o Alternative Cost of Equity Estimation Method Estimate the cost of equity that supports the currently observed stock price. Solve for the cost of equity that satisfies the following equation: Where (P/B) is the current market to book ratio, ROE is the average return on equity you are forecasting over the next 10 years and g is the forecast average earnings growth rate (or growth in Book value of equity) over the next 10 years. 4 Compare this implied (backdoor) cost of equity with the result obtained from the regression analysis. 5