Net Primary Productivity and Dissolved Oxygen Lab
advertisement

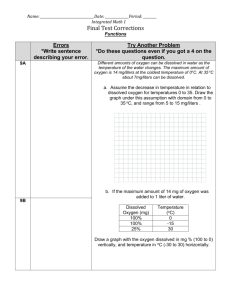
APES: Net Primary Productivity and Dissolved Oxygen Lab Name:_______________________ Introduction: In the atmosphere, the concentration of oxygen is about 200mL/L of air and in water it is usually between 5 and 10 mL/L. The concentration of dissolved oxygen in aquatic environments is very important to water quality. The amount of dissolved oxygen is dependent on many factors, such as salinity, pH, atmospheric pressure and especially temperature. Usually increasing temperature and salinity can generally cause a decrease in DO. The distribution of oxygen can be highly variable and affected by wind, currents and tides. Also since it is the partial pressure of oxygen that affects solubility, altitude can be an influence. At higher elevations, the air is less dense, therefore high altitude lakes contain less dissolved oxygen. At 4000m (~13,000ft) lakes have a DO about 2/3 the sea level value. Since some dissolved oxygen can come from photosynthetic plants, nutrients can play a role in DO values. In this lab, you will investigate the biological impacts on DO levels by measuring the photosynthetic and respiratory rates. Directions: 1. Go to Mrs. Schwichtenberg’s Wikipage 2. Click on NPP Lab Link on today’s date 3. Follow the directions below as your work through the tutorial. Make sure to read and do everything on the tutorial. Key Concept 1: Disolved Oxygen Availability 1. List and describe the 5 factors that affect the amount of DO in water. Work through Key Concepts 2 – 4. Click Next. Design of the Experiments A. Temperature vs. DO saturation - We will not be measuring DO in class. How does temperature affect the level of dissolved oxygen? For this experiment, the DO levels were recorded at 3 temperatures. Use the nomogram on your Formula sheet to calculate the saturation of oxygen. Table 1. Effects of Varying Water Temperatures on Dissolved Oxygen Saturation Water Temperature Dissolved Oxygen reading (mg O2/L) Saturation of Oxygen (%) (degrees C) From nomograph 5 6 mg O2/L 20 5 mg O2/L 30 3 mg O2/L 1. What is the effect of temperature on dissolved oxygen readings AND on the amount of oxygen (saturation) it can hold? 2. At water temperature, of 25C, what would be the concentration, in mg/L, of dissolved oxygen at 100% saturation? 3. RESEARCH IT on your own! Increased water heat causes thermal pollution. What are a. Sources of thermal pollution in streams, rivers and larger bodies of water? b. The effects of thermal pollution on aquatic life B. A Model of Productivity as a Function of Lake Depth 1. Go to Design of Experiments – A Model of Productivity as a Function of Lake Depth and review the experimental set-up. 2. Make sure that you ALSO complete the three “A Closer Look” sections to help you see productivity under Initial, Light and Dark situations. Hypothesis: Using an “if…then” hypothesis format, write a hypothesis on the effects of changing light levels will have on the levels of dissolved oxygen present in the different containers. C. Sample Problem 1. Read the sample problem scenario. 2. Use the formulas, your notes, and the images to complete the table below. DO NOT CLICK CHECK ANSWER UNTIL MRS. SCHWICHTENBERG APPROVES YOUR WORK! MRS. SCHWICHTENBERG APPROVAL _____________ % Light 0 2 10 25 65 100 Bottle Gross Productivity (LB – DB) Net Productivity (LB – IB) Graph the data above below for both GPP & NPP What is the effect of decreasing light levels on DO production in mg O 2/L? What is the effect of decreasing light levels on GPP? On NPP? * Take the quiz at the end of the tutorial. Write your score here: _____/______ Analysis of Data Samples with DO readings of (in mg O2/L) 7.95, 6.55, 5.6, 4.1, 7.3, 7.85 Table 3. Gross Productivity and Net Productivity for Experimental Bottles % Light DO reading Gross Productivity (LB – DB) Net Productivity (LB – IB) (mg O2/L) 0 2 10 25 65 100 Analysis and Applied Research (use the back of this page or additional pages if you need more room) 1. How does the level of light affect the rate of photosynthesis and respiration? 2. How does the level of light affect the GPP and the NPP? 3. At what light intensity would you expect there to be no gross productivity? No net productivity? 4. Would you expect the DO in water taken from a stream entering a lake to be higher or lower than the DO taken from the lake itself? Explain. 5. Would you expect the DO concentration of water samples taken from a lake at 7:00am to be higher or lower than samples taken at 5:00pm? Explain. 6. In the following drawings of identical containers with identical fish but with different volumes of water, which one A or B, would have more oxygen available to the fish? Explain. A 7. B Research it! The Chesapeake Bay currently suffers from nutrient overload, which results in the overproduction of phytoplankton. How will an overproduction of phytoplankton affect the SAVs (submerged aquatic vegetation – AKA: seaweed) that populate the bottom of the Bay? Make sure to include citations and a literature cited for this.