Circulatory System 2012 Study Guide - TCHS
advertisement

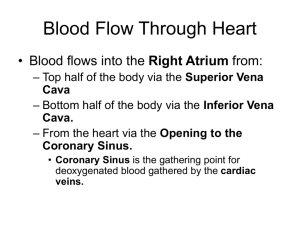
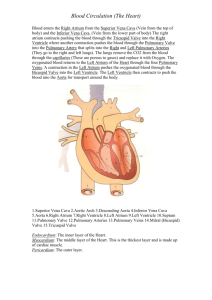
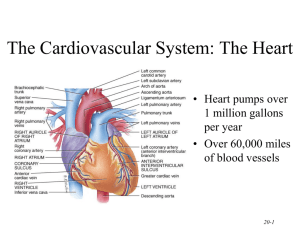
Anatomy Study Guide Name__________________________ Blood 1. Identify which is the Monocyte, lymphocyte, neutrophil, and eosinophil from the above pictures. a. ________________ b. ________________ c. ________________ d. ________________ 2. Leukemia refers to cancerous conditions of _______________________ 3. Hemorrhagic anemias result from ____________________ 4. What is hemoglobin? ______________________________ 5. What makes up hemoglobin? _____________________________________________ 6. What is Leukopenia? _________________________________________________________________ 7. A person with type B blood could receive blood from people with what type of blood? _________________________________________________________________ 8. Granulocytes called neutrophils are phagocytic and the most numerous of all white blood cell types. a. True b. False 9. Which blood type is called the universal donor? _____________________ 10. Which of the following is a regulatory function of blood? a. delivery of oxygen to body cells b. transport of metabolic wastes from cells c. prevention of blood loss d. maintenance of normal pH in body tissues 11. What are the phases of erythropoiesis? _________________________________________________________________________ 12. Which of the following might trigger erythropoiesis? a. hypoxia of EPO-producing cells b. decreased tissue demand for oxygen c. an increased number of RBCs d. moving to a lower altitude 13. An individual who is blood type AB negative, can receive blood from people with what blood type? _______________________________________________________ 14. When neither anti-A nor anti-B serum clots on a blood plate, the blood is type ________. 1. 2. 3. 4. 15. Place the following in correct developmental sequence:_____, ____, _____, ______ reticulocyte proerythroblast normoblast late erythroblast 16. Which of the following is not a cause of bleeding disorders? a. thrombocytopenia, a condition of decreased circulating platelets b. excess secretion of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) c. a defect in the clotting cascade d. vitamin K deficiency 17. What makes up the “formed elements? _____________________________________________ 18. What is plasma? _______________________________________________ 19. What are some characteristics of platelets? _________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 20. The formed element _________________ can kill parasitic worms. 21. Where and how is iron stored in the body? a. White blood cells b. In Red blood cells c. In the hemoglobin of Red blood cells d. Free flowing in the blood stream unbound to anything 22. Describe the function of the following leukocytes. a. Basophils b. Monocytes c. Erythrocytes d. Neutrophils e. Eosinophils. 23. What is Dipedesis? 24. What is polycythemia (symptoms/causes)? 25. When can erythroblastosis fetalis not possibly happen in the child of an Rh- mother? a. If the child is type O+ b. Child is Rh+ c. If the father is Rh+ d. If the father is Rh26. What organ regulates erythrocyte production? Heart Use the graph above to answer the following questions. Place the correct letter that corresponds to the correct question. 27. Atrial depolarization. ______________ 28. Point after which pressure begins to rise in the aorta. ___________ 29. Ventricular repolarization. ______________ 30. The myocardium receives its blood supply from the coronary arteries. a. True b. False 31. Congestive heart failure means that the pumping efficiency of the heart is depressed so that there is inadequate delivery of blood to body tissues. a. True b. False 32. What actually causes your heart sound? _________________________________________________ 33. Hemorrhage with a large loss of blood causes ________. a. a lowering of blood pressure due to change in cardiac output b. a rise in blood pressure due to change in cardiac output c. no change in blood pressure but a slower heart rate d. no change in blood pressure but a change in respiration 34. Why is the left ventricle thicker than the right ventricle? ______________________________________________________________________ 35. Blood within the pulmonary veins returns to what part of the heart? ____________________________________________________________ 36. The source of blood carried to capillaries in the myocardium would be the ________. a. coronary sinus b. fossa ovalis c. coronary arteries d. coronary veins 37. If cardiac muscle is deprived of its normal blood supply, damage would primarily result from ________. a. decreased delivery of oxygen b. a decrease in the number of available mitochondria for energy production c. a lack of nutrients to feed into metabolic pathways d. an inadequate supply of lactic acid 38. Which vessel of the heart receives blood during right ventricular systole? _________ 39. The location/function of the following involved in the conduction system of the heart: a. Purkinje fibers b. AV bundle c. SA node d. AV node 40. Know the following layers of the heart. a. Endocardium b. Epicardium c. Myocardium 41. Where is the tricuspid valve? ___________________________________________ 42. The tricuspid valve is closed ________. a. while the ventricle is in diastole b. when the ventricle is in systole c. while the atrium is contracting d. by the movement of blood from atrium to ventricle 43. During the period of ventricular filling ________. a. pressure in the heart is at its peak b. blood flows passively through the atria and the open AV valves c. the atria remain in diastole d. it is represented by the P wave on the ECG 44. What are Purkinje fibers? ________________________________________________________________________ 45. What is bradycardia? 46. What vessel carries oxygenated-rich blood from the lungs? 47. Which statement best describes arteries? a. All carry oxygenated blood to the heart. b. All carry blood away from the heart. c. All contain valves to prevent the backflow of blood. d. Only large arteries are lined with endothelium. 48. What is Foramen ovale? _________________________________________________________ 49. Damage of the ______________ is referred to as heart block 50. What does the P wave of a normal ECG indicate? 51. Know the function of the following valves. a. b. c. d. Pulmonary valve Bicuspid valve Aortic valve Tricuspid valve 10 1 2 Makes sure you know the parts of the heart, heart vessels and the valves. 3 9 4 8 5 7 6 52. Use the picture in the previous question to explain the pathway of blood through the heart (when it enters the right atrium all the way until it leaves through the aorta to the rest of the body). Make sure you include when the blood leaves the heart and goes to the lungs. Make sure that you use the following words: right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, left ventricle, tricuspid valve, bicuspid valve, aortic valve, Pulmonary valve, vena cava, aorta, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, and lungs Know the anatomy a heart. Blood Vessels 1. The largest artery of the body. 2. supplies the duodenum and stomach with blood 3. supplies the pelvic structures with blood 4. major supply to the cerebral hemisphere with blood 5. supplies the lower limbs with blood 6. Know the function and characteristics of the follow: 1. capillaries 2. large veins 3. large arteries 4. arterioles 7. What is pulse pressure? 8. What is the function of the hepatic portal vein? 9. The ductus venosus refers to ____________