Dentzer_3.01 notes - Westbrooks-Wiki
advertisement

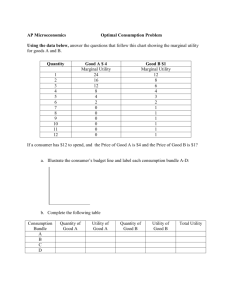
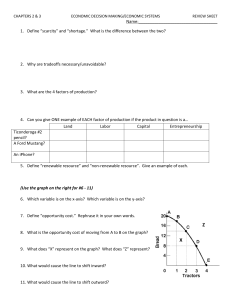
SEM I 3.01 Notes Objective: Explain economics and identify basic economic resources. Economics is the study of how to meet the unlimited wants of a society with its limited resources. Resources include all things used in producing goods and services. . Economic resources are land, labor, and capital that can be used to produce the needs and wants that people consume. Land, also known as a natural resource, includes everything contained in the earth or found in the seas. Labor, human resources, includes all workers in the economy, including full- and parttime workers, managers, and professional people in both the private and public sectors. Capital includes money to start and operate a business, as well as goods used in the production of other goods. Capital can be limited because they deteriorate through use or are of poor quality. For example, ______________ . Scarcity is a condition in which more goods and services are desired than are available. Scarcity forces people, businesses and nations to make choices. Unlimited wants with limited resources results in scarcity. Economic goods are tangible items. Examples: CD players or sports equipment Economic services are intangible. Examples: going to the circus Entrepreneurship incorporates the skills of people who are willing to take the risk of starting their own business. Entrepreneurs organize economic resources in order to create goods and/or services needed and desired in an economy. B. Describe the five economic utilities . Utility is an economic term referring to the added value or “usefulness” of a product. Five types of economic utility. Form utility is the value added by changing raw materials or putting parts together to make them more useful. Examples: __________ . Place utility is the value added by having a product where customers can buy it. Examples: playing a football game at a stadium Time utility is the value added by having a product at a certain time of year or a convenient time of day. Example: __________ . Possession utility is the value added by exchanging a product for some monetary value Example:_____________. Information utility is the value added by communicating with the consumer. Example: ______________________________________________________________. C. Discuss the three basic economic questions and the role of the government of each system. The three basic economic questions are: What ______________________________________should be produced? _________________________________goods and services be produced? ________________________should the goods and services be produced? In a market economy, there is ____________________________________________the three basic economic questions; the market answers them. Consumers decide what should be___________________________________. Businesses decide how____________________________________________. The people who have the money to purchase products___________________________ _____________________________. . In a __________________economy, the government answers the three basic economic questions. The government officials or leaders decide what should be ______________. The government runs the__________________________________________________. The government also decides who will________________________________________. In a traditional economy, the system is based on the ways________________________. For example, the __________________________and___________________________. Mixed economies are ___________________________market systems, nor are they completely controlled by________________________________________. They are a mix, or blend, of the two. All economies presently are__________________________. Capitalism. The people _________________________________________who represent their constituents’ interests. For example, the United States and Japan. Socialism. Although most socialist countries are_______________________, the socialist economy has__________________________________________________. The government tries to reduce the differences between the____________________. The socialist model is based on the________________________________________. Examples: _____________________ ___________________ _________________. Communism. Communist countries have a government that is run by_______________ ___________________________________________. People are assigned jobs. ______________________________are told what type of schooling they will receive. Examples: _____________________ ___________________ _________________. . D. Explain supply and demand. Supply is ___________________________________________________________and sell at a ____________________________during a certain period of time. Producers prefer to supply when the price is________________________; this is known as a sellers’ market. Demand is a consumer’s _____________________________________________at a given price during a certain___________________________________. Consumers prefer to buy when the price is_____________________; this is known as a ________________________market. The Law of Supply and Demand is an ________________________________that states the supply of a good or service will __________________________when demand is ___________________________and ________________________ when demand is__________________. Elasticity is the degree to which demand______________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________. Example: __________________________________________________________. Demand__________________________________. Elastic demand refers to how _________________________________________ _________________________________________________demand for that product. Example: __________________________________________________________. Inelastic demand refers to a condition in the market where ____________________ __________________________have very little affect on the ________for that product. Example: __________________________________________________________. Factors that affect the elasticity of demand Availability of substitutes. If a substitute is_____________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________. Example: __________________________________________________________. Example: __________________________________________________________. Example: __________________________________________________________. Brand loyalty. Many customers will only____________________________________. In general, they will accept________________________________________________. In this situation,_________________________________________________________. Example: __________________________________________________________. Example: __________________________________________________________. Price relative to income. When an __________________________________of a good or service does not have a major __________________________________________, the demand is usually______________________________. When an __________________________of a good or service has a major impact on a customer’s budget, the customer___________________________________________. In this case, the demand__________________________________________________. Example: __________________________________________________________. Example: __________________________________________________________. Luxury vs. necessity (want vs. need). When a product is a______________________ ________________________________. When a product is a luxury, demand is most likely to be elastic. Example: __________________________________________________________. Urgency of purchase. If a purchase must be made immediately, demand tends to be _________________________. Example: __________________________________________________________. E. Phases of a business cycle and the impact of each on the sports and entertainment industry. The business cycle is the __________________________________through four recurring phases –_____________________ __________________________ __________________________ _____________________________________.. Explain the phases of a business cycle. I.________________________(Peak) 1.____________________________________ 2. ____________________________________ 3. ____________________________________ 4. ____________________________________ 5. ____________________________________ II. ____________________________________ 1.____________________________________ 2. ____________________________________ 3. ____________________________________ 4. ____________________________________ III. ____________________________________(Trough) 1.____________________________________ 2. ____________________________________ 3. ____________________________________ 4. ____________________________________ IV.__________________________________________ 1.____________________________________ 2. ____________________________________ 3. ____________________________________ 4. ____________________________________ 5. ________________________________________