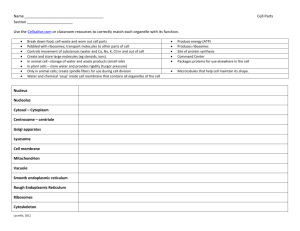
cell organelles
advertisement
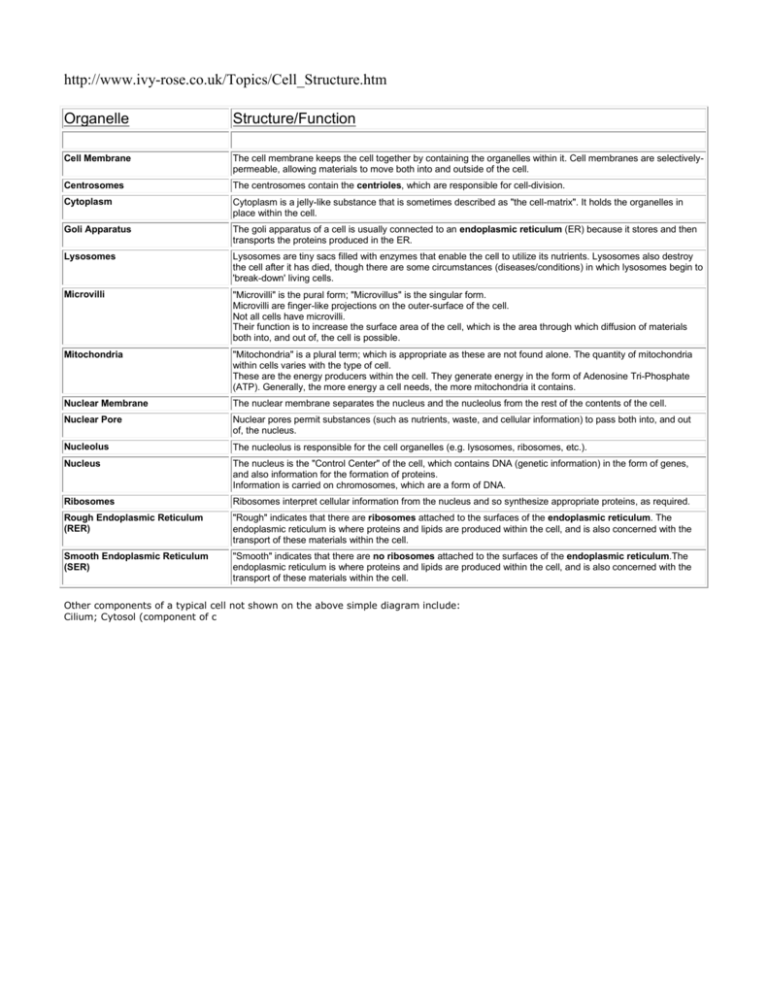
http://www.ivy-rose.co.uk/Topics/Cell_Structure.htm Organelle Structure/Function Cell Membrane The cell membrane keeps the cell together by containing the organelles within it. Cell membranes are selectivelypermeable, allowing materials to move both into and outside of the cell. Centrosomes The centrosomes contain the centrioles, which are responsible for cell-division. Cytoplasm Cytoplasm is a jelly-like substance that is sometimes described as "the cell-matrix". It holds the organelles in place within the cell. Goli Apparatus The goli apparatus of a cell is usually connected to an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) because it stores and then transports the proteins produced in the ER. Lysosomes Lysosomes are tiny sacs filled with enzymes that enable the cell to utilize its nutrients. Lysosomes also destroy the cell after it has died, though there are some circumstances (diseases/conditions) in which lysosomes begin to 'break-down' living cells. Microvilli "Microvilli" is the pural form; "Microvillus" is the singular form. Microvilli are finger-like projections on the outer-surface of the cell. Not all cells have microvilli. Their function is to increase the surface area of the cell, which is the area through which diffusion of materials both into, and out of, the cell is possible. Mitochondria "Mitochondria" is a plural term; which is appropriate as these are not found alone. The quantity of mitochondria within cells varies with the type of cell. These are the energy producers within the cell. They generate energy in the form of Adenosine Tri-Phosphate (ATP). Generally, the more energy a cell needs, the more mitochondria it contains. Nuclear Membrane The nuclear membrane separates the nucleus and the nucleolus from the rest of the contents of the cell. Nuclear Pore Nuclear pores permit substances (such as nutrients, waste, and cellular information) to pass both into, and out of, the nucleus. Nucleolus The nucleolus is responsible for the cell organelles (e.g. lysosomes, ribosomes, etc.). Nucleus The nucleus is the "Control Center" of the cell, which contains DNA (genetic information) in the form of genes, and also information for the formation of proteins. Information is carried on chromosomes, which are a form of DNA. Ribosomes Ribosomes interpret cellular information from the nucleus and so synthesize appropriate proteins, as required. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) "Rough" indicates that there are ribosomes attached to the surfaces of the endoplasmic reticulum. The endoplasmic reticulum is where proteins and lipids are produced within the cell, and is also concerned with the transport of these materials within the cell. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) "Smooth" indicates that there are no ribosomes attached to the surfaces of the endoplasmic reticulum.The endoplasmic reticulum is where proteins and lipids are produced within the cell, and is also concerned with the transport of these materials within the cell. . Other components of a typical cell not shown on the above simple diagram include: Cilium; Cytosol (component of c