Review key Part II
advertisement

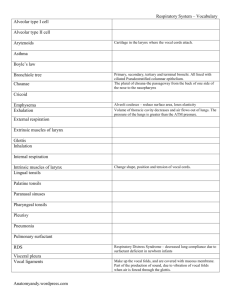
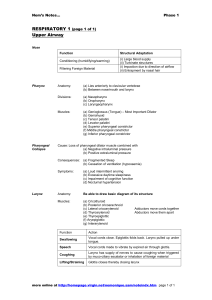
1. AP Unit 2 Comprehensive review part II Name: roster # date: The epiglottis is: a. Broad, flat fibro-cartilage structure b. Spoon-shaped c. forms the roof of the larynx d. all of these 2008 2. The epiglottis covers the glottis which is the opening of the: a. Lower airway c. Lower airways b. Larynx d. All of these 3. The base of the epiglottis is anchored to the: a. posterior internal surface of the thyroid cartilage of the larynx b. anterior internal surface of the thyroid cartilage of the larynx 4. TRUE/FALSE the epiglottis is attached to the vallencula which in turn is attached to the base of the tongue. 5. When the tongue moves upward, the epiglottis is: a. pulled over the glottis b. pulled off the glottis 6. the larynx is formed of three large external cartilages: a. the epiglottis d. a and b only b. the cuneiform cartilage e. a and c only c. the cricoid cartilage 7. The three pairs of small internal cartilages of the larynx are called the: a. arytenoid cartilage d. a, b only b. cuneiform cartilage e. a, b and c c. corniculate cartilage 8. TRUE/FALSE the glottis is a triangle created by the true vocal cords 9. To the a. b. c. right and the left of the true vocal cords are tissue folds that are called: the vestibular folds the false cords both 10. TRUE/FALSE The vocal cords come together and separate during quiet breathing so that the glottis is always slightly open. 11. The only time that the glottis is closed completely is during a. Singing d. a, b only b. Valsalva maneuver e. a, b and c c. during laryngospasm f. b and c 12. TRUE/FALSE To close the glottis completely requires not only bringing the vocal cords together but the person tightens all chest muscles at the same time 13. During a Valsalva maneuver a sudden surge of – pressure is created for expulsion phase of the cough. a. Positive b. Negative 14. To perform this Valsalva maneuver the person must --- forcefully against a closed glottis. a. Inhale b. Exhale 15. `The expulsion phase of the cough happens as the person --- the glottis. a. Suddenly closes b. Suddenly opens 16. Effects of a Valsalva maneuver include--- which will decrease the cardiac output: a. Decreased intra-thoracic pressure b. Increased intra-thoracic pressure c. Increase intracranial pressure as blood flow from the head is hampered d. A and c e. B and c 17. The function of the external cartilages of the larynx is: a. Protective b. To manipulate the vocal cords 18. During the act of swallowing: i. The food bolus moves backward and up into the hard palate ii. The food bolus moves backward and down into the orophrynx iii. The tongue goes up iv. The tongue moves down A. i , iii B. ii, iii C. i, iv D. ii, iv 19. 20. 21. 22. The most critical moment of the swallowing is when the food is: a. in the oral cavity b. in the laryngeopharynx c. in the esophagus d. in the larynx The soft palate closes off the: a. Nasal passage b. Glottis The tongue moves forward; a. The food bolus moves back b. The vallecula pulls the epiglottis closed The vallecula is: a. Cartilage attached to the base of the tongue b. Tissue attached to the base of the tongue c. also attached to the epiglottis d. A and c e. B and c c. Both c. The vallecula pushes the epiglottis closed d. A and b e. B and c 23. To cough effectively one must: a. Drop the diaphragm about 3-6 cm to get a 1-2 Liter volume into the lung b. Be able to keep the diaphragm down for an inspiratory hold c. Be able to close the glottis d. Be able to push the abdominal contents up into the diaphragm to create a positive pressure of +100 to +200 cm H20 e. All of these 24. Sitting up will facilitate coughing by: a. getting gravity to help raise the diaphragm during the expulsion phase b. getting gravity to help drop the diaphragm during the deep inspiratory phase 25. Peripheral distribution of gas during the inspiratory hold phase of 3 seconds of the cough can get air down to: a. The 3rd -4th branching c. The 13-15th branching th b. The 6-7 branching d. The alveoli 26. The true cords close the glottis for about 0 .2 seconds and the person exhales against this closure. The resulting intrathoracic pressure is a. +100 to + 200 cm H20 pressure. b. -100 to - 200 cm H20 pressure 27. TRUE/FALSE To assist the abdominal muscles, the feet must be on a flat surface 28. During the expulsion phase, the glottis flies open and the velocity of the cough exhalation can reach: a. 300-500 LPM. b. 300-500 mph