T2 CNM KEY - PESIT South Campus
advertisement

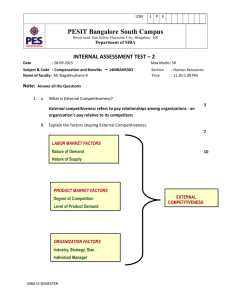
USN PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of MBA INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST – 2 Date : 28/09/2015 Max Marks: 50 Subject & Code : CONFLICT AND NEGOTIATION MANAGEMENT14MBAHR306 Section: III Sem –HR Name of faculty : Dr. J.SHANTHILAKSHMI Time 8.30- 11.00AM Note: Answer all questions 1 (a) Briefly discuss the causes for Team Conflict Leadership Power Structure Authority (b) Briefly explain the Cosier Schank model on Conflict Resolution This model focus on Programming and transforming the conflict in productive way Two Approaches are: 1.Devil’s Advocate decision Program 2.Dialectic decision model (3 marks) (7 marks) Devil’s Advocate Model(6 steps) 1.Proposed model course of action is generated 2.Devil’s Advocate is assigned to criticize the proposal 3.Critics are presented to Key decision makers 4.Any additional information relevant to issue is gathered 5.The decision to propose, adapt or discontinue the course of action is taken 6.Decision is monitored 1.A proposed course of action is generated 2.Assumptions underlying proposals are identified 3.Conflicting counter proposal is generated based on the various assumptions 4.Advocates of each position debates on the merits of each position 5.Decisions to adapt either of two positions are taken Decisions are monitored (c) Comment on the requirement for listening skills in Conflict management (10 marks) • Listening is composed of six distinct components theses dimensions will be affecting the way in which conflicts are resolved • Hearing: The physiological process of receiving sound and/or other stimuli. Attending: The conscious and unconscious process of focusing attentionon external stimuli. Interpreting: The process of decoding the symbols or behavior attended to. • • MBA III SEMESTER -HR USN PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of MBA • • • Evaluating: The process of deciding the value of the information to the receiver. Remembering: The process of placing the appropriate information into short-term or long-term storage. Responding: The process of giving feedback to the source and/or other receivers. 2 (a) What is Negotiation and how do you differentiate Negotiation from Collective Bargaining In determining whether the parties are “bargaining in good faith”, the relies on it’s totality-of-conduct concept rather than looking at individual actions. Whereas collective bargaining may not be focusing on Totality and it focus more on Win-lose (3 marks) (b) Write a note on the views related to gender in Negotiation (7 marks) 1.Relational View: Women focus more on the relationship among the parties and men focus more on the content Women focus more on interaction goal – men focus more on Task specific goals 2.Beliefs about ability and worth: Particularly in salary negotiation women are more likely to see their worth determined by employer It was also demonstrated that men expect to Earn more than women Also women may feel less comfortable operating in the social context of negotiation 3.Embedded View of Agency: Women tend not to draw strict boundaries between negotiating and other aspects of their relationship, they see that negotiation is a behaviour that occurs in relationship Men tend to demarcate the negotiation and other behaviours in the relationship and to signal the beginning and end 4.Control thru empowerment: Women are likely to seek empowerment where there is an interaction among all the parties in relationship to build connection and enhance everyone’s power Men may use power to achieve goals or force other party 5.Problem solving thru dialogue: Men use dialogue to convince other party and their position Uses various tactics to win 6.Perception and streotyping (c) Discuss the factors related to successful negotiation and Briefly explain the value claiming and value creating strategies Any Negotiation to be successful requires Planning Process Elements of Planning Process are: Defining the issues Assembling Issues and Defining the Bargaining Mix (Determine which issues are more important and determining whether issues are linked together) MBA III SEMESTER -HR USN PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of MBA Defining the interests (Directly related to focal issues, process based interest, Relationship based interests may be expressed) Defining limits and alternatives (Resistance points /alternatives) Defining one’s own objectives and opening bids Assessing the constituents and social context in which negotiation will occur Analysing the other Party Planning the issue presentation and defense Defining Protocol (10 marks) 3 Case study (Compulsory) (10 marks) Explain in detail on Thomas Kilman’s Model on Conflict Management Techniques and the characters of each style. The TKI is designed to measure a person's behavior in conflict situations. Individual’s behaviour in conflict situation may be described with two dimensions: (1) assertiveness, the extent to which the person attempts to satisfy his own concerns, (2) cooperativeness, the extent to which the person attempts to satisfy the other person's concerns These two basic dimensions of behavior define five different modes for responding to conflict situations such as Competing: Competing is assertive and uncooperative— an individual pursues his own concerns at the other person's expense. This is a power-oriented mode in which you use whatever power seems appropriate to win your own position—your ability to argue, your rank, or economic sanctions. Competing means "standing up for your rights," defending a position which you believe is correct, or simply trying to win. Accommodating: Accommodating is unassertive and cooperative the complete opposite of competing. When accommodating, the individual neglects his own concerns to satisfy the concerns of the other person; there is an element of self-sacrifice in this mode. Accommodating might take the form of selfless generosity or charity, obeying another person's order when you would prefer not to, or yielding to another's point of view. Avoiding: Avoiding is unassertive and uncooperative the person neither pursues his own concerns nor those of the other individual. Thus he does not deal with the conflict. Avoiding might take the form of diplomatically sidestepping an issue, postponing an issue until a better time, or simply withdrawing from a threatening situation. Collaborating: Collaborating is both assertive and cooperative the complete opposite of avoiding. Collaborating involves an attempt to work with others to find some solution that fully satisfies their concerns. It means digging into an issue to pinpoint the underlying needs and wants of the two individuals. Collaborating between two persons might take the form of exploring a disagreement to learn from each other's insights or trying to find a creative solution to an interpersonal problem. Compromising: Compromising is moderate in both assertiveness and cooperativeness. The objective is to find some convenient, mutually acceptable solution that partially satisfies both parties. MBA III SEMESTER -HR USN PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of MBA It falls intermediate between competing and accommodating. Compromising gives up more than competing but less than accommodating. Likewise, it addresses an issue more directly than avoiding, but does not explore it in as much depth as collaborating. In some situations, compromising might mean splitting the difference between the two positions, exchanging concessions, or seeking a quick middle-ground solution. MBA III SEMESTER -HR