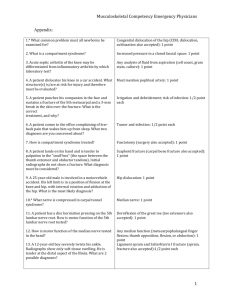
BoardII RevNotes - NYCC SP-01
advertisement

Associated Clinical Sciences Introitus - vaginal orifice. Gravida - number of pregnancies. Dyspareunia - pain during or after coitus. Para - number of live births. Dystocia - painful or difficult labor. Pseudocyesis - false pregnancy, pseudopregnancy. Dysmenorrhea - painful menstrual cycles, caused Menarche - first menstrual cycle. by secretion of prostaglandins form uterus. Climacteric - cessation of menses, menopause. Colostrum - initial breast milk secreted, contains IgA. Lanugo - fine hair covering newborns body. Not found in mature breast milk. Meconium - newborn’s first intestinal discharge. Vernix Caseosa - cheesy covering on skin of newborn. Lochia - vaginal discharge after delivery. Lactation - can cause normal amenorrhea. Mittleschmerz - ovulation pain. Alpha fetoprotein - increased amounts indicate neural tube defect. Chloasma gravidarum - mask of pregnancy, brownish pigmentation of the face. Hyperemisis gravidarum - pernicious vomiting of pregnancy. Cardinal signs of toxemia (HEP) Hypertension, Edema, Proteinuria. Preeclampsia - toxemia of pregnancy (3rd trimester) Eclampsia - toxemia of pregnancy with convulsions (3rd trimester). Braxton Hicks Contractions - intermittent contractions of uterus after 3rd month of pregnancy. AKA false labor. Embryonic stages - zygotemorulablastula. Signs of Pregnancy: Goodell - softening of the tip of the cervix. Hegar - entire cervix softens. Chadwick’s - bluish discoloration of the vagina. Piskacek - asymmetrical softening and enlargement of the uterus. Ladin - softened area denoting a change between cervix and body of the uterus. Ballottement - movement of the fetus upon pressure to cervix through vagina. Effacement - thinning of the cervix. Quickening - mother’s perception of fetal movement. Lightening - descent of uterus into pelvic cavity 2-3 weeks before labor. Engagement - baby’s head reaches the ischial spines. Stages of Labor: 1st stage - from first meaningful uterine contraction to full cervical dilation(10 cm). Longest stage. 2nd stage - from full dilation to delivery of the baby. 3rd stage - delivery of the baby to delivery of the placenta. Placental complications: Placenta Abrupta - early detachment of placenta from uterine wall. Placenta Previa - low lying placenta, usually interferes with internal cervical opening. Placenta Accreta - retained placenta, MC cause of post partum hemorrhage. APGAR scoring: Appearance(color), Pulse(heart rate), Grimace(reflex irritability), Activity(muscle tone), Respiration(respiratory effort). Moro Reflex - startle reflex in newborns. Rooting reflex - touch the cheek of a baby the head turns to that side. Down’s Syndrome - trisomy 21, mental retardation, low set ears, flat nose or bridge, simian crease on palm or sole. Characterized by an increased incidence of leukemia. Turner’s syndrome - 45X, female with short stature, low posterior hairline, short webbed neck, gonadal dysgenesis. Klinefelter’s Syndrome - 47XXY, male with small testes, gynecomastia, long legs and subnormal intelligence. Paget’s disease - can cause mammary duct carcinoma. Endometriosis - ectopic endometrial tissue (uterine lining). Adenomyosis - endometrial tissue found in the myometrium (muscular layer of the uterus). Leukoplakia - precancerous lesion of white patches on mucous membranes. Dermoid Cyst of the Ovary - teratoma (tumor made up of several germinal layers). Hydatidiform mole - benign trophoblastic tumor, high levels of human chorionic gonadotrophin (HCG). Choriocarcinoma - malignant trophoblastic tumor. Mastitis - localized engorgement of the breast with red streaks. Ovulation - surge of LH precedes, vaginal mucus stringy and clear. 1 Associated Clinical Sciences Uterine involution - occurs during post partum period. Gene Theory of Disease - Autosomal trait passed on by mother. Spontaneous Abortion - MC cause of first trimester abortions, usually attributed to chromosomal defects. CPR on child - 80-100 chest thrusts per minute. Herpes Simplex - causes aseptic meningitis in the neonate. Brachial Artery - best to palpate pulse on an infant. Capillary Hemangioma - typically appears after birthing process on the scalp. Hutchinson’s Signs - indicators of congenital syphilis; pegged teeth, deafness, interstitial keratosis. Karl Jung - collective unconscious. Sigmund Freud - Inner dynamics of the unconscious, free association. Tripartite of the personality: Id - the unorganized, instinctual part, basic instincts. Ego - the perceived self, here and now , reality testing portion. Superego - the conscience. Stages of development(child): Oral, Anal, Phallic. Psychological testing: Rorschach - Ink blot testing used to determine personality disorders. WISC - Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children, 5-16 years old. MMPI - Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory, personality testing. Stanford Binet - MC used intelligence test for young children. Psychological disorders: Psychosis - severe disorganization of the personality associated with depression, delusions and hallucinations. Neurosis - a form of maladjustment in which the person is unable to cope with anxieties, leads to the use of defense mechanisms. Schizophrenia - psychosis in which there is a lack of harmony between aspects of the personality. Involutional melancholia - psychotic behavior associated with the climacteric, accompanied by agitation, delusions, anxiety and paranoid reactions. Defense mechanisms: Reaction formation - the subject denies a disapproved motive or desire by giving strong expression to its opposite. Repression - a guilt or anxiety producing impulse or memory is denied by its disappearance from awareness. Ex: amnesiacs. Bury a memory and not deal with it. Regression - behavior characteristic of an earlier developmental stage. Suppression - disapproved impulses or desires are not overtly revealed, or acted upon. Sublimation - socially unacceptable motives or desires are expressed in socially acceptable forms. Changing behavior to accepted norms. Compulsion - neurosis characterized by an irresistible impulse to perform an act contrary to one’s better judgment or will. Obsession - neurosis characterized by recurrent thoughts, feelings, or impulses that the subject recognizes as morbid and which he feels a strong resistance. Narcissism - self-love or admiration. Affective disorder - major depressive episode. Hysterical - histrionics, theatrical gestures. Schizoid - introverted and withdrawn, emotionally cold and distant. Antisocial - psychotic/sociopath, acting out their conflicts with no remorse or guilt. Paranoid - suspicious attitudes leading to aggressive feelings. Electra complex - libidinous fixation of daughter toward father. Oedipus complex -libidinous fixation of son toward mother. Jacosta complex - libidinous fixation of mother toward son. Phaedra complex - the love and attraction between a stepparent and a stepchild. 2 Associated Clinical Sciences Jurisprudence: Slander - verbal, to say something false about another person. Libel - written, to write something false about another person. To recover one must prove damages. Evidence - anything presented in court used by the judge or jury in making a decision. Hearsay - evidence, which does not derive its value from the witness itself, but gained or acquired from another. Deposition - a sworn statement of fact given before a notary public can be used as evidence. Principal - one who retains an agent to act for him. Contract - a promise to perform for which consideration is given and for which the law recognizes a duty to perform. Must have: 1) mutual consent, 2) consideration, 3) competent parties, 4) object of contract must be legal, 5) reality of consent to contract. Offer + Acceptance = Contract. Informed consent - the patient must be informed of the dangers inherent with a procedure before consenting to it. Expert witness - a person qualified by special studies in special areas of knowledge, allowed to give their opinion. Privileged communication - confidential communication that does not have to be revealed in court. Husband/wife, doctor/patient, lawyer/client. Contributory negligence doctrine - a person may not collect damages if their own negligence contributed to the cause. Partnership responsibility - all partners are liable for the negligence of one another or of an employee. Release of one partner releases liability for all. Termination of partnership - In the event of death surviving partner can buy interest from the deceased estate. Subpoena - a written legal order requiring one to appear in court to give testimony. Summons - an official order to appear in court to respond as a defendant to a charge. Respondent superior - an employer is responsible for the torts (civil wrong) of their employee. Malpractice case - tried in a tort (civil wrong) court. Voir Dire - to speak the truth. Res ipsa loquitor - the thing speaks for itself. Res adjudicata - the matter has been decided. Dermatology: Pruritis - severe itching, cutaneous hyperesthesia. Intertrigo - superficial dermatisis in the folds of the skin. Pustule - small elevation of skin filled with lymph or pus. Vesicle - blisterlike elevation on the skin filled with serous fluid. Bullae - large blisters or skin vesicles filled with fluid, also called blebs. Wheal - round elevation of the skin with a white center and pale red periphery accompanied by pruritis. Nodule - a small node or aggregation of cells. Papule - red elevated area of the skin, solid and circumscribed. Often precede vesicle or pustule formation. Macule - discolored spots or patches on the skin, neither elevated or depressed. Ex: vitiligo, pellagra, rubella. Keloid - overgrowth of scar tissue due to abnormal amounts of collagen in the scar tissue. Albinism - melanocytes do not produce melanin no tissue pigment. Vitiligo - acquired idiopathic destruction of melanocytes resulting in patches of depigmentation (often having hyperpigmented border) Tinea infections - Mycotic (fungal) skin diseases occurring on various parts of the body. Diagnosis confirmed with a Wood’s lamp (UV light). t. barbae - beard t. capitis - head t. corporis - body, AKA ringworm t. cruris - groin/jock t. pedis - foot t. unguium - nails, AKA onychomycosis Stasis (not moving) dermatisis - persistent inflammation of the skin in the lower extremities with a tendency toward brown pigmentation. Associated with venous incompetence. Ex: bed sores, DM, overweight people. Stasis ulceration - commonly seen lower leg and ankle region with diabetes mellitus. Furuncle - staphylococcal infection of a hair follicle or sebaceous (oil secreting)gland. Carbuncle - multiple furuncles. Miliaria - AKA prickly heat, inflammation of sweat glands. Urticaria - AKA hives, characterized by formation of wheals and hives. Psoriasis - dry silvery scales usually on the extensor surfaces. Ex: elbows and knees. Dermatomyositis - Heliotropic rash on the eyelid. 3 Associated Clinical Sciences Rubella - AKA German measles, maculopapular rash 2-3 days. NB question - vaccinate mother to prevent in newborn. Rubeola - AKA measles, acute contagious disease marked by fever, catarrhal (inflammation of mucous membranes) symptoms and rose colored macular eruptions. Koplik’s spots - small red spots with blue white centers on the oral mucosa, usually precede cutaneous eruptions. Varicella - AKA chickenpox, childhood disease characterized by fluid filled subdermal lesions that pass through stages of macules, papules,vesicles and crusts. MC complication is secondary infection. Icthyosis - dry skin (xeroderma), AKA fish skin or scaly skin. Acne - papules, pustules, comedones and inflamed nodules. Inflamed hair follicle or sebaceous gland. Rosacea - chronic inflammation of the nose, cheeks and forehead, MC in middle-age to older people. Characterized by papules, pustules, telangiectasia, erythema and hyperplasia of the soft tissue of the nose. Pityriasis rosea - skin condition which appears in “herald” or “mother” patches, etiology unknown. Impetigo - superficial vesiculopustular lesions with bullae formation and honey colored crusts. Etiology strep or staph. Hyperhydrosis - overactive sweat glands. Lichen planus - pinhead sized papules that coalesce to form rough, scaly, polygranular, blue/purple lesions. Intense pruritis with lesions concentrated on flexor surfaces of arms, trunk and genitalia. Erysipelas - acute febrile disease, cellulitis, vesicles and bullae. Etiology: streptococcal. Pemphigus - uncommon, potentially fatal skin condition characterized by formation of bullae on skin and mucus membranes. NB question: middle aged Jewish male presents with multiple blister-like skin lesions. Dermatitis herpetaformis - chronic inflammatory disease characterized by erythematous, papular, vesicular, bullous, or pustular lesions with tendency to grouping. Intense burning and itching, primarily extensor surfaces. Alopecia capitis - hair loss on head. Alopecia universalis - hair loss over entire body. Hirsuitism - excessive hair growth in unusual places, especially in women. Increased androgen production or metabolism. Often seen with pregnancy. Addison’s disease - decreased adrenocortical hormones resulting in bronze colored skin, irregular patches of vitiligo. Cushing’s syndrome - increased glucocorticoids resulting in edema , hair loss, skin discoloration and purple striae. Icterus - AKA jaundice, pigmentation of the tissues, membranes and secretions with bile pigments Myopia - nearsighted, image formed before retina due to longer eye. Hyperopia - farsighted, image formed behind retina due to shorter eye. Astigmatism - irregular curvature of the cornea or lens causing diffusion of light rays on the retina. Sexually transmitted diseases (STD) Chlamydia - MC STD, causes non-gonococcal urethritis, non-specific cause, primary cause of Reiter’s syndrome. Pelvic pain and swelling, rectal stricture. Lymphogranuloma venerum - unilateral lymph node enlargement. Syphilis - caused by treponema pallidum, dx with dark field microscopy, tx with penicillin. Primary - hard painless chancre, well defined, VDRL+ days after chancre appears. Secondary - condylomata lata(flat vulvar warts), tiny brown spots on thorax, soles and palms. Tertiary - tabes dorsalis, gumma formation, not contagious in this stage. Congenital - Hutchinson triad (pegged teeth, deafness, interstitial keratosis), saber shin deformity. Gonorrhea - caused by neisseria gonorrhoeae, contagious catarrhal inflammation of the genital mucus membranes. Gram neg. diplococci, commonly leads to joint infections MC knee, female can be asymptomatic. Trichomas vaginalis - caused by parasitic protozoa, persistent burning, redness and frothy, greenish yellow discharge. Gardnerella vaginalis - caused by gram neg. bacilli, characteristic malodorous discharge, clue cells. Candidiasis - AKA moniliasis, yeast infection caused by candida albicans. White cheesy plaques. Seen in DM, pregnancy, babies (thrush). Haemophilus ducreyi - caused by gram neg. bacilli, forms soft painful chancroid, highly infectious. Molluscum contagiousum - pearly, smooth, waxy, dome shaped, umbilicated papules on the genitals/penis. Condylomata accuminata - bulbous vulvar warts caused by human papilloma virus. Parasites: Scabies - mite that burrows under the skin, causes intense pruritis. Pediculosis - AKA lice, crabs. P.capitis = head lice, P. corporis = body lice. Antidotes: Chemical - combines with poison to form harmless substance. Mechanical - prevents absorption. Physiological - counteracts poison by causing opposite physiologic effect. Universal - 2 parts activated charcoal / 1 part magnesium oxide / 1 part tannic acid / ½ ounce warm water. 4 Associated Clinical Sciences Hypertension: Systolic of =140 on 2 or more visits, and diastolic of =90 on 2 or more visits. Essential - AKA primary or idiopathic hypertension, no definite etiology. Benign - slow progression, chronic, relatively mild. Malignant - rapid progression with severe vascular damage. Seen with renal necrosis/failure. Category Very severe Severe Moderate Mild Systolic = 210 180-209 160-179 140-159 Diastolic = 120 110-119 100-109 90-99 Prescription medications: Bioavailability - portion of a drug that reaches the target tissue. Pharmacodynamics - absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of a drug. Tardive dyskinesia -slow, rhythmic automatic stereotyped movements caused by anti-psychotic medications. Ritalin - Attention deficit disorder (ADD). Organophosphate - cholinesterase inhibitor. Elavil - tricyclic antidepressant. Benzodiagazine - anxiety disorders. Dilantin - seizure disorders. Syrup of ipecac - emetic, induces vomiting. Amyl nitrate - cyanide poisoning. Prozac - most widely used anti-depressant used in U.S. Acyclovir - herpes. Over the Counter Medications NSAIDS - nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Ex: salicylates(aspirin), Acetominophen(tylenol), feldane. Acetominophen - overdose can cause liver damage. Salicylate poisoning - ringing/roaring in the ears, respiratory alkalosis, vomiting, tinnitus, deafness, dehydration. Expectorant - facilitates removal of mucus secretions, used to alleviate coughing. Lead poisoning - bluing of the gums, basophilic stippling. Sources - lead based paints, old plumbing with lead solder, battery factory employee - lead sulfate. Geriatric patients Arcus senilus - gray opaque ring at the edge of the cornea. Blood glucose and WBC count do not change with age. Alzheimer’s disease - diagnosis confirmed at autopsy. Arterial bifurcation and facial planes - sites for normal arterial degenerative changes. Osteoporosis - determine extent with immunoabsorbant assay. Glaucoma - causes irreversible decreased visual acuity. Multiple myeloma - MC dyscrasia in the elderly. Medicare patients - must have x-rays 12 months old for treatment by chiropractor. Pick’s disease - Alzheimer’s disease of the frontal lobe. Peripheral arterial disease - intermittent claudication in the elderly. Presbyopia - hardening of the lens with age leads to loss of accomodation and hyperopia. Prebycusis - hardening of the tympanic membrane with age leads to initial hearing loss in high frequencies. Asbestosis - asbestosis mesothelioma. Cotton - brown lung. Coal - pneumoconiosis, AKA black lung. Silica - silicosis emphysema. Croup - inspiratory stridor with dry cough, tx with humidified air. Cystic fibrosis - chronic lung disease with increased mucus secretions, pos. familial hx, neonatal intestinal obstuction. Eneuresis - bedwetting. Nocturnal eneuresis - nighttime bedwetting. Diphtheria - characteristic pseudomembrane formation, exotoxin formation can lead to myocarditis and neuritis. Raccoon sign - indicative of concussion. Venogram - confirms signs of thrombophlebitis. 5 Associated Clinical Sciences Trigeminal neuralgia - unilateral lancinating facial pain, no other neurological deficits noted. Legg Calve Perthes - no history of trauma, avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Erb’ palsy - damage to upper portion of the brachial plexus, C5/C6. Klumpke’s palsy - damage to the lower portion of the brachial plexus, C8/T1. Xan - lipid. Xanthoma = fatty tumor. Purulent otitis media - bacterial infection, TM reddens, looses landmarks and bulges laterally. Serous otitis media - viral infection, TM turns amber from serous fluid behind TM, fluid level and sometimes air bubbles. Phobias: indicating abnormal fear or aversion to a subject. Acrophobia - fear of heights. Agoraphobia - fear of open places. Claustrophobia - fear of confinement. Gynephobia - fear of women. Androphobia - fear of men. Ochlophobia - fear of crowds. Atopy - genetic predisposition. Homeostasis - dynamic equilibrium of the internal environment of the body. Metaplasia - conversion of one type of tissue into a form that is not normal for that tissue. Ischemia - local temporary deficiency of blood supply. Infarction - necrotic tissue following cessation of blood supply, caused by embolus or thrombus. Hypoxia - deficiency of oxygen. Embolus - a mass of undissolved matter present in a blood or lymphatic vessel. Thrombus - a blood clot that obstructs a blood vessel or cavity of the heart. Aortic aneurysm - 80% occur below the kidneys due to weaker arterial walls. Congestive heart failure - systolic failure with a dilated ventricle and low ejection fraction, orthopnea, hepatic distention. Mononucleosis - caused by Epstein Barr virus, atypical lymphocytes, lymphadenopathy, fatigue, heterophile AB test. Gower’s maneuver - patient unable to assume an erect posture without “climbing up” on themselves. Seen in patients with muscular dystrophy, indicates weak hip and knee extensors. Osteogenic sarcoma - most frequent malignancy observed in 15 year old with leg pain. Tyramine - increases blood pressure, found in cheeses and wine. BCP B6 levels. 6 General Diagnosis Pulmonary Diagnosis: Pneumonia: Pneumococcol, lobar distribution, rusty sputum. Klebsiella, current jelly sputum, commonly seen with alcoholics. Hemophilus Influenza - commonly seen with children. Mycoplasma Pneumonae - Walking pneumonia, commonly seen in adults. Cold agglutinin. Pneumocystis Carinii - Protozoan origin, commonly seen with AIDS patients. Viral - Mucopurulent productive cough. Gradual onset of symptoms. AKA walking pneumonia. Lung conditions atlectasis pleurisy acute bronchitis asthma emphysema pneumonia Breath sounds absent crackles(friction rub) rhonchi wheezing wheezing suppressed Note: Crackles = water, Resonant = air. Percussive note flat/dull normal normal normal hyper-resonant dull Respiration: Biot’s - seen w/ increased intracranial pressure, irregular periods of apnea alternating w/ with hyperapnea. Cheyne Stokes - breathing pattern characterized by a period of apnea lasting 10-60 seconds, followed by gradually increasing then decreasing respirations. Kussmaul - deep gasping respiration characteristic of air hunger or diabetic coma. Paradoxical - abnormal rib excursion with respiration, seen with rib fractures. Stertorous - respiration characterized by rattling or bubbling sounds. Stridulous - high pitched crowing sound or barking sound heard during inspiration caused by obstruction of the respiratory passageway. Meningitic or ataxic respiration - Diabetic ketoacidosis. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Ds (COPD) - Pursed lip breathing (Kussmal respiration), emphysema, chronic bronchitis. Pleurisy - Sharp superficial pain. Sheppleman’s test to Dx: Pain on contralateral side with lateral flexion. Diabetic coma - Increased respiration. Atelectasis - A collapsed or airless condition of the lung, no vesicular breath sounds. GI Diagnosis: Ulcerative colitis - bloody diarrhea, high fever. Regional enteritis- chronic diarrhea, weight loss, anorexia, enteropathic arthritis, AKA Crohn’s disease, terminal/regional ileitis. Hernia’s: Direct - above the inguinal ligament(sides of the pinky) *MC Indirect - through the ring(top of pinky), to the scrotum. Femoral - below the inguinal ligament. Examination is performed with the patient standing, palpate and have the patient cough. Absence of bowel sounds = advanced intestinal obstruction. Bilirubin: Direct = congutated = has come from the liver. Indirect = uncongutated = has not been to the liver. Liver cirrhosis - Increased direct and indirect bilirubin. Regional ilietis (Crohn’s) - ganulomatous lesions, intermittent bloody diarrhea, erythema nodosum. False positive guaiac test - Consumption of red meat. Hematochezia - Blood in the stool. Palmar erythema - Liver enlargement. Icterus - AKA jaundice, pigmentation caused by bile pigments, best seen in the sclera. 7 General Diagnosis GI Diagnosis: Gastric ulcer - Increased hypochondriac pain. Duodenal ulcer - Post prandial pain relieved by eating. Pancreatic cancer - Primary symptom anorexia, increased with males, cigarette smokers and high fat or meat diets. Portal hypertension - Jugular veins become distended in a seated position. Tympany - MC percussive note in the abdomen. Liver enzymes - AST(SGOT), ALT(SGPT). Pancreatitis - Pain relieved with postural changes. Portal hypertension - Abdominal venous hum, spider nevi. Serum ferritin - Iron/phosphate/protein complex. Iron combines with apoferritin on interstitial mucosa and is stored in the reticuloendothelial cells of the liver, spleen and bone marrow. “Ferrit” iron away to store it. Cardiovascular Diagnosis: P = Atrial depolarization. QRS = Ventricular depolarization, atrial repolarization. T = Ventricular repolarization. S1 = mitral and tricuspid closing S2 = Aortic and pulmonic closing Systole Diastole Valves - Mitral R S = stenotic Tricuspid R S Aortic S R = regurgitant Pulmonary S R Mi Tri regurgitates on Sys = Mitral and tricuspid regurgitates on Systole. PRTS = Pulmonic Regurgitation w/ Tricuspid Stenosis. ARMS = Aortic Regurgitation w/ Mitral Stenosis. Split S2 - Increases with inspiration. Increased ST segment = Aortic regurgitation. Atrial flutter - Saw tooth P waves. Atrial fibrillation - Irregular and multiple P waves. Premature atrial contractions - Premature P waves or deformed P waves. Ventricular fibrillation - Chaotic ECG can lead to death. Pansystolic murmur - Mitral regurgitation. Mitral stenosis - Diastolic heart murmur heard at the apex of the heart. Coarctation of the aorta - Congenital deformity Dx by pulse/BP variations from upper extremity to lower. Takayatsu’s Disease - Obliteration of the great branches of the aorta. Monckeburgs Medial Sclerosis - Calcification of medium sized muscular arteries. Leriche’s sign - Obstruction of the abdominal aorta bifurcation with B/L leg pain, impotence and intermittent claudication. Dissecting Aneurysm - Common in HTN, arachnodactaly and trauma. Polyarteritis Nodosa - Immunologic disorder of small and medium arteries usually at their bifurcation. Bacterial endocarditis - Splinter hemorrhages in nail beds. Essential hypertension - Dx by BP 140/90 on three separate occasions. Thoracic aortic aneurysm - Sx = substernal pain, dyspnea, tracheal tug. Coronary artery disease - Increased risk with increased ratio of total cholesterol to HDL. Myocardial infarction - Lab tests; CPK 1, SGOT 2, LDH 3. Diastolic blood pressure - Recorded when Karotkoff sounds disappear. Cardiac tamponade - Neck vein distention, paradoxical pulse, decreased heart sounds. Pulsus paradoxus - MC occurs with constrictive pericarditis. Pulsus bisferious - Pulse with two peaks for each systole. B/L ankle edema - First sign of right ventricular failure. Pulse pressure - Difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure. 8 General Diagnosis Tongue: Strawberry - scarlet fever, also raspberry color. Magenta - riboflavin deficiency. Black and hairy - oral antibiotic treatment. Beefy red tongue - Schistosomiasis, forced rate vomiting, malaise. Anemia: Decreased iron, can be caused by pregnancy, hemorrhage, chronic blood loss, decreased intrinsic factor, folic acid deficiency, B-12 deficiency. Increased reticulocyte count - successful anemia therapy. Hematocrit - can be used to monitor a patient’s improvement with anemia. Macrocytic anemia - Folic acid/ B12 deficiency, AKA Megaloblastic anemia. Dx with Schilling test. Microcytic anemia - Hypochromic anemia, decreased iron. Spoon nails. Koilonychia - Spoon shaped nails, associated with iron deficiency anemia. Pernicious anemia - Test AB with antiparietal cells, intrinsic factor B12. Aplastic anemia - Bone marrow stops producing RBC’S. Sickle cell anemia - Increased incidence in blacks, Hemoglobin S, Howell jolly bodies. Dx with hemoglobin electrophoresis. Thallasemia - Increased in Mediterranean people, microcytic, Cooley’s anemia. Thallasemia major - Target cells. Sideropenic anemia - AKA Plummer Vinson anemia. Hyperchromic anemia, splenomegaly, dysphagia and glossitis. Erythroblastosis fatalis - RH factor incompatible between mother and child, happens after first child. Coomb’s test Raynaud’ disease - Increased incidence in women. Abnormal vasoconstriction of the extremities upon exposure to cold or emotional stress. Phenomenon - Intermittent attacks of pallor, followed by cyanosis, then redness of digitsnormal. Scleroderma - CREST sign = Calcinosis, Raynaud’s, Esophageal dysfunction, Sclerodactaly, Telangiectasia. Breurger’s disease - Thromboarteritis obliterans, associated with male smokers, elevated sed rate. WBC distribution - Neutrophils 60% bacteria “60, 30, 8, 3, 0 - Never Let My Engine Blow.” Lymphocytes 30% viral Monocytes 8% chronic infxn. Right shift - mature cells Eosinophils 3% allergy, parasites Left shift - neutrophils, pyogenic infections Basophils 0% parasites Hypersensitivity reactions : Type I - Allergy, anaphylaxis, immediate. Type II - Antigen/AB at the cell surface eg; Goodpastures (lung & kidney). Type III - Antigen/AB extracellular fluid spaces. Eg; Arthus, serum sickness, glomerulonephritis. Type IV - Cell mediated or delayed reaction, antigen/ T-lymph. Eg; TB, contact dermatitis. Male Genitalia Disorders: Varicocele - Enlarged scrotal veins, feels like a bag of worms. Hydrocele - Fluid accumulation in the testicle, will trans-illuminate. Spermatocele - Cystic, painless will trans-illuminate, located superior and posterior to the testis. Epididymitis - Usually caused by infection secondary to chlamydia. Orchitis - Usually secondary to mumps, severe inflammation. Seminoma - Cancer, does not trans-illuminate, painless. Cryptorchidism - Undescended testes. Hypospadius - Urethral opening proximal to end of the penis. Epispadius - Fusion defect of the urethra. Phimosis - Inability to retract the foreskin. Paraphimosis - Inability of retracted foreskin to be reduced over the glans penis. Peyronie’s Disease - Similar to a Depuytren’s contracture, but of the fascia of the corpora. 9 General Diagnosis Diabetes Mellitus - Involves pancreas with decreased release of insulin. Symptoms include: Polydipsia, polyphagia, and polyuria. Type I - Children, insulin dependent. Type II - AODM, more insulin resistant. Long term treatment response test glycosylated hemoglobin. Diabetes Insipidus - Polyuria and polydipsia with decreased ADH. Syndromes: Guillian Bare syndrome - Post viral polyneuropathy, progressive muscular weakness, distal sensory distribution. Reye’s syndrome - Children under the age of fifteen post viral infection treated with aspirin. Tietze’s syndrome - painful, non-suppurative inflammation of the costochondral cartilage. Nephrotic syndrome - glomerular artery disease, proteinuria hypoalbuminemia, and edema. Wernicke’s syndrome- defective memory, disorientation seen in elderly. Horner’s syndrome - paralysis of cervical sympthetics, ptosis, meiosis, anhydrosis. Klippel Feil syndrome - congenital, short/wide neck, CS fusion, hemivertebra and limited ROM. Rheumatic fever - Post streptococcal infection, skin lesion called erythema marginatum. Anti-streptolysin O (ASO) - Test to determine streptococcal infections. Pel Ebstein - Cyclic fever pattern which lasts for several days and falls for several days, occurring in Hodgkin’s. Pastia’s lines - Associated with streptococcal infection. Moniliasis - Yeast infection. Atypical lymphocytes - Infectious mononucleosis. Migraine headache - Bandlike headache, increased daily stress levels, photosensitivity, aura and nausea. Pheochromocytoma - HTN, anxiety, diaphoresis and abrupt severe headache. Giant cell arteritis - AKA temporal arteritis, temporal headache, tenderness of artery, visual loss, facial pain. Decreased blood to the optic nerve leading to blindness. Meniere’s disease - Progressive deafness, tinnitus, vertigo, feeling of fullness/pressure in the ears. IgA - The principle immunoglobulin in exocrine secretions such as milk, saliva, tears, respiratory and intestinal mucin. IgD - Increased in persons with a high concentration of RH AB, AKA erythroblastosis fatalis. IgE - Atopic diseases increase concentrations, eg: allergies. Parasites. Binds to mast cells. IgG - The principal immunoglobulin in human serum. Crosses placenta. Major AB for antitoxins, viral and bacteria. Activates the complement cascade. IgM - Controls the A,B, and O blood group AB responses, most efficient in stimulating the complement cascade. Acute serous otitis media - Retraction of the tympanic membrane. Vertigo - Room seems to be spinning, result of a disturbance to the equilibratory apparatus. Multiple sclerosis - Hyperesthesia, nystagmus, scanning speech. Osteitis deformans (Paget’s) - Cotton wool skull, ivory vertebra, blade of grass sign. Multiple myeloma - Dx test serum electrophoresis. Increased IgG, anemia, renal lesions, increased in sixth decade. Ankylosing spondylitis - Ocular finding most common is anterior uveitis. Addison’s - Hypoadrenocorticism, hypotension, decreased BP, bronze skin, loss of hair. Cushing’s - Hyperadrenocorticism, upper truncal adiposity(buffalo hump), purple stria on the abdomen, hypertension, and hypertrichosis - growth of hair in excess of normal. Myxedema - Hypothyroidism, dry skin, periorbital edema that does not indent with pressure, macroglossia, thick lips. Cretinism - Congenital form of myxedema, arrested physical and mental development. Hyperthyroid - increased basal metabolic rate (BMR), exopthalmosis, tachycardia, hyperhydrosis, Sx: Increased temperature, fatigue, weight loss. AKA Grave’s disease. Hodgkin’s lymphoma - Lymphadenopathy, pruritis, solid tumor of the lymphoreticular system. Reed Sternburg cells in biopsy. Microcytic anemia, increased SED rate. Lymph nodes feel rubbery. 10 General Diagnosis Triad’s: Charcot’s (Multiple sclerosis) - SIN = staccato speech, intention tremor, nystagmus. Dejerine’s - aggravation of radiculitis due to: coughing, sneezing, straining at the stool. Parkinson’s - rigidity, resting tremor, mask facies. Grave’s - hyperthyroidism, exopthalmosis, goiter. Clinical sx of hands: Ulnar deviation - rheumatoid arthritis. Tetany - carpal spasm. Wrist drop - radial nerve involvement. Heberden’s nodes - DIP’s w/ osteoarthritis. Bouchard’s nodes - PIP’s w/ osteoarthritis. Haygarth’s nodes - MCP’s w rheumatoid arthritis. Signs: Clawhand - ulnar nerve involvement. Ape hand - no flexion of thumb, median nerve inv. Dupuytron’s contracture - thickening of the Palmar fascia. DeMusset’s - oscillation of the head due to aortic aneurysm or insufficiency. Murphy’s - inability to take a deep breath w/ Dr’s hand pressing into lower hepatic margin. Sign of gallbladder disease. Blumberg’s - AKA rebound tenderness, acute pain on abrupt release of pressure over abdominal lesion. Ischemia - local temporary deficiency of blood supply. Infarction - necrotic tissue following cessation of blood supply, caused by embolus or thrombus. Hypoxia - deficiency of oxygen. Embolus - a mass of undissolved matter present in a blood or lymphatic vessel. Thrombus - a blood clot that obstructs a blood vessel or cavity of the heart. Buerger’s disease - AKA thromboangitis obliterans. Primarily male smokers, legs involved w/ intermittent claudication. Madelung’s deformity - radial deviation of the hand due to increased ulnar length or decreased radial length. Basal body temperature is increased during the menstrual cycle and after ovulation. Pituitary gland - Master gland of the body, secretes hormones that regulate growth, reproduction, and metabolic activities. Corticospinal pathway = Pyramidal pathway. Milia - White pinhead sized papules on the face and sometimes the trunk of a newborn, keratin filled cysts. Apthos stomatitis - Painful oral ulcers with yellow borders surrounded by yellow/crimson hyperemic zone. Angular stomatitis - Decreased riboflavin. Weber test - Right lateralization = sensorineural loss of the left ear or conduction loss on the right. Argyll Robertson pupils - mitotic, accommodating, no consensual reflexes, associated w/ tabes dorsalis. Adie’s pupil - sluggish accomodation, no consensual reflexes, cause unknown. Hordeolum - AKA sty, inflammation of a sebaceous gland of the eyelid. Dacryocystitis - Localized pain and swelling to side of nose inferior to the inner canthus. Entropion - Inversion of the eyelid. Ectropion - Eversion of the eyelid. Preretinal hemorrhage - Single round large bright red spot with horizontal blood level on fundoscopic exam. Pterygium - Triangular shaped structure extending from the inner canthus to the border of the cornea with the apex toward the pupil. Basal cell carcinoma - Chronic ulceration/depression with a pearly raised border. Rarely metastasizes. Pilonidal cyst - Sacrococcygeal region, tuft of hair over the sacrum. Brucellosis - Sheep origin. Aids - Lymphadenopathy, fever, purple skin lesions, frequent bouts of infection. Dehydration - Increased albumin in the serum. Tophi - deposits of sodium biurate, seen in gouty arthritis. Folate deficiency - MC cause of malabsorption. CAGE questioning - Alcoholism/abuse. Nitrites in the urine - MC infection cystitis. Underlying malignancy - C/S lymph nodes discrete and oval. 11 Principles SI subluxation - Affects thigh abduction. Causalgia - Pain along distribution of a peripheral nerve. Lesion - Osteopathic equivalent of the subluxation. Pacinian corpuscles - Pressure. Ruffini endings - Temperature. Secondary polycythemia - Caused by smoking, altitude. Myelopathy - Cord compression. Sheurmann’s disease - Ankylosis of the T/S. Raynaud’s disease - Vasospasm in response to cold. Sudomotor - Sweat. Spinal manipulation causes somatoautonomic reflex. SI instability - Stabilize with intertrochanteric belt. Hypomobility/fixation - Kinetic intersegmental. Vasomotor centers - Reflex inhibition leads to hyperemia. Directional guidance - Function of the posterior motion segments or facets. Most sensitive to pain. C1 - Least likely to find foraminal encroachment, provides most rotation. Lateral horn - AKA interomediolateral cell column. Motor to the autonomics. Anterior horn - LMN, voluntary motor. Posterior horn - Sensory, dorsal columns. Prefrontal cortex - Anterior part of the frontal lobe. Periaqueductal gray matter - Produces endorphins leading to an analgesic effect. Typical thoracic vertebra - Has ten synovial articular surfaces. Sphenoid bone - Keystone bone of the skull, articulates with most cranial bones. Meric system - Based on the somatoautonomic reflex theory. Organ dysfunction associated with vertebral subluxations at corresponding levels or vice versa. Coronary problems - Occiput/C1, Vagus nerve. Heart T1-T4, sympathetic nervous system. Duodenal ulcer spasm at T5-T9 vertebral level. Stomach T5-T8 Gallbladder T6-T8 Kidney T11-T12 Prostate L2 Samuel Weed - named chiropractic. DD Palmer - Founder of chiropractic, concept of tone within the system, homeostasis = equilibrium. Three factors lead to subluxation: mechanical, chemical, psychic. B J Palmer - UC technique, HIO, cord compression hypothesis. Four criteria needed: mal-alignment, foraminal occlusion, nerve compression, and interference with nerve impulse transmission. H B Logan - Pelvic imbalance, sacrotuberous ligament. Andrew Taylor Still - founded osteopathy. Relates disease to vascular dysfunction. Korr - Osteopath who worked with hypersympathetic atonia. Hahneman - developed homeopathy, dilutions of a substance basis for remedy. Dejarnette - SOT technique. Cox - Flexion/distraction technique, McMannus tables. Carver - Structural theory of the spine, adapts to structural stress. Selye - Stress syndrome, neurodystrophic hypothesis, inhibit general adaptation syndrome. Somatoautonomic subluxation. Fred Illi - Responsible for the concept of hypermobility. Henri Gillet - Theory of hypomobility and fixation theory. Korr & Levet - Muscle responses in their chiropractic model. Spindle fixation, motor neurons, GTO’s. Wolf’s law - Structure responds to function. stress on a bone density. Bell Magende law - Demyelination of a nerve due to stress and loss of trophic supply over a period of time. Dentate theory - CNS irritation caused by rotation of the vertebral bodies. Dentate ligament connects pia mater to dura mater. Reflex muscle spasm - Result from proprioceptive irritation mediated by - motor neurons. Type III mechanoreceptors - GTO, measure tension. Muscle spindles - sensitive to length changes in muscle fibers. 12 Principles Theories (from Leach) Intervertebral subluxation Nerve compression Cord compression (BJ, HIO, upper cervical and Atlas/Axis) Fixation (Gillet) Vertebrobasilar arterial insufficiency Axoplasmic aberration Somatoautonomic reflex Neurodystrophic (Selye) Intervertebral subluxations are a common occurrence in the general population. Intervertebral subluxations can interfere with the normal transmission of nerve energy (i.e. , action potentials, etc.) Intervertebral subluxations in some severe cases (and even in the absence of fracture/dislocation) may irritate or compress the spinal cord. One type of subluxation is recognized by lessened mobility, soft tissue involvement, aberrant neural reflexes, and segmental facilitation. Cervical intervertebral subluxations may cause deflexion or compression of the vertebral arteries, which thereby gives rise to altered cerebral blood supply. Axoplasmic flow may be altered when the spinal nerve roots become compressed or irritated by intervertebral subluxations. Somatic afferent bombardment of dorsal horn cells, which may result from spinal fixations, can alter normal autonomic reflexes. Neural dysfunction is stressful to the viscera and other body structures, and this “lowered tissue resistance” can modify the nonspecific and specific immune responses and alter the trophic function of the involved nerves. Neurovascular compression syndromes: Scalenus anticus syndrome or cervical rib - Adson’s test. Costoclavicular - Eden’s test. Pectoralis minor or hyperabduction - Wright’s test. Autonomic nervous system: Purely motor system, involuntary motion, lateral horn. Monitored with visualized thermography. Sympathetics - Thoracolumbar cell bodies, fight or flight response, thoracolumbar T1-L2. Parasympathetics - Craniosacral, CN’s III, VII, IX, X and sacral plexus S2, S3, S4. System heart lungs eyes GI/colon, peristalsis blood vessels Neurotransmitters: Preganglionic Postganglionic receptors at target cells Sympathetics increase rate(fight or flight) deep breaths, dilate bronchi dilate decrease motility, secretions vasoconstrict Parasympathetics decrease rate(wine and dine) shallow breaths, constrict bronchi constrict increase motility, secretions vasodilate acetylcholine epi/norepinepherine adrenergic acetylcholine acetylcholine cholinergic Preganglionic fibers: Sympathetics - white rami communicantes, run from anterior nerve root to the sympathetic ganglionic chain located laterally to the vertebral body from the skull to the coccyx. Myelinated. Parasympathetics - run from the CNS to ganglia located on or near the organs they supply. Sympathetics - gray rami communicantes, from the sympathetic chain ganglia to the organs they supply. Unmyelinated. Parasympathetics - from the parasympathetic or autonomic ganglia to the organ. Postganglionic fibers: 13 Principles Reflex - undue irritation or stimulation of sensory receptors which set up an afferent barrage of the nerve system resulting in increased or decreased activity in the effectors of another area. Ex: irritation of the skin or muscles may result in an increase of cardiac rate (somato-sympathetic). Afferent - efferent, somato-visceral, viscero-somatic, somato-sympathetic, somato-somatic, viscero-visceral. Histeresis - Deformation caused by rapidly changing forces. Creep - Deformation caused by continuous forces. Proprioceptive insult hypothesis - Gamma motor gain. Segmental facilitation - Leads to aberrant neural reflexes Abnormal reflexes - Caused by afferent bombardment of the posterior horn. Reverberating impulses - Impulse spreads through synapses in self perpetuating cycles. Sclerotogenous pain - Dull and achy, burning, usually increased with motion. Chronic compression - Leads to focal nerve demylination. Nerve roots - Lack perineurium leaving them more susceptible to pressure than peripheral nerves. Neuropraxin - Associated with nerve compression theory. Parasympathetics - CN’s 3,7,9,10 and Sacral nerves S2,S3 and S4. Parasympatheticotonia - May result from sympathetic atonia. Axoplasmic aberration - trophic function. Causalgia - First sign burning pain long a peripheral nerve distribution. Neuralgia - Pain along the course of a nerve. Neuritis - Inflammation of nerve with pain, paresthesia or anesthesia, paralysis, diminished reflexes. Radiculitis - Inflammation of a spinal nerve root. Dermatomal and sharp pain. Referred pain patterns: Esophagus………upper back Stomach & duodenum…………RUQ and back Diaphragm…...right shoulder Pancreas……………LUQ, right shoulder, back Kidneys………………..flank Colon………………………….RLQ, LLQ, back Small intestine…..back, RLQ Gall bladder, biliary tract…..RUQ, right scapula Nerve injury: Traction - leads to conduction/transmission block. Compression: Acute - irritation, facilitation, excitation. Chronic - pressure, compression, inhibition, degeneration. Posterior horn Anterior horn Lateral horn Acute hyperesthesia hypertrophy vasodilation bronchodilation Chronic anesthesia atonia/flaccid vasoconstriction bronchoconstriction Baastrups syndrome - Long thoracic spine SP’s, kissing spinouses. Scoliosis - Sectional involvement, rotary scoliosis spinous to the concavity. Compensatory scoliosis - non structural scoliosis. Functional kyphosis - several adjacent vertebral segments form a posterior convexity due to muscular pull. C/S motion segments - C4/5 most likely to exhibit hypermobility and instability. Physiologic barrier - first barrier to joint motion. Hyperlordosis - increased with psoas hypertonicity. Quadriceps - primary stabilizer of the knee. Lateral atlas - patient side posture, pisiform contact. Sclerotomal pain - deep non-palpatory pain aggravated by abrupt movement. T4-T8 functional subluxation - referred pain to stomach or pancreas. 14 Practices Planes of motion: Saggittal = flexion/extension, Transverse = rotation, Coronal = lateral flexion The intersection of 2 planes results in motion in the third plane. Saggittal and transverse = lateral flexion Saggittal and coronal = rotation Coronal and transverse = flexion/extension Axis of motion: X-axis = flexion/extension +X = flexion -X = extension Y-axis = rotation +Y = left rotation -Y = right rotation Z-axis = lateral flexion +Z = right lateral flexion -Z = left lateral flexion Coupled motion - C/S and upper T/S spinous process rotates to convexity, body to concavity. Lower T/S and LS spinous process rotates to concavity, body to convexity. Grade reflexes (0-5) 0 - absent 1+ - hypoactive 2+ - normal 3+ - hyperactive 4+ - hyperactive with transient clonus 5+ - hyperactive with sustained clonus Reflexes -Biceps C5-C6 Triceps C7 Brachioradialis C6 Patellar - L4 Achilles - S1 Babinski - pathological, UMNL Ankle clonus - dorsiflex ankle Motor evaluation - Grade motor strength (0-5) 5 = full ROM with resistance, normal 4 = full ROM with some resistance, good 3 = full ROM with gravity, fair 2 = ROM present without gravity 1 = no ROM, traceable, palpable contraction 0 = no ROM, no traceable, palpable contraction, no joint motion Dermatomes Cervical spine: C1 - none C2 - above occiput C3 - below occiput C4 - nape of neck C5 - lateral brachium C6 - lateral antebrachium, thumb, 1st finger C7 - middle finger C8 - medial antebrachium, 4th & 5th fingers Thoracic spine: T1 - medial brachium T4 - nipple T7 - xiphoid process T10 - umbilicus T12 - above inguinal crease Lumbar spine: L1 - below inguinal crease L4 - medial leg to foot and big toe L5 - dorsum of foot S1 - lateral leg and foot Retrolisthesis - AKA extension malposition. Bilateral posterior disc - AKA flexion malposition. Luschka Trauma - AKA direct break, lateral malposition. Capsular Trauma - AKA rotary break, rotation malposition. Open wedge - AKA lateral flexion malposition, superiority. Toggle recoil - torque corrects inf. or sup. component, determined by anterior tubercle position on lateral X-ray. Infection - contraindication to HVLA. 15 Practices Gonstead: Emphasizes posteriority of the spinous as the primary basis for the subluxation listing. Doctor stands on the side of open wedge for adjustment, torque closes open wedge. Do not cross mid-line of the spine to make adjustment. R or L for spinous rotation, S or I for lateral flexion. Example: PRS = Posterior (spinous), Right (spinous), Superior(vertebral body) PRI = Posterior (spinous), Right (spinous), Inferior (vertebral body) PLS = Posterior (spinous), Left (spinous), Superior (vertebral body) PLI = Posterior (spinous), Left (spinous), Inferior (vertebral body) (superiority and inferiority denote open wedging) PRS-SP or PLS-SP indicates to contact spinous process. PRI-T or PLI-T indicates to contact transverse process. PRI-M or PLI-M indicates to contact mammillary process. Comparing Gonstead listing to alternate methods: Spinous listing TP or body listing PRS = LPI PLS = RPI PRI = LPS PLI = RPS = = T/S &L/S PLS-SP PRS-SP T/S PLI-T PRI-T Lat. Flex. Rotation Left = Left Right = Right = Right = Left = Left = Right PRS = LPI = left lat. flex. with left body rotation = a fixation of right lateral flexion and right body rotation. Adjust with a spinous contact standing on right, use your right (cephalad) hand pisiform. Thrust is applied with a clockwise torque to close open wedge on the right. PLS = RPI = right lat. flex. with right body rotation = a fixation of left lateral flexion and left body rotation Adjust with a spinous contact standing on left, use your left (cephalad) hand pisiform Thrust is applied with a counterclockwise torque to close open wedge on the left. PRI = LPS = right lat. flex. with left body rotation = a fixation of left lateral flexion and right body rotation. Adjust with a transverse (TS), or mammillary (LS) contact standing on left, use your left (cephalad) hand pisiform. Thrust is applied with a counterclockwise torque to close the open wedge on the left. PLI = RPS = left lat. flex with right body rotation = a fixation of right lateral flexion and left body rotation. Adjust with a transverse (TS), or mammillary (LS) contact standing on right, use your right (cephalad) hand pisiform. Thrust is applied with a clockwise torque to close the open wedge on the right. 16 L/S PLI-M PRI-M Practices Draw out the four directions a vertebrae can subluxate. Which ones are in right lateral flexion? Left? Which side is the convexity? Which side do you stand on to adjust? (convexity) Where would you contact? (spinous, lamina, transverse, mammillary) What torque do you use to correct? What side is up in side posture. How would you adjust with pull move? Push move? How does it translate into the triaxial system (X,Y,Z) Axis of motion: X-axis = flexion/extension +X = flexion -X = extension Y-axis = rotation +Y = left rotation -Y = right rotation Z-axis = lateral flexion +Z = right lateral flexion -Z = left lateral flexion Which represent normal coupling of the cervicothoracic vertebrae? Thoracolumbar? How would you describe each one for a spinous listing, transverse/body/articular pillar listing. For the transverse/ body/articular pillar listings describe them both on the side of anteriority. Describe what position the torso of the individual would present with. (antalgia) What motions would be restricted. What muscles might cause/increase the restriction? L5 special situation: Assume the sacrum is level. If L5 is an S listing (PRS or PLS), the scoliosis above the listing creates a curve so that the low side of L5 is on the convex side of the compensatory curve above it. You must not cross the spine to adjust. The spinous is rotated to the side of open wedge, so you adjust contacting the mammillary process. Ex: PLS-M Dr. on R (opposite open wedge) with L hand pisiform on mammillary process using counterclockwise torque. PRS-M Dr. on L (opposite open wedge) with R hand pisiform on mammillary process using clockwise torque. Atlas subluxations: According to Gonstead primary direction of subluxation is anterior. As the atlas rotates the lateral mass on the anterior side widens on an AP x-ray and the posterior side appears narrower. Four letters differentiate direction of subluxation: First = A for anteriority. Second = S or I for superior or inferior anterior tubercle. Corrected with torque. Third = Right or Left for laterality. Corrected by line of drive. Fourth = Anterior or Posterior for transverse process on side of laterality. Examples: ASRA, ASRP, ASLA, ASLP, AIRA, AIRP, AILA, AILP Pelvis subluxations: PSIS is the anatomical reference, same level as S2 tubercle. PI = PSIS posterior inferior, femur head superior, short leg on same side. AS = PSIS anterior superior, femur head inferior, long leg on same side. Sacrum moves opposite of the pelvis. PI ilium with AI sacrum, AS ilium with PS sacrum. IN = int. rot. (femur head compensates with ext. rot), EX = ext. rot(femur head int. rot.). IN = wider ilium shadow on x-ray. EX = narrower ilium shadow on x-ray. ASIN = lordosis (AS) and toe out (IN ilium). PIEX = lordosis (PI) and toe in (EX ilium). Obturator foramen vertically with PI and horizontally with EX on x-ray. Muscle groups of the pelvis: Gluteals work with hamstrings. Abdominals work with hamstrings. Erector spinae work opposite hip flexors (iliopsoas, rectus femoris) Abdominals and hamstrings lordosis in contraction. Hip flexors and erector spinae lordosis in contraction. Psoas spasm - external rotation of the femur. Piriformis spasm - sciatic nerve irritation. 17 Practices Obturator foramen: On x-ray the obturator foramen will present in varying positions according to subluxation. PI = vertical dimension. EX = horizontal dimension. AS = vertical dimension. IN = horizontal dimension. PIEX = increased vertical and horizontal dimensions. PIIN = increased vertical and decreased horizontal dimensions. ASIN = decreased vertical and horizontal dimensions. ASEX = decreased vertical and increased horizontal dimensions. Orthopedic Neurologic Evaluation Nerve Root Disc DTR Myotome Influence Dermatome Pattern C5 C4/5 Biceps Lateral arm C6 C5/6 C7 C6/7 Brachioradialis Triceps C8 C7/T1 Shoulder abduction deltoid, biceps Elbow flexion, wrist extensors Elbow & wrist flexion, finger extension Thumb extension, finger flexion, ulnar deviation Finger abduction, finger adduction T1 T4 T7 T10 T12 L1 L2 L3 L4 L1/2 L2/3 L3/4 L5 S1 L4/5 L5/S1 Patellar Achilles Hip flexion Hip flexion, thigh add. Knee extension, thigh add. Knee extension, ankle dorsiflexion, foot inversion, thigh adduction. Toe extension, heel walk Ankle plantarflexion & eversion, hip extension, knee flexion, toe walk S2 Lateral forearm, 1st and 2nd fingers Posterior forearm, middle finger Medial forearm, 5th & 6th digits, hypothenar region Medial brachium Nipple line Xiphoid Umbilicus Lower abdomen, above inguinal ligament Inguinal region Lateral upper thigh Medial thigh above knee Medial leg & medial sole of the foot Anterior leg, dorsum of foot Lateral leg, lateral side of foot, little toe Perineum & medial post thigh Cauda equina syndrome - B/L leg pain, loss of bowel and bladder function, refer to a neurologist. CNS/cord problem. Ganglion impars - Sacral parasympathetic ganglion located anterior to the coccyx. Hyperextension - C4/5 MC site injured. Hyperflexion - C5/6 MC site injured, most degenerative changes. Scapula - Inferior border standing/seated T7, prone T6. Root of scapular spine T3. Patella - MC subluxates lateral and superior. Patella alta = superior displacement. L/S - at L5/S1 IVF the L5 nerve root exits. Spinal canal increases in size from L1 to L5. Spinous deviate to concavity. C/S and T/S - spinous deviate to side of convexity. Tibial nerve - Posterior compartment, plantar flexion of the ankle. Tarsal tunnel - tibial nerve entrapment. Posterolateral disc herniation - pain down leg leaning to contralateral side. Ankylosing spondylitis - instruct patient on breathing exercises. 18 NMS Know orthopedic tests for NMS. Wexler scale: 0 = no reflex Muscle grading: 1= hyporeflexic 2= normal 3= hyperreflexic W/O clonus, 4= hyperreflexic with transient clonus 5= hyperreflexic with sustained clonus. O= no evidence of contraction 1= evidence of contraction but no movement 2= movement W/O gravity 3= movement w/gravity 4= slight resistance 5= full resistance. Main ascending pathways: Spinothalamic - C fibers, A delta, Pain and temperature. Decussate W/I 1-2 levels of entry into the spinal cord. Pain and temperature contralateral. Dorsal columns - 1A nerves, proprioception, fine touch, 2 pt, vibration, graphesthesia. Decussate at the cervicomedullary junction, information carried ipsilateral to this point. LMN = Nerve to muscle = vent. horn cell = ant. horn cell = motor neuron = final common pathway. UMN = Corticospinal tract = pyramidal tract (90% decussate) = voluntary movement. All other descending pathways are more primitive in nature = reflexive. UMN lesion - Inhibitory effect from corticospinal path will be dampened with an in DTR. UMN lesion vs Increased DTR’s Spastic paralysis Increased muscle tone Pathological reflexes Absent superficial reflexes Gaits: LMN lesion Decreased DTR’s Flaccid paralysis Decreased muscle tone No pathological reflexes Diminished superficial reflexes Waddling - MD, polio, dislocated hip. Steppage - Toe/foot drop (paralysis of the foot dorsiflexors) as in damage to the peroneal nerve. AKA Charcot Marie Tooth syndrome. Weak tibialis anterior muscle. Scissors - spastic paraplegia, knees scrape together. UMN lesion. Seen with cerebral palsy. Circumduction - Stroke will affect same side, hemiparesis. Trendelenburg - Lift leg weak contralateral gluteus medius. Weight shifts over weak G-med, acetabulum and femur support weight. Festinating or propulsion - .forward leaning posture, small shuffling steps seen with Parkinson’s, mask like facies. Ataxic/tabetic - wide gait, watches feet, slap foot on ground to help fire proprioceptors. Dorsal columns disease seen with tabes dorsalis. Motor ataxia - Cerebellar dysfunction. Irregular, unsteady, reeling, vertigo, wide based steps. Neurologic disorders: Brown Sequard syndrome: Hemisection of the spinal cord with the following neurological changes. Corticospinal ipsilateral below the site of the lesion, spastic paralysis. Spinothalamic - contralateral within 1-2 levels below site of the lesion, pain & temp. Dorsal columns - ataxia, proprioception, 2 point, vibratory discrimination ipsilateral below lesion. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis - motor neuron disease causing LMN signs in upper extremities, and UMN signs in lower extremities. Myasthenia gravis - sporadic muscular weakness due to defect at the myoneural junction, decreased acetylcholine. Cranial nerves involvement. Tabes dorsalis - ataxia due to loss of proprioceptive paths. Wallenberg - thrombosis of posterior inferior cerebellar artery causing vertigo, nausea, contralateral hemiparesis, hemianesthesia, loss of hearing, tinnitus & ataxia. Barre Lieou - vertigo, tinnitus, nausea associated with vertebral artery disturbance. Guillian Barre - acute polyneuropathy with muscular weakness and some sensory loss, usually preceeded by a nonspecific febrile (usually viral) illness one to three weeks prior. Syringomyelia - chronic progressive disease of the spinal cord, loss of pain & temp. Touch and pressure OK. Loss of sensation with a shawl like distribution. 19 NMS Disturbances in sensation: Agraphesthesia - inability to recognize traced or written letters/numbers/outlines on the skin. Asterognosis - inability to recognize familiar objects by sense of touch. Baragnosis - inability to distinguish between two different weights. Pallanesthesia - loss of vibratory sensation felt on the skin or bone. Akinesthesia - loss of sense of motion: extent , direction and weight. Dysesthesia - Abnormal sensations on the skin. Numbness, tingling, burning or cutting pain. Paresthesia - abnormal sensations on the skin. Numbness, prickling, tingling, increased sensitivity. Agnosia - loss of comprehension of auditory, visual or other sensations with sensory spheres intact. Aphasia - loss of ability to communicate through speech, writing, or signs. Anosmia - loss of sense of smell.. Akinesia - loss of muscle movement. Apraxia - decreased voluntary motor function, cerebrum. Tests for tetany: Chvostecks - Tapping over facial nerve (TMJ) causes spasmodic facial contraction ipsilaterally. Ca. Trousseau’s - Compression of the brachial artery causes carpopedal (wrist) spasm. Erb’s - Galvanic stimulation causes tonic contraction. Babinski responses - dorsiflexion of big toe and fanning of the other four toes. Babinski - upward plantar stroke of the foot from lateral to medial. Chaddocks - “C” shaped stroke around lateral maleolus. Oppenheim - stroke tibialis anterior. Gordon’s - squeeze calf musculature. Schaefer’s - squeeze the achilles tendon. Jaw jerk sign - CN V lesion. Westphal’s sign - Loss of any one dependent reflex. Homan’s sign - diffuse calf pain or behind knee upon forced dorsiflexion of the foot, indicates thrombophlebitis. Miner’s sign - patient arises from seated position with affected leg bent, balancing on healthy side, hand on chair. Gower’s maneuver - Pt “climbs up on themselves”, weak extensor muscles similar to miner’s sign. Seen with MD. Carpal tunnel syndrome - Median nerve compression, can be caused by lunate subluxation. Night pain. Meralgia paresthetica - Involves the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve. L2-L3 nerve roots. Anterior lateral thigh pain. Horner’s syndrome - Interruption of the C/S sympathetic chain. Ptosis, myosis, anhydrosis. Tic Douloureax - 5th cranial nerve involvement, bouts of severe lancinating pain along distribution of the trigeminal. Bell’s palsy - 7th cranial nerve involvement, unilateral facial paralysis of sudden onset. Erb’s palsy -UMN lesion, paralysis of the muscles of the shoulder and upper arm, C5and C6 roots. Klumke’s palsy - LMN lesion, atrophic paralysis of the forearm, C8 and T1 roots. Stretch reflex - Involves 1 interneuron that synapses with input sensory nerve to output LMN. Dorsal Root Ganglion (DRG) - Origination of most of the primary neurons of the sensory nerves. Sprain/strain - “T” in strain think tendon. Active vs. Passive test with O’Donahues maneuver. Passive - Muscle not involved with movement = ligament/joint = sprain. Active - muscle involved = tendon = strain. Causalgia - First sign burning pain long a peripheral nerve distribution. Neuralgia - Pain along the course of a nerve. Neuritis - Inflammation of nerve with pain, paresthesia or anesthesia, paralysis, diminished reflexes. Radiculitis - Inflammation of a spinal nerve root. Dermatomal and sharp pain. Superficial reflexes - Lost with both UMN and LMN lesion. Ciliospinal reflex - Pupil dilation following painful stimulation to skin of the neck. Autonomic modulation. Corneal reflex - CN V afferent, CN VII efferent. 20 NMS Orthopedic tests: C/S: Intrathecal pressure Increased - Valsalvas, Dejarines, Milgrams, Naffzigers. Compression maneuvers - Spurling’s, foraminal compression, Jackson’s compression, maximum foraminal compression Distraction - Hurts more with muscular involvement, increased pain with disc Soto Hall, Lindner’s, Brudzinski’s (leg flexion = meningitis), Kernigs. T/S Sheppleman’s - Ipsilateral = intercostal neuritis, contralateral = pleurisy. Chest expansion - 2” males, 1 ½” women. Decreased with AS. Swallowing - Decreased with AS, DISH, retrotracheal/pharyngeal swelling. Beevors - Deviation of the umbilicus, indicates side and general level of lesion. Lhermites - Shooting pain into the extremities. Chest compression - With rib fracture pain lateralizes to side of fracture. Forrestiere bowstring - Ipsilateral muscle contracts with AS. L/S SLR (Laseagues) 0-30 = hip, 30-60 = SI, 60> = nerve root. Indicates lateral disc bulge. WLR ( Fazjerstsan’s) - Indicates medial disc bulge. Braggards - Foot dorsiflexion, nerve root traction. Sicard’s - Great toe dorsiflexion, nerve root traction. Kemp’s - Ipsilateral facet, contralateral nerve root. Ely’s - Lateral femoral nerve irritation. Thomas - Iliopsoas tension. SI Nachlas - SI lesion, tight quads, anterior thigh pain. Hibbs - SI or hip depending on site of pain. Yeoman - anterior SI lesion. Gaenslen - SI or hip involvement. Neri bowing - Hamstring tightness, not nerve root traction. Shoulder: Calloway’s - dislocation of the humerus. Dugas - dislocation of the humerus. Apprehension - dislocation of the humerus. Codman’s - rotator cuff tear usually supraspinatus. Yergason’s - bicipital tendonitis or transverse humeral ligament. Weber’s test - 512 hz tuning fork placed on vertex of skull. Lateralization indicates air conduction loss on same side or sensorineural loss on side opposite lateralization. Rinne’s - 512 hz tuning fork placed on mastoid process, held until pt no longer hears then fork held in air beside ear. Negative if air conduction 2x longer than bone. Positive if bone conduction longer than air conduction. Schwabach’s - after pt can no longer hear air conduction with Rinne’s Dr listens to tuning fork for comparison. Barany - labyrinthine test, whirling or calorimetric test. Muscle tension HA - Unvarying dull HA, band like pattern. Classic migraine HA - Aura, throbbing phase, mood change. Brain tumor - Can present as weak lateral rectus muscle, HA, and elevated optic disc. Posterolateral sclerosis - AKA combined systems disease - Stocking glove distribution, B12 . Complication secondary to pernicious anemia. Duchenne’s MD - 50-100X increase in CPK, muscle wasting, waddling gait. Sudeck’s atrophy - RSDS with osteoporosis. Hegar’s sign - softening of the cervix. Polymyositis - Most definitive test is tissue biopsy to diagnose. Osteochondritis dessicans - Joint mice lateral aspect of the medial compartment of the knee MC site. Pelligrini Stieda - Partial avulsion of the MCL with resultant calcification. Order of shoulder dysfunction - Tendonitis bursitis capsulitis. Neurotrophic joint sx: Hx, joint effusion, sensitivity, with DM. Not a shooting type pain. Hematogenous osteomyelitis - Metaphyseal bone. 21 NMS Rotator cuff muscles (SITS) - supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, subscapularis. TFL - Patient externally rotates and abducts leg. Perthes test - Checks competence of the venous valves of 2 extremities. L4/L5 facet syndrome - Flank, groin and medial knee pain. Milwaukee brace - Scoliosis brace, use indicated if curve is 20 with rotation. Maxillary sinus - Can cause pain in upper teeth. Tibial nerve – Posterior compartment. Common peroneal nerve: Superficial peroneal nerve lateral compartment, foot eversion. Deep peroneal nerve ant compartment, foot dorsiflexion, dermatome between 1 st and 2nd toes. Peroneal nerve palsy - AKA Charcot Marie Tooth Syndrome. Shoulder depression - Tests dural sleeve adhesions. Closed pack = full extension. Open pack = full flexion. Babinski pronation - Examiner taps dorsum of supinated hand patient pronating hand. Piriformis syndrome - SLR with external rotation to test muscle integrity. Tennis elbow - Carpi radialis brevis, AKA lateral epicondylitis. Klippel Feil syndrome - Short web neck, low hairline, # of C/S vertebra with fusion, CNS affected. Cervical rib - Symptoms 4th and 5th metacarpal and medial forearm. Osteoid osteoma - Rare benign bone tumor composed of sheets of osteoid tissue, pain relieved by aspirin. Adduction of the thumb - Ulnar nerve, Froment’s paper sign. Scheuerman’s disease - Kyphotic curve unilateral rib curve, schmorl’s nodes. Acetabula protrusio - Femur heads protruding into the pelvic bowl, complication of RA, fracture, Pagets. Diabetes mellitus - Hip joint changes most common seen is avascular necrosis. Myasthenia gravis - Eyelid ptosis, severe facial weakness, recurring ocular fatigue, sx decrease with rest. Multiple sclerosis - Charcot’s triad = SIN - Scanning speech, Intention tremor, Nystagmus. Shock like sensation throughout the spine (Lhermitte’s). Transient blindness with optic disc neuritis. Olecranon bursitis - MC associated with gout. Tarsal tunnel syndrome - Causes numbness in the toes. Ankle pronation - causative agent of plantar fascitis. Multiple myeloma - Light chain immunoglobulins, MC dyscrasia in the elderly. Retinitis pigmentosis - Not associated with sudden loss of vision. Amaurosis fugax - Sudden transient loss of vision in one eye secondary to optic artery compression. Subarachnoid hemorrhage - Sudden onset like a blow to the head with fever and nuchal rigidity. Intention tremor - Cerebellar rigidity. Rhabdomyosarcoma - Malignant tumor of skeletal muscle. Myelopathy - Cord problem. Flexion - Greatest tension on the C/S. Soto Hall, Lindner’s, Lhermitte’s sign. Sjorgren’s disease - Xeropthalmia, Xerostomia, and RA. Popliteal artery - MC location for a lower extremity bruit. Thromboangitis obliterans - Young males, increased with smokers. Patellar tendonitis - AKA jumpers knee. Athetoid motion - Slow, writhing, worm like motion. Choreiform motion - Jerky dance like movement (Huntington’s - congenital, Syndeham’s - strep acquired). Sickle cell anemia - MC cause of avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Pes planus - Flat feet, normal posture in a one year old. Strabismus - Optic axes can not be directed to the same object. Brachioradialis - Radial nerve, C6. Nucleus ambiguous - Vagus nerve. Cardiac problems - Upper C/S subluxation/irritation, can influence vagus nerve flow to the heart. 22 X-ray Order of geographic densities (least to most )- Air, fat, water, bone, metal. Bremstralung radiation - AKA braking radiation. Useful X-ray Beam - 85% Bremstralung radiation. Aluminum filtration - Absorbs the less penetrating X-rays to decrease dose to the patient, ½ mm equivalent in the tube 2mm equivalent added for a total of 2.5mm. Filtration - primary purpose is to reduce skin dosage. Thermionic emission - Electrons boiled off the tungsten filament in the focusing cup. Quantum Mottle - “Noise” displayed on the film. Increased with faster film screen combinations. High energy - Implies high frequency and low wavelength. kVp - Refers to the quality of the X-ray beam, or penetrating power of the beam, determines contrast of image produced. Increase voltage = increased penetration. mA - Determines the number of electrons produced in the cathode, determines temperature of the filament. mAs - Quantity of x-rays, determines the density (darkness) of the image. Density - Degree of film darkness, increased mAs = increase in density. High kVp and low mAs = dose to the patient. kVp and contrast are inversely proportional. mAs and density are directly proportional. Heat units for single phase - mA x time x kVp = heat. Contrast - the range of density variations among the dark and light areas. Scale of Contrast - Short scale of contrast = decreased kVp. Short scale of contrast - high contrast or abrupt transition of densities. Long scale of contrast - low contrast or gradual transition of densities. Detail - 1) degree of sharpness/ definition. 2) radiographic contrast. Penumbra - Shadow, size directly related to image sharpness. Intensifying screens - intensify film image (95% of film exposure from light emitted by the intensifying screen) Big crystals = more light, less sharpness. Small crystals and thin emulsion = increased detail, sharpness. Primary purpose to reduce patient exposure. Fast screens decrease definition. Emit blue or green light. Emulsion - Active component of the X-ray film, contains thin layer of crystals and binding agent. Film tint - Blue or green tint added to film to improve contrast. Attenuation - Reduction in intensity of an x-ray beam as it passes through matter. Rectification - Converts AC to DC. Autotransformer - Steps up voltage from 110 or 220 to kV. Focal Spot - Tungsten target, does not affect patient exposure dose. Small focal spot leads to increased heat concentration or decreased dissipation. 99% of energy is lost as heat - only 1% is transferred as x-radiation. Cathode - negative (-), electrons boiled off tungsten element in focusing cup. Opposite charge of anode attracts electrons at about ½ the speed of light. Anode - positive (+), electrons strike anode and x-radiation produced. X-rays travel from the anode patientfilm at approximately the speed of light Anode heel effect - Angulation of the anode leads to decreased intensity of the beam from the outside of the anode. Focal Film Distance - long focal film distance increases definition, reduces distortion. Decreased Magnification - Decreased object to film distance(OFD) or increased tube to film distance(TFD). 15% Rule - Increase kVp 15% will need to decrease mAs 50% to maintain density. Minimum change in mAs needed to note change density on plain film = 50%. Roentgen - unit for describing exposure dose of x or gamma radiation. RAD - Radiation absorbed dose, the energy transfer of 100 ergs/gram of the absorbing material. REM - Roentgen Equivalent to Man, used to determine occupational worker dose, equivalent to absorption of 1 rad. MPD - Maximum permissible dose, 5(N-18) rads or 5 rads/year. 13 week period = 3 rads maximum Grid - Best method to minimize scatter radiation exposure to film. Grid ratio = Height : Width, Higher the ratio = increased dose to the patient to produce a quality radiograph. Fixing - Removes unexposed silver halides from the film, hardening the emulsion and preserves the image. Silver Reclamation - Recovered from the fixer. Developer - Purpose is to reduce the exposed silver halide crystals to metallic silver. Brings out latent image to a visual image. Increased temperature of developer will increase density of the film. Decreased temperature of developer will lead to increased development time. Excessive oxidation of developer fluid =brown film. Activator, retainer, preservative and hardener. Wash - Longest stage of manual development. 23 X-ray Kissing Artifact - Wet film touched together. Black Branching Artifact - Static electricity, increased with dry cold climates. Geometric factors - focal spot, FFD, OFD, motion, screen crystal size, film screen contact, alignment of film/part/tube. Increase definition - FFD, OFD, focal spot, crystal size. Latitude - the range between maximum and minimum exposure. Scatter radiation - x-rays which have undergone a change in direction after interaction with part being exposed. AKA - Secondary radiation, fog. Grid helps to absorb scatter from reaching the film. Inverse square law - intensity of the beam is inversely proportional to the square of the distance. I 1/ I2 = (D2/ D1)2. Law of Bergonie and Tribondeau - Proliferation of cells and their radiosensitivity. No x-ray during first trimester of pregnancy, or children. Wolf’s law - bone develops strength along the areas of greatest stress. Women of child bearing years - x-ray within 10 days following onset of menses. 10 day rule. Spondylosis - ankylosis of a vertebral joint. Spondylolysis - separation of the pars interarticularis. Anterolisthesis - anterior displacement (listing). Spondylolisthesis - spondylosis with anterior displacement. Myerding classification: percentage equivalent of anterior displacement. Grade 1 = 0-25%. Grade 2 = 25-50%. Grade 3 = 50-75%. Grade 4 = 75 -99%. Spondyloptosis = 100% anterior displacement. Inverted Napolean hat sign - AKA bowline of Brailsford, seen w/ advanced grade IV anterolisthesis or spondyloptosis. Isthmic spondyolisthesis - Greatest degree of slippage occurs during 2-10 years old. Scoliosis - lateral curvature of the spine. Simple - the vertebral bodies have rotated away from the scoliosis and into the concavity (Lovett neg.) Rotatory - the vertebral bodies have rotated into the scoliosis or into the convexity (Lovett positive) Lovett static - scoliosis with no body rotation. Cleft vertebra - failure of closure of the vertebral posterior arch. Hemivertebra - lack of development of half a vertebra, can lead to development of scoliosis. Spina bifuda - developmental anomaly of the neural arch. Occulta - usually insignificant, no protrusion of the cord or meninges. Manifesta - cystic swelling of the meninges (menigocele), cord (myelocele), or both (menigomyelocele). Knife clasp deformity - Elongated L5 spinous with spina bifuda occulta at S1 and pain with extension. Blocked vertebra - non segmentation or congenital fusion of two or more spinal segments. Klippel Feil Syndrome - Multiple blocked vertebra, Springle’s Deformity - elevated scapula. Tropism - asymmetrical or anomalous zygapophyseal joints. Baastrup’s - elongated spinous processes. AKA kissing spinouses. Gout - Increased uric acid concentration leading to deposition of crystals and tophi formation. Overhanging edge sign, avascular necrosis, juxta-articular erosions. Grossly inflammatory condition works from outside into the joint space. AKA lumpy bumpy arthritis. Rheumatoid Arthritis - Lab: RA factor, C-reactive protein, increased ESR. Early radiographic signs MC seen in the hands and feet. Uniform loss of joint space. Hands all fingers affected starts in MCP joints = Haygarth’s nodes. Can also affect PIP = Bouchard’s nodes, but never DIPS. BL and symmetrical distribution, periarticular soft tissue swelling, juxtaarticular osteoporosis, periarticular erosions and cysts, with uniform loss of joint space. Ligament laxity predominantly in hands with ulnar deviation of the fingers. Rarely see subchondral sclerosis. Can affect SI unilaterally. Pencil in cup deformity. Whittled appearance to periarticular bone. AKA Still’s disease in children. DDx: SLE. Osteoarthritis - AKA DJD. Progressive, non-inflammatory process. Asymmetric distribution, non-uniform loss of joint space, osteophytes, subchondral sclerosis, subchondral cysts, facet arthrosis, IVF stenosis, disc height and vacuum sign. UV arthrosis/facet arthrosis - C/S oblique, hourglass IVF = IVF encroachment. Erosive OA - Inflammatory variant of DJD involving DIP’s and PIP’s. Erosion’s = gull wing deformity, sclerosis, osteophytes, periostitis, ankylosis, and non-uniform loss of joint space. 24 X-ray Psoriatic arthritis - MC involves DIP’s, also interphalangeal and PIP’s with widened joint spaces, ray pattern, sausage digit due to increased swelling, pencil in cup deformity and rat bite erosions. Reiter’s - Triad of conjunctivitis, urethritis and polyarthritis usually following sexual exposure. Lateral foot heel spurs, SI erosion and sclerosis often unilateral, spine nonmarginal syndesmophytes Calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease AKA CPPD - Crystals deposited within the articular cartilage leading to thin linear cartilage calcification parallel to and separate from adjacent subchondral bone. Osteochondritis dessicans - MC site is lateral aspect of the medial femoral condyle. Joint mouse. Hydroxyapatite deposition disease AKA HADD, calcific bursitis - Calcification within a tendon, bursa, or other periarticular soft tissue. MC sites include shoulder, hip, and the cervical spine. Shoulder = clock dial positions 3 & 9 calcific bursitis, between 1 & 2 and 10 & 11 calcific tendonitis. Synoviochondrometaplasia - Synonyms include joint mice, synovial chondromatosis, osteochondromatosis, and osteochondral loose bodies. MC sites - knee, hip, ankle and hip. Can lead to formation of a Baker’s cyst. Baker’s cyst - Enlargement of the gastrocnemius-semimembranosus bursa, commonly seen in RA and synoviochondrometaplasia. Charcot’s joint - AKA neurotrophic joint. Six D’s: Distension -from effusion, Density -subchondral sclerosis, Debris-bony intraarticular fragments, Dislocation,, Disorganizaton-bag of bones, and Destruction of articular bone. Lack of subjective and objective pain. Commonly seen with diabetes and syphilitic tabes. Scheuermann’s disease - AKA juvenile kyphosis, vertebral epiphysitis. Dx from lateral film, at least three contiguous vertebra, irregular endplates, decreased disc height, increased kyphosis. MC middle to lower T/S, primarily teenagers. Myositis ossificans - Post traumatic calcification of muscular tissue. Sequestrum - Fragment of a necrosed bone that has become separated from surrounding bone. Involucrum - Covering of newly formed bone enveloping the sequestrum with infection of the bone. Geographic lesion - Circumscribed and uniformly lytic lesion. Ewings Sarcoma - Tumor most common seen in the diaphysis, onion skin layering. Chondroblastoma - Most common seen in the epiphysis, calcific matrix. Enchondroma - Most common benign tumor of the hand, Ollier’s disease = Multiple enchondromas. Giant Cell Tumor - Expansile destructive lesion at the end of long bones, can affect the joints. Pedunculated Osteoma - Paranasal sinuses. Unicameral Bone Cyst - Usually Dx by spontaneous fracture. Aneurysmal bone cyst - Expansile lesion. Ex: arch of the atlas. Osteopoikilosis - Widespread multiple circumscribed round or ovoid lesions of increased density. AKA bone measles. Hemangioma - Most common benign tumor of the spine, corduroy cloth vertebra. Osteopetrosis - Vertebra within a vertebra. Syndesmophyte - Bony outgrowth or ossification of a ligament that attaches to bone. DISH - Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis. Ossification of ALL with non-marginal syndesmophytes. Disc spaces and facets are spared. Dx on lateral film, difficulty swallowing, can be associated with diabetes. AKA Forestier’s disease. AS - Ankylosing Spondylitis. Initial marginal pencil thin syndesmophytes, can cause sclerosing of posterior motor units. Syndesmophytes thicken with time, B/L SI joint obliteration, decreased chest expansion. AKA Marie Strumpel’s disease. HLA-B27(+). Ortho test - Schober’s test. Paget’s - typically 50+ male, Ivory vertebra, blade of grass sign, cortical thickening, cotton wool skull, shepherd’s crook deformity, picture frame vertebra, saber shin deformity, protrusio acetabuli, bone expansion, increased hat size. AKA osteitis deformans. Lab Dx: Urinary hydroxyproline, alkaline phosphatase. Malignant degeneration to osteosarcoma. Brim Sign - Thickening of the cortex at the pectineal line and the pelvic rim. Seen with Paget’s. Multiple Myeloma - MC 1 malignant bone tumor. Bone scans are cold. MC sites spine, pelvis, skull, ribs and scapula. Punched out lesions, raindrop skull and vertebra plana. Lab findings Bence Jones proteinuria and reversed AG ratio. Fibrous dysplasia - Shepherd’s crook deformity, ground glass appearance, septations of bone giving cobweb appearance. Expansile lesions with cortical thinning. MC benign tumor of rib creating extrapleural sign. Rind of sclerosis around geographic lesion. AKA polyostotic fibrous dysplasia. Can be in vertebral bodies. 25 X-ray Monostotic Fibrous dysplasia - Short zone of transition, sclerotic ring often found in the neck of the femur. Tuberculosis - Likes apices of the lungs, can have calcified density in the lung field or miliary type lesions. Can also produce lesions in the spleen. Pott’s = TB of the spine Gibbus formation w/ angular kyphosis. Pancreatic calcification - midline calcification frequently seen with alcoholics. Sarcoidosis - Pulmonary signs include lymphadenopathy(1-2-3 sign, potato nodes), infiltrates and fibrosis. Scleroderma - Acro-osteolysis, soft tissue retraction, calcification and tapered fingers. CREST sign = Calcinosis, Raynauds phenomenon, Esophageal abnormalities, Scleroderma and telangiectasia. Prostate metastasis - Primarily blastic, likes spine and pelvis. Midline calcification AP pelvis above pubic symphysis. Parasites - Multiple calcific densities in muscles. Hyperparathyroidism - Rugger jersey sign, salt and pepper skull, increased serum calcium. Sub-periosteal on the radial side of the fingers with soft tissue calcification. Fracture - Need to have pieces to diagnose. Jefferson’s fracture - C1 compression fracture, burst fracture ring of the atlas, unstable needs to be braced. Hangman’s fracture - C2 decompression fracture, stable but needs bracing. Odontoid fracture - Three types: apical, transverse at the base, and transverse extending into the body of C2. Clay shovelers fracture - spinous process of C6 or C7. Galeazzi fracture - Proximal radius with dislocation of the ulna. Monteggia fracture - Proximal ulna with dislocation of the radius. Colle’s fracture - Posterior distal radius. Smith’s fracture - Anterior distal radius. Pott’s fracture - distal fibula. Boxer’s fracture - 2nd or 3rd metacarpal vs. Bar room fracture - 4th or 5th metacarpal. Jones fracture - Fifth metatarsal. March fracture - Stress fracture of metatarsal. Diastatic fracture - Separation of a partially moveable joint. Kummel’s fracture - compression fracture of a vertebra associated with osteoporosis. Anderson lesion - Fracture of pathologic calcification. Ex: Ankylosing spondylitis. Freiburg’s sign - Fracture of the 2nd and 3rd metatarsals avascular necrosis. Keinbock’s sign - Fracture of the lunate. Salter Harris fractures: Type 1 - through growth plate only; ex: slipped capital femoral epiphysis. Type 2 - through growth plate and metaphysis. Type 3 - through growth plate and epiphysis. Type 4 - through growth plate and both metaphysis and epiphysis. Type 5 - compression deformity. Risser’s Sign - Diffusion of iliac crest apophysis, used to determine skeletal maturity. Eisenstein Sign - Canal stenosis viewed from lateral film, posterior body line to spinolaminar line. Normal should be ½ or more than the width of the vertebral body. Pedicogenic stenosis. Chamberlain’s Line - Hard palate to the opisthion, > 5mm = to basilar invagination. McGregor’s Line - Hard palate to the base of the occiput, > 7mm = to basilar invagination. Martin’s Basilar Angle - Root of the nasion/sella turcica to ant.foramen magnum, 128-152. Check for platybasia. McNabb Line - Facet imbrication, parallel to inferior end plate draw line posterior. Should not cross the superior articulating facet of the inferior vertebra. Lateral lumbar oblique view. Rostrocaudal migration. Jackson’s cervical stress line - Flexion at C5/6, extension and neutral at C4/5. Ullmann’s Line - Draw line perpendicular at anterior portion of S1 endplate line, should not intersect L5 body. Indicates spondylolisthesis. Klein’s Line - Used to Dx slipped femoral capital epiphysis. C/S Gravity Line - Tip of odontoid to anterior C/7 vertebral body. L/S Gravity Line - L3 body center vertical line to anterior 1/3 of sacral base. AKA Ferguson’s line. Boehler’s angle of 35 degrees - Calcaneal compression fracture if < 28, dx from lateral foot. Ferguson’s angle (35-45) - sacral base angle to true horizontal. Mickulicz’s angle (120-130) - femoral neck angle, angle of declination between epiphysis and diaphysis of femur. 130 = coxa valga < 120 = coxa vara 26 X-ray Y Epiphysis - Acetabulum. Fabella - Sesamoid bone found in the lateral head of the gastrocnemius tendon proximally. Capitulum - Distal humerus , articulates with the radial head. Olecranon fossa - Posterior distal humerus, accepts olecranon process of the ulna. Coronoid process - Located on the anterior ulna, articulates with the trochlea. Coracoid process - Located on the scapula. Supracondylar fossa - Located on the humerus. Supraglenoid sulcus - Located on the humerus. Paraglenoid sulcus - Female pelvis lateral to SI joints, usually postpartum, often seen with OCI.. L/S IVF - Seen on the lateral film. ADI - Adult up to 3mm, children up to 5mm. Lateral flexion film - Tuck chin in and flex to chest. Anterior fat pad normally seen on an AP elbow. Dorsiplantar foot - 5 degree cephalad tube tilt. AP Coccyx - Caudal tube tilt. Medial oblique - View taken to visualize the proximal talofibular joint. Os trigonum - Accessory ossicle posterior to the tibia, superior to the calcaneus. Os vesalianum - Sesamoid bone proximal to the fifth metatarsal. LCP - Pseudo widening of the joint space, flattening and fragmentation of the femoral head. Legg Calve Perthes 3-12 YO, especially 5-7 5:1 male Limp with vague pain especially with abduction and int rot. AKA avascular necrosis of femoral head Subchondral fracture (crescent sign) 1 cause obscure - hereditary, trauma, endocrine, inflammatory, nutritional. 10% bilateral Slipped Femoral Capital Epiphysis 10-15 YO Increased in males Limp with hip pain to knee of obese adolescent. Femur displaces sup, ext rot, adduction of the neck on the head. Dx with Klein’s line on AP view 50% have a Hx of significant trauma Also assoc. with rickets & osteodistrophy 20-30% bilateral Lung Apices - Best seen on apical lordotic view. Silhouette Sign - Loss of the heart outline due to lung consolidation. Hahn’s venous fissure - Horizontal radiolucent cleft on lateral thoracic film. Pleural effusion - Best seen with the lateral decubitus view. Pneumoperitonium - Best seen with erect abdomen view. Megenblase - Stomach gas. Sudeck’s atrophy - post traumatic osteoporosis. Sickle cell anemia - Endplate biconcavity of all vertebral levels. Osteoid osteoma and Brodie’s abscess - Both have night pain relieved by aspirin. Brodie’s abscess - circumscribed area of bone destruction, pus, osteomyelitis. Osteochondrosis - degenerative changes in the ossification centers of the epiphysis of bones, particularly during periods of rapid growth in children. Stages: necrosis regeneration healing. Staghorn calculi - Calcification in the renal calyces. Eburnation - Laying down more bone. Pelligrini Stiedas Disease - Medial condyle injury of the knee with partial avulsion of the MCL with calcification. Mediums: pantopaque - myelograms telopaque - biliary barium sulfate - GI study 27 Orthopedics Lumbar Spine Orthopedic Tests Test Bechterew’s Bowstring Supine Braggards Supine Buckling Sign Supine Procedure Extend each knee alternately then both together Firm pressure on hamstring/ popliteal fossa SLR to pain, lower 5 dorsiflex foot SLR Disc Lesion Seated Instruct pt to stand from seated Ely’s Prone Heel to contra buttock Goldthwaith’s Supine SLR & WLR w/palpation of sacrum & lumbar SP’s Dr feels for fanning of SP’s Extend LS obliquely backward Kemp’s Lasegue’s Lindner’s Milgram’s Pt Position Seated Seated or standing Supine Supine Supine Minor’s sign Seated Neri Bowing Supine Flex hip, extend leg CS flexion, chin to chest Raise pt legs 6 inches & patient support legs Pt rises from seated position to standing Flex @ waist & knee Dr. extends SLR Supine leg @ knee Dr. raises patient’s extended leg Spinous Seated Dr. percusses SP w/ reflex hammer Supported Standing Dr. braces ilia & sacrum while Forward Flexion standing behind patient Valsalva Seated Inhale, hold & bear down lesion WLR Supine Dr. raises uninvolved leg 28 Findings + Disc involvement + Sciatic nerve irritation + 0-35 = extradural sciatica + 35-70 = suspect IVD lesion + Flexion of leg w/ traction on sciatic nerve + Medial disc = ipsi antalgia Lateral disc = contra antalgia + Anterior thigh pain = lateral femoral N. irritation + 0-35 = SI lesion + 35-70 = lumbosacral + 70-90 = lumbar joint pain + Same side = lateral disc bulge + Opp. side = medial disc bulge + Sciatic radiculopathy + Dural involvement, disc lesion + lumbar spine lesion - Peripheral lesion + Flexion of involved leg due to sciatica + Sciatica - No pain lumbar somatic + 0-35 = extradural involvement + 35-70 = disc involvement + 70-90 = lumbar joint pain + Lumbar fracture (localized) or disc lesion (radicular) + Lumbar involvement + Pain = space occupying + Medial or central disc, dura or lumbar somatic SI Joint/Hip Orthopedic Tests Test Pt Position Anterior Innominate Standing Fabere-Patrick Supine Gaenslen’s Supine Hibb’s Prone Iliac Compression Side posture Lewin-Gaenslen’s Side posture Procedure Findings Pt takes big step forward with good leg, bends forward at waist trying to touch the floor Leg in figure 4 position: flexion abduct, external rotation SI on table, flex opposite leg, extend thigh side being tested - apply pressure Max leg flexion @ knee push leg lat = int rot Involved side up Involved side up, flex inferior leg, extend superior leg Heel to ipsilateral buttock + Pain on affected side lower trunk or heel of affected side lifts off floor + w/pressure = SI/hip lesion + w/o pressure = inflammation + SI, hip involvement Nachlas Prone Ober’s Side posture Thomas Supine Trendelenburg Standing Instruct pt to raise foot of involved side off floor Yeoman’s Prone Dr. stabilizes involved SI, flex leg extend thigh Involved side up, thigh abducted and extended Involved side thigh actively flexed by pt w/ hands around knee + SI pain = SI lesion + Hip pain = hip lesion + SI involvement + Pain on extension = SI lesion + SI lesion, buttock pain or tight quads, ant thigh pain + Thigh remains abducted, suspect TFL or iliotibial band contracture + Involuntary flexion of opposite knee, indicates hip flexion contracture (iliopsoas) + Iliac crest on involved side drops suspect contralateral gluteus medius weakness + SI pain = Anterior SI ligaments Orthopedic Tests for Malingering Test Burn’s Bench Pt Position Flip Test Kneeling on table Seated Hoover’s Supine Magnuson’s Seated Mankopf’s Seated McBride’s Seated Procedure Findings Instruct pt to bend to touch floor while Dr. stabilizes legs Pt performs Bechterew’s or Dr. performs Lasegue sitting test Dr. supports heels, pt instructed to lift involved leg off table Ask pt to point to site of pain Distract pt then ask them to localize pain again Obtain pulse rate, irritate area of Chief Complaint, retake pulse Pt instructed to approximate foot to mouth. + Inability to perform test. Uses leg muscles not back muscles + No pain or tripod position 29 + Uninvolved side heel is not depressed toward table + Patient unable to point to same place twice + Lack of pulse rate increase by at least 10 percent + Patient refuses to attempt test Thoracic Spine Orthopedic Tests Test Pt Position Adam’s Sign Standing Beevor’s Supine Chest Expansion Seated Rib Motion Seated Schepelmann’s Sign Seated Spinal Percussion Seated Sternal Compression Valsalva lesion Supine Seated Procedure Findings Pt flexes at waist w/hands in + Rib hump/convexity = scoliosis prayer position, C/S flexed in Checked from anterior and anterior position posterior positions Pt performs a half sit-up w/hands + Deviation of umbilicus indicates behind head level and side of lesion Measure after pt exhales and + Decreased expansion suspect after max inhalation spinal ankylosis, pathology Males 2-3” normal or fracture Females 1-2” normal Dr. behind pt w/hands on flat on + Decreased expansion suspect back, thumbs on paraspinal muscles spinal ankylosis, pathology pt inhales or fracture Pt abduct arms, hands overhead + Pain on side of flexion = lateral flexion bilaterally intercostal neuritis + Pain opposite side of flexion = intercostal myofascitis or pleurisy Reflex hammer percussion of + Spinous process pain = osseous spinous processes and paraspinal injury or fracture musculature + Paraspinal muscle pain = soft tissue injury Dr. uses ulnar aspect of hand to + Localized pain at lateral border apply pressure AP on sternum of ribs indicates fracture Inhale, hold & bear down + Pain = space occupying Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Orthopedic Tests Test Pt. Position Adson’s Seated Allen’s Seated Costoclavicular Seated Halstead Seated Wright’s Seated Procedure Findings Radial pulse palpated, arm + Absence of radial pulse = supinated and slightly abducted compression of the head rotated and extended toward neurovascular bundle. affected side. Dr. externally + Paresthesia or radiculopathy in rotates and extends shoulder. upper extremity = compression of neural component Palpate radial pulse, abduct arm + Same as above to 90, elbow flexed to 90, externally rotate shoulder Pt turns head to opposite side Palpate radial pulse bilaterally + Same as above pt flex chin to chest examiner extends pt shoulders Palpate radial pulse, Dr traction’s + Same as above arm inferior, pt hyperextends neck Palpate radial pulse, arm supinated + Compression of axillary art. by examiner abducts arm pec. minor or coracoid process 30 Cervical Spine Orthopedic Tests Test Pt Position Barre-Lieou Seated DeKleyn’s Supine George’s Seated Hautant’s Seated Jackson’s Compression Foraminal Compression Maximum Foraminal Compression Maigne’s Seated O’Donoghue Maneuver Soto-Hall Seated Spurling’s Seated Underburgh’s Standing Seated Seated Seated Supine Valsalva lesion Seated Procedure Findings Pt rotates head maximally from side to side Hang head off end of table hyperextend and rotate History, auscultation, ROM and maneuver Arms held in front, hands supinated, rotate and extend head, eyes closed Dr. hands on head lat flex head apply inf pressure Pt in neutral position, Dr. Hands on head applies inferior pressure Pt actively rotates and hyperextends toward side radicular complaint Rotate and extend head for 30 seconds Resisted and passive ranges of motion Stabilize the sternum and passively flex neck to chest Soft vertical blow to top of patients head Outstretch arms, supinate hands rotate and extend head while marching in place Inhale, hold & bear down + Vertebral artery syndrome = vertigo, nausea, blurred vision +Stenosis or compression of the vertebral, basilar or carotid A + Vascular insufficiency of the vertebral artery + Stenosis or compression of the vertebral, basilar or carotid A + Pressure on nerve root + Same side = facet pathology or nerve root compression + Same side = facet pathology or nerve root compression + Stenosis or compression of the vertebral, basilar or carotid A + Resisted = muscular involvement + Passive = ligament involvement + Osseous, discal or ligamentous pathology + IVF compression or facet lesion + Stenosis or compression of the vertebral, basilar or carotid A + Indicates cerebellar involvement + Pain = space occupying Orthopedic Tests for Meningeal Irritation Test Procedure Findings Brudzinski’s Pt Position Supine Dr flexes chin to chest + Buckling of the knees Kernig’s Supine Dr flexes knee and hip to 90 then tries to extend lower leg + Pt flexes head/neck or responds with resistance or kicking motion 31 Orthopedic Tests For The Shoulder Test Pt. Position Anterior Apprehension Test Apley Scratch Test Seated Biceps Tendon Seated Calloway’s Test Seated Codman’s Drop Seated Dawbarn’s Sign Seated Dugas’ Test Seated Posterior Apprehension Test Subacromial Push Button Supine Supraspinatus Tendonitis Test Yergason’s Test Seated Seated Seated Seated Procedure Findings Flex, abduct & externally rotate affected arm, apply pressure to posterior shoulder Place affected hand behind head & touch opposite scapula, then place hand behind back & try to touch inferior aspect opp. scapula Flexion of pt elbow, Dr grasps wrist & ext. rot. arm vs. resistance Pt arms at side measure around shoulder girth at the acromial tip Dr passively abducts arm 90 then releases support + = Pain or look of apprehension and resists further testing, indicates ant. dislocation + = Pain indicating degenerative tendonitis of rotator cuff, usually supraspinatus tendon. + = Pain localized to biceps tendon indicates instability + = measurement indicates dislocation of the humerus + = Shoulder pain or hunching significant for rotator cuff tear usually supraspinatus tendon Apply pressure inf to the acromial + = Decreased pain w/abduction process: w/pain abduct arm past indicates subacromial bursitis 90 maintaining pressure Instruct patient to touch opposite + = Inability to touch opposite shoulder & bring elbow to chest shoulder, indicates dislocation Flex and int. rotate pt shoulder + = Pain or look of apprehension flex elbow. Dr applies posterior and resists further testing, pressure on the elbow = post. humeral dislocation Dr standing behind pt, apply + = Subacromial bursitis pressure to the subacromial bursa + = Pain indicates rotator cuff tear specifically supraspinatus tend. Arm at side, active abduction vs. + = Pain indicates degenerative resistance tendentious of supraspinatus tend. Pt elbow flexed, palpate biceps + = Pain in the intertubercular tendon & grasp hand w/opposite groove indicates biceps hand. Apply passive ext. rotation tenosynovitis or transverse w/resisted supination. humeral ligament Ulnar Tunnel Syndrome Orthopedic Tests Test Pt. Position Froment’s Paper Sign Seated Tinnel’s Sign or at the Elbow Seated Ulnar Tunnel Triad Seated Procedure Findings Elbow flexed, arm pronated fingers abducted. Place piece of between fingers, adduct fingers Elbow flexed to 90 degrees + Pt unable to hold paper between fingers when examiner pulls = indicates ulnar nerve paralysis + Hypersensitivity = neuritis tap groove between medial epicondyle and olecranon Inspect and palpate ulnar triangle 32 neuroma + Tenderness, ring finger clawing, hypothenar atrophy Orthopedic Tests For The Elbow Test Chair Test Medial Epicondylitis Chair Test Lateral Epicondylitis Cozen’s Pt. Position Standing Standing Seated Procedure Findings Face front of chair supinate hands, push chair to contract forearm flexors Face front of chair pronate hands, push to contract forearm extensors Arm pronated, wrist extended pt makes a fist. Pt actively + = Pain at medial epicondyle indicates medial epicondylitis + = Pain at lateral epicondyle indicates lateral epicondylitis + = Pain at lateral epicondyle indicates lateral epicondylitis Golfer’s Elbow Seated Mill’s Test Seated dorsiflexes Dr applies pressure to dorsum of hand. Arm supinated, elbow slightly flexed. Dr applies pressure at wrist to extend elbow, pt resists. Arm supinated, wrist, elbow and hand fully flexed. Dr passively extends elbow and pronates arm. + = Pain at medial epicondyle indicates medial epicondylitis + = Pain at lateral epicondyle indicates lateral epicondylitis Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Orthopedic Tests Test Pt. Position Phalen’s Seated Reverse Phalen’s Tinel’s Sign Seated Tourniquet Seated Seated Procedure Findings Abduct shoulders, both elbows flexed and arms pronated, wrist flexed, dorsum of hands touching Same as above with wrists extended and palms touching Supinate hand, tap palmar surface of wrist w/ reflex hammer Supinate arm, wrap sphyg cuff + Tingling of hand in median n. indicate neural compression + Same as above + Same as above + Same as above around wrist, pressure 20mm above resting diastolic pressure Stenosing Tenosynovitis Orthopedic Test Test Finkelstein Pt. Position Seated Procedure Findings Elbow flexed, arm pronated pt makes fist w/ thumb tucked inside fingers, actively ulnar deviate hand + Pain of abductor pollicus longus and extensor pollicus brevis tendons = de Quervain’s or Hoffman’s disease 33 Orthopedic Test For Hypersensitivity Test Libman’s Pt. Position Seated Procedure Findings Apply pressure to mastoid process to pain tolerance, repeat bilaterally Indicates patient pain threshold, can be used as index for later examination Procedure Findings Orthopedic Test For Thrombophlebitis Test Homan’s Sign Pt. Position Supine Dr. raises leg to 45 and squeezes + Deep calf or leg pain = indicates calf firmly, maintain pressure and thrombophlebitis dorsiflex foot Orthopedic Test For Arterial Insufficiency Test Pt. Position Buerger’s Test Supine Allen’s Test Seated Procedure Findings Elevate leg, consecutively + = If foot takes over one minute to dorsi/plantarflex foot for 2+ regain normal color indicates minutes, lower leg & sit pt up arterial insufficiency Raise arm, open/close fist for + = Delay of filling or 10 seconds 1 min. Lower arm while occluding indicates arterial insufficiency radial & ulnar artery, release radial, repeat test and release ulnar Orthopedic Tests For The Patella Test Pt. Position Procedure Findings Knee extended pt actively raises leg off table, if unable stabilize patellar tendon/repeat Knee flexed to 30 stress patella laterally + = Ability to raise leg w/tendon braced indicates patellar fracture + = Pt apprehension/quads contract Suspect chronic lateral patellar dislocation + = Floating sensation of the Dreyer’s Test Supine Patellar Apprehension Supine Patellar patella Ballottement Supine Knee extended or flexed to Patellar Grinding Supine comfort, apply posterior pressure to patella Knee extended, block patella inf & sup move in all directions. Sup, inf, med, lat and circumduct 34 indicates intraarticular swelling + = Pain w/pressure or movement indicates chondromalacia patella Orthopedic Tests For The Knee Test Pt. Position Abduction Stress Test (aka - Valgus) Adduction Stress Test (aka - Varus) Apley’s Compression Supine Apley’s Distraction Prone Bounce Home Test Drawer Sign Supine Lachman’s Supine McMurray’s Supine Supine Prone Supine Procedure Findings Stabilize lateral thigh, stress + = Pain at medial aspect of knee leg lateral at the ankle. Perform suspect medial collateral at full extension and 20-30 flexion ligament Stabilize medial thigh, stress leg + = Pain at lateral aspect of knee medial at the ankle. Perform at suspect lateral collateral full extension and at 20-30 flexion ligament Flex pt leg to 90, stabilize thigh + = Pain indicating a torn meniscus w/Dr’s knee, apply down pressure on respective side on pt foot and ext & int rotates Flex pt leg to 90, stabilize thigh + = Pain indicating a torn collateral w/Dr’s knee, grasp ankle w/hands + = Decreased pain confirms injury distract foot and ext & int rotates to meniscus Knee flexed, ankle supported. + = Inability to fully extend knee or Dr allows leg to fall into extension pain indicates meniscus Knee flexed, foot on table, Dr + = Excess anterior sliding of the braces foot w/thigh. Grasp tibia tibia indicates ACL rupture B/L, stress anterior &posterior Excess posterior sliding of the tibia indicates PCL rupture Knee flexed to 30, brace ant + = Instability indicates anterior femur, stress tibia anterior cruciate ligament Flex leg then int rotate leg + = Painful or audible click indicates w/ valgus stress, or ext rotate leg a torn meniscus. Int rot = lateral w/varus stress while extending leg meniscus. Ext rot = medial men. Orthopedic Tests For The Ankle Test Drawer Sign for the Ankle Pt. Position Supine Procedure Knee flexed foot flat on table, Dr braces foot w/thigh, grasp Tibia w/both hands exert ant/post stress on the tibia. Lateral Stability Test Supine Grasp/support foot, apply passive inversion stress Medial Stability Test Supine Grasp/support foot, apply passive eversion stress Findings + = Increased gapping. Posterior shift indicates ant. talofibular ligament. Anterior shift indicates posterior talofibular ligament. + = Increased gapping. Indicates tear of ant. Talofibular ligament or calcaneofibular ligament + = Increased gapping. Indicates deltoid ligament tear. Orthopedic Tests For Ankylosing Spondylitis Test Schober’s Pt. Position Standing Forestierre Bowstring. Standing Procedure Findings th 10 cm span marked from 5 + = Skin measurement is = 14 cm. lumbar cephalad. Pt performs Normal measurement 15 cm. maximum forward flexion, remeasure distance between marks. Pt laterally flexes to one side, + = Pt recruits ipsilateral erector Repeat on opposite side spinae to perform lateral flexion 35