Practice Test with Answers 2012
advertisement

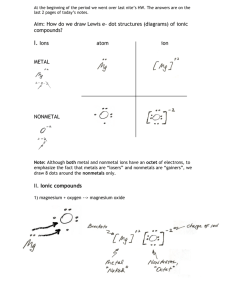
Grade 9 Academic Science Unit Chemistry Practice Test Answers Part A. Multiple Choice 1. Anything with mass and volume? a. Element b. Space c. Matter d. Subatomic Particles 2. If a substance remains the same, but its STATE changes, it is an example of a. Physical Property b. Physical Change c. Chemical Property d. Chemical Change 3. It has a negative change and virtually no mass. a. Electron b. Element c. Neutron d. Proton 4. What is the correct number of NEUTRONS in Sodium if it has a mass of 23 and an Atomic Number of 11 a. 11 b. 12 c. 23 d. 34 5. What is a PURE SUBSTANCE made up of MORE THAN ONE element? a. Element b. Compound c. Solution d. Mechanical Mixture e. Heterogeneous Mixture 6. What is the MAXIMUM number of electrons in Orbit #2? a. Two b. Four c. Eight d. Eighteen 7. Which element is a NOBLE GAS? a. Hydrogen b. Oxygen c. Helium d. Potassium 8. How many DIFFERENT ELEMENTS are in the chemical formula CH3COOH? a. 3 b. 6 c. 8 d. 0 9. What does this WHMIS symbol represent? a. Toxic b. Biohazardous c. Flammabl d. Corrosive 10. What is the IONIC CHARGE of the nitrogen ion? a. 1+ b. 2+ c. 3+ d. 3e. 2f. 1g. No charge 11. What is the correct chemical name of the following compound: Mg2Cl? a. Magnesium chlorine b. Magnesium II chorine c. Magnesium chlorate d. Magnesium chloride 12. What type of bond is used to create the ammonia compound NH4? a. Covalent bond b. Ionic bond c. Electron bond d. Electrical bond 13. What is the IONIC CHARGE of the polyatomic ion in the chemical formula for phosphoric acid (H3PO4)? a. No charge b. 1c. 3 d. 314. “Total Mass of the Products must equal Total Mass of the Reactants” refers to what chemical rule? a. Rule of Mass b. Law of Conservation of Mass c. Law of Concentration of Mass d. Equal Product-Reactant Mass Rule 15. What type of chemical reaction will occur in the following equation: Ca(OH)2 + HCl? a. Decomposition b. Double Displacement c. Single Displacement d. Synthesis 16. In an IONIC COMPOUND, the positive charge always comes first. What is it called? a. Anion b. Positive Ion c. Cation d. First Ion 17. What SUBATOMIC PARTICLES occur in the NUCLEUS of an atom? a. Neutrons and Electrons b. Only Protons c. Protons and Electrons d. Protons and Neutrons Part B – Bohr Rutherford Diagrams Draw a Bohr-Rutherford Diagrams for the following elements 18. Calcium 19. Oxygen Part C – Short Answer 20. There are many ways of changing the RATE of a chemical reaction. Name two. Add more reactant Heat Make more surface area Add a catalyst 21. There are four clues of chemical change. Name three A new colour will appear Heat or light is given off Bubbles of gas form A solid material forms from a liquid...called a PRECIPITATE 22. On the very first day of class, we learned that Lithium (Li), Sodium (Na) and Potassium (K) all reacted with water. They all burned and produced a gas. We discovered these elements were in the same GROUP (Column #1 of the Periodic Table, and as such, they have one electron in their outer shell. We also learned that Potassium reacted MOST VIOLENTLY…it burned and, if the gas was collected, exploded. Two reasons for the more violent reaction was presented. Name ONE. Outer electron was further away from attracting + charge Other electrons cloudy the attraction Part D – Fill in the Charts Use the Periodic Table to complete the chart Chart 1 – 9 marks Element Element Symbol Atomic Number Number of Protons Number of Electrons Number of Neutrons Atomic Mass Cadmium Cd 48 48 48 64 112 Mercury Hg 80 80 80 121 201 Francium Fr 87 87 87 136 223 Chart 2 – Ionic Charge Determine the Ionic Charge for each of the following Element Ionic Charge Ca +2 Br -1 N -3 Chart 3 – Name the Compound 2Al2O3 Mg + Chemical Formula Chemical Name NaCl Sodium chloride K2O Potassium oxide MgF2 + 3O2 F2 2KCl Ca 4Al + 2HCl 2K + CaCl2 + H2 Cl2 Decomposition Synthesis Decomposition Single Displacement Grade 9 Academic Science Unit Chemistry – Practice Test Part A. Multiple Choice 1. Anything with mass and volume? a. Element b. Space c. Matter d. Subatomic Particles 2. If a substance remains the same, but its STATE changes, it is an example of a. Physical Property b. Physical Change c. Chemical Property d. Chemical Change 3. It has a negative change and virtually no mass. a. Electron b. Element c. Neutron d. Proton 4. What is the correct number of NEUTRONS in Sodium if it has a mass of 23 and an Atomic Number of 11 and one electron in its outer shell? a. 11 b. 12 c. 23 d. 34 5. What is a PURE SUBSTANCE made up of MORE THAN ONE element? a. Element b. Compound c. Solution d. Mechanical Mixture e. Heterogeneous Mixture 6. What is the MAXIMUM number of electrons in Orbit #2? a. Two b. Four c. Eight d. Eighteen 7. Which element is a NOBLE GAS? a. Hydrogen b. Oxygen c. Helium d. Potassium 8. How many DIFFERENT ELEMENTS are in the chemical formula CH3COOH? a. 3 b. 6 c. 8 d. 0 9. What does this WHMIS symbol represent? . a. Toxic b. Biohazardous c. Flammable d. Corrosive 10. What is the IONIC CHARGE of the nitrogen ion? a. 1+ b. 2+ c. 3+ d. 3e. 2f. 1g. No charge 11. What is the correct chemical name of the following compound: Mg 2Cl? a. Magnesium chlorine b. Magnesium II chorine c. Magnesium chlorate d. Magnesium chloride 12. What type of bond is used to create the ammonia compound NH4? a. Covalent bond b. Ionic bond c. Electron bond d. Electrical bond 13. What is the IONIC CHARGE of the polyatomic ion in the chemical formula for phosphoric acid (H3PO4)? a. No charge b. 1 c. 3+ d. 314. “Total Mass of the Products must equal Total Mass of the Reactants” refers to what chemical rule? a. Rule of Mass b. Law of Conservation of Mass c. Law of Concentration of Mass d. Equal Product-Reactant Mass Rule 15. What type of chemical reaction will occur in the following equation: Ca(OH)2 + HCl? a. Decomposition b. Double Displacement c. Single Displacement d. Synthesis 16. In an IONIC COMPOUND, the positive charge always comes first. What is it called? a. Anion b. Positive Ion c. Cation d. First Ion 17. What SUBATOMIC PARTICLES occur in the NUCLEUS of an atom? a. Neutrons and Electrons b. Only Protons c. Protons and Electrons d. Protons and Neutrons Part B – Bohr Rutherford Diagrams Draw a Bohr-Rutherford Diagrams for the following elements 18. Calcium 19. Oxygen Part C – Short Answer 20. There are many ways of changing the RATE of a chemical reaction. Name two. 21. There are four clues of chemical change. Name three 22. On the very first day of class, we learned that Lithium (Li), Sodium (Na) and Potassium (K) all reacted with water. They all burned and produced a gas. We discovered these elements were in the same GROUP (Column #1 of the Periodic Table, and as such, they have one electron in their outer shell. We also learned that Potassium reacted MOST VIOLENTLY…it burned and, if the gas was collected, exploded. Two reasons for the more violent reaction was presented. Name ONE. Part D – Fill in the Charts Use the Periodic Table to complete the chart Chart 1 Element Element Symbol Atomic Number Number of Protons Cd Number of Electrons Number of Neutrons 48 80 Francium Atomic Mass 201 Fr 223 Chart 2 – Ionic Charge Determine the Ionic Charge for each of the following Element Ionic Charge Ca Br N Chart 3 Chemical Formula Chemical Name NaCl K2O PART E – Complete (if required), Balance AND Define the TYPE of chemical reaction for the following chemical equations Al2O3 Mg + HCl ____________________________ _____________________________ + O2 F2 KCl Ca Al + K + Cl2 _____________________________ _____________________________