File
advertisement

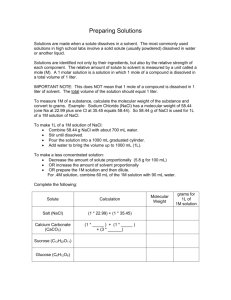
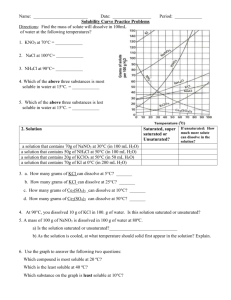
Name__________________________ Date________________Period______ Chapter 12 Practice Test Solutions 1. What is a solute? What is a solvent? How do you tell which is which? 2. If 5.5 grams of sodium chloride is dissolved in 94.5 grams of water which is the solute? Which is the solvent? 3. What is a solution? Another name for a solution is a _____________________ mixture. 4. What does soluble mean? Is sucrose soluble? 5. Is milk a homogeneous or heterogeneous mixture? Why? 6. Mud mixed with water and oil mixed with water are two examples of what type of heterogeneous mixture? 7. Fog is an example of this type of mixture, which is an intermediate of solutions and suspensions. 8. How can we tell whether or not something is an electrolyte? 9. Draw a picture representing a solid NaCl crystal and a picture of NaCl dissolved in H2O. State which will conduct electricity. 10. If you dissolve all the salt you can in a glass of water, the resulting mixture would be classified as _______________________. 11. What is a supersaturated solution? 12. What type of compounds are immiscible with water (remember water is polar)? Give two specific examples. 13. What type of compounds are miscible with oil (remember oil is nonpolar)? Give two specific examples. 14. Why does warm soda go flat faster than cold soda? 15. What does partially soluble mean? Give two examples of substances that are only partially soluble in water. 16. In a dynamic equilibrium of a saturated solution the two processes that are occurring at the same rate are ____________________________ and ________________________________. 17. At 20 degrees celcius, 36 grams of NaCl will dissolve in 100 g of water. If you heat the water to 70 degrees, 115 grams will dissolve. Cooling the solution back to 20 degrees creates a solution containing solute in excess of the amount it could contain if it were at equilibrium. This solution is called ___________________________________. 18. What effect does temperature have on the rate of dissolution? Explain why it affects the rate. 19. What effect does surface area have on the rate of dissolution? Why? 20. What effect does agitation have on the rate of dissolution? Why? 21. In general, how does temperature affect solubility? 22. How many grams of NaOH are required to prepare 550.0 mL of a 4.00 M solution? 23. A procedure calls for 0.340 moles of sucrose. How many milliliters of a 0.225 M sucrose solution would you use? 24. How many milliliters of isopropyl alcohol would you use to prepare 870mL of a 20% (v/v) solution of isopropyl alcohol? 25. A solution is made with 0.078 L of isopropyl alcohol and enough water to make 0.150 L of solution. What is the concentration of isopropyl alcohol? 26. How many grams of sucrose are in 540 g of 26.5% (w/w) sucrose solution? 27. How many grams of KCl are in 2.5 kg of .92% by mass KCl solution? 28. Express .02450 ppm in ppb. 29. Define endothermic. 30. Define exothermic. Name__________________________ Date________________Period______ Chapter 12 Practice Test Solutions 1. What is a solute? What is a solvent? How do you tell which is which? 2. If 5.5 grams of sodium chloride is dissolved in 94.5 grams of water which is the solute? Which is the solvent? 3. What is a solution? Another name for a solution is a _____________________ mixture. 4. What does soluble mean? Is sucrose soluble? 5. Is milk a homogeneous or heterogeneous mixture? Why? 6. Mud mixed with water and oil mixed with water are two examples of what type of heterogeneous mixture? 7. Fog is an example of this type of mixture, which is an intermediate of solutions and suspensions. 8. How can we tell whether or not something is an electrolyte? 9. Draw a picture representing a solid NaCl crystal and a picture of NaCl dissolved in H2O. State which will conduct electricity. 10. If you dissolve all the salt you can in a glass of water, the resulting mixture would be classified as _______________________. 11. What is a supersaturated solution? 12. What type of compounds are immiscible with water (remember water is polar)? Give two specific examples. 13. What type of compounds are miscible with oil (remember oil is nonpolar)? Give two specific examples. 14. Why does warm soda go flat faster than cold soda? 15. What does partially soluble mean? Give two examples of substances that are only partially soluble in water. 16. In a dynamic equilibrium of a saturated solution the two processes that are occurring at the same rate are ____________________________ and ________________________________. 17. At 20 degrees celcius, 36 grams of NaCl will dissolve in 100 g of water. If you heat the water to 70 degrees, 115 grams will dissolve. Cooling the solution back to 20 degrees creates a solution containing solute in excess of the amount it could contain if it were at equilibrium. This solution is called ___________________________________. 18. What effect does temperature have on the rate of dissolution? Explain why it affects the rate. 19. What effect does surface area have on the rate of dissolution? Why? 20. What effect does agitation have on the rate of dissolution? Why? 21. In general, how does temperature affect solubility? 22. How many grams of NaOH are required to prepare 550.0 mL of a 4.00 M solution? 23. A procedure calls for 0.340 moles of sucrose. How many milliliters of a 0.225 M sucrose solution would you use? 24. How many milliliters of isopropyl alcohol would you use to prepare 870mL of a 20% (v/v) solution of isopropyl alcohol? 25. A solution is made with 0.078 L of isopropyl alcohol and enough water to make 0.150 L of solution. What is the concentration of isopropyl alcohol? 26. How many grams of sucrose are in 540 g of 26.5% (w/w) sucrose solution? 27. How many grams of KCl are in 2.5 kg of .92% by mass KCl solution? 28. Express .02450 ppm in ppb. 29. Define endothermic. 30. Define exothermic.