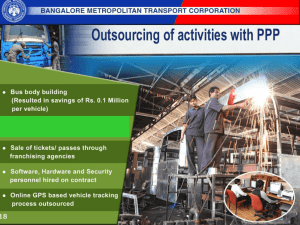
cabinet decisions - Press Information Bureau
advertisement

YOUTH AFFAIRS & SPORTS YOUTH AFFAIRS A Scheme for the development and empowerment of adolescent launched to assist NGOs and educational institutions for taking up programmes & projects focussing the needs of the adolescent (10-19 years). A National Committee under the Chairpersonship of Secretary (YA&S) set up for preparation of the draft National Plan of Action under National Youth Policy. Various convergence strategies worked out with other ministries like Culture, Tourism, Women & Child Development, Health & Family Welfare, NACO and others. The Report of the National Commission for Youth presented to Parliament. All but two recommendations accepted. Nehru Yuva Kendra Sangathan drawn up a multi-pronged strategy for empowering Youth Clubs and volunteers. Rashtriya Sadbhavna Yojna approved to harness the energies of the youth and sensitize them towards the needs of community. “Gandhi Gramodaya Sankalp Abhiyan – Model Village Project” launched under Nehru Yuva Kendra Sangathan on October 2, 2004. A comprehensive Management Information System developed right up to the youth club level for the offices of the NYKS to effectively assess progress under various programmes. The Rajiv Gandhi National Institute of Youth Development, Sriperumbudur, Tamil Nadu, strengthened with setting up of five Divisions in different disciplines. SPORTS Arrangements for the conduct of the Games finalized by the Group of Ministers with the emphasis on planning for and creation of required infrastructure till 2007. A National Anti Doping Agency (NADA) as an autonomous Government Society being set up for undertaking, promoting and supporting all anti-doping activities in the country. Categorizing of sports disciplines as a dynamic concept based on their performance in International Games like Olympics/Asian Games/ Commonwealth Games decided. With a focus on Olympics, an Olympic to Olympic long-term development plan being implemented. To make the functions of various National Sports Federations (NSFs) more transparent, Observers appointed in the important disciplines to check the proceedings in important deliberations of the Federations, including those related to selection of players for international teams Sports Authority of India (SAI) approved the establishment of 10 new Army Boys Sports Company (ABSCs) at Delhi Cantt., Bhopal (MP), Secundrabad (AP), Lucknow(UP), Faizabad (UP), Ramgarh Cantt. (Jharkhand), Meerut(UP), Leh(J&K), Jaipur (Rajasthan) and Ahmednagar (Maharashtra). Under the National Talent Search Contest Scheme (NTSC) implemented by SAI, 25 Navodaya Vidyalayas would be adopted during the year 2005-2006. Fifty-eight Local Rural Tournaments at district level with an estimated cost of Rs. 1.5 crore sanctioned in North-East. Two Special Area Games (SAGs) being set up to tap sports talent in remote rural, tribal and coastal areas. 1 More than 200 elite sportspersons being assisted for training as well as foreign exposure and participation in international tournaments under various schemes of the Ministry. 1354 projects assisted under the Sports infrastructure schemes during 2004-05 with a central assistance of Rs. 38.99 crore. A Plan of Action has been approved and is under implementation to observe the Year 2005 as the International Year for Physical Education and Sports as declared by UNESCO. GENERAL As a first ever exercise, Gender Budgeting has been drawn up allocating about 30 per cent of Plan Budget covering various schemes for women beneficiaries for the year 2005-06. With a view to provide adequate representation to SC / STs and OBC, a stipulation has been made that while sanctioning funds due representation should be given to them in all schemes and programmes. To ensure transparency and access to information, a Sports Portal called “Sportal” (http://sportal.nic.in) launched in November, 2004. *** LAW & JUSTICE Common Minimum Programme of the UPA Government envisages enforcement of the law without fear or favour and also pledges enacting of Model Comprehensive Law to deal with communal violence. Judicial Reforms and revamping of the legal system given top priority. The Government commits to speed up clearance of backlog of cases in High Courts and Lower Courts besides deliberating with Chief Justices of High Courts and Judges of the Supreme Court to smoothen this process. Action taken for upgrading infrastructure facilities and for appointment of additional staff in all the courts of the country. Prevention of Terrorist Activities Act (POTA) abolished and decided to suitably amend the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act, 1967. Phukan Commission inquiring into the Tehalka episode dissolved. Legal Services Authorities scheme being strengthen to give Free Legal Aid to deserving class. National Legal Literacy Mission launched to benefit millions of poor and disadvantaged sections of the society. **** STATISTICS AND PROGRAMME IMPLEMENTATION Modernisation of Statistical System underway. Work relating to Economic Census of the country begun. Process of updating Social Statistics expedited. Social Development Index to be brought out. 2 Human Development Index on the cards. National Statistical Commission taking shape. Hand Book for urban, rural and local self-government. System for maintaining data-base of key indicators at Block level. Statistical profile of Social Indicators by 2015. Report on Millennium Development Goals. Monitoring of Central projects streamlined. New Guidelines for MPLADS. ***** DEVELOPMENT OF NORTH-EAST The Department of Development of North Eastern Region (DONER) upgraded to a Ministry in order to sharply focus on development issues of the North-Eastern Region. The North Eastern Council (NEC) restructured with Minister, DONER as its Chairman. Major initiative to seek international cooperation for development of the North-Eastern Region in 5 core Sectors - road, urban development, trade and investment, water resources and energy. Under the scheme of Non-Lapsable Central Pool of Resources (NLCPR), 80 new projects sanctioned to the North-Eastern States at a cost of Rs.601.21 crore. In the Central Budget of 2005-06, Rs.9306 crore earmarked for expenditure in the North-Eastern States, an increase of 51.7 per cent over 2004-05. Indian Institute of Management (IIM) to be set up in the North-Eastern Region. ***** DEVELOPMENT OF NORTH-EAST The Department of Development of North Eastern Region (DONER) upgraded to a Ministry in order to sharply focus on development issues of the North-Eastern Region. The North Eastern Council (NEC) restructured with Minister, DONER as its Chairman. 3 Major initiative to seek international cooperation for development of the North-Eastern Region in 5 core Sectors - road, urban development, trade and investment, water resources and energy. Under the scheme of Non-Lapsable Central Pool of Resources (NLCPR), 80 new projects sanctioned to the North-Eastern States at a cost of Rs.601.21 crore. In the Central Budget of 2005-06, Rs.9306 crore earmarked for expenditure in the North-Eastern States, an increase of 51.7 per cent over 2004-05. Indian Institute of Management (IIM) to be set up in the North-Eastern Region. ***** PANCHAYATI RAJ Seven Round Table Conferences of State Ministers of Panchayati Raj held to formulate a draft Action Plan towards achieving the objective of strengthening of Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) to enable them emerge as institutions of self-government as envisioned in the Constitution. A set of around 150 points emerged through consensus at the conclusion of the Round Table Conferences. A Council of Ministers of Panchayati Raj of States/Union Territories constituted under the Chairmanship of the Minister of Panchayati Raj to monitor the implementation of the 150 recommendations. A Committee of Chief Secretaries of States and State Panchayati Raj Secretaries constituted under the chairmanship of the Secretary (Panchayati Raj) to monitor the progress on the implementation by States and UTs of the 150 recommendations. A process of visiting each of the States/UTs initiated to review the progress in implementing the points for action agreed upon in the Round Tables. A task force of State secretaries set up for working out modalities for implementation of Centrally Sponsored Schemes through PRIs in all States and Union Territories. A National presentation made on Rural Business Hubs, “Economic Empowerment Through Panchayats”, in collaboration with Confederation of Indian Industry. ***** TRIBAL AFFAIRS The benefit of insurance coverage under ‘Janashree’ scheme of Life Insurance Corporation of India given to Primitive Tribal Groups for the security. Rs. Two crore released to the UT Administration of Anadaman & Nicobar Islands for resettlement and rehabilitation of Tsunami affected PTGs. 4 A number of developmental projects taken up for the improvement in Human Development Index of the Scheduled Tribe population and creation of critical infrastructure in tribal areas. Steps taken to formulate a Scheduled Tribe (Recognition of Forest Rights) Bill. Comprehensive Land Based Plan taken up for development of STs. Planning Commission constituted a Task Group on development of Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes with focus on the tribal areas taking the social, economic and geographical parameters into consideration. An amount of Rs.330 crore released for infrastructure development projects and establishment of Eklavya Modern Residential Schools. The State government asked to conferownership rights in respect of Minor Forest Produce including tendu patta on the Scheduled Tribes. Need-based schemes in the area of education for ST population being implemented. National Overseas Scholarship approved for continuation till 2007. Rajiv Gandhi National Fellowship Scheme conceived to provided fellowships for M.Phil and Ph.D. courses. A quarterly newsletter “Janjatiya Jagran” stated to create awareness among the people about the various schemes being implemented for the welfare of the STs. *** EXTERNAL AFFAIRS High priority given to relations with Neighbours. Engaged in a sustained and comprehensive dialogue with Pakistan. Establishing strategic and cooperative partnership for peace and prosperity with China. Engaged in broad range of discussions with US while maintaining both maturity and dynamism in relations between the two countries. The visit of the Prime Minister of Canada resulted in a Joint Statement highlighting many initiatives including strengthening the India-Canada partnership in advancing collaboration in Science & Technology and creation of Tsunami warning system for Indian Ocean countries. Visits of the Russian President, Deputy Prime Minister, Defence and Foreign ministers resulted in establishing multifaceted relations with Russia that include establishing new banking links and identifying IT and energy as areas and facilitating business travel and tourism both ways. The possibility of trilateral cooperation in the economic field between Russia, China and India also being explored. Growing recognition of India as an indispensable partner of the European Union, now consisting of 25 members, seeking strategic partnership with India Efforts being made to develop energy relationship with the Central Asia. India’s “Look East policy” furthering a partnership with the ASEAN countries and adopting of document on “ India – ASEAN Partnership for Peace, Progress and 5 Prosperity” symbolising that India now forms the inner core of the countries in ASEAN’s political relationship with the rest of the world. India’s relations intensified with West Asia, Gulf & Arab World as well as with the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) with which India signed a Framework Agreement for Economic Cooperation and also facilitated Indian citizens in the region by establishing a 24-hour Helpline Centre in Saudi Arabia. The Government also decided to send no troops to Iraq. The ‘Focus Africa Policy’ led to a greater exchanges of high level visits, greater economic and technical cooperation, both bilateral as well as within the context of the African Union and India’s contribution to peace – keeping operation in several African countries. Intensifying relations with Latin America & Caribbean region by engaging the political leaders of Latin America for support on bilateral and multilateral issues and extending relief assistance to countries such as Jamaica, Grenada and Bahamas. .To ensure a more consultative approach in Indian foreign Policy, a mechanism initiated for domestic developments by coordinating with other Ministries and agencies as well as with State governments, particularly those which border India’s neighbours. Indian Diplomacy, Multidimensional and Consultative process based on National Consensus and needs of the times Number of Haj pilgrims from India increased and subsidy restored. ***** ENVIRONMENT & FORESTS Draft National Environment Policy (NEP) released. Further reforms initiated in grant of environmental clearances. "Good practices" adopted in regulatory procedures such as environmental clearance, forestry clearance, Coastal Zone Regulation, Genetic Engineering Approval Committee and experimentation on animals. Guidelines framed covering utilization and care of animals to be used in testing, research and training. The State and UT Governments requested not to resort to eviction of tribals and forest dwellers. Need based diversion of forest land below one hectare allowed for providing basic developmental facilities for tribals and other dwellers of forest fringe villages. Action plan prepared to address the natural ecological phenomenon of gregarious flowering of muli bamboos, having high social and economic implications in the North -East. India currently number one in terms of the number of projects accorded the host country approval and under consideration by the CDM (Clean 6 Development Mechanism) Executive Board, as per the provisions of Kyoto Protocol. Production of ozone-depleting Halons phased out. Meeting of the Like Minded Megadiverse Countries, hosted by India, helped in evolving a common position for developing an international regime on Access and Benefit Sharing. ***** RURAL DEVELOPMENT Allocation for cash component of Sampoorna Grameen Rozgar Yojana enhanced from Rs.4500 crore during 2004-05 to Rs.5500 crores during 2005-06. National Food for Work Programme launched in 150 most backward districts of the country w.e.f. November 14, 2005. While allocating enhanced outlay for 2005-06 50 lakh MT of foodgrains and Rs.4500 crores from 20 Lakh MT of foodgrains and Rs.2020 crore during 2004-05. A National Employment Guarantee Bill introduced in Lok Sabha. A new State Institute of Rural Development established in Bihar with a sanctioned amount of Rs. 335 lakh. As part of the capacity building of NGOs, over 50 workshops/training programmes organized with the participation of 1500 NGOs. Guidelines for Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana revised. For additional resource generation under PMGSY through funding from external multilateral funding agencies a Rs. 2000 crore loan agreement signed with the Asian Development Bank for Rural Roads projects in Jharkhand, Rajasthan, H.P. and U.P. In North-east, proposals of 3000 road works cleared upto March 2005 with an allocations of Rs.1130 crore. On completion of these proposals, in the North Eastern States, 10000 km of rural roads will be constructed to provide connectivity for 3300 habitations in the North East States. 4371 Watershed projects sanctioned during 2004-2005. The ceiling on construction assistance under the Indira Awaas Yojana enhanced from Rs. 20,000 to Rs. 25,000 per unit for the plain areas and from Rs. 22,000 to Rs. 27,500 for the hilly/difficult areas. The ceiling on upgradation of unserviceable kutcha house to pucca/semi pucca house also enhanced from 10,000 to Rs.12,500 for all areas. Out of 1111029 Dwelling Units under IAY completed during the period 2004-05, 555313 houses allotted in the name of women and 308350 houses allotted jointly in the name of both husband and wife. Outlay for Swarnjayanti Gram Swarozgar Yojana enhanced from Rs.800 crore in 2003-04 to Rs.1000 crore in 2004-05. 7 First special project under SGSY sanctioned performing artists living below the poverty line. Seven pilot projects launched under Provision of Urban Amenities in Rural Areas to field test the strategy and Rs.10 crore sanctioned during 2004-05. Out of 1413254 Swarozgaris assisted under the Swarnjayanti Gram Swarozgar Yojana during the year 2004-05 817361 (57.84 per cent)women SHGs and Individual Swarozgaries assisted. To give Special emphasis on drinking water supply and sanitation the budget allocation increased by 43.93 per cent from Rs.3300 crore in 2004-05 to Rs. 4750 crore in 2005-06. Under the Total Sanitation Campaign, 121.31 lakh individual household toilets, 4774 sanitary complexes, 1.37 lakh school toilet blocks, 23,326 anganwadi toilets, 3459 rural sanitary marts constructed so far. First ever Nirmal Gram Puraskar successfully organized along with release of national mass media campaign. for livelihood improvement of *** NON-CONVENTIONAL ENERGY SOURCES A District Advisory Committee (DAC) conceptualized in every district to oversee the implementation of renewable energy programmes. A total of 403 remote villages/hamlets electrified under Remote Villages Electrification Programme during 2004-05. A programme for providing “energy security” in villages through biomass and other renewable energy sources formulated. 20th August – to be observed as ‘Rajiv Gandhi Akshya Urja Diwas’ every year to focus attention on the deployment of renewable energy systems and devices in rural and urban areas. Out of a target of 3075 MW grid-interactive renewable power capacity addition during the 10th Plan period, over 1200 MW capacity added through wind, small hydro and biomass power in the country in last one year. The first 2 MW wind turbine installed at Chettikulam, Tirunelveli District, Tamil Nadu. About 1,00,000 biogas plants installed during 2004-05. Around 16,530 solar photovoltaic lighting systems and 59.4 kWp solar photovoltaic power plants installed. 8 Biomass power projects aggregating to 140 MW capacity installed creating fresh employment and income generation opportunities specially in rural areas. Over 1,50,000 m2 of collector area installed in the country for solar water heating in domestic, industrial and commercial sectors making the cumulative installed collector area over one million m2. A solar steam cooking system consisting of 20 dishes of 12.6 m2 area each and producing 1200 kg. of steam everyday commissioned at Global Hospital and Research Centre, Mount Abu. Two plants, first time in India, commissioned for Energy Recovery from Urban and Industrial Wastes. Bi-monthly News Letter “Akshay Urja” released in Hindi & English for widely popularizing renewable energy throughout the country. --RAILWAYS With advancements in railway technology, Indian Railways grown to a national net work of 63,221 route kilometers, moving on an average 1.58 million tons of freight and 14 million passengers per day. A total of 1211 kms of Broad Gauge lines comprising of 150 kms of new lines, 779 kms of Gauge Conversions and 282 kms of Double Lines added during 2004-05. An outlay of Rs 493 crore provided to Rail Vikas Yojna during 2005-06 to execute 34 projects which form part of the Golden Quadrilateral and Port connectivity routes. Several innovative taken to provide World class infrastructure in the Railways which include bridge improvement and rehabilitation, 5566 kms. of track renewal, development of RORO (Roll on Roll of) wagons for transportation of trucks, trial of corrosion resistant aluminum body wagons, introduction of crew friendly cabs and new initiatives to develop guard friendly brake-vans. Safety standards recorded a phenomenal improvement as consequential train accidents come down to 234 during the year. A proposal to set up Rail Land Development Authority through an amendment to the Railway Act 1989 approved by the Cabinet and a bill to this effect introduced in Rajya Sabha. No increase in passenger fare in the Rail Budget 2005-06. Integrated Train Enquiry System as well as National Train Enquiry System established to provide updated position of trains to the passengers. The Railways being reoriented to work for the advantage of the poor and common man with the introduction of Kulhar, the earthen pot, milk products in the form of Lassi, 9 Matha (buttermilk), transportation of farm products from green growing areas to the major consumption centres by refrigerated vans and handloom and khadi in the Railways. Uttar Sampark Kranti Express flagged off by Prime Minister and the Jammu TawiUdhampur Rail line dedicated to the nation at Udhampur. The Mumbai Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminal declared as World Heritage Site by UNESCO. This is the only Railway station in the world that has been bestowed this honour. ***** SPACE Indian Remote Sensing Satellite CARTOSAT-1 and HAMSAT successfully launched by PSLV –C6 from Sriharikota. A state-of-the-art Second Launch Pad (SLP) established at Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC) SHAR at Sriharikota. First educational satellite ‘EDUSAT’ launched in September 2004 by indigenous Geo-synchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV). The airdrop test of the instrumented Space-capsule Recovery Equipment (SRE) successfully conducted on August 2004 from Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC). The first cluster of three satellite based Village Resource Centres (VRC) inaugurated and would provide information related to land records, natural resources, interactive farmers’ advisory etc. A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) signed with the French Space agency, CNES, for the development and launch of an atmospheric satelliteMegh-Tropiques A project to design and launch a satellite, ASTROSAT approved. The Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) with the participation of Indian Industry, successfully developed Automatic Weather Stations (AWS) to be deployed in various parts of the country. ****** COMPANY AFFAIRS Concept Paper on a comprehensive revision of Companies Act, 1956 issued. An expert committee appointed to suggest amendments to the new companies Bill to make it more effective. An Investor Education and Protection Fund set up to protect the interests of the small investors A new system developed to lodge online complaints by investors and depositors against companies. A special cell created to monitor and target the vanishing companies as also to ensure all possible remedial measures. 10 Ambitious e-governance initiatives launched to re-position the Ministry of Company Affairs as an organization capable of fulfilling the stakeholders’ aspirations. Electronic filing of company documents initiated through an interactive and paperless registration process on Internet. Simplified Exit Scheme 2005 launched to enable the defunct companies get their names struck off the Registrar of Companies through a simplified procedure. ***** MINES The long pending revision of royalty on major minerals (other than Coal, Lignite and Sand for stowing) and Dead Rent notified. Out of 188 Reconnaissance Permits for a total area of 2,54,307 sq. kms, 23 reconnaissance permits granted for an area of over 34,642 sq. km during 2004-05. The Government approved NALCO’s second phase expansion proposal at a cost of Rs. 4,091.51 crore. On the completion of expansion project, NALCO’s Bauxite mining capacity will increase from the present 48 lakh tons to 63 lakh tons, of Alumina production from 15.75 lakh tons to 21 lakh tons and of Aluminium production from 3.45 lakhs tons to 4.60 lakh tons. NALCO earned highest ever net profit of Rs. 1,222.33 crore during the year 2004-05 with an all time record sales turnover of Rs.4,437.97 crore. Mineral Exploration Corporation Ltd. (MECL), made a net profit of Rs. 244 lakh after a gap of 14 years and added 4232 million tons of mineral reserves to the national inventory during 2004-05. Hindustan Copper Ltd. (HCL), another loss making PSU, made a net profit of Rs.52.07 crore against a projected loss of Rs. 67.67. It has re-commissioned its Khetri Mine. Emphasis being laid on modernization of land, aerial and marine survey systems of the Geological Survey of India (GSI) through acquisition of the latest technology. GSI covered 2,958.50 sq. km. area by specialized thematic mapping, 13,876 sq. km. by geochemical mapping and 6,978 sq. km. by ground geophysical mapping. GSI led the XXIII Indian Antarctica Expedition and also declared by the Government a nodal agency on landslide studies. Besides other minerals, GSI added 2,987 million tons of coal and 98 million tons of lignite to national mineral inventory. 11 GSI took up post Tsunami studies in Andaman group of islands and recorded nearly 6,500 aftershocks. IBM during the year inspected 2238 mines, pointed out 2251 violation cases, rectified 1125 cases and approved 586 mining plans and schemes. ***** MINISTRY OF TOURISM Record tourist arrival and foreign exchange earnings increased from Rs. 16,429 crore to Rs. 21,828 crore India declared amongst top 5 tourism destinations amongst 134 countries by the leading tourists journal of USA. ‘Incredible India campaign’ awarded ‘PATA Gold award’. India appointed chairperson of WTO task force to draw strategy for rehabilitation of tourism in Tsunami affected areas. The country also assigned the role of lead country for tourism in BIMSTEC region. Revival of tourism in J & K taken up as one of the top priorities and a special package for tourism revival in the state. Boost to rural tourism with 31 rural sites identified to develop as rural tourism and get benefited economically. Incentives provided for augmenting budget accommodation for domestic tourist through budget proposals. Initiatives launched in the sphere of Medical Tourism and Cruise Tourism in partnership with the private sector to make India emerge as a major global hub. Setting up of Conference centres to increase India’s share in the growing business of Meetings, Incentives, Conferences and Events (MICE) segment. Night Bazaars to provide healthy cultural entertainment and a unique shopping experience to the tourists. A scheme embarked on to design and produce world class souvenirs to give glimpses of Indian handicrafts. Infrastructure upgradatation in Buddhist circuits taken up in a big way. To expedite creation of world-class tourism infrastructure in the country, State Governments being pursued to set up single window clearance system. 12 Atithi Devo Bhavah”- campaign re-instilling a sense of responsibility towards tourists and re-enforcing the confidence of foreign tourist towards India as a preferred holiday destination. ***** FOOD, PUBLIC DISTRIBUTION & CONSUMER AFFAIRS DEPARTMENT OF FOOD AND PUBLIC DISTRIBUTION Decentralised procurement implemented in 10 States/UTs, including non-traditional States like Bihar, Assam, Jharkhand, Tamil Nadu and Karnataka resulting in the procurement of an additional sixteen lakh MT of foodgrains and considerable saving in freight. Storage and transit losses came down from 1.26 per cent during 2000-01 to 0.91 per cent during 2004-05. 13 lakh MT of godown space de-hired. National Policy on Bulk Handling, Storage and Transportation of Foodgrains under implementation. Legislation on Negotiable Warehouse Receipts to increase liquidity in rural areas through banking sector under consideration. Identification of additional 50 lakh Antyodaya Anna Yojana households at the ‘risk of hunger’ started while 33.22 lakh households issued special ration cards. Guidelines issued for issue of ration entitlement slips to migrant labour, displaced persons and homeless, besides coverage of ‘AAY left-outs’ for BPL cards. FCI Bonds worth Rs. 4023 crore floated at an average rate of 7.14 per cent. To improve the efficiency of FCI, a study by Mckinsey instituted. Food subsidy contained at Rs. 25,774 crore in 2004-05, despite expansion of Antyodaya Anna Yojana (AAY), freezing of Central Issue Price and increased off take under TPDS and various welfare schemes. Tuteja Committee Report on revitalization of sugar industry submitted which is under the consideration of the Government. 13 Import of raw sugar under Advance Licence Scheme allowed to ensure availability of sugar for domestic consumption and the period of fulfilment of export obligation of white sugar out of the imported raw sugar raised to 36 months from 24 months. As on February 28, 2005, a total of Rs. 11,872.5 crore paid towards cane arrears, leaving a balance of Rs. 1,754.57. A total of Rs. 408.6 crore paid as buffer subsidy to sugar mills to defray the carry-over cost and liquidation of cane arrears, besides disbursing Rs. 78.08 crore towards reimbursement of internal transport and freight charges on export of sugar. The rate of interest for advance to sugar sector reduced by two percentage points below the prevailing bank rate of 6.9 per cent in order to ease the liquidity of enterprising sugar mills. The statutory minimum price of sugarcane fixed at Rs. 74.5 per quintal for the year, 200405, Rs. 1.5 per quintal more than the previous sugar year, 2003-04. DEPARTMENT OF CONSUMER AFFAIRS A National Consumer Helpline inaugurated. The helpline (Toll free telephone No. 160011-4000) guides, informs and advises consumers regarding consumer related problems. Antyodaya Anna Yojana cardholders exempted from payment of the stipulated fee for filing cases in the district forum of consumer court for cases up to Rs. one lakh. A Standing Committee constituted for promotion of consumer causes and for highlighting consumer interest to the forefront of all operations in Government, public and private sectors. A Consumer Activist Group set up within the Department comprising senior officials and experienced persons. Three Committees constituted for preparing a module for consumer clubs, for drafting a National Consumer Policy and for suggesting a suitable mechanism for handling consumer complaints. Computerisation of consumer forums in the country completed at a cost of Rs. 48.64 crore. An amount of Rs. 10.2 crore released to three State Commissions of Uttaranchal, Chhattisgarh and Jharkhand and for 53 newly created district forums of 12 States for strengthening infrastructure facilities. 14 The value of derivatives trading in all the commodities increased from Rs. 1,30,214 crore in 2003-04 to Rs. 5,00,000 crore in 2004-05. ***** DEPARTMENT OF WOMEN AND CHILD DEVELOPMENT The Infant Milk Substitutes, Feeding Bottles and Infant Foods Act, 1992 and its Amendment Act, 2003 protected against the repeal by the forthcoming Food Safety and Standards Bill 2005 through concerted efforts of the Department. The intersectoral coordination with sky partners and nutrition namely health and family welfare, food and public distribution, elementary education and literacy upscaled. Instructions issued to all State governments to include iodized salt under the public distribution system and the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and the Director General of Indian Council of Medical Research requested to expedite launching of the double fortified salt in the country with a view to address the widespread problem of nutritional anaemia. National guidelines on Infant and Young Child Feeding developed, printed in Hindi and English languages and released. Expert Consultations on important nutritional issues like infant and young child feeding, micronutrient malnutrition held and decisions communicated to the state Secretaries for Implementation. Regional Consultation Meet on Nutrition organized for North Eastern States in February 2005 to facilitate greater focus on malnutrition reduction in these States. Review of National Nutrition Policy (1993) undertaken by the Working Group in 2004. Meeting of Executive Committee of National Nutrition Mission held. Nutrition Education and Awareness Generation intensified. Twenty-seven video films on nutrition under the title ‘Poshan aur Rashtra Nirman’ produced in Hindi, English, Bangla and Assamese languages by Food and Nutrition Board. A 30-episode radio sponsored programme on ‘Poshan aur Swasthya’ in 12 regional languages and 8 North Eastern languages broadcast through AIR. A Wall Calendar (Poster Calendar) on Nutrition for 2005 was printed in Hindi and English and widely disseminated in the country. 15 ******* URBAN EMPLOYMENT & POVERTY ALLEVIATION National Urban Renewal Mission (NURM) to provide basic services to the urban poor for fulfillment of their basic needs, including security of tenure, housing, water supply, sanitation, education, health care and social security cover in 60 cities. Other cities to be covered by Integrated Housing & Slum Development Programme by combining the VAMBAY and NSDP Schemes. HUDCO declared a Mini Ratna in August, 2004. HUDCO floated a subsidized loan scheme at 6.5% for repairs, retrofitting and reconstruction of new houses for economically weaker sections in Tsunami affected areas against 7.5% presently applicable for EWS schemes. Guidelines on the Foreign Direct Investment in Townships revised Allocation for National Slum Development Programme enhanced from Rs.363.94 crore to Rs.700 crore. During 2004-05, 68636 micro enterprises set up to assist the urban poor in self employment and 106394 urban poor given skill up gradation training under Swarna Jayanti Shahari Rojgar Yojna. A Task Force under the Chairmanship of Secretary set up in the Ministry with the objective to evolve a viable micro-credit mechanism for the urban poor/informal sector. During 2004-2005, Central subsidy of Rs. 269.41 crore was released for the construction of 1,13,004 dwelling units and 35,086 toilet seats under Valmiki Ambedkar Awas Yojana (VAMBAY). Rs. 82 crore released to various agencies for the execution of 18 projects in the North eastern region.Also sanctions issued for setting up 0ne Bamboo Mat Production Centre in Assam,Tripura,Meghalaya and Mizoram. Housing project comprising 218 dwelling units for Comptroller and Auditor General of India (CAG) & 74 dwelling units for Central Government Employees completed at Ahmedabad. Also the housing project comprising 720 dwelling units was completed at Noida, U.P at a total cost of Rs.85 crores. The First Model Demonstration Houses of 252 dwelling units under VAMBAY scheme executed in 9 months by the Building Mat erials and Technology Promotion Council to promote proven innovative, eco-friendly and cost-effective building materials and construction technologies. 16 Propagation of cost-effective and Environment Friendly Technology being undertaken. Construction of demonstration houses under VAMBAY Scheme in 11 States, model toilets in Delhi and demonstration structures using bamboo based building components in Mizoram and Tripura initiated *********** MINISTRY OF OVERSEAS INDIAN AFFAIRS A focused and business like Pravasi Bhartiya Diwas-2005 organised at Mumbai. Simplification of the application forms and procedures for grant of Overseas Indian citizenship (OIC) to Indian community in 16 specified countries underway. Extension of the facility of OIC to all those PIOs, who migrated from India after 26 January, 1950 to countries that permit dual citizenship announced Codification and Publication of a compendium of facilities available to the Overseas Indians under different schemes of the various Ministries. Guidelines for inter-country adoption of children being revised with a proposal for NRIs/PIOs to be deemed on parity with resident Indians. Protection of interests of the migrant Indian workers abroad and their welfare to be streamlined and strengthened. Pravasi Bhartiya Bima Yojana to have streamlined claim settlement procedures and additional benefits to the emigrant workers. Possibility of providing legal assistance to migrant workers in distress as part of insurance package being examined. Working of the offices of the Protectors of Emigrants to be computerized and Smart cards issued to workers, going abroad, with a view to ensure protection from exploitation of vulnerable categories of workers. A two-pronged strategy being proposed to safeguard the interests of Indian women proposing to marry or already married to NRIs. Pilot projects being launched to help PIOs tracing their roots. . ***** HEAVY INDUSTRIES AND PUBLIC ENTREPRISES 17 Redeeming its pledge in the National Common Minimum Programme (NCMP) to revitalize the Public Sector, a Board for Reconstruction of Public Sector Enterprises (BRPSE) established. All privatization being considered by the Board for Reconstruction of Public Sector Enterprises on a transparent and case to case basis while privatization revenues to be used for designated social sector schemes Initiatives taken to give full managerial and commercial autonomy to successful profit making PSEs operating in competitive environment. Profit making companies not to be privatized. Chronically loss making companies either to be sold off or closed after giving the workers their legitimate dues and compensation. Idea to induct independent directors of repute to make the Boards of Directors more professional mooted. CPSEs proposed to be empowered with enhanced financial powers to enable them to make quicker decisions relating to investments and joint venture. Strengthening the corporate governance practices in the CPSEs. Reviewing of Navratna and Miniratna scheme. The common parameters set in the MoU Guidelines for all PSEs other than Social Financial , Trading and Consultancy PSEs. Public Enterprises Survey 2003-04 laid in Parliament and indicated a remarkable improvement in the overall performance of the 242 CPSEs. MINISTRY OF HEALTH & FAMILY WELFARE The National Rural Health Mission (2005-12) throughout the country with special focus on 18 States. The next phase of the Reproductive & Child Health Programme (RCH-II) to be launched, at a projected Outlay of Rs. 40,000 crore over the next five years. Anti Retroviral Therapy to AIDS patients through 25 Hospitals and partnership on HIV/AIDS expanded with inclusion of other organizations. Ensuring the services of Sexually Transmitted Diseases Clinic, Voluntary counseling and testing centers and Prevention of parent to child transmission Clinics in each district hospital in the country. The goal set to achieve complete interruption of polio-virus transmission in 2005. 18 Introduction of AD syringes in immunization sessions throughout the country in 2005. Additional support to the States for vaccine delivery and mobilization of children in immunization session sites by ASHAs and other service providers. Expansion of Hepatitis B Immunization programme in well-performing States where the DPT 3rd dose coverage is 80 per cent and above. A low osmolarity ORS launched. The National Breastfeeding Partnership to promote breastfeeding in the country. Integrated Management of Neo Natal and Childhood Illness (IMNCI) plan launched in 4 districts in each of Maharashtra, Gujarat, Delhi, Haryana, Orissa, Madhya Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Rajasthan & Utrranchal. In response to Tsunami disaster, a framework for Management of Childhood Illnesses in Emergencies prepared. By February 2005, 957 million population in 51 districts across the country have access to the programme. It is proposed to cover the whole country under the revised NCT TB Control Programme during 2005. For the first time in India. a web based resource centre developed for preparing TB communication materials. Reduction in malaria cases to 1.71 million in 2004 by up scaling of anti malaria operations. Establishment of over 4 lakh fever treatment depots and drug distribution centres through village based volunteers to make anti malaria drugs available at the doorsteps. Malaria and other vector borne diseases in Tsunami affected areas in Andaman and Nicobar Islands effectively controlled by providing additional man and material support PUBLIC HEALTH Sale of Tobacco Products within a radius of 100 yards of Educational Institutions throughout the country banned under the Provisions of Comprehensive Tobacco Control Legislation. National Mental Health Programme introduced in 47 new districts across the country National Programme on Prevention and control of Deafness under preparation subject to the approval of the Planning Commission. NATIONAL CANCER CONTROL PROGRAMME (NCCP) 19 Revised National Cancer Control Programme (NCCP) put in place to bridge the gaps in the availability of cancer treatment facilities in the country. Under the RCC scheme of the revised NCCP, the quantum of assistance enhanced to a one time assistance of Rs.3 crore instead of existing assistance of Rs.75 lakh per year. The quantum of assistance under Oncology grant enhanced from Rs.2 crore to Rs.3 crore. NATIONAL PRORAMME FOR CONTROL OF BLINDNESS Vision 2020: The Right to Sight launched on 10.10.2004. NATIONAL LEPROSY ELIMINATION PROGRAMME National goal of elimination of leprosy to be achieved by December 2005. Leprosy prevalence rate declined from 2.44 to 1.76 by March 2005 (Provisional) NON-COMMUNICABLE DISEASE CONTROL PROGRAMMES National Programme for cardiovascular diseases/stroke and National Programmes on Diabetes. INTEGRATED DISEASES SURVEILLIANCE PROJECT (IDSP) launched in November 2004. Second phase of the project to cover 12 States in the year 2005. EMERGENCY MEDICAL RELIEF More than one hundred doctors consisting of physicians, psychiatrics, general duty medical officers, public health specialists and paramedical workers sent to the Tsunami affected coastal areas A wide spectrum Formulary of proprietary medicines containing 504 medicines put in place for CGHS beneficiaries. ESTABLISHMENT OF AIIMS LIKE INSTITUTIONS Implementation of the Pradhan Mantri Swasthya Suraksha Yojana (PMSSY) for establishment of six AIIMS- like institutions in the underserved States and upgradation of seven medical institutions in other six States given a go-ahead. PARA-MEDICAL MATTERS Paramedical and Physiotherapy Councils Bill to regulate and maintain the standards of certain paramedical professions and physiotherapy / occupational therapy approved by the Cabinet. A revised scheme of Development of Nursing Services approved for implementation during Tenth Plan. The scheme provides for enhanced assistance for training programmes for nurses and for strengthening of the schools of nursing in the States. 20 PNDT DIVISION Central Supervisory Board constituted to monitor the implementation of the Act under the Pre-conception & Pre-natal Diagnostic Techniques (Prohibition of Sex Selection (PNDT) Act,. INTRAHEALTH PORTAL A portal designed by the NIC called Intrahealth was launched by the Hon’ble Minister of Health and FW on 21st March 2005. This portal will help disseminate information to the employees within the Ministry. It would particularly help in file tracking, expenditure monitoring, monitoring of important projects and maintain employees database. DEPARTMENT OF AYUSH AYUSH wings opened in District Hospitals. 8 Specialty Clinics/Polyclinics established and essential drugs were supplied to 8152 Ayurveda, Sidha, Unani and Homoeopathic Dispensaries in Rural and backward areas Mainstreaming AYUSH services as a part of the proposed National Rural Health Mission and the ongoing programmes. Integrated North Eastern Institute of ISM&H planned to be set up at Pasighat in Arunachal Pradesh to ensure reach of AYUSH services in North Eastern Areas. Permission for setting up of 14 new colleges of AYUSH systems including 2 National Institutes for Siddha and Unani Medicine granted. *** DEPARTMENT OF FERTILISERS In the light of the Government’s National Common Minimum Programme (NCMP), the issue regarding the feasibility of revival of the closed Fertilizer-producing Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs) prepared by Projects and Development India Limited. Urea, a controlled fertilizer and decontrolled phosphatic and potassic fertilizers made available to farmers of the country including poor and marginal farmers at subsidized selling prices. A budgetary provision of Rs.16253.90 crore made for subsidy on fertilizers during 200506. Government borne additional burden of subsidy to the tune of approximately Rs.3,000/crore during 2004-05 as compared to the budgetary allocation for this period, keeping its commitment to give highest priority to Agriculture. A Working Group constituted to review the effectiveness of Stage-I and II of New Pricing Scheme (NPS) for urea units and to formulate a policy for urea units for Stage – III commencing from 1.4.2006. 21 Policy announced for setting up new urea projects and expansion of existing urea projects for augmenting the domestic production capacity of urea. Government formulated a policy for conversion of existing naphtha/FO/LSHS based urea units to natural gas/LNG as feedstock. The sale of Urea (205.49 lakh MT), DAP (60.77 lakh MT) and MOP (23.10 lakh MT) registered an increase of about 5 per cent, 10 per cent and 40 per cent respectively during the year 2004-05 as compared to the sales of 2003-04 Urea (195.8 lakh MT), DAP (55.2 lakh MT) and MOP (16.47 lakh MT). All the major fertilizers made available to the farmers in the country at the same prices as prevailed during 2002-03 despite hike in the overall prices. *** HUMAN RESOURCE DEVELOPMENT The Central Advisory Board of Education reconstituted. Seven Committees of CABE set up. Under Sarva Siksha Abhiyan 66,147 Elementary Schools opened, 33,777 additional classrooms constructed, 3.10 lakhs additional Teachers appointed, about 6.5 crore girls and children belonging to SCs and STs studying in Elementary Schools, given free textbooks and 134% step up in SSA fund outlay for 2005-06 over 2004-05. National Mission of SSA under Prime Minister set up. Kasturba Gandhi Balika Vidyalaya (KGBV) Scheme, for establishment of girl’s residential Upper Primary Schools, launched in August, 2004, to promote education of disadvantaged girls in Educationally Backward Blocks of the country. 717 KGBVs sanctioned during 2004-05. Mid-Day Meal Scheme revised in September, 2004, to provide cooked meal to all Primary School children. About 11 crore children being benefited. Education Cess @ 2% levied on all Central taxes to fulfil Government’s commitment to provide and finance universalized quality basic education. Outlay for Elementary Education in 2005-06 is more than double compared to that in 2004-05. National Commission for Minority Education Institutions set up. Revision of the National Curriculum Framework for School Education (NCFSE) taken up. 22 The power to decide on the fee structure restored to the Indian Institutes of Management. Decision taken to restore the Central University status of the University of Allahabad and conversion of Manipur University into a Central University. The assistance given to Non-Government Organizations along with instances of denial of assistance to secular institutions like the Gandhian Institute of Studies being reviewed. A comprehensive review of the Indian Council of Historical Research ordered for strengthening the institution to enable it to realize its full autonomous potential. A Bill for regulating the fee structures in professional institutions drafted for consultation with the stakeholders. A Committee of experts constituted under the Chairmanship of Prof. C.N.R. Rao, to examine all relevant issues pertaining to the entry of foreign universities in India. In pursuance of the Reconstruction Plan announced by the Prime Minister on 17-18 Nov. 2004, the Government of J&K accorded sanction for the setting up of 13 new colleges including two women’s colleges and total Literacy Campaign proposals for Kargil and Doda approved. Concerned about the problem of reports of examination stress, exercise initiated to bring about examination reforms. The Central Board of Secondary Education initiated steps to improve the examination system. Steps being taken to bring about transparency in the functioning of the accrediting and affiliating bodies including AICTE, UGC, CBSE, NCTE etc. ***49 MINISTRY OF TEXTILES Hosiery and knitwear from the SSI sector dereserved. Allocation to TUFS enhanced to Rs.435 crore, along with an additional capital subsidy of 10 per cent for the processing sector. Duties on specified textile machinery items, raw materials and spare parts for manufacture of such machinery brought down from 20 per cent to 10 per cent whereas the existing concessional duty of 5 per cent on some other machinery continued. Apparel Parks being set up for Export Scheme to promote of modern apparel units at major growth areas with grant upto Rs.17 crore for infrastructure work, training and common facilities. Textile Centres Infrastructure Development Scheme introduced with the objective of modernizing infrastructure facilities at major textile centres; sixteen projects already sanctioned. 23 Merger proposed of the TCID and APE Schemes into one restructured “Scheme for Integrated Textile Parks” for speeding up the implementation of the Schemes and to actualize the vision of attaining the export target of $50 billion by 2010. Establishment of an institution of National Excellence for imparting Fashion Business Education with International Benchmarking proposed. The Technology Upgradation Fund Scheme further fine tuned to increase rapid investments in the targeted sub-sectors of the textile industry. For the textile processing sector only, a credit linked capital subsidy at the rate of 10 per cent, in addition to the existing 5per cent interest reimbursement approved and for small scale textiles and jute industries, the rate of credit linked capital subsidy enhanced from 12per cent to 15per cent. All the NTC workers’ dues amounting to Rs.1800 crore including on VRS paid. To clear, scour, dry, dehair and card the Pashmina, a Pashmina Dehairing Plant at Leh set up with an expenditure of Rs.8.25 crore. Policy Guidelines revised for “Vanya Silk cultivation” under the Forest Conservation Act, 1980 whereby cultivation of all varieties of Vanya Silk (Tasar, Eri & Muga) on its identified host plants in forests by the tribal and non-tribal rearers is treated as a forest based activity. National Jute Policy’ 2005 announced. In Handicrafts sector 112 new projects sanctioned to undertake Baseline Survey & Mobilization under Baba Saheb Ambedkar Hastshilp Vikas Yojana Scheme, aiming to cover about 30,572 artisans and formation of nearly 1800 Self Help Groups of 16 new Common Facility Centres sanctioned. The Satellite Centre of IICT in Srinagar and Craft Development Institute commenced functioning generated additional 9228 employment during the year. Decision taken to develop a trademark for Handloom on lines similar to “Wool mark” and “Silk Mark” to enable handloom products to develop with a distinct identity. Freeing the Handloom Sector from the CENVAT Chain. The Powerloom Sector Group Workshed Scheme approved 5 Hi-Tech Weaving Park projects to give employment to 12,000 persons. *** SMALL SCALE INDUSTRIES AND AGRO & RURAL INDUSTRIES New programmes formed to revamp the Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC) and for the modernization of coir, handlooms, power looms, garments, rubber , cashew, handicrafts, food processing, sericulture, wool development, leather, pottery and other cottage industries. New Scheme on Performance and Credit Rating of Small Scale Industries launched to help them on better assessment by financial institutions for their working capital and investment requirements. Setting up of a National Commission on Enterprises in the unorganized/informal. 24 De-reservation of 108 items reserved for exclusive manufacture in the small scale sector ranging from textile products to agricultural implements to facilitate technology upgradation and enhance competitiveness. The investment limit raised in plant and machinery from Rs. 1 crore to Rs. 5 crore in respect of 7 items of Sports Goods reserved for manufacture in the small scale sector. The small and medium enterprises fund of Rs.10,000 crore operationalised by the SIDBI since April 2004. The strength of industrial growth during 2004-05 is particularly striking in view of shocks like Tsunami, a deficient monsoon, and a third oil shock. ***** 39 SHIPPING, ROAD TRANSPORT & HIGHWAYS DEPARTMENT OF SHIPPING Sethusamudram Ship Channel Project put on fast track. New Maritime Policy and National Maritime Development Programme on the anvil. Renewed focus on development of Inland Water Transport (IWT). Guidelines for regulation of tariff by TAMP, revised and issued. Tonnage Tax introduced. Foundation Stone of International Container Transshipment Terminal (ICTT) at Cochin Port laid. Third Container Terminal at Jawaharlal Nehru Port approved. Second Container Terminals at Chennai and Tuticorin Ports approved. ISPS Code implemented. Record traffic handled at major Ports. Record profit of Shipping Corporation of India. Hindustan Shipyard Ltd. and Hoogly Dock & Port Engineers Ltd. to be revived. Indian Maritime University (IMU) to be set up. Work on formulation of Cruise Shipping Policy started. ILO Convention No. 108 concerning Seafarers' Identity Document ratified. First indigenous aircraft carrier being built by Cochin Shipyard. 25 DEPARTMENT OF ROAD TRANSPORT & HIGHWAYS Implementation of NHDP Phase-I and II accelerated. NHDP Phase-III approved, 6 projects awarded and 28 to be awarded soon. NHDP Phase IV, V, VI and VII in the pipeline. Special Package for Roads in North-East and J&K. A big push to public-private partnership. The Control of National Highways (Land and Traffic) Act 2002 brought into force. Information Technology (Smart Card) introduced in Road Transport sector. *** WATER RESOURCES A pilot scheme for repair, renovation and restoration of water bodies directly linked to agriculture approved with an outlay of Rs. 300 crores. A scheme for Flood Control in Brahmaputra and Barak Valley of Assam with an estimated cost of Rs. 150 crores approved, and works taken up in Assam, Tripura and Mizoram. Schemes for Rain Water Harvesting & Ground Water Recharge formed. Support provided for improvements in irrigation system through 133 Command Area Development Schemes. Support to State Governments for completion of irrigation projects under Accelerated Irrigation Benefits Programme. Schemes and feasibility reports on Interlinking of Rivers prepared. The Committee of environmentalists, social scientists and other experts on Interlinking of Rivers constituted to address environmental, social and ecological consensus while preparing the Detailed Project Reports on Interlinking of Rivers. *** 26 FOOD PROCESSING 17 The Ministry of Food Processing Industries (FPI) increased its interactions with the State Governments for developing the FPI sector as the State Nodal Agencies (SNAs). A conference of State Ministers of Food Processing held to discuss the need to frame an integrated Food Law, National Food Processing Policy and lowering of sales tax and other taxes on food products. The Draft National Policy of Food Processing and Vision prepared for a speedy development of the food processing sector. To rationalise the multiplicity of food laws, a Group of Ministers (GoM) set up to suggest legislative and other changes to formulate a modern and integrated food law. A Draft Integrated Food Law (IFL) cleared by the GoM. A National Institute of Food Technology and Management (NEFTEM) to be set up to develop world-class food technologists and train entrepreneurs and managers in the food industry. Investors’ meets in the FPI sector for the North Eastern Region and J&K held to deliberate on ways and means for promoting food processing industries in the region. An International Investment Conference to be organised in August, 2005. The Government to support the establishment of one modern food processing industry/food park in each Parliamentary constituency besides, 10 mega food parks in the country. The Government allowed under Income Tax Act, a deduction of 100 per cent of profit for five years and 25 per cent of profits for the next five years in case of new agro processing industries. Excise duty on dairy machinery reduced to zero and on meat, poultry and fish reduced from 16 per cent to 8 per cent. For making value addition in palm oil sector, customs duty on refined palm oil fixed at 75 per cent. Paddy Processing Research Centre at Thanjavur, Tamil Nadu to be upgraded and modernized and have institutional tie-ups with Jadavpur University, West Bengal. A Fishery Development Council (FDC) and Meat Development Board (MDB) to be constituted. ***** MINISTRY OF PLANNING 27 Additional funds provided to both centre and state governments for implementing NCMP based objectives- SSA, employment guarantee scheme, rural health, ICDS and road network in north-eastern region given greater attention. Strategy evolved to expedite implementation of cross-sectoral NCMP are - reports of inter-ministerial task groups set up for the purpose sent to Prime Minister. Special Purpose Vehicle being set up to finance infrastructure in specified sectorsroads, ports, airports and tourism to benefit most. Task force constituted to promote trade and investment opportunities in north- eastern region. Standing committee working to address inter-sectoral issues related to tribal development. Backward regions grant fund set up- rs.5,000 crore provided this year. Committee under chairmanship of Prime Minister is working to finalize roadmap for creating world class infrastructure delivering services. recommendations on civil aviation and national highway sector finalized. Another committee under chairmanship of Prime Minister working to initiate policies aimed at developing quality infrastructure in rural areas. Intensive dairy development project being launched to ensure remunerative prices for milk. Marine fishing policy formulated to promote integrated development of marine fisheries. More funds for elementary education to meet UPA Government commitment to universalization of access to basic education. To generate supplementary wage employment &food security national food for work programme launched in 150 most backward states. Efforts are on to secure atleast 100 days of work to one adult member of every poor household- national rural employment guarantee bill tabled. More funds provided for education and economic development of minorities. Pilot project launched in 25 states to repair, renovate and restore water bodies linked to agriculture. Rs. 300 crore provided this year. National harvesting scheme for SC and ST farmers announced. One lakh irrigation units to be covered, Rs. 150 crore schemes for critical anti-erosion works in Brahmaputra-Barak basin approved. Nine states will benefit from the scheme. National urban renewal mission for fast track planned development of 60 selected cities being launched. Jute Technology Mission being proposed to further develop and mordernise jute industry. URBAN DEVELOPMENT 51 National Urban Renewal Mission prepared with an outlay of Rs.5,500 crore in the current financial year 2005-06. National Mission Mode Project on e-Governance in municipalities to be launched in August, 2005 in 35 cities with million plus population 28 National Urban Information System (NUIS) to be implemented in 137 towns/ cities in the first phase. National Urban Transport Policy finalized. Draft Master Plan for Delhi-2021 notified and the final plan to be ready by December 2005. Draft Regional Plan 2021 published by NCR Planning Board. An amount of Rs.114.5 crore released for infrastructure development in North Eastern Region including Sikkim for 29 projects. First underground section of 4 km. from Vishwa Vidyalaya to Kashmere Gate of the second line inaugurated. The underground line from Vishwa Vidyalaya to Central Secretariat and the third line from Indraprastha to Dwarka (25.65 km.) to be completed by June 2005 and March 2006 respectively. Delhi Development Authority allotted 12,659 houses during the year. CPWD completed 860 units of various types of General Pool Residential Accommodation and 35,250 Sq.m of General Pool Office Accommodation in addition to 4,517 residential units for other Ministries & Police Organizations A project for setting up permanent resettlement of Tsunami affected people in Andaman & Nicobar islands and Pondichery taken up. Under the Scheme for Infrastructural Development in Mega Cities, a sum of Rs.303.12 crore released to Chennai, Kolkata, Hyderabad, Bangalore and Mumbai. A total of 206 new water supply projects for towns having population less than 20,000 were sanctioned under Accelerated Urban Water Supply Programme. Four proposals for setting up desalination plant at Ramanathapuram & Keelakarai in Tamil Nadu, Bheemunipatnam in Andhra Pradesh, Gopalpur in Orissa and Muthialpet in Pondicherry approved. Solid Waste Management and Drainage in 10 selected Airfield Towns started functioning. About 19 new infrastructure projects at an estimated cost of Rs.1,272 crore with loan component of Rs.824 crore sanctioned by the National Capital Region Planning Board during the year. ****** 29 PETROLEUM AND NATURAL GAS For intensive exploration of oil and gas in the country, global competitive offer of fifth round under the New Exploration Licensing Policy (NELP-V) launched with 20 blocks (6 deepwater, 2 shallow water and 12 on land blocks) for receipt of bids by 31 May 2005. For the first time data on all the blocks made available online and promotional campaign drew huge response. Three oil & gas discoveries announced by ONGC- one in the western offshore and two in the eastern offshore in KG basin while Oil India discovered oil & gas in Assam. RIL-Niko consortium’s development plan for their gas discovery in Krishna-Godavari in deep water approved at an estimated investment of $ 2.47 billion. OVL acquired exploration blocks in Australia, Egypt, and Qatar; OVL & Oil India obtained interests in a block in Ivory Coast while OIL – IOC consortium acquired one block in Libya. Efforts to harness alternative sources of gas expected to lead to first commercial production of Coal Bed Methane (CBM) in the country in 2006-07 in the 16 CBM contracts signed in first two rounds. Steps taken to offer more blocks under 3rd round of CBM by the end of 2005. To convert commercially non-producible coal from deeper layers into gas, a move initiated to utilise Underground Coal Gasification technology. “Indian Strategic Petroleum Reserves Limited” a special purpose vehicle was incorporated to set up strategic crude oil storage of 5 million ton at Mangalore, Vizag and third location in or near Mangalore to cater to sudden supply disruptions. Natural gas import initiatives through transnational pipelines and in the liquefied form pursued. Petroleum Ministry authorised to negotiate pipeline gas imports from Iran through Pakistan. For pipeline gas imports from Myanmar through Bangladesh, a draft MoU for approval by respective Governments prepared. GAIL and IOC signed an agreement with M/s NIGEC (National Iranian Gas Export Corporation to import 7.5 MMTPA of LNG from Iran paving way for detailed discussions in this regard and on participation of Indian companies in Iranian oilfields. A long pending decision taken to undertake construction of Kochi Liquefied Natural Gas Terminal and the capacity of the proposed terminal to be raised to 5 MMTPA from the earlier plan of 2.5 MMTPA. The first ever Ministerial Round Table of the principal Asian oil producers and buyers held with a view to promote stability, security and sustainability in the Asian oil economy through regional cooporation. To reinforce diplomatic thrust for energy security, an Advisory Committee on Oil Diplomacy for Energy Security constituted. An Advisory Committee on Synergy in Energy set up with a view to making oil PSUs domestically & globally competitive for 30 achieving national objectives of energy security and for suggesting appropriate structure of the oil PSUs. Steps taken to encourage/streamline supply and use of bio-fuels for blending with petrol and diesel as the resources like ethanol, bio-diesel and hydrogen hold a significant potential to supplement efforts to reduce import dependence for hydrocarbons. The OMCs in cooperation with the State government are experimenting with running biodiesel blended diesel buses in Gujarat, Haryana and Maharashtra.. A Hydrogen Corpus Fund set up with a corpus of Rs 100 crore through contribution of oil and gas companies and the Oil Industry Development Board (OIDB) for supporting research & development in various aspects of hydrogen. A number of fiscal measures taken to contain the adverse impact on common man of the unprecedented rise and volatility of international oil prices since late 2003/early 2004, distressingly escalated since mid-2004. Petrol prices frozen since November, 2004. Effected excise & customs duty reductions on three different occasions bringing down duties to on domestic LPG and PDS kerosene to zero level besides reductions in customs duties on crude oil and excise & customs duties on petrol and diesel. A pilot project approved for strengthening distribution of kerosene under PDS in 10 per cent of the blocks (nearly 600) to ensure its availability to consumers. Against a demand of 111.17 million tons of products in the country in 2004-05 refining capacity stood 127.37 million tons per annum (MMTPA) up from 118.37 MMTPA during 2003-04. Petroleum sector emerged as a big exporter with net-exports increasing by 69 per cent in 2004-05 to reach Rs.28,385 crore from Rs.16,781 crore in 2003-04. Clean auto fuels in the country made available for supplying Euro-III fuels in Metro and 7 other major cities and Euro-II in the rest of India by April 01, 2005. Barring Euro-II diesel in 7 States, all the other stipulations of Mashelkar Committee to be fully covered by October, 2005. ***** PERSONNEL, PUBLIC GRIEVANCES AND PENSION Right to Information Act passed. The Cabinet approved setting up of second Administrative Reforms Commission to prepare a detailed blue print of public Administration system . 31 Conference of Chief Secretaries organised to focus on good governance, administrative reforms and related issues and model code of governance finalised and circulated to all Chief Secretaries of States.. Cabinet endorsed/approved setting up of National Institute for Smart Government as a not-for-profit Company with equity of 49 per cent by Government and 51 per cent by the private sector. A Digital Repository to disseminate the knowledge of best practices in the area of Good Governance being launched shortly. So far 105 Information Facilitation Counters set up by different Ministries/Departments. Organizations awarded for successfully implementing e-Governance initiatives during the National Conference on e-Governance. Workshops organized at Bhopal, Chennai, Delhi and Kolkata for creating awareness and building capacities in the area of Record Management. Eleven films on good governance practices of States produced. 78 Reports of various Administrative Reforms Commissions/Committees spanning from pre-British era till date being digitized. The presentation on best practices of the States being organized every month to share the experiences with other States. ***** 14 DEFENCE Reduction of troops in Jammu & Kashmir as a confidence building measure. A Department of Ex-Servicemen Welfare created to look into the welfare of the ExServicemen and their family members. The budget allocation for defence ministry increased to an all time high of Rs. 83,000 crore keeping in view the increased need for modernisation of armed forces. Recommendations of the Phase I of the AV Singh Committee Report involving restructuring of the officers’ cadre in the three services implemented. Exhibitors from 13 countries attended the fifth International Aerospace exhibition, Aero India-2005 held in Bangalore. Army, Navy, Air Force and Coast Guard carried out the unprecedented massive relief and rescue operations in aid of Tsunami victims and during the recent snow avalanche in J&K. A group of ministers constituted to go into the issue of ‘One Rank One Pension’ Scheme for retired servicemen. 32 The first indigenously built Sukhoi MK-I aircraft inducted in the Air Force. The first batch of five indigenously manufactured Main Battle Tank Arjun rolled out of the Heavy Vehicles Factory, Avadi in Tamil Nadu. Manufacturing of country’s first aircraft carrier - Air Defence Ship, formally begun in Kochi. The new South Western Command of the Indian Army inaugurated in Jaipur. The Agni-II Missile, Prithvi-III, a modified version of surface-to-surface missile Supersonic Anti-Ship Cruise Missile Brahmos successfully flight tested. The Indian Air Force recorded lowest accident rate last year as compared to other Air Forces of the world during the last 35 years. IAF Cheetal Helicopter set a new world record of landing at an attitude of 25, 150 ft. Air Marshal Padmavathy Bandopadhyay taken over as the first lady Air Marshal of the Indian Air Force. A new Coast Guard Station commissioned at Jakhau, Gujarat. Air Force held joint exercise with the Air Force of South Africa and Singapore. A joint Indo-UK Command post planning exercise Emerald Mercury held. India and Russia signed a protocol on military technical cooperation. Kelkar Committee set up to recommend changes in the acquisition procedure and enabling a greater participation of private sector in Defence production. ******* 10 CULTURE National Mission for Manuscripts launched the first ever National Survey of Manuscripts and established over 40 manuscript research and manuscript conservation centres all across the country. Structural conservation of 678 monuments including World Heritage Monument undertaken by the Archaeological Survey of India during the year. The ASI executed Ajanta-Ellora Conservation and Tourism Development Project (Phase I) and also carried out chemical preservations on the paintings of Ajanta, Sanchi Stupa, Shiv Temple, Rajasthan, Khajuraho Temples and painted ceilings of the Taj Complex. Documentation work of antiquities of site museums of the ASI taken up besides the completion of digital documentation at Sarnath, Nalanda, Nagarjuna Konds, Chennai, Goa and Delhi. 33 Registration of antiquities undertaken in Andhra Pradesh, Uttranchal, Goa, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Tripura, Sikkim, Chhatisgarh, Jharkhand, Kerala, Pondichery, Lakshadweep, Daman & Diu. A digitization programme for converting rare books and manuscripts into digital format initiated at the National Library Kolkata, Rampur Raza Library and Khuda Baksh Library. Seventy five years of the historic Dandi March observed. Central Advisory Board on culture set up. A National Folk Theatre Festival organized as an annual event under the Zonal Cultural Centres at Kolkata. The new building – Bhasha Bhawan, of the National Library, Kolkata inaugurated with State-of–the-art facilities. ***** POWER The National Rural Electricity Infrastructure and Household Electrification Programme launched to provide access to electricity to all households in five years. The Centre will provide 90 per cent capital subsidy under the scheme. The Government announced the National Electricity Policy which aims at accelerated development of power sector, providing supply of electricity to all areas and protecting interests of consumers and other stakeholders. The Centre has issued guidelines for competitive bidding for determination of tariff for procurement of power by distribution licensees as provided for in the Electricity Act, 2003. Power generation during the year 2004-05 registered a 5.2 per cent growth. 2000 MW fresh capacity added by NTPC during the year. The Central Electricity Authority completed preparation of pre-feasibility reports of 162 schemes with an aggregate installed capacity of over 47000 MW under the 50000 MW hydro-electric initiatives. 78 schemes of capacity of 34,020 MW with first year indicative tariff below Rs.2.50/Kwh selected for taking up detailed S&I and preparation of DPRs. 57 schemes aggregating to an installed capacity of 27.816 MW have already been allotted to CPSUs/State Power Utilities for preparation of DPRs. 34 7 schemes of capacity of 1415 MW allotted to IPPs by State Governments for preparation of DPRs. Since January, 2004, 11 independent power producers facilitated to arrive at financial closure for an installed capacity of about 4000 MW entailing an investment of Rs.15000 crores. Investment sanctions granted for 7 new transmission systems including strengthening of the national grid. An Expert Committee on Energy Policy actively pursuing the Accelerated Power Development and Reforms Programme aimed at bringing about techno-commercial revival of the distribution system. Review of the Electricity Act, 2003 being carried out and the concern of the stakeholders pertaining to affordability and availability of power for the rural poor being addressed through the Electricity policy and the Tariff policy. An Appellate Tribunal for Electricity under Section 110 of the Electricity Act notified and to be operationalised soon. 567 projects costing Rs.19,489 crores approved and Rs.5541 crores released under APDRP and Rs.956 crores incentive released to six states. A comprehensive awareness creation programme for energy conservation launched. ******* 27 LABOUR The rate of interest, 9.5 per cent, on Employees Provident Fund amount of subscribers for 2002-03 and 2003-04 approved as recommended by the Central Board of Trustees. “Rajiv Gandhi Shramik Kalyan Yojana”, the first of its kind, launched to provide unemployment allowance to workers during involuntary unemployment. About 20000 establishments with six lakh members brought within the purview of the Employees Provident Funds & Miscellaneous Provisions Act, 1952. As EPF dues Rs. 1,894.82 crore recovered from the defaulting establishments. Employees State Insurance Corporation (ESIC) increased eligibility wage ceiling from Rs.6,500 to Rs.7,500 netting in about 1.10 lakh more workers. ESI Scheme extended to new geographical areas bringing in 1.50 lakh additional employees within its coverage; additional 8,000 factories and establishments brought within its coverage following intensive surveys in implemented areas. ESI Scheme extended to educational institutions as also to all municipal corporations, municipalities, cantonment board areas and other notified town areas. 35 Labour Minister held consultations with Employers and Central Trade Unions to build a consensus on labour reforms and called for adequate social security net for workers. The Payment of Wages Act, 1936 being amended prescribing more stringent grievance redressal machinery for workers. Cabinet approved amending of the Factories Act to allow women to work in night shifts with adequate safeguards. Unorganized Sector Workers’ Bill 2004 being redrafted in consultation with social partners to promote well being of workers in the unorganised sector as envisaged in the NCMP. Housing subsidy per unit for beedi workers doubled and eligibility ceiling also increased. One time grant of Rs. 2 crore to be given to State governments, ESIC and NGOs for construction of hospitals for beedi workers. Five hundred existing ITIs, to be upgraded at an estimated cost of Rs. 160 crore for imparting skills to workers to meet international standards and new ITIs sanctioned in Jammu & Kashmir and North Eastern States. Tripartite consultation process further strengthened to deal with workers’ issue. One hundred more National Child Labour Projects launched to rehabilitate children withdrawn from work that includes sanction of 1362 Special schools of 50 children each. ESIC medical relief teams deployed to Tsunami affected areas for providing emergency medical services including free supply of drugs and dressings to the affected people. Employees Provident Fund Organisation made special arrangements for expeditious disposal of claims and facilitate payment of provident fund and pension to the families of the members of the Fund killed in Tsunami fury. ***** 22 HOME AFFAIRS Infiltration in Jammu and Kashmir come down by 61 per cent and number of violent incidents by 24 per cent. High-powered Task Force constituted to implement the Reconstruction Plan for Jammu and Kashmir. Bus service from Srinagar to Muzaffarabad begun. Terrorist violence in North-East went down by 19 per cent. 36 Committee to review Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act, 1958 constituted. POTA repealed. Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act, 1967 amended to incorporate necessary provisions for fighting terrorism. Standing Committee of Chief Ministers of Naxal affected States headed by Union Home Minister to be set up to initiate and pursue a coordinated approach to curb Naxal violence. Comprehensive revision of Security Related Expenditure Scheme to help Naxalaffected States. Action initiated on the report of the Committee on police reforms. Special packages of Rs.2822.17 crore sanctioned for relief and rehabilitation work in Tsunami-hit Andhra Pradesh, Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Pondicherry and of Rs.821.88 crore for A&N Islands. Disaster Management Bill passed in Parliament & Disaster Management authority being created through an executive order. A Centrally funded coastal security scheme approved. Action plan prepared for activating the Inter-State Council. A new Commission on Centre-State relations being set up. National Integration Council reconstituted. Action Plan on Good Governance prepared. Bill to deal with communal violence drafted and getting refined. Tamil declared a classical language. Visa regime for some categories of Pak nationals liberalized. Overseas Citizenship of India to be granted to all overseas Indians who migrated from India after January 26,1950. ****** 25 INFORMATION & BROADCASTING 37 The Direct-to-Home TV channels became a reality with the launch of the Ku band transmission of “DD Direct plus” and30 free-to-air TV channels, 14 channels of private broadcasters and 12 AIR channels. A total of 10,000 dish receive units being provided in the uncovered villages of Himachal Pradesh, Rajasthan, Uttaranchal, Karnataka, Chattisgarh, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh & North Eastern States. Doordarshan launched two new-dedicated channels in collaboration with Lok Sabha Secretariat to telecast Live the whole Parliamentary proceedings of Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha. A dedicated educational channel EDUSAT for education in collaboration with ISRO launched. Seven major studio centres at Delhi, Mumbai, Bangalore, Hyderabad, Chennai, Kolkata & CPC (Delhi) made fully digital whereas eight small studio centres at Jammu, Daltonganj, Gangtok, Panaji, Raipur, Gulbarga, Pondicherry & Port Blair partially digitalized. Agriculture broadcast received a shot in the arm with the launch of dedicatd agricultural channel. Presently ‘Kisan Vani’ is being broadcast from 96 AIR stations. Digital uplink capabilities provided at AIR Kolkata, Hyderabad, Bangalore, Thiruvananthapuram, Bhopal and Ahmedabad. A meeting of the stakeholders on Broadcast content held to decide a quasi-Judicial autonomous body for regulating content on television channels. The State Information Ministers Conference SIMCON-XXV was organized after a gap of four years to decide on core issues like rationalization of Entertainment Tax, issues related to piracy sensitization of State on contents of Television Channels, registration of cable operators and promotion of DTH services. Special attention was given towards reaching out to the people of Jammu and Kashmir and the North East during the year e.g., film festivals in Jammu and Kashmir and Tripura. Indian Institute of Mass Communication in collaboration with Nagaland University started a PG diploma course in mass communication. The second SAARC Editors Conference organised in New Delhi. A meeting of the Group of Experts on the establishment of the SAARC Media Development Fund, the first of its type, organized. 38 An agreement was signed between the Chandigarh Press Club and the Lahore Press Club for initiation of a regular interaction process. India and Afghanistan signed an to cooperate and expand ties in areas covering radio and television broadcasting, films and exchange of journalists. The Ministry and its media units played a key role in disseminating critical information in the affected areas. PIB launched intra-PIB, intranet on a highly interactive platform, for better communication with field offices and to serve as a tool for professional activities. The Chennai and Aizawl offices have already launched their own sites in Tamil and Mizo respectively. PIB issued 54,338 press releases and 4,077 features including illustrated features. Over one-lakh photo prints were distributed to the Press. A total of 914 press conferences and workshops on various issues ranging from female foeticide and rural development to internet organised. An Economic Editors’ Conference held after three years besides the Fifth Editors’ Conference on Social Sector Issues attended by over 350 economic editors and financial writers and 200 editors/senior journalists respectively, from different parts of the country. As part of the Platinum Jubilee Celebrations of the historic Dandi March, the Films Division released a DVD of the film on Dandi Yatra entitled “The Great Salt March”. The Directorate of Advertising and Visual Publicity put up an exhibition on the freedom struggle. The Publications Division brought out books like the World of Ezra Mir, Indian Railways-Glorious 150 years, Guru Nanak Se Guru Granth Sahib Tak, Gandhi-A Pictorial Biography in its endeavour to preserve the history and culture of India besides four multimedia interactive CDs on subjects of culture and heritage monuments and three CDs on world heritage monuments. ****** 44 SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY National Biotechnology Development strategy finalised. Roadmap for research in agricultural biotechnology for next ten years and for pred. A new therapeutic anti-tuberculosis molecule “Sudoterb” developed. This will clear the n to the current level of 6 to 8 months. 39 A common man’s computer with an entry level price of Rs. 10,000 unveiled. The ding IT solution to many problems faced by people especially in rural areas. A leading Indian IT company in collaboration with 18 of the best of acedemic and R&D ble, versatile and cost effective bio-information package-bio suite for genomic and rational drug design. Three facilities of clinical proteomics being established in Delhi focusing on screening p for most of the chronic diseases. Establishment of two interdisciplinary centres for stem cell research and tissue une taken up. Nano-Science and Technology Mission ready for launching. Saras-the first Indian civilian aircraft for the future test flown. Department of Ocean Development is poised to install Tsunami warning system for National Institute of Ocean Technology establishing a one lakh litre per day capacity hadweep. The Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services, Hyderabad started onal Fishing Zone advisories using satellite data for cholorophyll and sea surface temperature. Indigenously developed data buoys to improve capabilities of short and long term weather Mapping the Neighbourhood Programme at present being implemented in 20 schools in panded to cover 30,000 schools. In the area of health care new vaccines and diagnostics developed indigenously are under Under the societal programme of the Department of Biotechnology more than 12,000 d income generating activities. Specific S&T Programme for empowerment of women initiated with a view to promote priate technology, transfer of proven technologies and demostration of live technology models to benefit A Women Scientists Scheme instituted to provide opportunities to women scientists to ing those who had to suffer breaks in their career. Supports given to programmes relating to Science and Technology Application for nursery training for income generation and demonstration of pearl culture technology to create scientific and projects sanctioned under Tribal Sub-Plan. *** 40 PARLIAMENTARY AFFAIRS The 13th All India Whips Conference held on 4-6 February 2005 in after a gap of 7 years. Hyderabad Client’s Charter of Ministry of Parliamentary Affairs brought out. Three Sports events for Members of Parliament organised. Manual for Handling Parliament Work in Ministries revised. A Handbook of Ministry of Parliamentary Affairs prepared. Brochure on Transaction of Business in Parliament updated. ***** PARLIAMENTARY AFFAIRS The 13th All India Whips Conference held on 4-6 February 2005 in after a gap of 7 years. Hyderabad Client’s Charter of Ministry of Parliamentary Affairs brought out. Three Sports events for Members of Parliament organised. Manual for Handling Parliament Work in Ministries revised. A Handbook of Ministry of Parliamentary Affairs prepared. Brochure on Transaction of Business in Parliament updated. ***** STEEL The apparent consumption of finished steel during 2004-05 stood at 334.00 lakh tonnes, which is higher by 7.2 per cent as compared to 311.69 lakh tonnes for the corresponding period last year. 41 The export of steel during 2004-05 estimated to be 42.00 lakh tonnes. A new National Steel Policy formulated which target production of over 100 million tonnes of steel by 2020. Initiative to merge IISCO with SAIL taken. Initiatives also taken to rationalize iron ore prices by the Public Sector Iron Ore Companies. An expert group constituted to suggest guidelines to be followed by State Governments in recommending to the Government of India mining lease for iron ore, chrome ore and manganese ore. In the year 2004-05, SAIL’s profit before tax expected to be Rs. 5739 crore in comparison to 2628 crore during 2003-04. Several steps taken to ensure availability of steel and stabilize the price in the domestic market. **** SOCIAL JUSTICE AND EMPOWERMENT National dialogue initiated with trade & industry on affirmative action and reservation in Private Sector for Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes. National Commission constituted for economically backward sections among religious and linguistic minorities. Two Bills introduced in Parliament to grant constitutional status to National Commission for Minorities. Tenure of National Commission for Safai Karamcharis extended upto December 2007. 25 successful women entrepreneurs belonging to SCs, OBCs and honoured. Minorities Over Rs. 111 crore spent on implementation of Act to prevent atrocities against SCs. Emphasis on promotion of quality education among Scheduled Castes students. 42 National Scholarship Scheme for SC students extended upto 2007. 2,800 meritorious girl students belonging to minorities granted scholarship of Rs. 10,000 each. Authorised share capital of National Minorities Development & Finance Corporation enhanced for Rs. 500 crore to Rs. 650 crore. Rs. 1.47 crore provided for development of Wakf properties. Scheme for providing assistive devices for persons with disabilities extended to uncovered and inaccessible areas. Around 15.93 lakh children with disabilities identified and 10.7 lakh among them enrolled in schools. Special camp for disabled organised in Tanzania during the President’s visit. Child help-line service for children in distress extended to 11 more cities. Swift relief organised for victims of Tsunami in affected States/UTs. ****** 43