Yr 11 Mock Exam Revision Topic Key Words Revision Guidelines A
advertisement
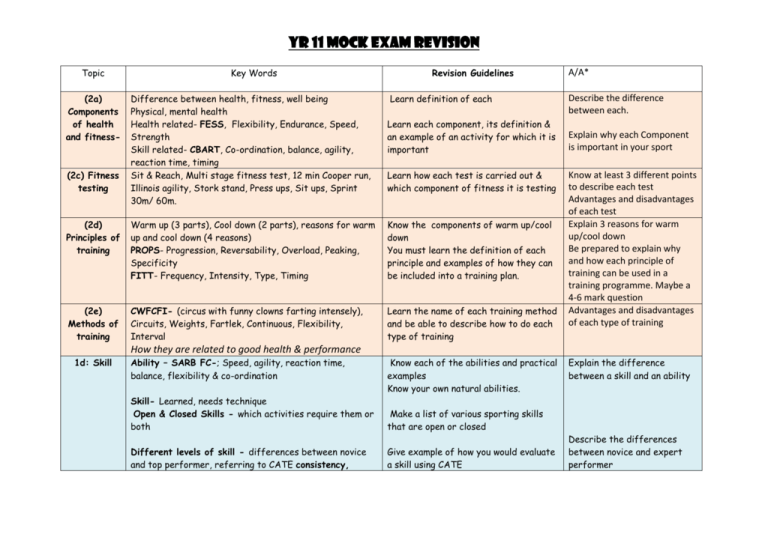
Yr 11 Mock Exam Revision Topic (2a) Components of health and fitness- (2c) Fitness testing Key Words Difference between health, fitness, well being Physical, mental health Health related- FESS, Flexibility, Endurance, Speed, Strength Skill related- CBART, Co-ordination, balance, agility, reaction time, timing Sit & Reach, Multi stage fitness test, 12 min Cooper run, Illinois agility, Stork stand, Press ups, Sit ups, Sprint 30m/ 60m. Revision Guidelines Learn definition of each Learn each component, its definition & an example of an activity for which it is important Learn how each test is carried out & which component of fitness it is testing (2d) Principles of training Warm up (3 parts), Cool down (2 parts), reasons for warm up and cool down (4 reasons) PROPS- Progression, Reversability, Overload, Peaking, Specificity FITT- Frequency, Intensity, Type, Timing Know the components of warm up/cool down You must learn the definition of each principle and examples of how they can be included into a training plan. (2e) Methods of training CWFCFI- (circus with funny clowns farting intensely), Circuits, Weights, Fartlek, Continuous, Flexibility, Interval Learn the name of each training method and be able to describe how to do each type of training A/A* Describe the difference between each. Explain why each Component is important in your sport Know at least 3 different points to describe each test Advantages and disadvantages of each test Explain 3 reasons for warm up/cool down Be prepared to explain why and how each principle of training can be used in a training programme. Maybe a 4-6 mark question Advantages and disadvantages of each type of training How they are related to good health & performance 1d: Skill Ability – SARB FC-; Speed, agility, reaction time, balance, flexibility & co-ordination Know each of the abilities and practical examples Know your own natural abilities. Skill- Learned, needs technique Open & Closed Skills - which activities require them or both Make a list of various sporting skills that are open or closed Different levels of skill - differences between novice and top performer, referring to CATE consistency, Give example of how you would evaluate a skill using CATE Explain the difference between a skill and an ability Describe the differences between novice and expert performer Yr 11 Mock Exam Revision energy, time & adaptable Learning & developing skill - Demonstration, copying, practice, trial & error and role model. Also learning information processing model- Input, Decision Making, Output, Feedback. Types of Feedback ; Intrinsic, Extrinsic, Knowledge of Performance, Knowledge of results Motivation Reasons for mental preparation; Lower arousal & Mental levels, reduce anxiety, focus on task, improve Preparation performance, boost confidence Ways of relaxing: relaxation (calming music, meditation, going for a walk), mental rehearsal (thinking about a skill) & focusing (blocking out surroundings, self talk) Effects of training on the body Example of each way of learning skill Practice using the IPM and putting a skill in the place of the words. Describe 2 characteristics of each type of feedback Give examples of each type Make a list of the different ways of relaxing Advantages and disadvantages of each way of learning Describe how decision making is affected by experience, anticipation, selective attention. Advantages/disadvantages of each type Describe effects of mental preparation on performance Know the difference between intrinsic & extrinsic and list examples of both types. Arousal- Over/under arousal Motivation: Intrinsic & extrinsic & arousal Goal Setting: SMARTER & 2 types of goals process and target goals List skill within your own sports and set yourself targets according to SMARTER SHORT & LONG term effects of exercise on the body Diet – 7 essential components of a healthy diet & effect of this on performance. Over & under eating Somatotyping & effects of age, gender and List long and short term effects f exercise on body Remember: Short term= immediately eg. within training session Long Term= period of time eg/ weeks. Describe Inverted U theory of arousal and effects of over/under arousal on performance Give Reasons for goal setting Identify Long+ Short term Effects of Describe effect of long + short term effects on body Describe 3 effects of each factor on performance Yr 11 Mock Exam Revision (1a) Skeleton Joints Synovial joints Range of movement (1b) Muscles disability on fitness Alcohol and smoking and its affects on performance Drugs: Painkillers, steroids, beta blockers, stimulants, diuretics, blood doping all factors on performance Functions of skeleton PSMB- Protection, Support, Movement, Blood production 3 Types of bone & their roles- Long, Flat, Irregular Names of 20 main bones 3 types of joint-FSF fixed, slightly moveable, freely moveable 4 types of synovial (freely moveable) joint- Ball & Socket, Hinge, Pivot, Gliding Structure of synovial joint- Synovial fluid, membrane, capsule, cartilage, ligaments, tendons. Identify the functions on the body Practise labelling all the major bones in the skeleton and describe what job they do in the body FEAAR- Flexion, Extension Adduction, Abduction, Rotation, Possible injuries at joints (sprains, cartilage damage) Structure & function of major muscles Types of muscle in the body – 3 types- involuntary, cardiac & voluntary, 12 different muscles Working muscles - How muscles contract/ relax, Antagonistic pairs, Role of prime mover, antagonist, synergist. tendons Muscles for endurance & power - fast & slow twitch and their suitability to performance in different sports Effects of exercise on muscles - how improved muscle functioning can improve performance Isotonic (movement)- Concentric and Eccentric, Isometric (no movement takes place Advantages/disadvantages of each drug Practise drawing a synovial joint, including all of the structures mentioned opposite. .Cut out some sporting action pictures from the newspaper and label which movements are occurring at each joint Practise labelling the major muscles of the body. List sports that require predominantly fast & slow twitch fibres. Cut out some sporting action pictures from the newspaper, label which movements are occurring at each joint & which muscles are working to create that movement. MUST HAVE PRACTICAL EXAMPLES Explain why each function of skeleton is needed. Describe characteristics of each type of synovial joint Describe structure and role of each component of synovial joint. MUST HAVE PRACTICAL EXAMPLES Describe characteristics of 3 types of muscle Explain how muscles produce movement (4 marks) Describe difference between fast/slow twitch Describe effect of exercise on muscles Explain with e.g’s diff types of contraction Yr 11 Mock Exam Revision REMEMBER- Reversibility- use it or lose it! If you don’t revise, you won’t remember!! All of your notes are in your books. If there is anything you don’t understand, look on: http://www.toothill.notts.sch.uk/html/deptpage.asp?d=pe&p=gcse www.bbc.co.uk/gcsebitesize www.s-cool.co.uk www.brianmac.co.uk Past papers available at http://www.ocr.org.uk/qualifications/gcse/physical_education/index.html The hardest part is applying this knowledge to real situations so for each section make sure that you have a working example that you can apply to your sport!!!







