IntroFinal
advertisement

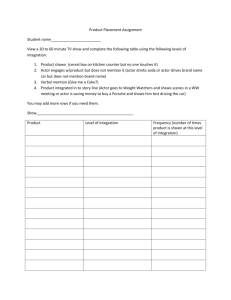
INTRODUCTION TO THEATRE Final Exam I. Selected Response. Select the response that best defines each of the following words (1 point each) 1._____Thespis a. The first actor b. Famous American actor c. Famous British actor d. The first director 2._____ Floor Plan a. The layout of the set b. The overhead diagram of the stage and set c. The drawing showing where al the sets will be stored d. A list of all the set and stage pieces 3._____Dionysus a. Greek Playwright b. Greek god honored by the dramatic contests c. Greek god of Drama d. Greek Actor 4._____Principals a. The tech people involved in running the show b. The main characters in a play c. The person who hires the director and pays the bills for a production d. Characters in a play that do not give lines 5._____Skene a. A hut used in ancient Greek theatre for changing costumes and masks b. The acting area in the ancient Greek theatre c. The scenery in the ancient Greek theatre d. The name for the script in ancient Greek theatre 6._____Publicity Manager a. Person responsible for considering the needs of the audience b. Person responsible for selling tickets c. Person who handles the advertising and promotion of a play d. All of the above 7._____Dialogue a. Lines spoken between two or more actors b. Lines spoken by one actor alone on stage c. Lines spoken by one actor revealing his inner thoughts d. All of the above 8._____Mystery Play a. A medieval play depicting biblical history b. Medieval play about mysterious characters c. Medieval play depicting the life of saints d. A contemporary play about detectives 9._____Motivation a. The reason behind the action, and reaction of characters b. The reason why a director chooses a certain play c. The reason why an actor choose a certain part d. All of the above 10._____Pagaent Wagon a. Wagon on which a passion play is performed b. Stage on wheels on which medieval plays were performed by guilds c. Stage on wheels for touring companies d. All of the above 11._____Sophacles a. Playwright of the Greek tragedies b. Playwright of the Greek comedies c. Roman Playwright d. Actor in ancient Greek theatre 12._____Stanislavski a. Author of a book directing b. Author of the “method” approach to acting c. Famous actor of French stage d. Famous director of English stage 13._____ Morality Play a. A play about the lives of saints b. A play from the Restoration period c. A medieval play relating to Christian ideals and morals d. A play about a passionate experience between two people 14._____Chorus a. Group of actors who related background information and reactions to the action of the play in Greek theatre b. Reoccurring lyrics in songs c. Singing and dancing non speaking roles in a musical d. All of the above 15._____Areana Stage a. Stage that requires a proscenium arch b. Type of stage completely surrounded by the audience. c. Stage where the audience sits in front of the stage d. All of the above 16._____Technical Director a. Person responsible for designing a set b. Person responsible for lighting c. Person responsible for costumes d. Person responsible for overseeing all technical aspects of the theatre 17._____Projecting a. The control of the volume and quality of the voices so that it can be heard clearly. b. The reason behind what an actor says and does c. Walking to the front of the stage d. All of the above 18._____Improvisation a. Making up the lines to a script b. Making up movements to an actor c. The impromptu portrayal of a character without any preparation or script Designing the costume for an actor 19._____Propties (props) a. The property in which the theater is housed b. The room where the costumes and makeup are stored c. All the stage furnishings, including small items handled or brought on by the actors d. Everything in the theatre that is owned by the production company 20._____House manage a. Person responsible for cleaning the theatre b. Person responsible for hanging the lights c. Person responsible for handling the money d. Person responsible for considering the needs of the audience 21._____Characterizantion a. Putting together all the facets of a character to bring life and interest to that character. b. The physical look of a character c. How a character would sound d. Putting on a costume to make an actor look the part 22._____Blocking a. The parts of a set b. Building a set c. The movement of the actor as set by the director d. An actor getting in the way of another actor 23._____Curtain Call a. A cue to raise and lower the curtain b. The appearance of a plays cast in response to audience applause at the end of a play c. Closing the curtain at the end of a play d. Opening the curtain at the beginning of the play 24._____Stage Business a. Anything about a play having to do with money b. The business of the theatre c. The advertising in the playbill d. Small action performed by an actor, for example opening a letter or picking up a book. 25._____Patomime a. The art of acting without words or props b. The art of moving on stage c. Using stage props d. Small actions made away from the focus of action 26._____”Illusion of the first time” a. Spontaneity and freshness at each performance b. A book on method acting c. A type of lighting technique used by lighting designers d. The first performance of a play 27._____Fresnel a. A spotlight with a stepped lens b. A lighting instrument that throws a strong hard edged light c. A set piece from the French Renaissance d. An acting technique using gestures 28._____The restoration period of theatre was brought about when the royal family was restored to the throne and this person took his/her place as king/queen: a. Charles I b. Charles II c. Elizabeth I d. None of the above 29._____The renaissance was most prominent in a. England b. France c. Italy d. All of the above 30.______Scipt Scoring a. Grading the quality of the script b. Giving the actor guidance on how to deliver lines c. Paraphrase existing lines d. All of the above II. Complete the following chart (1 points each) Genre Low Comedy Definition High Comedy Example #1 Example #2 Type of low comedy: Type of low comedy: Type of high comedy: Type of high comedy: Tragedy Pantomime Improvisational Theatre III. Measurement: In ¼” = 1’ scale, find the following: (1 point) 1. 10 feet is equivalent to ________ inches 2. 16 feet is equivalent to ________ inches 3. 30 feet is equivalent to ________ inches 4. 21 feet is equivalent to ________ inches 5. 40 feet is equivalent to ________ inches Measurement: In ¼” = 1’ scale, find the following: 6. 3 inches is equivalent to ________ feet 7. 5 ½ inches is equivalent to ________ feet 8. 6 ¾ inches is equivalent to ________ feet 9. ¾ inches is equivalent to ________ feet 10. 4 ¼ inches is equivalent to ________ feet IV. On the graph on the answer sheet, label each box with the appropriate stage areas. (1 point each) V. Fill in the blank with the best answer. (1 point each) 1. In order to have good projection you must speak from this part of your body __________ 2. The __________ in a play is working against the protagonist. 3. __________ is restating part of a text in your own language. 4. At the outset of the play the playwright introduces the characters and sets the scene; this part of the play in called the __________ 5. A monologue is a speech given by one character to another where as a __________ is a speech given by one character to reveal his/ her thoughts to the audience. 6. The turning point of the play is called the __________ 7. A farce is an example of a __________ Comedy 8. A play in which the protagonist fails to achieve their desired goal is a __________. 9. _________ is in charge of the artistic vision of the play. 10. The first step in applying stage makeup is applying __________. VI. BCR Answer each of the following questions in complete sentences (5 points each) 1. What is the function of the Greek Chorus? 2. What is “role scoring”? what is “Script Scoring”? How does each help an actor? VII. On the floor plan provided label the following areas (1 point each) 1. Proscenium arch 2. Apron 3. Upstage 4. Downstage 5. Stage Right 6. Stage Left wing 7. Orchestra Pit 8. Light Bar 9. Backdrop 10. Grand Drape Draw a 4’ x 8’ x 2’ Platform with 2 steps center stage (5 points each) VIII. In an extended Constructed Response, using any play you have studied this semester, trace the character development of any two characters and explain how those characters relate to the stages of dramatic structure of that play. (Graphic Organizer: 5 points; Essay 20pts)