Chapter 4 Syllabus
advertisement

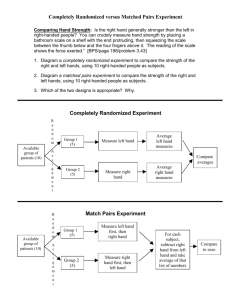
Continue: Chapter 3 - Describing Relationships Chapter 4 Syllabus - AP Statistics - A Sampling and Experimentation Designing Studies NAME: Chapter Objective: Students will learn appropriate ways to produce data. This includes planning and conducting research as well as collecting data from a study before performing a statistical analysis with the gathered information. Day 1 10/9 TOPICS: ▪Explanatory vs. Response Variables ▪Scatterplots: Form, Direction, & Strength ▪Calculating & Interpreting Correlation ▪LSRL ▪ Interpreting Slope and y intercept ▪ Residuals and Residual plots ▪Coefficient of Determination Day 2 10/11 Chapter 3 Review – QUIZ TODAY!!! Chapter 3 Project Due: ___Oct. 15th___ 3.1 – Scatterplots and Correlation 3.2 – Least Squares Regression I. Concepts and Skills to Master: ►Identify explanatory and response variables in bivariate situations ►Construct and interpret a scatterplot ►Calculate and interpret correlation ►Identify outliers and explain their effects on correlation ►Identify, calculate, and construct the equation of a least-squares regression line ►Interpret the slope and y intercept of a least-squares regression line ►Calculate and interpret residuals ►Construct and interpret residual plots ►Explain the dangers of extrapolation ►Use the least-squares regression line to predict values of the response variable ►Use the standard deviation of the residuals and r2 to determine how well the line model fits the data II. Assignments A. Anscombe’s Data Exploration B. Quiz 3.2A and Quiz 3.2C C. Chapter 3 Content Q & A D. Chapter 3 Quiz III. Homework A. Read section 4.1 and complete Reading Guide 4.1 Chapter 3 Project Due Next Class 3.1 & 3.2 Review (Scatterplots, Correlation, Least-Squares Regression) I. Concepts and Skills to Master: See Day 1 (other side) and Chapter 3 Syllabus II. Assignments A. Warm Up B. Homework Q & A C. Chapter 3 - Technology Tips for TI D. Group Work - Review Assignment – Chapter 3 III. Homework A. Study for Chapter 3 Test (Includes Chapters 1 – 3) B. Complete Chapter 3 Project Day 3 Chapter 3 Project Due!!! 10/15 TEST TODAY!!! CHAPTERS 1-3 TEST HOMEWORK: Read section 4.1 and complete Reading guide section 4.1 Complete Gallup Poll Activity – due October 19th Day 4 10/17 TOPICS: ▪The idea of a sample survey ▪How to sample badly ▪How to sample well ▪Random Sampling ▪Other Sampling Methods ▪Inference for sampling ▪Sample surveys: What can go wrong? Day 5 10/19 TOPICS: ▪Observational Study vs. Experiment ▪How to experiment badly ▪How to experiment well ▪Experimental Design Principles ▪Inference ▪Blocking ▪Experiments: What can go wrong? ▪Matched Pairs Design Day 6 10/23 Day 7 10/25 QUIZ Chapter 4 Intro Activity 4.1 – Sampling and Surveys I. Concepts and Skills to Master: ►Identify the population and sample in a sample survey ►Identify voluntary response samples and convenience samples ►Know how bad sampling methods can lead to bias ►Distinguish a simple random sample from a random sample or cluster sample and give advantages and disadvantages of each sampling method ►Describe how to use Table D to select a simple random sample (SRS) ►Explain how undercoverage, nonresponse, and question wording can lead to bias in a sample survey II. Assignments A. Warm Up B. 4.1 Guided Notes C. Random Number Technology Lab D. 4.1 Multiple Choice and Free Response handout III. Homework A. Chapter 4 After you Read: Concepts 1 and 2 (handout 65-67) B. Textbook: page 230 #37-43 4.2 – Experiments I. Concepts and Skills to Master: ►Distinguish between and observational study and experiment ►Explain lurking variables can lead to confounding ►Identify the components of an experiment ►Describe a completely randomized design for an experiment ►Describe how to avoid the placebo effect in an experiment ►Distinguish between a completely randomized design and a randomized block design ►Understand the importance of the three principles of experimental design ►Define in context “statistically significant” ►Know when a matched pairs experiment is appropriate and how to implement such a design II. Assignments A. Warm Up – 4.1 Recap [Review 4.1 Guided Notes] B. Classwork: After You Read: Concepts 1, 2, and 3 (handout 69-72) C. Activity – Experiment Title: Distracted Driving D. Template for Analyzing Experiments handout – see syllabus III. Homework Chapter 4 – Strive for 5 MC Practice and FRQ Read 4.1 and 4.2 Textbook summaries (p.225, p.252) ASSIGNMENTS: CHAPTER 4 Review for QUIZ Cholesterol Activity (Randomized Design vs. Matched Pairs) Activity Response Bias Group Project p.267 – DUE: TBA Discuss Template for Analyzing Experiments HOMEWORK: Complete 4.1 and 4.2 Practice Quiz handout Study for Quiz CHAPTER 4 QUIZ CLASSWORK/HOMEWORK: CW: Extra Credit Points (Chapters 3 and 4 Crossword Puzzles) HW: Response Bias Project ***END OF QUARTER 1*** CHAPTER 4 BIG IDEA & ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS Enduring understanding (Big Idea): Students will understand relationships between two variables including how to describe, analyze, model, and use them. Also that association does not necessarily mean causation. Moreover, for linear relationships how to make predictions and determine what can be explained. Essential Questions: 1. Why must data be collected according to a 5. Why are Control, Randomization and Replication well-developed plan and how does that important in designing and implementing an affect the validity of information for a experiment conjecture? 6. What are the differences between observational 2. Why must this plan include clarifying the studies and experiments? question and deciding upon a method of 7. What is required to establish a causation data collection and analysis? relationship? 3. How can we fairly represent a group, so 8. When there are known sources of systematic that we can draw conclusions from data variation, how can we design experiments to drawn from a sample of that group? reduce variation in the results? 4. What is the difference between random 9. When should we Block or use Matched Pairs? selection and random assignment, how are 10. What is the difference between clusters, strata, each used and to what purpose? and block? CHAPTER 4 VOCABULARY & OBJECTIVES Students will know: Sampling and Experimentation: Planning and conducting a study A. Methods of data collection B. How to plan and conduct surveys: C. How to plan and conduct experiments D. Generalizability of results and types of conclusions that can be drawn from observational studies, experiments and surveys Vocabulary: Bias, Blocking, Causation (Cause and Effect), Cluster, Cluster Sample, Completely Randomized Design, Confounding, Control, Convenience Sample, Data Ethics, Double-blind, Experiment, Experimental Units, Lurking Variable (Other Variable), Matched pairs design, Nonresponse, Observational Study, Placebo, Placebo effect, Population, Random Assignment, Randomized block design, Replication, Sample, Simple Random Sample (SRS), Statistically significant, Strata, Stratified Random Sample, Subjects, Table of Random Digits, Treatment, Undercoverage, Voluntary Response Sample See back for Anaylzing Experiments Template Students will be able to… 1. identify: populations, samples, voluntary response samples, convenience samples, simple random sample, stratified random sample, cluster sample 2. use a random number table to select a simple random sample 3. avoid bias particularly from undercoverage, nonresponse, and wording 4. distinguished between observational studies and experiments 5. understand confounding blocking, matched pairs, statistically significant 6. identify experimental units, subjects, factors, treatments 7. understand the importance of random assignments of treatments 8. describe a completely randomized design for an experiment 9. distinguish between completely randomized design and a randomized block design