Microscope Drawing Magnification Worksheet
advertisement

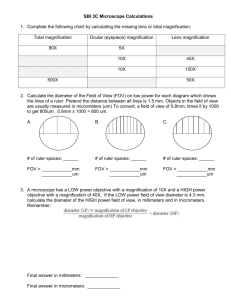
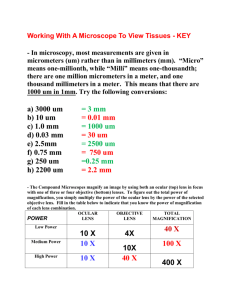
Name:_______________________ Date:_____________ HOW TO DETERMINE DRAWING MAGNIFICATION 1. Measure your low power field of view (FOV) using the mm scale on a clear ruler. Ex: 4.5mm 2. Make note of Low, Medium and High power magnification. Ex. Low = 4x, Medium 10X, High 45X 3. Calculate the field of view for medium and high power. Example: If the power magnification on Low = 4x and the FOV = 4.5 mm, then you can figure out the FOV for medium and high using the following method: Medium High 4. 10x 40x FOV = 4.5 mm x (4/10) = 1.8 mm FOV = 4.5 mm x (4/40) = 0.45 mm Look at the specimen and estimate how many specimens will fit across the diameter of the field. Example: 6.5 specimens (widthwise) fit across the HIGH power field 5. Calculate the actual size of the specimen. Actual Size = field of view # of specimens across(width or length?) Actual Size = 0.45 mm 6.5 specimens (w or l?) = 0.069 mm / specimen (w or l?) 6. Draw your specimen using the drawing rules. 7. Measure your specimen drawing in mm. Use the same dimension as used in estimating the number of specimens across the field of view (i.e. width or length). 8. Calculate the magnification of your drawing. Drawing Magnification = Drawing Measurement (mm) (width or length?) Actual Size (mm) (width or length?) = 20mm ÷ 0.069mm = 290 X (round to whole number) Drawing Magnification Problem Set Use the estimated fields of view of the microscopes to complete the following questions. (High 40x FOV = 0.45 mm) 1. A cell is observed to stretch half way across the high power field. How long is the cell? 2. Many ponds often have a green scum on the surface. This scum is a tangled mass of stringy algae filaments. Looking at a filament under high power shows four cells arranged end to end across the field of view. a. What is the diameter of the high power field of view in millimeters? b. How long is each cell approximately? 3. 15 cells are observed across the centre of the high power field. How long is each cell? 4. A cell is observed under high power to be about half the field diameter. A student draws the cell 25cm in length. What is the magnification of the drawing? 5. A student draws a cell diagram 24mm long. She writes 400X below the diagram. How large is the actual cell? 6. A cell is 80 m in length. If drawn 600 times actual size, how long will the drawing be in cm? (HINT: 1 micrometer = 0.001 millimeters) 7. 5 onion cells are counted across the centre of the high power field. One cell is drawn 18mm long. Calculate the drawing magnification. 8. 40 potato cells are counted across the centre of the medium field of view. One cell is drawn 2cm long. What is the drawing magnification? 9. The diameter of a hair is estimated to be one tenth of the diameter of the medium power field. It is drawn 4cm wide by a student. What is the drawing magnification? 10. Copy the chart and complete: Drawing Size 10mm Actual Size 100mm Drawing Magnification 4mm 3X 10cm 25X 150mm 15mm 0.8cm 8mm Drawing Magnification Problem Set Answers 1. high power FOV = 0.45 mm 2. a. high power FOV = 0.45 mm AS = 0.45 mm ÷ 2 = 0.225 mm b. AS = 0.45 mm ÷ 4 = 0.1125 mm 3. high power FOV = 0.45 mm AS = 0.45 mm ÷ 15 = 0.03 mm 4. high power FOV = 0.45 mm AS = 0.45 mm ÷ 2 = 0.225 mm DM = 250 mm ÷ 0.225 mm = 1111 X 5. DM = DS ÷ AS 400 X = 24 mm ÷ AS AS = 24 mm ÷ 400 AS = 0.06 mm 6. AS = 80 micrometres = 80 x 10-6 metres = 80 x 10-4 centimetres = 8 x 10-3 cm DM = DS ÷ AS 600 X = DS ÷ 8 x 10-3 cm DS = (600)(8 x 10-3 cm) DS = 4.8 cm 7. high power FOV = 0.45 mm AS = 0.45 mm ÷ 5 = 0.09 mm DM = DS ÷ AS DM = 18 mm ÷ 0.09 mm = 200 X 8. low power FOV = 4.5 mm medium power FOV = 4.5 mm (4/10) = 1.8 mm AS = 1.8 mm ÷ 40 = 0.045 mm DM = DS ÷ AS DM = 20 mm ÷ 0.045 mm = 444 X 9. medium power FOV = 4.5 mm (4/10) = 1.8 mm AS = 1.8 mm ÷ 10 = 0.18 mm DM = DS ÷ AS DM = 40 mm ÷ 0.18 mm = 222 X 10. DM = DS ÷ AS Drawing Size Actual Size Drawing Magnification 10mm 100mm 0.1X 12 mm 4mm 3X 10cm 0.4 cm 25X 150mm 15mm 10X 0.8cm 8mm 1X