Characteristics of element - CAC
advertisement
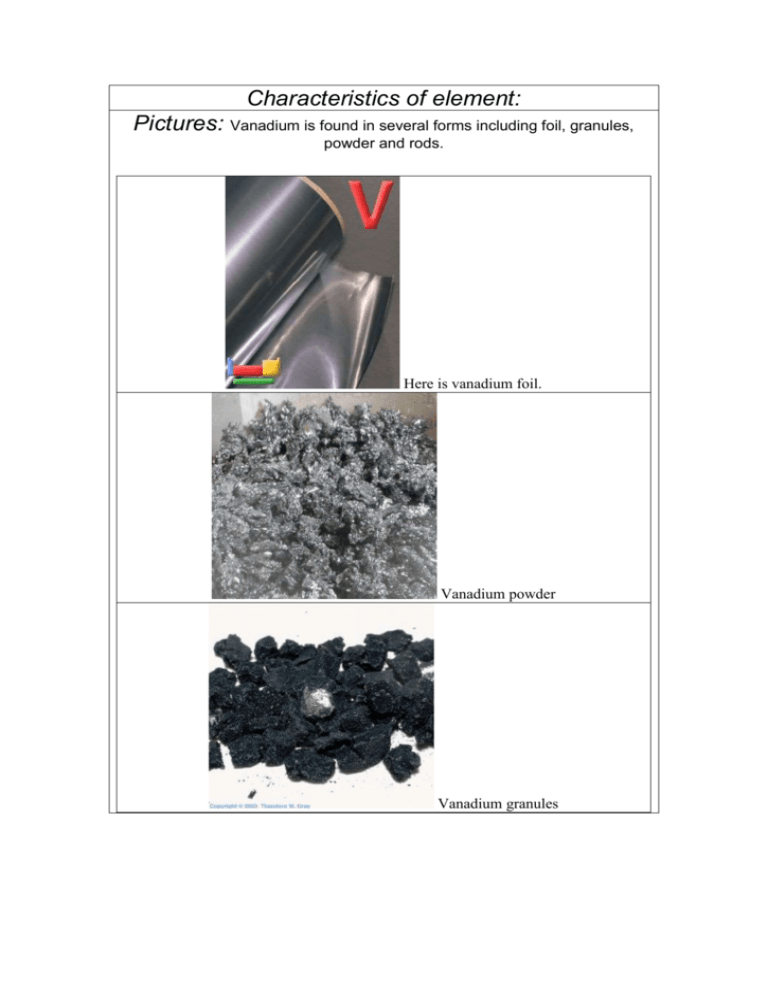
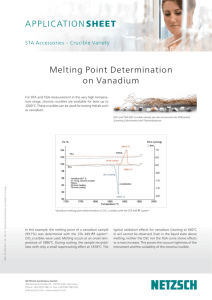
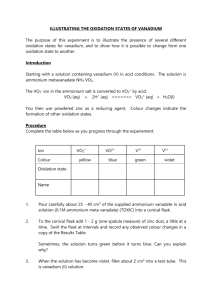
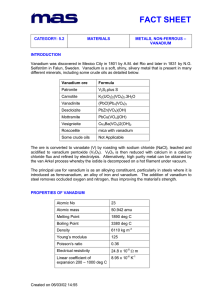
Characteristics of element: Pictures: Vanadium is found in several forms including foil, granules, powder and rods. Here is vanadium foil. Vanadium powder Vanadium granules And finally, vanadium rod. The above pictures are adapted with permission from Theodore Gray's Periodic Table Table web site, an excellent source of element pictures, interactive pictures, and videos. Appearance: Pure vanadium is classified as a greyish silvery metal; it is soft and ductile, that is, it conducts electricity. When it is subjected to alkalis, sulphuric acid, hydrochloric acid, or salty water, it does not corrode (does not get eaten away) easily. The metal oxidizes readily above 660°C to form V2O5. Vanadium is not found as a free metal in nature, but it is found as a compound in many minerals, such as carnotite, roscoelite (a mica), vanadinite, mottramite, and patronite. It is a white-to-gray metal, and is often found as crystals. Pure vanadium has no smell. It usually combines with other elements such as oxygen, sodium, sulfur, or chloride. Vanadium and vanadium compounds can be found in the earth's crust and in rocks, some iron ores, and crude petroleum deposits. It is also present in some crude oils. Vanadium has been identified in the spectra of the sun and other stars. Vanadium oxide is a yellow-orange powder, dark-gray flakes, or yellow crystals. Diagram: FIND GOOD ONE ON NET Chemical characteristics: * Name: vanadium * Symbol: V * Atomic number: 23 * Atomic weight: 50.9415 (1) * CAS Registry ID: 7440-62-2 # Standard state: solid at 298 K (standard state is inferred from the melting and boiling points of the element) 23 V Vanadium 50.9415 23 Atomic Number: 50.9415 Atomic Weight: 2183 K (1910°C or 3470°F) Melting Point: 3680 K (3407°C or 6165°F) Boiling Point: 6.0 grams per cubic centimeter Density: Solid Phase at Room Temperature: Metal Element Classification: