Review Questions
advertisement

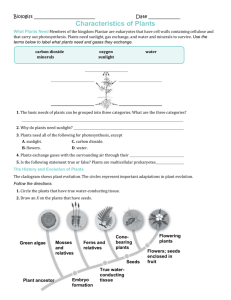
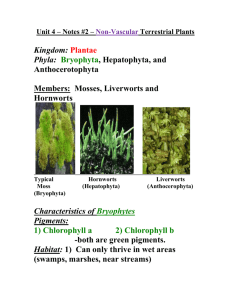
Cheyenne Cheung, Cody Rubin, Vanessa Ghofrani Chapter 19 project 10/28/09 Review Questions 1) What is another name for transposons? a) jumping genes b) switching genes c) plasmid d) fatty acid 2) In replicative transposition, is the original copy still maintained in the chromosome? a) Sometimes b) Always c) Never d) Only during cell division 3) What is a transposon? a) A body cell b) A cancerous tumor c) DNA pieces that relocate d) A step in the process of plant cell division 4) What is the haploid stage of the plant cell called? a) Sporophyte b) Gametophyte c) Alternation of generations d) Gamete 5) What is the diploid stage of the plant cell called? a) Sporophyte b) Gametophyte c) Alternation of generations d) Gamete 6) What are the haploid cells called? a) Spores b) Sex cells c) Gametes d) Gonads 7) What is cell culture used for? a) Testing purposes b) to cultivate proteins c) to observe mold d) for entertainment Cheyenne Cheung, Cody Rubin, Vanessa Ghofrani Chapter 19 project 10/28/09 8) What is the first step in growing a cell culture? a) Put it on a Petri dish b) Cut up a sample of small pieces of tissue c) Put a growth factor with the cells d) Treat the cells with diluted water 9) What are the 3 types of life cycles? a) Mammals, reptiles, amphibians b) cell, human, bacterial c) human, fungi and some protists including some algae, and plants and some species of algae d) plants, cells, animals 10) This type of transposon includes extra genes in their movement. a) insertion sequences b) the bacterial transposon c) the double transposon d) composite transposons Question Explain one of the benefits of transposons. Answer: answers may vary Transposons scatter genes throughout the genome and provide a means for genomic change and variation. Transposons also bring multiple genes for antibiotic resistance into a single R plasmid by moving the genes to that location from different plasmids. An R plasmid contains one or several transposons with resistance genes which help control resistance to various drugs Composite transposons can help bacteria adapt to new environments. Short Answer: Describe the sexual life cycles for humans and fungi/some algae and plants. Be sure to specify the type of cell division taking place (mitosis or meiosis) and whether or not the organism is haploid or diploid, along with other terminology. Be specific! Cheyenne Cheung, Cody Rubin, Vanessa Ghofrani Chapter 19 project 10/28/09 Answer: Humans: Haploid cells called gametes are produced in the gonads (testes or ovaries) by meiosis, which reduces the chromosome number by half. A sperm (n) and an egg (n) combine in fertilization to produce a zygote, which is diploid (2n). The zygote goes through mitosis and development, only undergoing meiosis in the gonads. Fungi and Algae: Two gametes combine in fertilization, forming a diploid zygote. However, the zygote undergoes meiosis before developing. However, the haploid cells produced don’t undergo meiosis. They divide by mitosis and so the adult organisms are haploid. The only diploid stage is the zygote stage. Plant answer: This life cycle includes both diploid and haploid multicellular stages, called alternation of generations. the diploid stage is called the sporophyte. Sporophytes divide by meiosis, which produces a haploid cell called a spore. Spores do not fuse with other cells, and divide by mitosis (which keeps chromosome number the same). This produces a haploid stage called the gametophyte. Since the gametophyte stage is haploid, it makes gametes by mitosis. Fertilizatoin with another gamete produces a diploid zygote, which then turns into the next sporophyte generation. Questions 1. What is name of this cycle? 2. What is the process that leads from Sporophyte to haploid spores? 3. Is Sporophyte haploid or diploid? Is Gametophyte haploid or diploid? Cheyenne Cheung, Cody Rubin, Vanessa Ghofrani Chapter 19 project 10/28/09 Multiple choice Answer Key 1) a. jumping genes 2) b. always 3) c. DNA pieces that relocate 4) b. Gametophyte 5) a. Sporophyte 6) c. Gametes 7) a. testing purposes 8) b. cut up a sample of small pieces of tissue 9) c. human, fungi and some protists including some algae, and plants and some species of algae 10) d. Composite transposons