ασκηση 9η :συνδεση ηλεκτρικων αντιστασεων σε σειρα
advertisement

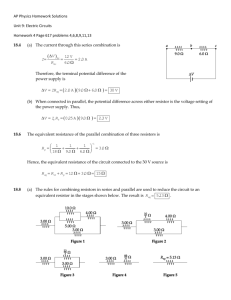
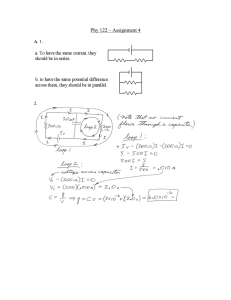
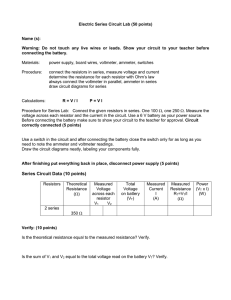
SERIES RESISTOR CIRCUIT THE EQUIVALENT SERIES RESISTANCE 1. We’ve made the following circuits to verify the math type of the equivalent series resistance. The software that we’ve used is called Electronics’ Work Bench 2. We have completed the following table from the indications of the multimeter. TABLE 1: resistance (ohm) R1 R2 R3 Req R1+R2+R3 (using a calculator) 50 100 150 300 300 3. Conclusion: We can find the equivalent resistance if we add all the resistances of the circuit Req = R1+R2+R3 THE CURRENT OF THE CIRCUIT 1. We’ve made the following circuit to verify that when we connect resistors in a series circuit the current which flows through each one of them it’s of the same value. 2. We’ve made the following circuit to verify that when we connect resistors in a series circuit: We can find the source voltage: E = U1 + U2 + U3. The source voltage is divided in as many parts as the number of the resistors in the circuit. We measure the greater part of the voltage on the resistor with the greater value. 3. We have completed the following table from the indications of the ammeter and the voltmeter. TABLE 2: R, I, U in a series resistor circuit Resistance R [Ω] R1 50 R2 100 R3 150 Req 300 Current Ι[Α] I1 0.04 I2 0.04 I3 0.04 Voltage U [V] U1 2 U2 4 U3 6 E 12