Electric Circuit Lab
advertisement

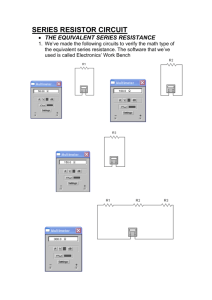
Electric Series Circuit Lab (50 points) Name (s): Warning: Do not touch any live wires or leads. Show your circuit to your teacher before connecting the battery. Materials: power supply, board wires, voltmeter, ammeter, switches Procedure: connect the resistors in series, measure voltage and current determine the resistance for each resistor with Ohm’s law always connect the voltmeter in parallel, ammeter in series draw circuit diagrams for series Calculations: R=V/I P=VI Procedure for Series Lab: Connect the given resistors in series. One 100 , one 250 . Measure the voltage across each resistor and the current in the circuit. Use a 6 V battery as your power source. Before connecting the battery make sure to show your circuit to the teacher for approval. Circuit correctly connected (5 points) Use a switch in the circuit and after connecting the battery close the switch only for as long as you need to note the ammeter and voltmeter readings. Draw the circuit diagrams neatly, labeling your components fully. After finishing put everything back in place, disconnect power supply (5 points) Series Circuit Data (10 points) Resistors Theoretical Resistance () Measured Voltage across each resistor V1 V2 Total Voltage on battery (VT) Measured Current I (A) 2 series 350 Verify: (10 points) Is the theoretical resistance equal to the measured resistance? Verify. Is the sum of V1 and V2 equal to the total voltage read on the battery VT? Verify. Measured Resistance RT=VT/I () Power (VT x I) (W) Circuit + Diagram: (10 points) Conclusions (10 points) 1. Which filament has more resistance, a 40 W or 100 W bulb? 2. A 40 W and 100 W bulb are connected in series. Which glows brighter? 3. As you add more resistances to a series circuit, what happens to the overall resistance and total current in the circuit? 4. Do lights use less energy in series or parallel circuits? 5. What safety devices are used in your house to prevent overloading?