ALLUSION Defn
advertisement

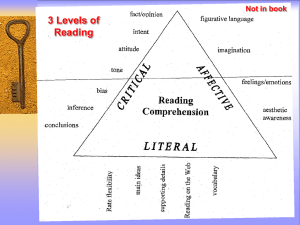
ALLUSION The allusion is an effective stylistic tool. Essentially, it is a reference, explicit or indirect, to a person, place or event, or to another literary, bibilical or mythological work or passage. It is left to the reader or hearer to make the connection. In order to be effective, all allusions rely upon a collective understanding—of literature, popular culture and history. They are powerful tools which help readers connect to the text. There are several types of ALLUSIONS. LITERARY ALLUSION A literary allusion alludes to a person, place, event or line in a well known literary work. Example #1: Look at the title for the essay which explains the dangers of bee keeping: “To Bee Keep or Not to Bee Keep” This title alludes to a famous line in Shakespeare’s Hamlet “To be or not to be” NOTE: The writer’s name is never mentioned—only the famous line, or part of it. A literary allusion can also refer to a famous character or event in a well known piece of literature Example #2: Sam walked down the street waving his stick in the air and muttering obscenities under his breath. Across the street John snickered, turned to Jimmy and snidely stated, “Who does Sam think he is? Potter? “ To understand the meaning of this line, the audience needs to recognize that John is alluding to Harry Potter, the famous young wizard in the literature series. POPULAR ALLUSION A popular allusion alludes to a person, place, product or event in the present, or near present. Example #1: A bomb detonated in the basement of Muriel’s apartment. It was no 9/11, but it was sufficiently terrifying for Muriel to abruptly end her visit to New York. 9/11 alludes to the bombing of the Twin Towers on September 11/2001. The meaning relies upon the audience’s collective experience to understand why Muriel would leave New York. Example #2:He’s no Barack, but he can sure charm the ladies in the audience. To understand this observation, the audience needs to understand that the author is referring to Barack Obama and his excellent oratorical(speaking) skills. HISTORICAL ALLUSION An historical allusion alludes to a person, place or event in the PAST. e.g. Bob captured the tree fort and celebrated his victory with a dance. Susan rolled her eyes and said to Betty, “It’s not like he just captured Vimy Ridge, for heaven’s sake.” This alludes to the Canadian victory during WWI; lke all allusions, it relies upon the general knowledge of its audience. BIBLICAL or MYTHOLOGICAL ALLUSION Mythological and biblical allusions are often used in Western literature. Authors make allusions to people, events or places in the Christian Bible and to Roman or Greek mythology. Example #1 George had sired many sons with many ladies; a modern day Zeus but without the omnipotent powers to stop these women from wreaking their vengeance. The author compares George to Zeus, the all powerful Greek god who sired hundreds of children, both mortal and immmortal. Example #2 New York is wicked, but it’s no Sodom and Gommorah. The author is emphasizing that New York might be dangerous, but it isn’t as terrifiying or immoral like the biblical cities of Sodom and Gommorah.