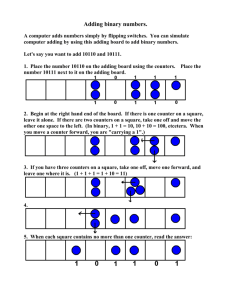
Act out the Situation
advertisement

Act out the Situation Level A Teacher’s Notes Strategy: Level A Act out the Situation Tallest and Smallest 1st Problem Who is the tallest in the group? Who is the smallest in the group? 2nd Problem Who is the tallest in the class? Who is the smallest in the class? This is done in groups. Use the knowledge from the group answers to do Problem 2. Teacher’s Notes Strategy: Level A Act out the Situation Let’s Go Shopping Resources: Worksheet for each child Previous Knowledge: Addition and subtraction within 10 Solution: 1. teddy 8p + ball 2p = 10p rabbit 7p + cart 3p = 10p 2. teddy 8p + ball 2p = 10p rabbit 7p + ball 2p = and 1p left 9p rabbit 7p + cart 3p = 10p cart 3p + duck 5p = and 2p left 8p cart 3p + ball 2p = and 5p left 5p duck 5p + ball 2p = and 3p left 7p duck 5p + duck 5p = 10p 3. duck and ball and a cart 5p + 2p + 3p 10p Extension: The child could list the combinations of things he could buy for 10p and still have some money left. Solution as shown in 2 Let’s Go Shopping Name: ……………………………………………. teddy 8p cart 3p ball 2p rabbit 7p duck 5p Put 10 (1 pences) in your purse. 1. What 2 things can you buy for 10p and have no change left? I can buy a ………………………………..and a …………………………………………… 2. Can you buy another two things for 10p? …………………………… What are they? I can buy a …………………………………….. and a …………………………………….. 3. Can you buy 3 things for 10p? ………………………………………………. What are they? I can buy a ………………………………………and a ……………………………………. and a ………………………………………………….. Teacher’s Notes Strategy: Level A Act out the Situation Around the Table Resources: 2 red, 2 blue and 2 green counters per child A card to act as a table for each child. 1 problem sheet per group. Previous Knowledge: Solution: An understanding of “opposite” and “next to” Around the Table Name: …………………………………………. There are six children to sit at the table. Two are wearing red jumpers; two blue jumpers and the other two are wearing green jumpers. Children wearing the same colour jumpers cannot sit next to each other or opposite each other. Can you find where they will sit? Use your counters and card to help you. Show your answer by drawing it and colouring the circles. Act out the Situation Level B Teacher’s Notes Strategy: Level B Act out the Situation Hoops Resources: The children themselves, 3 hoops (3 colours) Previous Knowledge: Nil 1. Ask all 3 members of the group to stand in the hoops. Jasmine 2. 3. 4. Duncan Laura How many ways can the pupils arrange themselves in the 3 hoops? How can we remember who’s been where? When Jasmine is in the red hoop, how many ways can Duncan and Laura be arranged in the other hoops? Encourage systematic recording:J J D D L L Solution: 6 arrangements JDL JLD DJL DLJ LJD LDJ D L J L J D L D L J D J Teacher’s Notes Strategy: Level B Act out the Situation Line Up Resources: The children Previous Knowledge: Nil 1. Choose a group of four girls and three boys. 2. Ask the group to line up with no two boys together and no two girls together. 3. Ask if it is possible to stand in a ring with two boys together and no two girls together. Extension: 1. Discuss with the group the numbers of girls and boys needed to make a line with no two boys together and no two girls together. 2. Discuss the numbers of girls and boys needed to make a ring with no two boys together and no two girls together. Solution: Line: Numbers of boys and girls must be consecutive numbers. Circle: Numbers of boys and girls must be equal. Teacher’s Notes Strategy: Level B Act out the Situation Counters Resources: Worksheet, counters Previous Knowledge: Addition to 10 Solution: 6 counters – 5 spaces 6 counters/6 spaces 7 counters/6 spaces 7 counters/7 spaces 8 counters/7 spaces 8 counters/8 spaces Counters Name: …………………………………………………… a) Put 6 counter in a line. How many spaces are there between them? 6 Arrange the counters so that there are b) spaces. Put 7 counters in a line. How many spaces are there between them? Arrange 7 counters so that there are c) 7 spaces. Now put 8 counters in a line. How many spaces are there between them? Arrange 8 counters so that there are 8 spaces. Act out the Situation Level C Teacher’s Notes Strategy: Level C Act out the Situation Who’s “It”? Resources: Worksheet for each child Previous Knowledge: Counting in a circle Children may begin to solve the problem by acting out the situation simply guessing who was first. Working backwards will probably occur to them later, or using a diagram might help. Solution: Start at Mark and keep counting on thirteen, crossing out the names you reach. The result will be that Lisa will be left in at the end. Therefore leave Jane last who is opposite Lisa start at David. Who’s “It”? Name: ……………………………………… Eight children gather to play ‘Hide-and Seek’. To decide who is to do the seeking and finding, they stand in a circle singing a number rhyme with thirteen words. Counting clockwise, this meant that every thirteenth children was ‘out’. The last child left was Jane. Where did the count start? Ian David and Kirsty Jane and Kerry Lisa Mark Tariq There are a few ways of working out this problem. Try with a group of eight children from your class. Teacher’s Notes Strategy: Level C Act out the Situation Cover the Square Resources: Worksheet Previous Knowledge: Must distinguish between columns and also understand diagonals. Solution: B R R R B B R B R Cover the Square Name: ……………………………………………. Use 5 red counters and 4 blue ones. Place them on the square so that each column and row has 2 red and 2 blue You must not have 3 counters of the same colour in any row, column or diagonal. Act out the Situation Level D Teacher’s Notes Strategy: Level D Act out the Situation Weighing Resources: Previous Knowledge: Boxes for each group of children containing five items of differing weights. A balance for comparing weights. Nil The items in each box have to be ordered by weight. The children do this by comparing relative weights. A balance may be used if appropriate. Do not use weights or a calibrated scale. After the task has been completed a teacher-led lesson compares the results and methods used. Teacher’s Notes Strategy: Level D Act out the Situation Hop and Slide Resources: Previous Knowledge: Pegs and pegboards or squared paper with counters (two colours). Nil Before the lesson you need to place five chairs in a row at the front of, and facing, the class. Select two boys and two girls to occupy four of the five seats. “The four people sitting in front of you are frogs! The problem they have is to move so that the boy frogs change places with the girl frogs. These frogs can only Move in the following ways: They can slide along an empty chair; They can jump over one frog into an empty chair” Contd. Teacher’s Notes Level D Hop and Slide (contd.) When there have been several attempts at the problem you may decide to stop the action and seek ideas from the rest of the class. Continue with action and discussion until the problem has been solved. “Did anyone notice how many moves it took”? The challenge is to exchange places in as few moves as possible. Let the frogs have another go at doing it – the rest of you count the number of moves. Keep a note of the slides and jumps. An alternative approach is to ask the children to direct the ‘frogs’. Recording the moves on the board using ‘s’ and ‘j’ will help develop the idea of using shorthand notation; in order to distinguish between the girls and boys you could use different colours. At any one time you can change the focus of action from the class to groups or pairs. Give the children suitable materials to try out the activity themselves. Remind them to keep a record of their slides and jumps. Try: 1 girl and 1 boy (and 3 chairs) 3 girls and 3 boys (and 7 chairs) 4 girls and 4 boys (and 9 chairs) Solution: Contd. Teacher’s Notes Level D Hop and Slide (contd.) Solution: The following table shows the underlying patterns (for teacher’s reference only). Number of frogs of each colour 1 2 3 4 Number of ‘jumps’ over the frogs 1 2 3 4 Number of ‘slides’ to adjacent squares 2 4 6 8 Total number of moves needed 3 8 15 24 Teacher’s Notes Strategy: Level D Act out the Situation Hop to It! Resources: Usual classroom equipment. Counters or similar to represent stepping stones. Previous Knowledge: Little more than addition of whole numbers and systematic organisation. Encourage the children to act out the situation at their desks using counters or similar to represent stepping stones. Alternatively use sheets or card laid out on the classroom floor. At the end of the lesson discuss ways of listing the jumps and how to list in a systematic way. Solutions: 1. (s,l) 2. There are five ways with three stepping stones. (s,s,s,s,s) (l,s,s) (s,l,s) (s,s,l) and (l,l). 3. No. of stones 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 No. of ways 1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34 55 89 4. Adding consecutive numbers gives the next number. 5. 89. 6. The sequence is called the Fibonacci sequence. Hop to It! Name: …………………………………………. Freddy frog wishes to cross a river. He does not like getting his feet wet so he is going to use stepping stones. He can jump two gaps with a long hop. With a short hop he can only jump one gap. To cross where there are two stepping stones, he can either do three short hops, which can be written down (s, s, s)………………. …….or he can make a long hop followed by a short hop, which can be written down (l,s). 1. There is another way for Freddy to cross the river. Write it down. 2. On the way home he sees another crossing place where there are three stepping stones. How many different ways can he cross the river at this point? List all the ways. Hop to It! (contd.) Name:…………………………………………….. 3. Now try to find how many different ways there are of crossing the river for different numbers of stepping stones. Record your results in a table. Number of stepping stones 0 Number of different ways of crossing 1 1 2 3 4. Find a rule that links each of the numbers in the bottom row of the table. 5. How many different ways will there be to cross the river at a point where there are nine stepping stones? 6. Find out the name of the sequence of numbers in the bottom row of the table. 4 Act out the Situation Level E Teacher’s Notes Strategy: Level E Act out the Situation Change the Triangle Resources: Pencil and paper. Counters. Previous Knowledge: Nil Children could work in pairs. Teacher explanation, possibly getting class to demonstrate the answer to question 1. Children’s response to Q3 will vary with ability, some can demonstrate with counters where more able children would supply a diagrammatic answer. The objectives of this series of questions are: a) Trial and improvement practice. b) Communicating via diagrams. Solutions: Diagrammatic solutions on separate sheet. Number of counters 1 3 6 10 15 21 28 36 45 55 Number of moves 0 1 2 3 5 7 The rule is “Divide by 3, ignoring the remainder.” 9 12 15 18 Teacher’s Notes Level E Change the Triangle (contd.) Diagrammatic Solutions: Contd. Teacher’s Notes Level E Change the Triangle Diagrammatic Solutions. (contd.) 28 counters 36 counters Contd. Teacher’s Notes Level E Change the Triangle Diagrammatic Solutions: 45 counters (contd.) Change the Triangle Name: ………………………………………………………………………….. A triangle made with 10 counters can be changed from this to this by moving only 3 counters. 1. Show how this can be done. (If having difficulty try triangles with 3 counters then 6 counters first). 2. Make a triangle with 15 counters. Show how to turn (invert) this triangle in as few moves as possible. 3. Show how to invert other triangles of 21, 28 etc. counters in the smallest number of moves possible and make a table of your results. Number of counters Number of moves 3 6 10 3 15 21 4. Have you noticed anything when making your moves or making your table? Explain what you have noticed. Teacher’s Notes Strategy: Level E Act out the Situation Take to Win Resources: A pile of coins, counters etc. Previous Knowledge: Nil Emphasise that it is a strategy to win that the child is trying to get. Once they have that, he or she will win all the time. Solution: The player who wishes to win must leave 5 for his opponent to take from. No matter what he takes you win. He takes 1 you take 3 He must lift last one He takes 2 you take 2 He must lift last one He takes 3 you take 1 He must lift last one Extension: You can take up to 4 at a time. Now what is your strategy to win? Take to Win Name: ……………………………………… This is a game for two players. Start with a pile of counters, or coins, or matchsticks. Rules: 1. Each player plays in turn and must lift 1, 2, or 3 coins from the pile. 2. The player forced to remove the last coin loses the game. Play the game with your friends and see if you can determine a winning strategy.