LAB 5 Key Concepts
advertisement

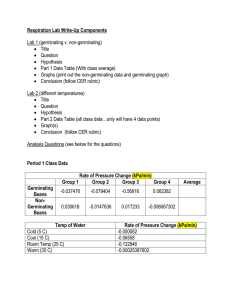
KEY CONCEPTS LAB 5 – Cellular Respiration Some Key Review Concepts Cellular respiration occurs in most cells of both plants and animals. It takes place in the mitochondria, where energy from nutrients converts ADP to ATP. ATP is used for all cellular activities that require energy. The equation for cellular respiration is: glucose + oxygen + ADP carbon dioxide + water + ATP Lab Design Observe evidence for respiration in pea seeds and investigate the effect of temperature on the rate of respiration. To do so, you can measure (1) the amount of glucose consumed, (2) the amount of oxygen consumed, (3) the amount of carbon dioxide produced. In this lab we are going to measure the amount of oxygen consumed by using a respirometer. By submerging the respirometer under water we know that no air will enter the respirometer. The amount of water that enters the respiromter is directly proportional to the amount of oxygen used up by the organism in the respirometer. Analysis of Results After you have collected data for the amount of oxygen consumed over time by germinating and nongerminating peas at two different temperatures, you can compare the rates of respiration. Let's review how to calculate rate. Rate = slope of the line, or In this case, y is the change in volume, and x is the change in time (10 min). You will find that germinating plants had a high respiratory rate, while non-germinating plants had a low respiratory rate.