Biology Summer Exam (Unit 1: The Study of Life and Unit 2: The Cell)
advertisement
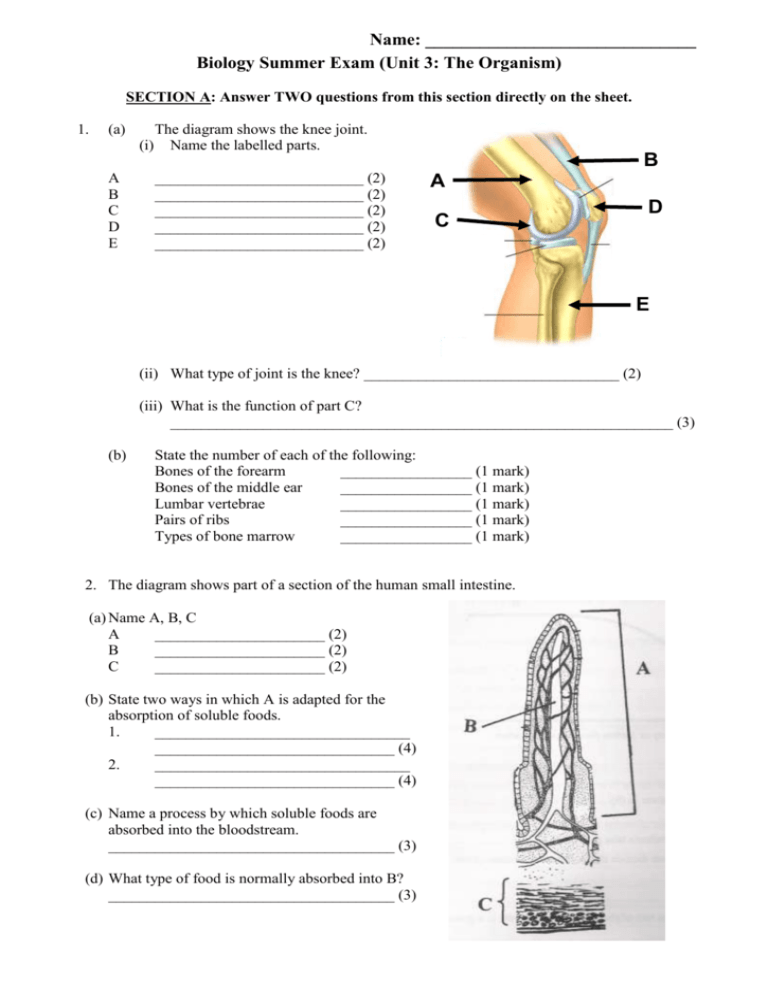
Name: ______________________________ Biology Summer Exam (Unit 3: The Organism) SECTION A: Answer TWO questions from this section directly on the sheet. 1. (a) (i) A B C D E The diagram shows the knee joint. Name the labelled parts. ___________________________ (2) ___________________________ (2) ___________________________ (2) ___________________________ (2) ___________________________ (2) B A D C E (ii) What type of joint is the knee? _________________________________ (2) (iii) What is the function of part C? _________________________________________________________________ (3) (b) State the number of each of the following: Bones of the forearm _________________ (1 mark) Bones of the middle ear _________________ (1 mark) Lumbar vertebrae _________________ (1 mark) Pairs of ribs _________________ (1 mark) Types of bone marrow _________________ (1 mark) 2. The diagram shows part of a section of the human small intestine. (a) Name A, B, C A ______________________ (2) B ______________________ (2) C ______________________ (2) (b) State two ways in which A is adapted for the absorption of soluble foods. 1. _________________________________ _______________________________ (4) 2. _________________________________ _______________________________ (4) (c) Name a process by which soluble foods are absorbed into the bloodstream. _____________________________________ (3) (d) What type of food is normally absorbed into B? _____________________________________ (3) SECTION B: Answer ONE question from this section on the answer sheets provided. (all questions carry equal marks) 1. Answer any two of (a), (b), (c) in this question only. (Total 60 marks) (a) (i) Draw a labelled diagram of a motor neuron. Give a function for three of the parts labelled. (ii) Give two differences between a motor neuron and a sensory neuron. (iii) Name the type of neuron that connects sensory and motor neurons. (12) (9) (6) (3) (b) (i) What is meant by a synapse? (3) What is meant by a synaptic cleft? (3) (ii) Describe, with the aid of a labelled diagram, how an impulse arriving at one side of a synapse can give rise to an impulse at the other side of the synapse. (12) (iii) Name one disorder of the nervous system and state a possible cause, prevention, and treatment for the named disorder. (12) (c) (i) State two differences between nervous and hormonal actions. (6) (ii) Distinguish, giving an example in each case, between exocrine and endocrine glands. (9) (iii) In the case of one named endocrine gland give the name of the hormone it produces and its function. (9) (iv) State a deficiency symptom of this hormone and mention one way in which the deficiency may be corrected. (6) 2. Answer all parts to this question. (Total 60 marks) (a) (i) State a precise location in the human body at which red blood cells are made. (3) (ii) State two ways in which red blood cells differ from typical body cells e.g. from the cheek lining. (6) (b) Use your knowledge of the human vascular and excretory systems to answer the following: (i) Explain the terms: plasma; glomerular filtrate. (3) (ii) Explain why red blood cells are normally absent from glomerular filtrate. (3) (iii) The concentration of glucose is the same in plasma and glomerular filtrate. Why is this? (3) (iv) Why is glucose normally absent from urine? (3) (v) Following a period of heavy exercise an athlete may produce only a small volume of concentrated urine. Explain this observation and give an account of the process that concentrates the urine. (12) (c) (i) Describe the structure of the lymphatic system. (ii) Give an account of the three functions of the lymphatic system. (6) (18) 3. Answer all parts to this question. (Total 60 marks) (a) (i) Distinguish between breathing and respiration. (6) (ii) Breathing rate in humans is controlled by the concentration of a gas dissolved in blood. Which gas is this? (3) (iii) State two factors that would increase the rate of breathing. (6) (b) The diagram shows the human breathing system. B A C (i) Name the parts labelled A, B, C, D. (ii) Where do the cilia occur in this system? What is their function? (iii) State precisely the events that take place at D. How is D adapted for these events? D (12) (3) (3) (9) (9) (c) Asthma and bronchitis are common disorders of the breathing system. Answer the following in relation to one of these disorders. State the disorder to which you refer. (i) State one possible cause of the disorder. (3) (ii) Suggest one way in which a person might adapt his/her lifestyle to minimise the effects of the disorder. (3) (iii) Give an example of a treatment for the disorder. (3)





