Energy Flow
advertisement

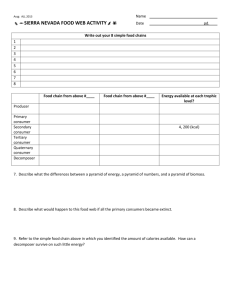
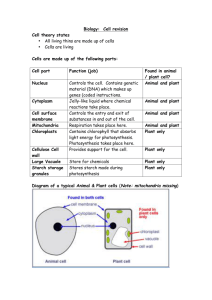
7th Grade/Science UNIT: Biology Concept: Energy Flow Generalizations TEKS: 5 All living matter and energy flow through ecosystems. The student knows that interactions occur between matter and energy. 7. 5A – Recognize that radiant energy from the sun is transformed into chemical energy through the process of photosynthesis. 7. 5C – Diagram the flow of energy through living systems including food chains, food webs, and energy pyramids. (Supporting Std) DCAs, CCAs, Benchmarks, TAKS Grade 8 Describe the energy conversion that occurs during photosynthesis Illustrate the process of photosynthesis Explain the energy roles of producers, consumers, and decomposers in food webs and food chains Follow the flow of energy from the sun to the top level of an energy pyramid and calculate the available energy that gets transferred to each level of the pyramid. Create food webs, food chains, and energy pyramids. MISCONCEPTIONS: Students may think that plants obtain their energy directly from the sun and don’t have to go through photosynthesis. Plants have multiple sources of food (heterotrophic as well as autotrophic). Students may think that carbon dioxide, water, and minerals are food. Students may think that plants feed by absorbing food through their roots. Students may think that plants use heat from the sun as a source of energy for photosynthesis Students may think that sunlight is a food. Students may think that sunlight is composed of molecules. Students may think that sunlight is “consumed” in photosynthesis. Students may think that plants absorb water through their leaves. Students may think that plants produce oxygen for our benefit. Students may think that plants do not take in oxygen or give off carbon dioxide Students may think that air is all one thing (oxygen) and not a mixture of gases Student Expectation: Formal Assessment: Clarification: Notes to Teacher: NOTES: Students may not be able to make the connection between first level consumers with herbivores, and second level consumers, third level consumers with carnivores and omnivores. Students may not understand how the arrows of a food web impact the path of energy through producers, Page 1 7th Grade/Science Key Academic Vocabulary: Food chain Producers Chlorophyll Photosynthesis consumers, and decomposers. In food chains, make sure you explain why the arrows in a food chain diagram point from the organism being eaten to the organism doing the eating to show the flow of energy up through the chain. Students may not have enough background knowledge of plants and animals to classify them as consumers, producers, decomposers, and scavengers or to place them in food chains and food webs In energy pyramids, make certain that you stress that the most energy is available at the producer level. Also stress that each organism in an energy pyramid uses 90% of the energy for its own life processes. Only 10% of the energy is available to the next level consumer. Make sure students realize that 10% of the original source of energy is passed on at each level. Remember to emphasize that decomposers are often left out of food chain diagrams. But, remember that decomposers, such as bacteria and fungi, are always the final link in a food chain. Remember to express to your classes that most of the energy that enters an ecosystem comes from the sun. (exception – bacteria at bottom of ocean) Review composition of gases found in the atmosphere Food web Consumers (primary, secondary, tertiary, etc.) Omnivores Chemical energy Energy pyramids Ecosystem Decomposers Herbivores Radiant energy Carnivores Vertical Alignment: 6th Grade 6.12E Describe biotic and abiotic parts of an ecosystem in which organisms interact. 6.12F Diagram the levels of organization within an ecosystem including organism, population, community, and ecosystem. 6.9A Investigate methods of thermal energy transfer Before After 8th Grade 8.11A Describe the producer/ consumer, predator/prey, and parasite/host relationships that occur in food webs in marine, freshwater and terrestrial ecosystems. 8.11B Investigate how organisms and populations in an ecosystem depend on and compete for biotic and abiotic factors such as quantity of light, water, range of temperatures, or soil composition. 8.11C Explore how short and long- term environmental Page 2 7th Grade/Science including conduction, convection, and radiation. Core Instruction: Engage Explore Universal Generalization: Food Web Explore – Outcomes influence how computer activity things interact. Drawing a Prairie Food Web Sunkist Demo Energy Pyramid GIZMO (student) and (teacher) Elodea lab - Influencing the Rate of Photosynthesis Mini-ponds changes affect organisms and traits in subsequent populations. Explain Students will explain what they observed in the explore activities Elaborate Drawing a Food Web Evaluate ESL Labeling food Chain ESL Create a Food Chain Picture It Photosynthesis Photosynthesis Notes – for Cornell notes Food Chain Checkers CATALYST Process of Photosynthesis Photosynthesis ppt Energy Pyramid PowerPoint Analyze a food Web Energy Pyramid Wkst Ecosystem and Food Web Analysis Warm up to Photosynthesis #1 - Food Web ppt Warm up to Photosynthesis #2 Who’s Who in a Food Chain? (PPT) Catalyst #1 Producers/ Consumers/ Predators Photosynthesis Poker Chip Demo Catalyst #2 Food Webs Catalyst #3 Relationships in ecosystems Catalyst #4 – Changes effect survival of species On-Line Food Web Games Food Web Quiz (ppt) Food web labeling Page 3 7th Grade/Science Flow of Energy Test Photosynthesis Food from Light Energy Pyramid Practice Problems Page 4