climate graph detective - Geographical Association
advertisement

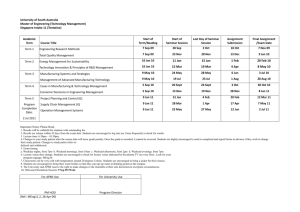
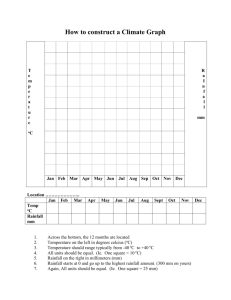
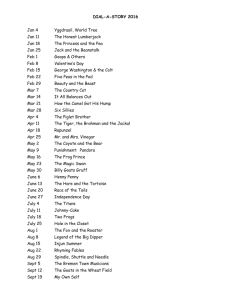
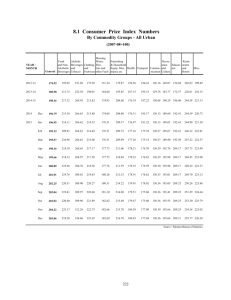
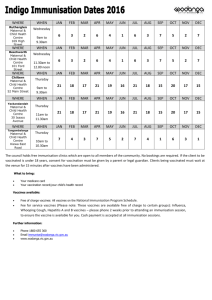
Geography with ICT in Key Stage 3 Year 9: Thinking about climates 1: climate graph detective Rationale and context for the lesson The lesson described below could form part of a sequence of learning on world biomes and would need to follow the study of weather and climate and ecosystems. It offers a neat way of combining the skills learned in the study of climatic and vegetation maps using atlases. The lesson is designed to review both pupils’ learning and the teaching on the topic. By the end of this lesson all pupils will have completed a climate graph using ICT and most should be able to apply skills of interpreting climate graphs and knowledge of biomes and climate to correctly identifying the location of most climate graphs to regions/biomes. Some pupils will be able to choose a country not included in the activity and predict what the climate graph may look like with reasoned accuracy. The following curriculum content can be assessed: KS3 NC Orders for Geography: 2a,d,e,f, 6e.i,e.ii; KS3 NC Orders for ICT: 1c, 2a, 3a,b; Thinking skills: information processing, reasoning; Key Skills: Application of number, Information technology, Problem solving. Pupil prior learning Pupils would need to know the location of world biomes and have an idea of which climates are associated with which biomes. It is helpful if pupils are familiar with using spreadsheets (such as Excel) and drawing graphs, however, pupils who do not have confidence in using these packages can use the help sheet. Pupils should know how to minimise programs to move between Word and Excel and have a sound knowledge of how to copy and paste ICT expertise needed by the teacher Being able to copy and paste from one document to another. Ability to minimise and work between two software packages (Word and Excel) Ability to use Excel to draw graphs Resources for the lesson Atlases World map posters Biomes poster (good for use with lower ability pupils) Rainfall and temperature graphs instruction sheet (see below) Climate graph detective instruction sheet (see below) Rainfall and temperature statistics for a number of places around the world (see below) Sample of completed spreadsheet and graph (see climategraphs1.xls) Adapting the activity and follow-up Pupils could be asked to carry out the same activity for regions within countries. For example, for climatic regions within India or Brazil. The lesson also links to tourism, i.e. pupils investigate holiday activities and relate them to the biome, e.g. Egypt and camel safaris. 1 ICT Lesson plan – climate graphs downloaded from: www.geography.org.uk Rainfall and Temperature Graphs instruction sheet 1. Collecting the data The data has been downloaded into a Word document in the following file: Humanities – Geography - GCSE Climate stats Open a Word document and find your data. Open a new document in Excel. Go back to Word, then highlight the Rainfall Data and Months (not the total). Paste this into Excel. Copy the Temperature data in C and paste this beneath the Rainfall Data. 2. Drawing the rainfall and temperature graph To draw the graph in Excel: Highlight all the data Click on the Chart symbol on the toolbar. Select Custom and then the option ‘Line Column on 2 axes’. Select Next. Choose suitable titles for the graph and both axes. For the purpose of the quiz, you need to print a graph without a title. X = months first Y = rainfall second Y = temperature. Locate the graph as a separate chart. Select ‘Finish’. In order for all the graphs to be compared easily, it may be necessary to make the scales similar for the rainfall and temperature. The scale that the class will use is 0 to 220 (mm) for rainfall and -20 to +30 (°C) for temperature. Right click on the Y-axes, then select Format axis then select Scale. Maximum = 360 Minimum = 0 Major unit = 20 Complete the above for temperature axis. Maximum = 30 Minimum = -20 Major unit = 5 Copy the graph and paste it into a new Word document. Drag it out to fill the whole page. Write on the top of the page the number you were given. Now Print your graph. 2 ICT Lesson plan – climate graphs downloaded from: www.geography.org.uk ‘How much do you know about climatic regions and ecosystems?’ Climate Graph Detective You will need to locate the following cities in the atlas and then annotate your copy of the world map to locate them. City London UK City Kiev In Salah Algeria Tomsk Russia Manaus Brazil Tunis Tunisia Harare Zimbabwe Cape Town South Africa Rome Italy Oslo Norway Coppermine Canada Jakarta Indonesia Berlin Germany Windhoek Namibia Christchurch New Zealand Vancouver Canada Graph No Country Graph No Country Russia You will now look at a series of climate graphs. Using your geographical knowledge and detective skills, you should enter in the table above, what number graph you think represents each country. Extra Select a couple of examples and say why you made the climate/country match that you did. Extra Take a country not studied and draw what you think the climate graph may look like. Explain the shape you have drawn. 3 ICT Lesson plan – climate graphs downloaded from: www.geography.org.uk Rainfall and Temperature statistics Windhoek, Namibia Located at about 22.57°S 17.10°E. Height about 1728m above sea level. Average Temperature °C Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year 23.3 22.1 21.0 18.9 15.9 13.2 13.2 15.8 19.2 21.6 22.5 23.4 19.2 Average Rainfall mm Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year 78.1 80.3 78.7 37.7 6.6 1.2 0.7 0.9 2.8 11.8 26.9 41.7 365.1 Jakarta, Indonesia Located at about 6.18°S 106.80°E. Average Temperature °C Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year 25.8 25.9 26.3 26.8 26.9 26.6 26.3 26.5 26.9 26.9 26.6 26.2 26.5 Average Rainfall mm Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year 341.6 301.8 209.8 134.6 108.1 90.2 59.0 47.7 68.8 106.4 139.1 207.6 1821.0 Oslo, Norway Located at about 59.03°N 10.50°E. Height about 6m above sea level. Average Temperature °C Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year -0.1 0.0 1.3 4.8 10.9 15.0 17.1 16.3 13.0 9.6 5.0 1.8 8.2 Average Rainfall mm Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year 55.1 37.1 71.4 37.4 40.8 49.7 58.5 69.1 65.6 90.2 69.3 52.2 704.9 Cape Town, South Africa Located at about 33.97°S 18.60°E. Height about 42m above sea level. Average Temperature °C Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year 21.0 21.2 20.0 17.4 15.1 13.3 12.5 13.0 14.3 16.2 18.2 19.9 16.8 Average Rainfall mm Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year 15.9 15.2 21.6 49.5 91.7 105.4 91.2 82.6 54.3 39.6 24.2 19.3 612.5 Tunis, Tunisia Located at about 36.83°N 10.19°E. Height about 3m above sea level. Average Temperature °C Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year 10.4 10.8 12.8 15.2 18.3 22.6 25.5 26.3 23.9 19.5 14.8 11.7 17.7 Average Rainfall mm Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year 61.6 52.4 45.6 38.4 22.2 10.4 3.3 7.2 32.0 54.9 53.5 62.9 446.1 4 ICT Lesson plan – climate graphs downloaded from: www.geography.org.uk Tomsk, Former Union Of Soviet Socialist Republics Located at about 56.43°N 84.90°E. Average Temperature °C Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year -18.8 -16.5 -9.9 -0.2 8.4 15.3 18.2 15.2 9.1 0.7 -10.5 -17.0 -0.5 Average Rainfall mm Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year 26.9 17.9 21.9 25.6 44.8 61.1 73.6 67.9 44.2 47.7 46.0 34.0 512.6 Kiev, Former Union Of Soviet Socialist Republics Located at about 50.40°N 30.40°E. Average Temperature °C Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year -5.6 -4.7 0.3 8.1 15.3 18.8 20.4 19.0 14.0 8.0 1.2 -3.1 7.6 Average Rainfall mm Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year 37.7 34.4 38.9 44.8 51.8 69.1 77.1 64.4 46.7 43.3 45.4 43.5 598.3 Christchurch, New Zealand Located at about 43.50°S 172.50°E. Height about 8m above sea level. Average Temperature °C Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year 17.3 16.9 15.4 12.2 9.2 6.4 6.0 7.6 9.7 12.4 13.7 16.1 11.9 Average Rainfall mm Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year 47.6 37.2 60.5 60.1 81.3 49.7 64.9 44.7 38.6 35.2 45.6 46.2 612.1 Berlin, Germany Located at about 52.47°N 13.40°E. Height about 50m above sea level. Average Temperature Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year °C -0.9 0.5 3.5 8.4 13.5 17.1 18.5 17.9 14.2 9.0 3.9 0.9 8.9 Source: derived from GHCN 1. 3198 months between 1701 and 1990 Average Rainfall mm Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year 42.4 33.2 34.5 39.7 52.6 75.5 57.4 60.4 47.6 39.1 46.8 51.1 580.7 Coppermine, Canada Located at about 67.80°N 115.10°W. Height about 0m above sea level. Average Temperature °C Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year -29.0 -29.7 -26.4 -17.3 -5.6 3.9 9.6 8.4 2.6 -6.9 -20.1 -26.0 -11.3 Average Rainfall mm Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year 11.7 8.4 12.5 14.4 13.9 18.4 31.9 40.9 29.9 27.7 15.9 12.0 238.5 Roma, Italy 5 ICT Lesson plan – climate graphs downloaded from: www.geography.org.uk Average Temperature °C Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year 7.2 8.3 10.5 13.7 17.8 21.7 24.4 24.1 20.9 16.6 11.7 8.4 15.4 Average Rainfall mm Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year 80.0 70.9 68.6 66.8 51.5 34.1 16.3 24.4 69.2 113.3 110.7 97.1 802.9 Harare, Zimbabwe Located at about 17.82°S 31.02°E. Height about 1471m above sea level. Average Temperature °C Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year 20.2 20.0 19.6 18.4 15.8 13.4 13.5 15.7 18.8 21.1 20.8 20.3 18.1 Average Rainfall mm Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year 190.4 176.7 106.8 32.5 10.1 2.8 1.2 2.3 6.6 31.8 93.1 173.1 830.5 Manaus, Brazil Located at about 3.13°S 60.00°W. Average Temperature °C Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year 26.0 26.0 25.9 26.0 26.2 26.3 26.5 27.2 27.5 27.5 27.1 26.6 26.6 Average Rainfall mm Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year 263.9 262.0 297.9 282.7 203.7 103.1 66.9 45.6 63.0 111.1 161.0 219.8 2087.5 In Salah, Algeria Located at about 27.20°N 2.40°E. Average Temperature °C Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year 14.3 16.8 20.9 25.2 30.5 35.7 36.8 36.5 33.0 26.8 20.2 14.0 26.1 Average Rainfall mm Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year 1.6 3.4 1.2 2.0 0.4 0.1 0.0 0.3 0.5 1.6 1.2 3.0 15.8 London, UK Located at about 51.50°N 0.30°W. Height about 5m above sea level. Average Temperature °C Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year 4.2 4.6 6.1 8.7 12.1 15.3 17.2 16.7 14.2 10.4 6.8 4.9 10.1 Average Rainfall mm Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year 48.0 38.9 39.9 42.2 47.3 52.1 59.5 57.2 55.4 62.0 59.0 52.9 615.0 Vancouver, Canada Located at about 49.18°N 123.10°W. Height about 3m above sea level. 6 ICT Lesson plan – climate graphs downloaded from: www.geography.org.uk Average Temperature °C Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year 2.7 4.4 6.1 8.9 12.3 15.1 17.3 17.1 14.3 10.0 5.9 3.7 9.8 Average Rainfall mm Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year 145.7 121.4 102.3 69.2 55.8 47.1 31.3 37.0 59.6 116.3 154.6 171.5 1106.6 7 ICT Lesson plan – climate graphs downloaded from: www.geography.org.uk Thinking about climates 1: climate graph detective - Lesson Plan Learning objectives Learning outcomes Geography We are learning to: Draw climate graphs Interpret climate graphs Consider the practical use climate graphs for people, e.g. usefulness when choosing a holiday ICT We are learning to: 1c, 2a, 3a, 3b Plot two values on a graph in Excel Produce accurate and correctly labelled graphs Interchange between two software packages Geography What I am looking for is: Pupils being able to apply their skills of interpreting climate graphs and knowledge of biomes and climate to be able to correctly identify the location of most climate graphs to regions/biomes. Starter 5 minutes Challenge 15 minutes Development 15 minutes Plenary 5 minutes ICT What I am looking for is: Accurate, well labelled graphs An understanding that there are many different graphing tools in Excel yet they have to be appropriate to the task Match the country to the biomes - provide pupils with a list of countries and ask them to identify which biomes they would be associated with, for example: Ethiopia – deserts, Italy – Mediterranean, Sweden – coniferous forests, Brazil – tropical forests. Thinking skills activity - provide made up images of animals and ask pupils which biomes they think they belong to and justify the reasons. Alternatively provide pictures of animals and ask where would you find them (county and biomes). Why did you think this? Pupils are given climatic data for one country (see Rainfall and temperature statistics) and a copy of the instruction sheet. They should use them to produce a climate graph in Excel, and then print it off. A completed example of is shown on the attached Excel file (see attachment 1). Each printed graph should be given a number rather than a title. Back in the classroom the world map posters are displayed around the room. Using the climate graphs detective sheet, pupils move around the class with the numbered graphs and must decide which climate graph matches which location. The pupils’ ideas are drawn together in a question and answer session, and they are given the correct answers for the location of each graph. Use a travel brochure to highlight the fact that pupils should be fully aware of the climatic regions of the world and what the fauna and flora may be like. This may be useful when planning a holiday. Ask pupils where they would like to go for a holiday and what vegetation and fauna they would expect to find there. Ask pupils for other reasons why climatic regions are important for geographers. You could also ask pupils to think about the possible impact of global warming on biomes (to lead into work to be done in the next lesson). 8 ICT Lesson plan – climate graphs downloaded from: www.geography.org.uk