Grade 10 Optics Unit Outline - vandanabathlagrade910science
advertisement

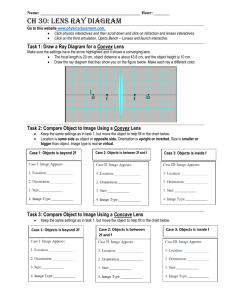
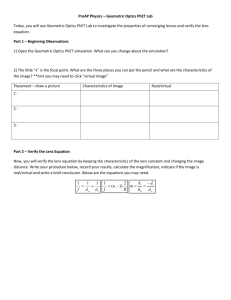
SNC2D – Physics: Light and Geometric Optics Grade 10 Optics Unit Test Outline (page numbers from Science Perspectives 10, Nelson) Lesson Topic, Concepts, Terms Pages 1 What is light and how is it produced? What are different sources of light? Bioluminescence, chemiluminescence, incandescence, fluorescence, phosphorescence, electric discharge, triboluminescence, LED (light emitting diode) 2 The Electromagnetic Spectrum Math Review: Re-arranging equations, unit conversions, scientific notation 464-466 3 Uncertainty, significant digits and rounding Handouts 4 The Ray Model of Light – light travels in straight lines transparent, translucent, opaque 5 Law of Reflection: angle of incidence = angle of reflection 6 Finding images in a mirror using the Law of Reflection 7 Refraction of light – what is refraction? What are different refraction phenomena? Mirages, apparent sunset, apparent depth 8 Index of Refraction equation and calculations c n v 463, 470-476 479 480-485, 489491 515-519 524-528, 535537 Total internal reflection, critical angle: optical waveguides/fibres, diamonds, prisms 9 Types of lenses (converging and diverging), applications of lenses Principal axis, lens axis, focal length, primary focus, secondary focus 551-552 10 Images produced by Lenses: Drawing ray diagrams for converging lens systems Parallel ray, centre ray, focal ray Describing images using SALT (Size, Attitude, Location, Type) Real and virtual image 554-556 11 Thin Lens Equation and Magnification Problems 562-564 h d 1 1 1 , M i i f do di ho do 12 Review 13 Unit Test - Thursday, April 19 (Day 1), Friday, April 20 (Day 2) SNC2D – Physics: Light and Geometric Optics Grade 10 Optics Unit Test Review 1000 m = 1 km 100 cm = 1 m 1000 g = 1 kg 1000 mg = 1 g 60 s = 1 minute 60 minutes = 1 hour c n v 1 1 1 f do di 10 mm = 1 cm c = 3.00 × 108 m/s M hi d i ho do 1. Name 3 uses of optics in any of the following fields: medical, scientific, environmental, everyday applications. 2. Fill in the following table on different sources of light: Type Incandescence Definition Example Light created from heating Light created by living organisms Chemiluminescence Firefly, angler fish Glow stick Energy is absorbed and immediately re-emitted as a different wavelength CFL bulbs Light created by friction or crushing Duct tape, lifesaver mints Light created from high voltage electricity Lightning Phosphorescence Light-emitting diode SNC2D – Physics: Light and Geometric Optics 3. What is the difference between fluorescence and phosphorescence? 4. What would be the advantages and disadvantages of using fluorescent lighting in your home instead of incandescent? 5. Place the following types of electromagnetic waves in order from smallest wavelength to largest wavelength: x-rays, visible light, radio waves 6. While traveling down the highway (posted speed limit: 100 km/h), you estimate that you are traveling 20 m/s. Will you get ticketed for speeding? Write down your conversion factors, and show all your steps. 7. Write the following in scientific notation, and then round each of the original numbers to 3 significant digits. Scientific notation Rounded to 3 significant digits 0.006087 43, 300.78 g 8. Do the following conversions: 37,500 mg to kg 9. What is the Law of Reflection? 0.0035 km to cm SNC2D – Physics: Light and Geometric Optics 10. For the plane mirror below, draw a normal to the mirror, a light ray that reflects at an angle of reflection of 60 degrees, and its incident ray. Clearly label the incident ray, normal, reflected ray and angle of incidence and angle of reflection. Mirror #2 11. Draw the virtual image (the image in the mirror) for the following object. The dark line is the mirror. 12. Draw a sketch of a light ray traveling from glass (index of refraction, n = 1.52) into water (n = 1.33). Make sure you draw a normal and show whether the ray bends towards the normal or away from the normal. glass water SNC2D – Physics: Light and Geometric Optics Table #1: The Index of Refraction of Various Media Medium Index of Refraction (n) Air/vacuum 1.00 Water 1.33 Ethyl alcohol 1.36 Quartz 1.46 Vegetable oil 1.47 Acrylic 1.49 Glass 1.52 Zircon 1.92 Diamond 2.42 13. Would you expect light passing through glass to travel faster or slower than through ethyl alcohol? 14. When light travels from water to glass, would it bend towards the normal or away from the normal? 15. Explain why an acrylic stirring rod is almost transparent when submerged in vegetable oil compared to when it is placed in water. 16. The speed of light in a mysterious substance is 2.04 × 108 m/s. Calculate the index of refraction and check values in Table #1 above to determine what the substance is. Use the GRASS method, show all steps. 17. A futuristic science fiction novel writes about a very special material with an index of refraction of 0.90. What is the speed of light in this material? Write down all givens, show your steps (algebra or formula triangle). Why would this material be so special? SNC2D – Physics: Light and Geometric Optics 18. In the novel Lord of the Flies, a band of marooned boys use the eyeglasses of a nearsighted boy to focus light and start fires for warmth and cooking. However, diverging lenses are required to correct nearsightedness, and cannot be used to start fires. Sketch a converging and a diverging lens and then sketch what happens to parallel rays when they pass through the lenses to show why diverging lenses cannot be used. 19. For the following converging lens system, measure the focal length. Label the principal axis and the lens axis. Use the rules for drawing ray diagrams (Parallel Ray, Centre Ray and Focal Ray) for converging lenses to find the resulting image. Describe the image using SALT (Size, Altitude, Location, Type). 2f f f 2f 20. For the following converging lens system, draw a ray diagram to show why no focused image is formed (i.e. you should be able to show that a Parallel Ray and a Centre Ray do not converge in this case). 2f f f 2f SNC2D – Physics: Light and Geometric Optics 21. An object located 20 cm away from a converging lens produces a focused image 15 cm away from the lens on the other side of the lens. (a) (b) (c) (d) What is the magnification of this lens system? What kind of image is produced (real or virtual)? Is the image upright or inverted? What is the focal length of the lens? 22. A converging lens with a focal length of 15 cm has a 50 cm tall object placed 30 cm away from the lens. (a) (b) (c) (d) Where will the focused image be produced? What kind of image is produced, and what is its attitude? What is the magnification of this lens system? How tall is the image? 23. Give 2 common examples of refraction phenomena. 24. Give 2 examples of applications that make use of total internal reflection.