Horizons World Geography Fall Final review
advertisement

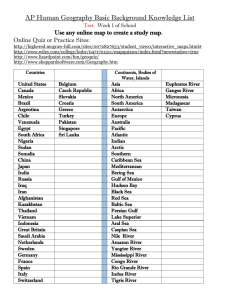
Horizons World Geography Fall Final review 1213 Refer to your notebook, units 1,2,3,4, 8(toolkit) and specific chapters or pages in the book for help. Concepts/terms you need to understand in order to think geographically and to complete this review GEOGRAPHY OCEAN CURRENTS STANDARD OF LIVING SPATIAL DIFFUSION CONTINENTALITY FLOOD HUMAN PATTERNS DEVELOPMENT TSUNAMI PROCESSES INDEX VOLCANIC ACTIVITY COLUMBIAN LIFE EXPECTANCY EXCHANGE EL NINO INFANT MORTALITY PANDEMIC RENEWABLE RATE RESOURCE GLOBALIZATION LESS DEVELOPED NON-RENEWABLE TECHNOLOGY COUNTRY RESOURCE CONNECTIVITY NEWLY VEGETATION HUMAN/ INDUSTRIALIZED RESOURCE ENVIRONMENT COUNTRY INTERACTION (HEI) BARRIERS MORE DEVELOPED FORMAL REGION ASSISTS COUNTRY FUNCTIONAL TEMPERATURE COMMERCIAL REGION PRECIPITATION AGRICULTURE PERCEPTUAL LANDFORMS SUBSISTENCE REGION LANDLOCKED AGRICULTURE CONVERGENCE DESERT OUTSOURCING DIVERGENCE MOUNTAIN DEVELOPMENT RIVER INFRASTRUCTURE CLIMATE VALLEY WEATHER PLAIN POPULATION SEASON BARRIER ISLAND PYRAMID PLATE TECTONICS BIOME MIGRATION TYPES EROSION TROPICS POPULATION SOIL BUILDING TEMPERATE DENSITY SPHERES OF THE FRIGID URBANIZATION EARTH DESALINATION MEGALOPOLIS ELEVATION ARABLE SETTLEMENT LATITUDE WIND SYSTEMS SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT URBAN SPRAWL PUSH/PULL FACTORS POINT OF VIEW PUBLIC POLICY NATIONALISM PATRIOTISM INNOVATION WAR TRADE ANIMISM CHRISTIANITY HINDUISM BUDDHISM JUDAISM ISLAM SIKHISM MONOTHEISM POLYTHEISM INDUSTRIALIZATION INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION GIS GPS PRIMARY SOURCE SECONARY SOURCE AERIAL PHOTO MAP Complete the following items in preparation for the final exam Completed reviews = +10 on your final exam grade. (Must be hand written) WG 1 HISTORICAL GEOGRAPHY – units 1,2,3,4, + chapter 1 1. Use the example of the English language to analyze how geography and spatial diffusion have influenced events in the past and shaped our world today. 2. Describe spatial diffusion using the Columbian Exchange (page 136 graphic) and American Pop Culture (baseball, soccer, new foods, music, clothing, slang, etc…) WG 2 CHANGE OVER TIME – units 2,3,4, + chapter 2, 5 (Just the Columbian Exchange part) 3. How have the physical characteristics and the human character of the US changed over time? 4. What resources have been valued in the past vs. those valued now and surmise a few that may be valued in the future. Explain the change in use of resources over time – use petroleum as your example. WG 3 PHYSICAL PROCESSES AND SYSTEMS – unit 2, + chapter 2 5. Contrast climate vs. weather 6. Explain why seasons change. 7. Describe how these physical processes work: tectonics, erosion, soil building, glaciation 8. List the layers/spheres of the earth and describe how these physical processes (tectonics, erosion, soil building, and glaciation) affect each sphere. WG 4 PHYSICAL PATTERNS AND CHARACTERISTICS – unit 2, + chapter 2, 3 9. How do physical processes influence or affect elevation, wind systems, ocean currents, and position on a continent (continentality). 10. How do mountain barriers influence - temperatures on coasts and inland, - precipitation and - climate region distributions? 11. Which physical processes (tectonics, erosion, soil building, and glaciation) lead to the temp/precip/ climate patterns you observe? 12. What physical processes (tectonics, erosion, soil building, glaciation) create the following landforms: deserts, mountains, rivers, valleys, plains, barrier islands… 13. How does climate create the biomes in the tropical zones, temperate zones, and frigid zones? WG 5 DEVELOPMENT – unit 1,3,4, chapter 4, section on economics 14. Consider these 2 places and their unique characters: USA v India. How is the place influenced by Economics, Social/Cultural, Political and Environmental (ESPN) elements to make them each unique? 15. How does a geographer interpret development of a country socially, economically and politically? 16. Measure and classify at least 3 of these countries (USA, Mexico, India, China, Russia, Japan, Bangladesh, Sudan) as Less Developed, Newly Industrialized or More Developed by giving evidence from the Human Development Index (HDI). WG 6 URBANIZATION AND SETTLEMENT – units 1,4, + chapter 4, section on urbanization 17. List examples of human and physical features that influence the sizes and distributions of settlements. 18. How have these processes (urbanization, transportation, access to resources, changes in economic activities) caused changes in settlement patterns? WG 7 POPULATION GEOGRAPHY –unit 4, + chapter 4, section on population 19. Describe the differences in the population pyramids you would find in the following countries: USA, Mexico, India, China, Russia, Japan, Bangladesh, Sudan. Google population pyramids if needed. 20. Using population data such as population pyramids, infant mortality rates, etc… predict the future population trends for 3 of these countries: USA, Mexico, India, China, Russia, Japan, Bangladesh, Sudan. 21. Give examples of push and pull factors using ESPN to explain the routes/flows of human migrations. 22. Explain the trends in world population growth and the distribution of that growth (think about MDC’s, NIC’s, LDC’s, etc…) 23. Explain how these examples (spatial diffusion, connectivity, standard of living, pandemics and loss of local culture) have either benefitted/+ or been a challenge/- regarding globalization. WG 8 INTERDEPENDENCE/HEI – unit 1,2,3,4, + chapter 1 24. How do people a. depend on the physical environment? (Hint: include influences of culture and technology) b. adapt to the physical environment? (Hint: include influences of culture and technology) c. modify the physical environment? (Hint: include influences of culture and technology) 25. Think extreme weather events such as floods, tsunamis, volcanic activity, El Nino and analyze the consequences on interactions between humans and the environment. 26. What is the economic relationship between settlements and the environment? 27. What is the political relationship between settlements and the environment? 28. How does sustainable development connect settlements and the environment? 29. How does the use of renewable resources connect settlements and the environment? 30. How does the use of non-renewable resources connect settlements and the environment? WG 9 REGIONS - unit 1, + chapter 1 31. Identify how these factors create regions (climate, vegetation, language, trade networks, political units, river systems, religions). 32. Describe these types of regions: Formal, Functional, Perceptual using 3 examples in the USA WG 12 RESOURCES – units 2,3,4, 33. How are the location, pattern, and movement of products, money and people tied to the a. creation of key natural resources? Distribution of key natural resources? Management of key natural resources? 34. What is the environmental impact and economic impact of the development, use and scarcity of natural resources on policies of a government? (Use water resources and petroleum as your examples) WG 15 CITIZENSHIP – unit 4 35. How does Point of View influence the development of public policies and decision-making at local, state, national and international levels? Think about policies in Texas, US, the UN and EU. 36. How do cultural beliefs such as nationalism and patriotism influence citizenship, public policies and decision making? Use USA, Egypt, China and India as examples WG 16 ELEMENTS OF CULTURE - Units 1,5 + chapter 4: section on culture 37. Describe how these regions have distinctive cultural patterns: Texas, US, South Asia, East Asia, North Africa, Western Europe, Latin America 38. Describe these elements of culture: language, religion, beliefs, customs, institutions and technologies 39. Give examples of how groups perceive their own and other cultures, places and regions differently 40. Compare life in urban and rural areas using ‘ESPN’ to evaluate changes to those areas. WG 17 CULTURE and REGION – Units 1,5 + chapter 4: section on culture 41. How do these elements of culture (language, religion, land use, education and customs) make specific world regions distinctive? Think about South Asia, East Asia, North Africa, Western Europe, Latin America and what cultural elements make each region unique. 42. Describe the major religions of the world (animism, Buddhism, Christianity, Hinduism, Islam, Judaism, and Sikhism) and their spatial distribution. 43. Use ESPN to compare opportunities for women, ethnic and religious minorities and other underrepresented populations around the world. 44. Evaluate the contributions and experiences of diverse groups to multicultural societies. WG 18 CULTURAL CHANGE AND DIFFUSION – units 3,5,6 + chapter 4: section on culture 45. How have cultural changes in places (think about South Asia, East Asia, North Africa, Western Europe, Latin America) been influenced by migration, war, trade, innovation and diffusion? 46. Explain how these examples are examples of cultural convergence or cultural divergence: a. spread of democratic ideas, US fast food franchising, English language, technology, global sports such as soccer/futbol or baseball. 47 What are the causes and effects of conflicts between people in cases of modern genocide and terrorism 48 Give examples of cultures that maintain traditional ways and traditional economies. WG 19/20 SCIENCE TECHNOLOGY AND SOCIETY – unit 1,4 49 How have technological innovations like air conditioning and desalinization allowed people to adapt to life in specific environments/regions? 50 Give examples of how advances in technology applications in agriculture (Green Revolution) and the gathering of natural resources (such shale oil) have impacted economics, the environment and culture/society of places such as USA, Mexico, India, China, Russia, Japan, Bangladesh, Sudan. 51 Explain the impact of information technologies like the internet, GPS and GIS on human interactions at local, regional and global levels. 52 Using ESPN, explain how technology such as medical advancements and changing trade patterns have had an effect on the levels of development of countries such as USA, Mexico, India, China, Russia, Japan, Bangladesh, Sudan. WG 21 SOCIAL STUDIES SKILLS – units 1,2,3,4 + chapter 1: section on skills 53. How do geographers evaluate the validity of these tools: primary sources, secondary sources, aerial photographs, maps? 54. In what ways to geographers use these tools in their study of geographic processes and the patterns those processes create? 55. Explain the significance of these locations: ALPS, ANDES, HIMALAYAS, SIERRA MADRES, INDIA, CHINA, SINGAPORE, MEXICO, USA, RUSSIA, JAPAN, BANGLADESH, SUDAN, SOUTH KOREA, VIETNAM, CANADA, FRANCE, GERMANY, 7 CONTINENTS, MIDDLE EAST, EAST ASIA, CENTRAL AMERICA UNIT 8 TOOLKIT – DEFINE THESE GEOGRAPHY TOOLKIT HELPERS > PSOS, ESPN, L/A/N/D, Mr. HEiLP, PED/GING/PING, HIE, ABC’s OF CULTURE, CLIMATE GUY – FRIGID/TEMPERATE/TROPICS, Label Climate guy using your ‘foldy’ climate map