SS107
advertisement
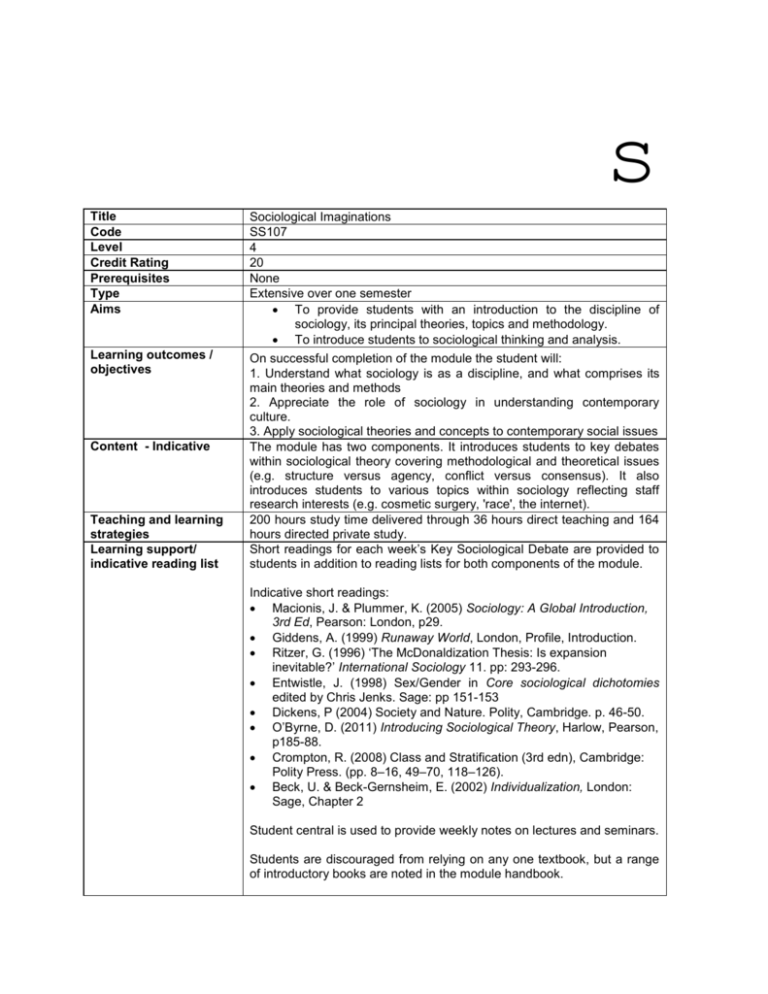
s Title Code Level Credit Rating Prerequisites Type Aims Sociological Imaginations SS107 4 20 None Extensive over one semester To provide students with an introduction to the discipline of sociology, its principal theories, topics and methodology. To introduce students to sociological thinking and analysis. Learning outcomes / objectives On successful completion of the module the student will: 1. Understand what sociology is as a discipline, and what comprises its main theories and methods 2. Appreciate the role of sociology in understanding contemporary culture. 3. Apply sociological theories and concepts to contemporary social issues The module has two components. It introduces students to key debates within sociological theory covering methodological and theoretical issues (e.g. structure versus agency, conflict versus consensus). It also introduces students to various topics within sociology reflecting staff research interests (e.g. cosmetic surgery, 'race', the internet). 200 hours study time delivered through 36 hours direct teaching and 164 hours directed private study. Short readings for each week’s Key Sociological Debate are provided to students in addition to reading lists for both components of the module. Content - Indicative Teaching and learning strategies Learning support/ indicative reading list Indicative short readings: Macionis, J. & Plummer, K. (2005) Sociology: A Global Introduction, 3rd Ed, Pearson: London, p29. Giddens, A. (1999) Runaway World, London, Profile, Introduction. Ritzer, G. (1996) ‘The McDonaldization Thesis: Is expansion inevitable?’ International Sociology 11. pp: 293-296. Entwistle, J. (1998) Sex/Gender in Core sociological dichotomies edited by Chris Jenks. Sage: pp 151-153 Dickens, P (2004) Society and Nature. Polity, Cambridge. p. 46-50. O’Byrne, D. (2011) Introducing Sociological Theory, Harlow, Pearson, p185-88. Crompton, R. (2008) Class and Stratification (3rd edn), Cambridge: Polity Press. (pp. 8–16, 49–70, 118–126). Beck, U. & Beck-Gernsheim, E. (2002) Individualization, London: Sage, Chapter 2 Student central is used to provide weekly notes on lectures and seminars. Students are discouraged from relying on any one textbook, but a range of introductory books are noted in the module handbook. Assessment Brief description of module and/or aims Area examination boards Module team/authors Semester Offered Site where delivered Date first approved Suitable journals include Sociological Research Online, Sociology and Sociological Review 1. 1,500 word essay: Assesses learning outcome 1. 40% 2. Examination. Assesses learning outcomes 2 and 3. 60% This module gives students an opportunity to learn about the main parameters of contemporary sociology and to apply sociological theories and concepts to the contemporary social world. SASS Undergraduate James Ormrod (Module Coordinator), Neil Curry, Steve Brown, Chris Wyatt, Graham Sharp, Mark Erickson, Jayne Raisborough, Mark Bhatti, Natalie Pitimson, Kanwal Mand 1 Falmer and Hastings 1998 Date of last revision Date of approval of this version Version number Replacement for previous module Field for which module is acceptable and status in that field Course(s) for which module is acceptable and status in course 2011 2012 School home External Examiner School of Applied Social Science Dr Ben Pitcher (Oct 2011 to Sept 2015) Allocation of study hours to activities 10 credits = 100 learning hours 5 Compulsory: BA (Hons) Applied Social Science BA (Hons) Social Science BA (Hons) Sociology and Social Policy BA (Hons) Criminology and Sociology BA (Hons) Applied Psychology and Sociology BA (Hons) Politics and Sociology BA (Hons) Media Studies and Sociology BA (Hons) Sociology and English Literature BA (Hons) Sociology and Community History BA (Hons) Education and Sociology Activity Study hours % 36 18 164 82 SCHEDULED Lectures, seminars, tutorials, project supervision, demonstrations, practical classes and workshops, supervised time in workshop/ studio, fieldwork, external visits, work-based learning GUIDED INDEPENDENT STUDY Independent study including wider reading/ practice, follow-up work, completion of assessment tasks, revision etc PLACEMENT Learning away from the University that is not a year abroad or work-based learning Assessment tasks Activity Further details % Type of assessment tasks WRITTEN Exam 40 1500 word essay 60 Summative assessment tasks which lead to the award of credit or which are required for progression (expressed as a %) Written exam COURSEWORK Written assignment/ essay, report, dissertation, portfolio, project output PRACTICAL Oral assessment and presentation, practical skills assessment OTHER Set exercises assessing application of knowledge, analytical, problem-solving or evaluative skills







