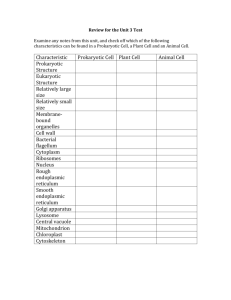
AP Biology Cell Exam Study Guide
advertisement
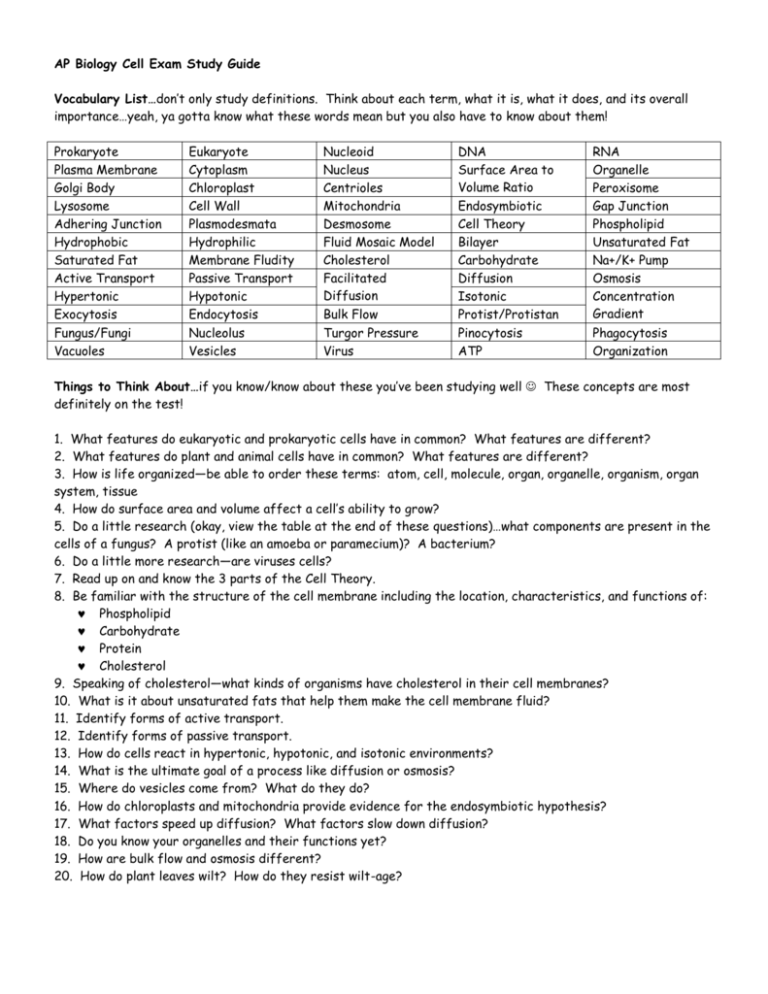
AP Biology Cell Exam Study Guide Vocabulary List…don’t only study definitions. Think about each term, what it is, what it does, and its overall importance…yeah, ya gotta know what these words mean but you also have to know about them! Prokaryote Plasma Membrane Golgi Body Lysosome Adhering Junction Hydrophobic Saturated Fat Active Transport Hypertonic Exocytosis Fungus/Fungi Vacuoles Eukaryote Cytoplasm Chloroplast Cell Wall Plasmodesmata Hydrophilic Membrane Fludity Passive Transport Hypotonic Endocytosis Nucleolus Vesicles Nucleoid Nucleus Centrioles Mitochondria Desmosome Fluid Mosaic Model Cholesterol Facilitated Diffusion Bulk Flow Turgor Pressure Virus DNA Surface Area to Volume Ratio Endosymbiotic Cell Theory Bilayer Carbohydrate Diffusion Isotonic Protist/Protistan Pinocytosis ATP RNA Organelle Peroxisome Gap Junction Phospholipid Unsaturated Fat Na+/K+ Pump Osmosis Concentration Gradient Phagocytosis Organization Things to Think About…if you know/know about these you’ve been studying well These concepts are most definitely on the test! 1. What features do eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells have in common? What features are different? 2. What features do plant and animal cells have in common? What features are different? 3. How is life organized—be able to order these terms: atom, cell, molecule, organ, organelle, organism, organ system, tissue 4. How do surface area and volume affect a cell’s ability to grow? 5. Do a little research (okay, view the table at the end of these questions)…what components are present in the cells of a fungus? A protist (like an amoeba or paramecium)? A bacterium? 6. Do a little more research—are viruses cells? 7. Read up on and know the 3 parts of the Cell Theory. 8. Be familiar with the structure of the cell membrane including the location, characteristics, and functions of: Phospholipid Carbohydrate Protein Cholesterol 9. Speaking of cholesterol—what kinds of organisms have cholesterol in their cell membranes? 10. What is it about unsaturated fats that help them make the cell membrane fluid? 11. Identify forms of active transport. 12. Identify forms of passive transport. 13. How do cells react in hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic environments? 14. What is the ultimate goal of a process like diffusion or osmosis? 15. Where do vesicles come from? What do they do? 16. How do chloroplasts and mitochondria provide evidence for the endosymbiotic hypothesis? 17. What factors speed up diffusion? What factors slow down diffusion? 18. Do you know your organelles and their functions yet? 19. How are bulk flow and osmosis different? 20. How do plant leaves wilt? How do they resist wilt-age? AND here’s the cheats I promised about cell organelles in different types of cells… Cell Type Cell Cell Nucleus Nuclear Cytoplasm Vacuole Wall Membrane Membrane Bacteria *Y Yes No No Yes Protist No Yes Yes Yes Yes Some times ****Y Fungus **Y ***Y No Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes *****N Plant Animal Chloroplast Prokaryote or Eukaryote Yes P Some times No Yes No E E E E *Bacterial cell walls are composed of peptidoglycan, a carbohydrate and protein mix. **Fungus may have a cell wall made of chitin, another polysaccharide (if you have ever seen an insect’s shed exoskeleton then you have seen chitin). ***Plant cell walls are composed of cellulose. ****Protists don’t really have storage vacuoles…they may have a food vacuole similar to a phagocyte that an animal cell forms when it sucks in a particle for digestion. Some protists also have contractile vacuoles to regulate water content—they fill up with water and compress the water out when they are full. As a byproduct, the compression of the contractile vacuole may cause movement for the protist. *****Animal cells use vesicles, not vacuoles to move things in and out of the cell. Animal cells do not store waste and water long term inside like a plant cell. Remember, vesicles originate from two organelles in the cell. After a product leaves the rough ER it will be wrapped in a vesicle provided by the smooth ER for transport to the golgi. The golgi will also wrap a finished cell product in a vesicle to prepare it for exocytosis. All materials for vesicles (the lipids) are prepared by the smooth ER. Other Practice Questions…try your hand at these to get your brain juices…oh wait—this is AP Biology…so to get your neurotransmitters flowing! a. ribosome b. mitochondrion c. lysosome d. golgi body e. endoplasmic reticulum 1. site of polypeptide (protein) assembly 2. cellular digestion and disposal of biological materials occurs here 3. aerobic respiration (to make ATP) occurs here 4. RNA is translated into protein with the help of this organelle 5. secretory proteins (proteins that are going to be secreted) are packaged here 6. involved in lipid production and protein transport 7. the hemoglobin of mammals and birds (the protein that carries oxygen around the body) would be synthesized here 8. sugar metabolism (the use of sugar to make energy) occurs here 9. Four of the five answers are related by a common observation. Select the exception: a. Hooke b. Galileo c. Schwann d. Schleiden e. Virchow 10. Four of the five statements are portions of a well known theory. Select the exception: a. cells are the structural and functional components of living things b. cells arise from preexisting cells c. all organisms are composed of cells d. cells are the basic living unit of organization in living things e. all cells have a nucleus 11. Four of the five statements are familiar organelles in the cytoplasm. Select the exception: a. nucleolus b. mitochondrion c. ribosome d. Golgi body e. chloroplast 12. Four of the five items listed are organelles found in eukaryotes. Select the exception: a. mitochondrion b. Golgi body c. Nucleoid d. Lysosome e. Vacuole 13. Four of the five answers listed below are composed of membranes. Select the exception: a. endoplasmic reticulum b. granum c. plasma membrane d. chromosome e. nuclear envelope 14. Four of the five answers listed below are chloroplast features. Select the exception: a. stroma b. granum c. microbody d. pigment d. ATP 15. Four of the five answers below are features of membrane extensions. Select the exception: a. amyloplast b. centriole c. microtubule d. basal body e. 9 + 2 arrangements 16. Four of the five answers below are types of intracellular junctions. Select the exception: a. tight junctions b. gap junctions c. plasmodesmata d. adhering junctions e. microvilli 17. Four of the five answers below are bound by membranes. Select the exception: a. mitochondrion b. ribosome c. chromoplast d. vacuole e. lysosome a) simple diffusion b) bulk flow c) osmosis d) active transport e) endocytosis 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. process used by white blood cells to digest bacteria process specifically removes water molecules across a differentially permeable membrane explains the movement of any kind of molecule from areas of higher to lower concentrations tendency of molecules to move more rapidly when they move together movement of molecules against a concentration gradient 23. Four of the five answers below are characteristics of the plasma membrane. Select the exception: a. phospholipid b. fluid mosaic c. lipid bilayer d. inert & impermeable e. hydrophobic tails 24. Four of the five answers below are factors affecting simple diffusion. Select the exception: a. temperature b. pressure c. characteristics of membrane d. size of molecules e. concentration gradient 25. Four of the five answers below result when a cell is placed in hypertonic solution. Select the exception: a. wiltin g b. plasmolysis c. turgidity d. limpness e. shriveling 26. Four of the five answers below are related by energy requirements. Select the exception: a. water potention b. osmosis c. bulk flow d. active transport e. diffusion 27. Four of the five answers below are related by energy requirements. Select the exception: a. active transport b. endocytosis c. facilitated diffusion d. exocytosis e. Na+/K+ Pump ANSWERS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. A C B A D E A B B E A C D C A E B E C A B D D C C D C