How Does Cell Organelle Dysfunction Affect Homeostasis? SB1
advertisement

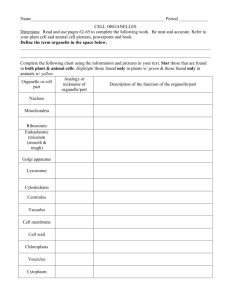
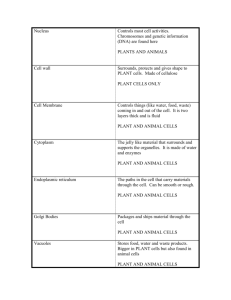
How Does Cell Organelle Dysfunction Affect Homeostasis? SB1: Students will analyze the nature of the relationships between structures and functions in living cells. a. Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis and cell reproduction. Introduction: Cell organelles play vital roles in the life and function of the cell and organism. Most of the time, our organelles function properly and we are able to live happily and healthy each day. However, occasionally individuals may be born with malfunctioning organelles. This can lead to various kinds of symptoms and diseases. Task: Step 1: Investigate the connections between dysfunctional organelles and disease. Complete disease/syndrome and organelle chart on the following page by matching the disease or syndrome with the affected organelle using the symptoms as clues. Once the organelle has been matched with the correct disease or syndrome, list the normal function of the organelle. For each disease explain how the dysfunction of the organelle affects homeostasis at the cellular level and organism level. Step 2: Solve medical case studies Read each case study and determine the name of the disease and which organelle is responsible for the disease symptoms based on the information from the chart completed in Step 1. Write at least one paragraph explaining the diagnosis to parents of the patient for each case study. Remember you are the expert and need to explain to the parents the name of the disease, the name of the organelle and how the malfunctioning organelle is responsible for the disease. Case Studies: Case Study 1 – Adam Adam was a pleasant, happy infant who seemed to be developing normally until about 5 months of age. Able to roll over and sit for a few seconds, suddenly he seemed to lose those abilities. Soon, he no longer turned and smiled at his mother’s voice, as he had before, and he did not seem as interested in his crib mobile as he once was. Adam’s parents became concerned and took him to the doctor. The doctor ran several tests and noticed that there was a heavy startle reaction. After looking into Adam’s eyes the doctor also noticed a cherry red spot on the retina of the eye. Case Study 2 - Scarlett Scarlett’s parents did not have an ultrasound and were shocked when she was born with a small body, skeletal deformities including short limbs. Unfortunately for Scarlett’s parents she only lived for 3 weeks due to serious health issues. Case Study 3 - Lisa Lisa is a 4 month old child who was brought into the E.R. after a violent coughing spell that produced a large amount of phlegm (mucus) and difficulty breathing. The parents told the doctor that they had recently noticed a salty taste to Lisa’s skin when they kissed her. Case Study 4 - Nicole For the first 2 months, baby Nicole seemed fine. At 3 months she developed a severe viral respiratory infection. As she fought the infection she began to have problems sucking and turning her head. Because of the issues with eating she wasn’t gaining weight. She also became irritable and cried almost continuously. The parents took Nicole to the doctor who ran several tests. The test results showed lesions on the brain and brain stem. Disease/Syndrome Symptoms Cystic Fibrosis Chokingly thick mucus in the lungs; frequent lung infections; clogged pancreas; digestive problems; salty sweat. Salt has problems leaving and entering the cells of the lungs and pancreas. Infant appears normal until the age of 3 to 6 months. Lose of the ability to turn over, crawl and sit up. Infants develop exaggerated startle response and may also have a cherry-red spot in the eye. Symptoms result due to the lack of an enzyme to breakdown fatty substances in nerve cell. Infant has a small body, short limbs and other skeletal abnormalities. Due to serious health problems infants are stillborn or die soon after birth. Abnormalities are due to proteins not being packaged and moved to the endoplasmic reticulum. Infants with the syndrome have trouble swallowing or sucking, leading to a failure to thrive. This usually occurs after a viral infection. They also become irritable and cry continuously. Lesions on the brain and brain stem are other symptoms of the disease. Tay-Sacs Achondrogenesis Leigh’s Disease Affected Organelle Normal Function of Organelle