File - Moldenhauer, Lucas
advertisement

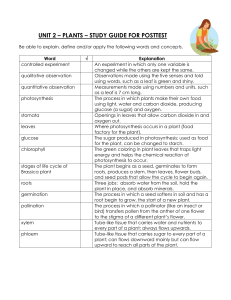
Plant Unit Day 1 (preferably a Friday) Lucas Moldenhauer Grade Level: 10 Subject(s) Area: Biology Materials Needed: Biology: Sixth Edition: Campbell and Reece Plant notes power point Power point handouts for students Radish Lab handout Radish Seeds Potting soil Small Styrofoam cups Water Standards : HS-LS2-3.-Construct and revise an explanation based on evidence for the cycling of matter and flow of energy in aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Objectives : Students will demonstrate knowledge of basic plant properties and structures Students will apply direction to planting radishes. Learning Activities : Introduce Plant unit and hand out radish lab Have students split into teacher assigned groups Instruct them to complete the “set-up day” portion of the lab Clean up Hand out notes Start presentation on plants Assign reading pg 720-726 Name___________________ Period___________________ Date____________________ Light effect of plant growth *Everyone will turn in this sheet individually* Set-up day -There are 3 pots at each station. -Bring the pots, one at a time, to the soil and uniformly fill them till the soil is about 2-3 inches deep. -Plant 15 radish seeds just below the surface of the soil in each pot. -Water evenly -Now we wait for 3 days to the seeds germinate -If you have any questions or problems, I will be walking around to help. Day 1: -Pick 5 plants from each pot that are roughly the same size and remove the rest -Label the each pot with an A, B, or C, and your initials -Measure the height of each plant and get an average for each pot. Record the results in the table -There are a number of different colors of saran wrap, pick 3 -Cover each pot with a section of saran wrap. Do not double up on colors. -Label each pot with an A, B, or C and write what color each is represents in the table below. -Write a Hypothesis (below the table) of what you believe will happen to your plants in relation to each color on the pots Days 2, 3, 4 - Measure the height of each plant and get an average for each pot. Record the results in the table -Water evenly Day 5 - Measure the height of each plant and get an average for each pot. Record the results in the table -Represent your results on the graph. (It is up to you how you do this) -Clean up your planting stations and dispose of them properly -Rewrite your hypothesis, if needed, and answer the questions that follow the lab Table 1 aaaaDayaaaa Aa Pot Aa Color: aPot Baa Color: A Pot Caa Color: 1 2 3 4 5 Hypothesis:____________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Revised hypothesis :_____________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ What 3 colors would you use if you could do the experiment again? Why would you use these colors? (use complete sentences) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 1. Which plant group showed the fastest growth rate? 2. Which group showed the slowest? 3. What was the control in the experiment? Why do we need a control? 4. If you wanted to increase crop yield what light exposure would be the most help? Why is this? 5. Draw a diagram of the radish plant. Label at least 7 things including the roots, stem, and leaves. Plant Unit Day 2 (preferably a Monday) Grade Level: 10 Subject(s) Area: Biology Materials Needed: Biology: Sixth Edition: Campbell and Reece Plant notes power point Photosynthesis assignment Guideline papers Standards : HS-LS2-3.-Construct and revise an explanation based on evidence for the cycling of matter and flow of energy in aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Objectives : Students will demonstrate use of measuring tools Students will demonstrate knowledge of cell functions in plants Learning Activities : Students will measure and water plants Continue lecture on Plants (should get to slide 14) Give time to complete formative assessment on slide 14 (may work in groups) Hand out photosynthesis assignment and guideline papers Explain that tomorrow will be a work day Assessment : Vocab review formative assessment Photosynthesis Research and Reflection Paper Find 2 articles on photosynthesis. -Find a scholarly source (refer the handout on finding credible sources) -Use a mainstream search engine like Google to find another source One or both of the articles should include the following information -definition of photosynthesis -chemical formula for photosynthesis -function and definition of chlorophyll, grana, and photophosphorylation -difference between light dependent and light independent reactions -function of xylem and phloem in photosynthesis Write a 2 page reflection paper that answers that meets the following criteria: -Double spaced -Use in-text citation when necessary -Includes an introduction, body, and conclusion and reference page -Compares both sources (how are they similar or different? Are both credible, why or why not? Which source was easier to find? Why do you think this is?) -Explains the entire process of photosynthesis (including the chemical equation) -Demonstrates knowledge of terms -Include what you thought of photosynthesis before reading the article and what you have learned (may use first person in this section) This is an informational and opinion paper. Blend the two together to explain and reflect on the process of photosynthesis and demonstrate knowledge of research techniques. Finding credible sources A source is generally considered scholarly if it has been subject to peer review or further study. An article being scholarly does not always mean that the information is credible. Many articles are submitted to journals and are peer reviewed with information that is speculation or at least not yet considered fact. It is our job as readers to interpret the credibility of sources always question information. Below are some guidelines to identifying credible sources and some websites that make it easier to find scholarly material. Steps to determine if a source is credible: 1) Think about how reliable you need the information to be. Everyone has different standards for credibility, and often this depends on how the information is going to be applied. a. Is your topic something that has been studied academically? b. Does it matter if the information refined? c. If you're writing an academic paper in a university setting, you need to be especially strict about sources, focusing specifically on scholarly article. 2) Consider the medium with which you are working. Generally, the more that is invested into the creation and publishing of the material, the more likely you are to find reliable information. For example, printed material has a higher cost of production than an Internet blog, which anyone can publish for free. 3) Research the author a. Where does the author work? b. If the author is affiliated with a reputable institution or organization, what are its values and goals? Do they benefit financially by promoting a particular view? c. What is his or her educational background? d. What other works has the author published? e. What experience does the author have? Is s/he an innovator, or a follower and promoter of the status quo? f. Has this author been cited as a source by other scholars or experts in the field? 4) Check the date. Find out when the source was published or revised. In some subject areas, such as the sciences, having current sources is essential 5) Investigate the publisher. If the publisher is a university press, the source is likely to be scholarly. 6) Determine the intended audience. Scan the preface, table of contents, index, abstract, and the first few paragraphs of the article or of a few chapters. Is the tone, depth, and breadth appropriate for your project? 7) Evaluate the source's sources. Citing other reliable sources is a sign of credibility. 8) Identify bias. If the source's author is known to be emotionally or financially connected with the subject, be aware that the source may not fairly represent all views. 9) Investigate the financial or funding sources for sponsored research. Determine the sources of funding for the study conducted to get an idea of the potential influences on the study. Various sources of funding can sway the information presented or the way a study is conducted in order to align with their own agendas. List of scholarly search engines: - http://www.ebscohost.com/academic/science-reference-center http://academic.research.microsoft.com/ http://www.jstor.org/ http://landing.questia.com/lp18/?refid=jg_usca_se1_agacademic&gclid=CJesnLz5x70 CFY6Rfgod3qsApw Citing your sources properly When using information from a source, it is sometimes best to include exact statements from the source. Be careful not to use too many as you want the paper to be your own. If you are taking something word-for-word from a document, surround the statement with quotations and follow it with an in-text citation of the author’s last name, the page number, and the year of the source. If you use information from a source that is not an exact quote, follow the information with an in-text citation including the author’s last name and the year of the source. Example “It was the best of times, it was the worst of times” (Dickens, pg 1, 1859). The results of the study indicated that migration patterns of deer where directly proportionate to temperature (Smith, 2013). Multiple sentences can be written using information from a source before an in-text citation is needed. If a quote is used, a citation is needed directly after it. Scholarly science articles are written in APA format. For the purposes of this class we will use APA for Works Cited pages. Every source that is used for in-text citation needs to appear in the Works Cited page This list provides the information necessary to identify and retrieve each source. Order: Entries should be arranged in alphabetical order by authors' last names. Sources without authors are arranged alphabetically by title within the same list. Authors: Write out the last name and initials for all authors of a particular work. Use an ampersand (&) instead of the word "and" when listing multiple authors of a single work. e.g. Smith, J. D., & Jones, M. Titles: Capitalize only the first word of a title or subtitle, and any proper names that are part of a title. Pagination: Use the abbreviation p. or pp. to designate page numbers of articles from periodicals that do not use volume numbers, especially newspapers. These abbreviations are also used to designate pages in encyclopedia articles and chapters from edited books. Indentation*: The first line of the entry is flush with the left margin, and all subsequent lines are indented (5 to 7 spaces) to form a "hanging indent". Underlining vs. Italics*: It is appropriate to use italics instead of underlining for titles of books and journals. Two additional pieces of information should be included for works accessed online. Internet Address**: A stable Internet address should be included and should direct the reader as close as possible to the actual work. If the work has a digital object identifier (DOI), use this. If there is no DOI or similar handle, use a stable URL. If the URL is not stable, as is often the case with online newspapers and some subscription-based databases, use the home page of the site you retrieved the work from. Date: If the work is a finalized version published and dated, as in the case of a journal article, the date within the main body of the citation is enough. However, if the work is not dated and/or is subject to change, as in the case of an online encyclopedia article, include the date that you retrieved the information. Plant Unit Day 3 Grade Level: 10 Subject(s) Area: Biology Materials Needed: Photosynthesis article Standards : HS-LS1-2.-Develop and use a model to illustrate the hierarchical organization of interacting systems that provide specific functions within multicellular organisms. HS-LS2-3.-Construct and revise an explanation based on evidence for the cycling of matter and flow of energy in aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Objectives : Students will apply skills in working independently. Students will demonstrate quality searching and writing strategies. Students will demonstrate knowledge of the system of photosynthesis and how it relates to an organism as a whole. Learning Activities : Ask the students to take out a sheet of paper and write down 3 things that they remember from the first assigned reading. These things could include defining a term, explaining a system, or explaining a table or diagram of information in the book. . Ask students to form their answers into complete sentences and use proper grammar Collect formative assessment. Students will water plants Rest of day will be spent working on the paper. (read it, take notes, form an idea for the paper) Explain that the paper is due in 5 class periods Assign reading for tomorrow pg. 783-788 and 794-799 Plant Unit Day 4 Grade Level: 10 Subject(s) Area: Biology Materials Needed: Biology: Sixth Edition: Campbell and Reece Plant notes power point Standards : HS-LS1-2.-Develop and use a model to illustrate the hierarchical organization of interacting systems that provide specific functions within multicellular organisms. HS-LS2-3.-Construct and revise an explanation based on evidence for the cycling of matter and flow of energy in aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Objectives : Students will demonstrate knowledge of sexual and asexual reproduction in plants Students will demonstrate knowledge of monocots and dicots Learning Activities : Students will water and measure plants Continue plant notes Hand out clickers (explain how to use if needed) Go through questions on PowerPoint (attached separately) If some students appear to be struggling with the material, have class discussion and some re-teaching, possibly continuing to the next day. Plant Unit Day 5 Grade Level: 10 Subject(s) Area: Biology Materials Needed: Biology: Sixth Edition: Campbell and Reece Plant notes power point Flower dissection lab handout Standards : HS-LS2-3.-Construct and revise an explanation based on evidence for the cycling of matter and flow of energy in aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Objectives : Students will demonstrate knowledge of flower structures Learning Activities : Students will water and measure plants Finish notes on plants Give handout for flower lab. It will be the day after tomorrow Students will work independently lab questions for remainder of class time Remind them that the finishing out the radish lab will be tomorrow Name__________________ Period__________________ Date____________________ Flower Dissection Lab Background Information: Every flower consists of a set of adaptations that help to ensure successful reproduction. For example, flowers often have bright colors, attractive shapes, and pleasing aromas. These traits help them attract insects and other animals that will carry pollen grains from flower to flower. Pollination also occurs by means other than animals carrying the pollen. For some flowering plants, the wind plays an important role in transferring pollen from plant to plant. The seed-bearing plants that produce flowers are angiosperms. The flower produces the seeds, each of which contains a new plant embryo. The parts of the flower are usually found in whorls, or rings. Petals are one of the sets of whorls. They attract pollinators. Sepals lie outside the petals. They protect the bud. The reproductive organs, the stamens and pistils, lie inside the petals. A stamen is a male reproductive part. It consists of an anther that is held up by a filament. The anther produces pollen grains. A pistil is a female reproductive part. Its top is called the stigma. It is sticky to ensure that when pollen grains land on it, they stick to it. The middle supporting structure is the style, and the large base is the ovary, where the eggs are produced (Pre-lab questions) 1. What type of plants produce flowers? Circle Answer: Gymnosperms, Angiosperms, Ferns, Bryophytes 2. Why do plants produce flowers and fruits? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 3. What are the reproductive parts of the flower? ____________________ and ____________________ 4. Define Monocot: ______________________________________________________________________________ 5. Define Dicot: ______________________________________________________________________________ 6. List and define the three parts of the Pistil. 7. List and define the two parts of the stamen. __________________________________________ Label the structures of the flower (Lab Day) Procedure: 1. Locate the outermost layer of flower parts. These are the sepals. Carefully remove the sepals. a. Record the number of sepals, attach one, and describe the function in your data table. 2. Identify the petals. These form the next layer of flower parts. Carefully remove each petal. a. Fill in the data table on the next page. b. What advantage to the flower are colorful petals? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 3. Now locate the stamen. These male flower parts should now be exposed. a. Record the number of stamen, attach one, and describe the function in your data table. b. What do anthers produce? _____________________________________________________________________________ c. Name the flower part that elevates the anther. ______________________________________________________________________________ d. Why is it important to elevate the anthers? ______________________________________________________________________________ e. Describe two different ways that a pollen grain can get to the stigma of a pistil. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ f. Flowers usually contain more stamen than pistils. Why do you think this is? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 4. The female flower part remains. a. Record the number of pistils, attach one, and describe the function in your data table. b. Name the flower part that elevates the stigma. _________________________________________________________________________ c. Why is it important to elevate the stigma? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ d. How does the structure of the stigma aid in pollination? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ e. Which parts of the flower develop into the seeds? ______________________________________________________________________________ f. When fertilized, what will the ovary grow into? _____________________ 5. Leaf: Attach a leaf from your plant in the space below. 6. Is this specimen a monocot or dicot? Explain at least 2 reasons how you know this (Use complete sentences. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Flower part Sepal Petal Stamen Pistil/Carpal Number Attach one of each part below of Description of function Plant Unit Day 6 Grade Level: 10 Subject(s) Area: Materials Needed: Biology: Sixth Edition: Campbell and Reece Light exposure lab handout Standards : HS-LS1-2.-Develop and use a model to illustrate the hierarchical organization of interacting systems that provide specific functions within multicellular organisms. HS-LS2-3.-Construct and revise an explanation based on evidence for the cycling of matter and flow of energy in aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Objectives : Students will demonstrate knowledge of effect of light in a plant system Learning Activities Quick discussion of final day of the lab and concept questions Students will follow direction for the final day of the lab and complete the handout and graph Clean up Collect handout Assessment : : Radish Lab handout Plant Unit Day 7 Grade Level: 10 Subject(s) Area: Biology Materials Needed: Biology: Sixth Edition: Campbell and Reece Flowers for lab Crossword worksheet Standards : HS-LS1-2.-Develop and use a model to illustrate the hierarchical organization of interacting systems that provide specific functions within multicellular organisms. HS-LS2-3.-Construct and revise an explanation based on evidence for the cycling of matter and flow of energy in aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Objectives : Students will work independently Learning Activities : Hand out crossword (modified one for those who need it) Rest of class period spend on crossword and study guide (will not be collected for grade) Remind them that flower dissection lab is tomorrow and to have the pre-lab done Plant Vocabulary Crossword Across 5. External to vascular tissue 7. Structures that have the potential to form a vegetative branch 8. Stacks of thylakoids like pancakes 9. Process of converting energy from a light-excited electron into the pyrophosphate bond of an ADP molecule 10. Transports food to non-photosynthetic parts 12. Life cycle of sexual reproductive plants 15. Photosynthetic material in plants (makes them green) 24. Transports water 25. Roots that arise above ground are 26. Water conducting elements in xylem 27. Alternating systems of nodes 28. Where leaves attach Down 1. The “skin” of the cell 2. Outside layer of cell, animals don't have 3. The anchor of the plant 4. Extend the surface area of roots 6. Form within the ovules 9. The stalk of the leave which connects the leave to the stem 11. Produce sperm 13. Enclose and protect the floral bud before it opens 14. Where the growing of the stem takes place 16. Main source of photosynthesis 17. Brightly colored organ that serves to attract insects and other pollinators 18. Waxy coating that helps leaves retain water 19. Produce eggs 20. contains ovary and ovules 21. internal to vascular tissue 22. grains that produce sperm 23. consists of anther and filament Plant Vocabulary Crossword After 4 or 5 questions, there is a word bank in bold. complete the puzzle Use these words to *if the term is more than one word, write it as one word in the puzzle* Across 5. External to vascular tissue 7. Structures that have the potential to form a vegetative branch 8. Stacks of thylakoids like pancakes 9. Process of converting energy from a light-excited electron into the pyrophosphate bond of an ADP molecule (Grana/Axillary buds/cortex/ Photophosphorylation) 10. Transports food to non-photosynthetic parts 12. Life cycle of sexual reproductive plants 15. Photosynthetic material in plants (makes them green) 24. Transports water (Xylem/ Alternation of generations/Phloem/Chlorophyll) 25. Roots that arise above ground are 26. Water conducting elements in xylem 27. Alternating systems of nodes 28. Where leaves attach (Tracheids/ Adventitious roots/Stems/Nodes) Down 1. The “skin” of the cell 2. Outside layer of cell, animals don't have 3. The anchor of the plant 4. Extend the surface area of roots 6. Form within the ovules (Roots/Epidermis/Embryo sacs/Cell Wall/Root Hairs) 9. The stalk of the leave which connects the leave to the stem 11. Produce sperm 13. Enclose and protect the floral bud before it opens 14. Where the growing of the stem takes place (Sporophytes/Petiole/Terminal Bud/Sepals) 16. Main source of photosynthesis 17. Brightly colored organ that serves to attract insects and other pollinators 18. Waxy coating that helps leaves retain water 19. Produce eggs (Gametophytes/Cuticle/Petals/Leaves) 20. contains ovary and ovules 21. internal to vascular tissue 22. grains that produce sperm 23. consists of anther and filament (Pith/Pollen/Carpel/Stamen) Plants Study Guide: Chapter 35 Plant Structure and Growth: -What are the three basic organs of plants? -Know difference between root and shoot system and their main functions. -Know structures and functions of root system -Taproot -root hairs -advantageous roots -root tip -apical meristem -Know the structures and functions of parts stem -node/internode -terminal bud -axillary bud -Be able to label a stem diagram. -What are leaves the main source of? -What connects leaves to stems? -Be able to identify monocot vs Dicot leaf -What are the three types of tissues that make up plant organs? -What is vascular tissue and what are the two types? -What are the water conducing elements of xylem? -Know parts of ground tissue -Know what a cuticle is and what it is made of. -What is the “skin of a cell? -Be able to explain how plant cells are different than animal cells. (things only plant cells have) -What do plant and animal cells have in common? Chapter 38 Plant Reproduction and Biotechnology: -What types of life cycle to plants have? -Explain sporophyte and gametophyte -Understand life cycle diagram -Know structures and functions of Flower parts -anther -Ovary -ovules -stamen -Parts of carpel -Sepal -embryosacs -Be able to label a flower diagram similar to the one on page 785 -Know difference between monoecious and dioecious -Know difference between mega and microspores -What is asexual reproduction and how does is work in plants? -Know what fragmentation and apomixes are Photosynthesis: -definition of photosynthesis -chemical formula for photosynthesis -function and definition of chlorophyll, grana, and photophosphorylation -difference between light dependent and light independent reactions -function of xylem and phloem in photosynthesis Plant Unit Day 8 Grade Level: 10 Subject(s) Area: Biology Materials Needed: Flower dissection lab handout Flowers for lab Paper towels Tape Standards : HS-LS1-2. Develop and use a model to illustrate the hierarchical organization of interacting systems that provide specific functions within multicellular organisms. Objectives : Students will demonstrate content review knowledge through discussion Students will demonstrate understanding of structure and functions of plants through lab activity Students will connect real-world observation with text support through lab activity Learning Activities : Short review discussion o Photosynthesis o Different parts of a plant o Why flowers are important o Difference in function for photosynthesis and reproduction Go through lab report explaining each section Divide class into lab groups Hand out flowers Complete lab Clean up Collect lab handout Collect crossword Remind them that photosynthesis paper is due tomorrow and that we will be playing review Jeopardy Assessment : R Flower dissection lab handout Crossword puzzle activity eflection: Try to get one monocot and one dicot for each group (lilies and roses) I showed interest but could have showed more enthusiasm for the material Modeling how to remove the pedals and cutting open the flower would have worked better More explanation of the table at the end of the lab Overall, the lesson went very well not many changes Plant Unit Day 9 Grade Level: 10 Subject(s) Area: Biology Materials Needed: Jeopardy game Standards : HS-LS1-2.-Develop and use a model to illustrate the hierarchical organization of interacting systems that provide specific functions within multicellular organisms. HS-LS2-3.-Construct and revise an explanation based on evidence for the cycling of matter and flow of energy in aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Objectives : Students will demonstrate knowledge of vocabulary and themes of unit Learning Activities : Collect photosynthesis paper Divide class into 4 teams Play jeopardy vocabulary game Winners get 10 extra credit, second place 5, third place 2 Remind students that tomorrow is a work day. Final touches may be on paper and time to work on the study guide. Jeopardy vocabulary game I used this site to make a jeopardy game https://www.superteachertools.net/jeopardyx/editor.php This is the edit page. The site allows you to play through the game and keep score. Category #1: Monocot vs. Dicot Question 1: Stem vascular bundles look like monkey faces Answer 1: Monocot Question 2: have 2 seeds 5 Answer 2: Dicot Question 3: Flow ers grow in multiples of 4 and 5 Roots grow randomly into the ground Answer 3: Leaf veins are reticulated Monocot Answer 5: 25 Answer 1: Eukaryotes Question 2: The â€o skin― of the cell Answer 2: Question 3: Answer 3: Answer 4: Ground tissue Question 5: Waxy coating that helps leaves retain w ater Category #3: Question 1: Also called vegetative reproduction Question 2: Uses alternation of generations life cycle Question 3: Va 10 Vascular tissue Question 4: Pith and cortex make up this Va 5 Epidermis Xylem and Phloem make up this Va Cell stucture and types of tissue Question 1: Plants are eukaryotes or prokaryotes? Va 20 Dicot Category #2: Va 15 Answer 4: Question 5: Va 10 Dicot Question 4: Va Answer 5: Cuticle Va 15 Va 20 Va 25 Sexual vs. Asexual Reproduction Answer 1: Asexual reproduction Answer 2: Sexual reproduction Answer 3: Va 5 Va 10 Va Sporophytes produce Sperm Question 4: 15 Answer 4: Gametophytes produce Va Egg Question 5: 20 Answer 5: The separation of a parent plant into parts to re-form w hole pla Category #4: Va Fragmentation 25 Flow ers Question 1: Answer 1: Brightly colored organ that serves to attract insects and other p Va Petals Question 2: 5 Answer 2: Produce sperm (flow er structure) Va Pollen Grains Question 3: 10 Answer 3: Consists of anther and filament Va Stamen Question 4: 15 Answer 4: Enclose and protect the floral bud before it opens Va Sepals Question 5: 20 Answer 5: Form w ithin the ovules Va Embryo sacs Category #5: 25 Photosynthesis Question 1: Answer 1: Photosynthetic material in plants (makes them green) Va Chlorophyll Question 2: 5 Answer 2: Process of converting energy from a light-excited electron into Va Photophosphorylation Question 3: 10 Answer 3: take place in the stroma (happens in the dark) Light Independent Process (or Dark Reac Question 4: Answer 4: Stacks of thylakoids like pancakes Grana Question 5: 15 Va 20 Answer 5: Chemical equation for photosynthesis Va 6H2O+6CO2----->C6H2O6+6O2 Va 25 Final Jeopardy (optional) Final Question Final Answ Structures that have the potential to form a vegetative branch Plant Unit Day 10 Grade Level: 10 Subject(s) Area: Biology Objectives : Students will work independently Learning Activities Today is a work day. Students can work on finishing photosynthesis paper and study guide for tomorrows’ test Collect photosynthesis paper Walk around and monitor progress/answer any questions Assessment : : Photosynthesis paper Plant Unit Day 11 Grade Level: 10 Subject(s) Area: Biology Objectives : Students will demonstrate knowledge of material through a written test Learning Activities Collect any late photosynthesis papers Explain parts and expectations of test Hand out test Assessment : : Unit test on plants Name________________ Period_________ Date______________ Plants Test True and False (2 points each) (put a T for true and a O for false. If an answer is false, rewrite the question to make it true in the space provided) 1. ___ Roots are the main source of photosynthesis in plants is the roots. ________________________________________________________________________ 2. ___ Xylem and phloem are the two parts are vascular tissue in plants. ________________________________________________________________________ 3. ___ Light independent reactions happen in the stroma. ________________________________________________________________________ 4. ___ Sexual reproduction is also called vegetable reproduction. ________________________________________________________________________ 5. ___ Ground tissue is made up of pith and cortex. ________________________________________________________________________ Multiple Choice (2 points each) (Circle the most correct answer to complete the sentence or answer the question) 1. What is the function of a cuticle on a leaf? a. Helps photosynthesis b. Helps retain water c. Makes leaves look better d. Helps plants grow taller 2. Plants are _____________ a. Prokaryotes b. Trikaryotes c. Eukaryotes d. Guekaryotes 3. What the part of a leaf that attaches to stems? a. Petiole b. Lateral bud c. Zone of elogation d. blade 4. Leaves attach to the stems at ____________. a. Zone of maturation b. Cuticle c. Frond d. nodes 5. Which of the following is NOT a main part of plant? a. Root b. Stem c. Flower d. Leaves Matching ( 1 point each) (match the letter representing the terms in the word bank to the statement that best fits its definition) 1. ___ Extend the surface area of roots. 2. ___ Sporophytes produce 3. ___ The “skin” of a cell 4. ___ Where leaves attach 5. ___ Gametophytes produce 6. ___ Roots that arise above ground 7. ___ Where growing of the stem takes place 8. ___ Where photosynthesis occurs in plants. Makes them green. 9. ___ Life cycle of plants 10. ___ Made in the ovule of a flower a. terminal bud f. embryo sacs b. alternation of generation g. advantageous roots c. sperm d . root hairs e. epidermis h. eggs i. chlorophyll j. nodes Label the flower structures on the diagram below (1 point each) Word bank: Petal, sepal, stalk, stigma, ovule, receptacle, anther, filament Short answer (5 points each) (Write a small paragraph containing no more than 5 sentences answering the questions below) 1. Briefly describe the differences between monocots and dicots. (Give at least 5 examples) ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 2. What do plant cells have that animal cells don’t? (At least 2) What are some structures that they share? (at least 3) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Essay (10 points) (answer every part the question completely. You must have an introduction, body, and conclusion. You must use complete sentences. If you need more room, you may write on the back of the test) Give a summary of the photosynthesis process. Include the photosynthesis equation, what the end result of photosynthesis is, where reactions take place, and a brief explanation of the roles xylem and phloem. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Name________________ Period_________ Date______________ Plants Test (Modified) True and False (2 points each) (put a T for true and a O for false. If an answer is false, rewrite the question to make it true in the space provided) 6. ___ Roots are the main source of photosynthesis in plants is the roots. ________________________________________________________________________ 7. ___ Xylem and phloem are the two parts are vascular tissue in plants. ________________________________________________________________________ 8. ___ Light independent reactions happen in the stroma. ________________________________________________________________________ 9. ___ Sexual reproduction is also called vegetable reproduction. ________________________________________________________________________ 10. ___ Ground tissue is made up of pith and cortex. ________________________________________________________________________ Multiple Choice (2 points each) (Circle the most correct answer to complete the sentence or answer the question) 6. What is the function of a cuticle on a leaf? e. Helps photosynthesis f. Helps retain water g. h. 7. Plants are _____________ e. Prokaryotes f. g. Eukaryotes h. 8. What the part of a leaf that attaches to stems? e. Petiole f. g. Zone of elogation h. 9. Leaves attach to the stems at ____________. e. f. Cuticle g. h. nodes 10. Which of the following is NOT a main part of plant? e. Root f. Stem g. Flower h. Leaves Matching ( 1 point each) (match the letter representing the terms in the word bank to the statement that best fits its definition) (Pick from the letters next to the question) 11. ___ Extend the surface area of roots. (a,d,e,) 12. ___ Sporophytes produce (c,h,f,) 13. ___ The “skin” of a cell (a,d,e) 14. ___ Where leaves attach (d,a,e,) 15. ___ Gametophytes produce (c,h,f,) 16. ___ Roots that arise above ground (b,j,a,) 17. ___ Where growing of the stem takes place (a,d,j) 18. ___ Where photosynthesis occurs in plants. Makes them green. (i,b,f,) 19. ___ Life cycle of plants (b,I,f,) 20. ___ Made in the ovule of a flower(b,g,e,) a. terminal bud f. embryo sacs b. alternation of generation g. advantageous roots c. sperm d . root hairs e. epidermis h. eggs i. chlorophyll j. nodes Label the flower structures on the diagram below (1 point each) (pick from the letters next to the terms in the word bank) Word bank: Petal(C,H,D), sepal(C,H,D), stalk(F,H,E), stigma(A,B,F), ovule(C,G,F), receptacle (E,F,H), anther, filament(C,H,D) Short answer (5 points each) (Write a small paragraph containing no more than 5 sentences answering the questions below) 3. Briefly describe the differences between monocots and dicots. (Give at least 5 examples) (Key words to use: Parallel/reticulated veins. Multiples of 3s/ multiples of 4s and 5s. Vascular bundle in ring/ scattered vascular tissue. One seed/ two seeds ) ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 4. What do plant cells have that animal cells don’t? (At least 2) What are some structures that they share? (at least 3) (cell wall, chloroplast, nucleus, ER, ribosomes, golgi apparatus, mitochondria) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Essay (10 points) (answer every part the question completely. You must have an introduction, body, and conclusion. You must use complete sentences. If you need more room, you may write on the back of the test) Give a summary of the photosynthesis process. Include the photosynthesis equation, what the end result of photosynthesis is, where reactions take place, and a brief explanation of the roles xylem and phloem. (key words: light reactions, dark reactions, grana, _____________----- C6H2O6+6O2, Oxygen, nutrients) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Name____KEY____________ Period_________ Date______________ Plants Test True and False (2 points each) (put a T for true and a O for false. If an answer is false, rewrite the question to make it true in the space provided) 11. _O__ Roots are the main source of photosynthesis in plants is the roots. ________Leaves are the main source of photosynthesis__________________________ 12. _T__ Xylem and phloem are the two parts are vascular tissue in plants. ________________________________________________________________________ 13. _T__ Light independent reactions happen in the stroma. ________________________________________________________________________ 14. _O__ Sexual reproduction is also called vegetable reproduction. _______Asexual reproduction is also called vegetable reproduction_________________ 15. __T_ Ground tissue is made up of pith and cortex. ________________________________________________________________________ Multiple Choice (2 points each) (Circle the most correct answer to complete the sentence or answer the question) 11. What is the function of a cuticle on a leaf? i. Helps photosynthesis j. Helps retain water k. Makes leaves look better l. Helps plants grow taller 12. Plants are _____________ i. Prokaryotes j. Trikaryotes k. Eukaryotes l. Guekaryotes 13. What the part of a leaf that attaches to stems? i. Petiole j. Lateral bud k. Zone of elogation l. blade 14. Leaves attach to the stems at ____________. i. Zone of maturation j. Cuticle k. Frond l. nodes 15. Which of the following is NOT a main part of plant? i. Root j. Stem k. Flower l. Leaves Matching ( 1 point each) (match the letter representing the terms in the word bank to the statement that best fits its definition) 21. _d__ Extend the surface area of roots. 22. _c__ Sporophytes produce 23. _e__ The “skin” of a cell 24. _j__ Where leaves attach 25. _h__ Gametophytes produce 26. _g__ Roots that arise above ground 27. _a__ Where growing of the stem takes place 28. _i__ Where photosynthesis occurs in plants. Makes them green. 29. _b__ Life cycle of plants 30. _f__ Made in the ovule of a flower a. terminal bud f. embryo sacs b. alternation of generation g. advantageous roots c. sperm d . root hairs e. epidermis h. eggs i. chlorophyll j. nodes Label the flower structures on the diagram below (1 point each) Word bank: Petal (C), sepal (D), stalk (F), stigma (A), ovule (G), receptacle (E), anther (B), filament (G) Short answer (5 points each) (Write a small paragraph containing no more than 5 sentences answering the questions below) 5. Briefly describe the differences between monocots and dicots. (Give at least 5 examples) ________________________________________________________________________ ________1 point awarded for each example listed in answer ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________ 6. What do plant cells have that animal cells don’t? (At least 2) What are some structures that they share? (at least 3) ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________One point for each similarity (3) and one point for only plants (2) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________ Essay (10 points) (answer every part the question completely. You must have an introduction, body, and conclusion. You must use complete sentences. If you need more room, you may write on the back of the test) Give a summary of the photosynthesis process. Include the photosynthesis equation, what the end result of photosynthesis is, where reactions take place, and a brief explanation of the roles xylem and phloem. 3 points- includes introduction body and conclusion 1 point- includes equation 2 points- discusses xylem and phloem accurately 2- discusses light and dark reactions 1-discusses what end result is (nutrients, and oxygen) 1-proper grammar