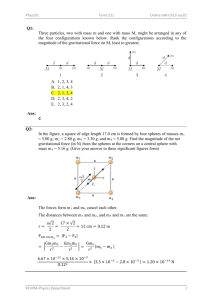
HONORS PHYSICS SPECIAL & GENERAL THEORY OF
advertisement

HONORS PHYSICS SPECIAL & GENERAL THEORY OF RELATIVITY REVIEW This review does NOT cover all topics in the unit. You are still responsible for concept worksheets, homework, and ppt slides 1) Two fixed navigation beacons mark the approach lane to a star. The beacons are in line with the star and are 60Mm apart. A spaceship approaches the star with a relative velocity of 0.90c and passes the beacons. The passage of the ship between the beacons is timed by an observer on the ship. The time interval of the passage is closest to: A) 510ms B) 97ms C) 220ms D) 39ms E) 58ms 2) A right-angled construction frame ABC, when measured at rest, has dimensions as follows: AB=17.00m, AC= 10.00m, and BC=13.75 m. The frame is given a velocity of 0.64c, relative to the space platform, in a direction parallel to AC. The dimensions of the moving frame are measured simultaneously by observers on the platform. The length BC measured by these observers is closest to: A) 12 m B) 8 m C) 14 m D) 16 m E) 10 m 3) The captain of spaceship A observes enemy spaceship E escaping with a relative velocity of 0.48c. A missile M is fired from ship A, with a velocity of 0.72c relative to ship A. The relative velocity of approach of missile M, observed by the crew on ship E, is closest to: A) 0.30c B) 0.37c C) 0.24c D) 0.34c E) 0.27c 4) If you were in a spaceship traveling at a speed close to the speed of light (with respect to earth) you would notice that A) your pulse rate is different than normal. B) your mass is different than normal. C) some of your physical dimensions were smaller than normal. D) None of these effects occur. 5) Which of the following depends on the observer's frame of reference? A) the length of a meter stick B) the mass of the proton C) the half-life of a muon D) all of the given answers 6) You are in a windowless spacecraft. You need to determine whether your spaceship is moving at constant nonzero velocity, or is at rest, in an inertial frame of Earth. a) You can succeed by making very precise time measurements. b) You can succeed by making very precise mass measurements. c) You can succeed by making very precise length and time measurements. d) You cannot succeed no matter what you do. 7) A spaceship is approaching Earth at approximately 0.80c measured relative to Earth. The spaceship directs a laser beam forward directly through your physics classroom window. You measure the speed of this light to be: a) 0.2 c b) 0.8 c c) 1.0 c d) 1.8 c 8) Simultaneity is: a) dilated. b) absolute. c) invariant d) relative. 9) The Michelson-Morley experiment established that: a) there is no observable ether wind at the surface of Earth. b) the ether moves at “c” as Earth travels in its orbit. c) the ether is an elastic solid that streams over Earth. d) Earth does not move with respect to the Sun. 10) Einstein's Principle of Equivalence states a. that the inertial mass is identical to the gravitational mass. b. that light is deflected as it passes by a large mass by the mass' gravitational field. c. that the space around a large mass is actually warped by the very presence of the mass. d. that constant acceleration is completely equivalent to a uniform gravitational field. e. none of the above. 11) According to the theory of relativity, a. as the speed of light is approached, time slows down and approaches zero. b. as the speed of light is approached, time speeds up and approaches infinity. c. as the speed of light is approached, distance shrinks and approaches zero. d. a & c e. none of the above 12) Which of these follows from the theory of relativity? a. Mass is relative to one’s frame of reference. b. Time is relative to one’s frame of reference. c. Distance is relative to one’s frame of reference. d. all of the above e. none of the above 13) Which work established Einstein’s international reputation? a. early work at the patent office b. publication of the special relativity theory c. calculations for the general relativity theory d. prediction of light bending during a solar eclipse e. establishing the time dilation principles Questions 14-16: 14) A proton has a kinetic energy that is equal to its rest mass energy. The speed of the proton is closest to: A) 0.50c B) 0.87c C) 0.75c D) 0.71c E) 0.25c 15) The total energy of the proton is closest to: A) 5.69 ×10-11 J B) 2.07 ×10-10 J C) 8.77 ×10-10 J D) 1.50 ×10-10 J E) 3.01 ×10-10 J 16) The momentum of the proton is closest to: A) 5.01 ×10-19 kg ∙ m/s B) 2.51 ×10-19 kg ∙ m/s C) 8.68 ×10-19 kg ∙ m/s D) 2.89 ×10-19 kg ∙ m/s E) 4.34 ×10-19 kg ∙ m/s 17) A relativistic proton has a momentum of 1.0×10-18 kg ∙ m/s. The rest energy of a proton is 0.150 nJ. The kinetic energy of the proton, in nJ, is closest to: A) 0.16 B) 0.25 C) 0.22 D) 0.19 E) 0.13 18) The speed of the proton is closest to: A) 0.93c B) 0.87c C) 0.95c D) 0.89c E) 0.91c 19) As a rocket is moving past Earth, an Earthling measures its length to be 325m, while the captain on board radios that her rocket’s length is 1150m. a) How fast is the rocket moving relative to Earth? b) What is the total energy of a 75.0-kg crewman as measured by (i) an observer at rest in the rocket and (ii) an observer at rest on Earth? TRUE OR FALSE 20) The speed of light depends upon the velocity of the light source relative to the observer. 21) A clock moving at high speed relative to an observer appears to run slow. 22) The General Theory of Relativity includes the effects of gravity. 23) An accelerating observer feels heavier in exactly the same way as if the strength of gravity had increased. 24) General Relativity does not predict: a) Length contraction b) Time dilation c) Light bending d) Black holes e) That mass curves spacetime 25) Which of the following is not relative in the Special Theory of Relativity: a) Intervals of time b) Motion c) Lengths d) The speed of light 26) The effects predicted by Special Relativity are not normally noticed in everyday life because: a) Everyday velocities are small compared to the speed of light b) The Earth’s gravity is extremely weak c) The Earth is free falling as it orbits the Sun d) Typically we experience only very small accelerations e) The Earth is not an inertial frame, so Special Relativity does not apply 27) What is the mass of the products of a nuclear fission reaction compared to the mass of the original products? a) greater b) less c) the same d) varies according to the reaction 28) What is the mass of the products of a nuclear fusion reaction compared to the original elements? a) greater b) less c) the same d) varies according to the reaction 29) How do fusion and fission differ? a) Fission occurs with light elements; fusion occurs with heavy elements. b) Fusion requires a great deal of energy; fission releases a great deal of energy. c) Fission release energy by splitting large nuclei; fusion fuses small nuclei d) All of the above are correct. 30)The equation E=mc2 illustrates that: a) travelling at the speed of light converts matter into energy b) rest mass and energy are equivalent c) energy can be converted into mass d) matter can be converted into energy e) b, c, and d 31) Bill is standing on earth. A spaceship of proper length 50 meters flies past. Bill measures the spaceship as having length 40 meters. What is the speed of the spaceship? a) 0.8c b) 0.6c c) 0.4c d) None of the above. 32) The reason why the traveling twin cannot simply apply time dilation to calculate the age of his stationary twin is: a) The relevant events do not occur at the same place in his frame. b) A moving observer cannot apply time dilation in the same way a stationary one can. c) Time dilation only applies in gravitational fields, and not in free space. d) During the trip he is in a non-inertial reference frame. ANSWERS: 1) B 2) C 3) B 4) D 5) D 6) D 7) C 8) D 9) A 10) D 11) D 12) D 13) D 14) B 15) E 16) C 17) D 18) D 19) a) 0.959c b) (i) 6.75 ×1018 J, (ii) 2.39×1019 J 20) F 21) T 22) T 23) T 24) A 25) D 26) A 27) B 28) B 29) C 30) E 31) B 32) D